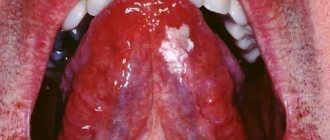
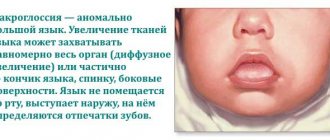
We are used to the fact that we need to go to the dentist if we have problems with our teeth or gums. What to do if you have inflammation of the tongue or glossitis? Dentists identify more than 10 types and subtypes of infection. The infection can be caused by both fungus and bacteria. Viral infection is less common. Inflammation can be caused by a lack of certain vitamins and minerals, or hormonal changes. There are many reasons for the disease, so it is important to identify what exactly caused the inflammatory process.
Causes of glossitis
- improper oral hygiene;
- bacterial infection;
- fungal infection;
- heavy metal poisoning;
- bad habits (smoking, alcoholism);
- congenital pathologies of the tongue (folded tongue);
- allergic reaction;
- tongue injury (often caused by malocclusion);
- oral infections;
- lack of iron in the body;
- burn of the mucous membrane (hot food or drinks);
- infectious diseases (AIDS, tuberculosis, scarlet fever, measles).
Structure of the area under the tongue
Everything that is located under the tongue is called the floor of the mouth. This:
- nerve endings;
- hyoid bone;
- hypoglossal muscles;
- salivary gland;
- connecting folds called frenulums;
- vessels.
Each element of the floor of the mouth serves its own purpose and is irreplaceable. Only if all muscles, tissues, glands and nerves are healthy does the tongue function normally. If there is pain under the tongue, then we are talking about pathology.
The most common types of glossitis
The most common occurrences in dental practice are:
- acute catarrhal glossitis;
- tongue abscess;
- desquamative glossitis.
Acute catarrhal glossitis is the most common type of inflammation. Inflammation can be caused by microbes or mechanical damage to the tongue. The predominant symptoms are pain, redness and swelling.
A tongue abscess is the appearance of an abscess in the tongue. The abscess can be superficial, under the mucous membrane, or maybe in the thickness of the tongue. Abscesses in the thickness of the tongue, in addition to pain in the tongue, can cause a disturbance in the general condition. A person develops a fever, a headache, and weakness. Most often occurs due to injury to the tongue.
Desquamative glossitis, also known as “geographic tongue,” most often appears in children. It appears in the form of various spots on the tongue, which look like a white coating, alternating with areas of pink mucous membrane. There are no changes other than appearance. Scientists have identified a clear reason for it. The main factors are believed to be bacteria, allergic reactions and hormonal imbalances.
Stomatitis in a child: symptoms, causes
The description of stomatitis in a child deserves special attention. The specificity of stomatitis that occurs in the mouth of a young child is that the disease is a consequence of a weakened or not fully formed immune system. Therefore, the stomatitis reaction manifests itself clearly and the course of the disease is accompanied by severe symptoms.
Symptoms of stomatitis in a child:
- The oral mucosa turns red and swelling appears.
- Characteristic stomatitis ulcers form in the mouth, which are located either singly or in groups. The localization of ulcerative formations during stomatitis in a child is different: wounds and blisters appear on the tongue, on the palate, mucous membrane or in the throat. The nature of the lesions depends on the form of the disease and on what factors triggered the reaction (infections, allergies, vitamin deficiency, etc.).
- The development of stomatitis in the baby’s oral cavity is accompanied by an increase in the child’s body temperature (up to 38-39 degrees).
- The baby’s submandibular lymph nodes increase in volume and become painful on palpation.
- The child becomes lethargic, drowsy, capricious and whiny.
The baby has a hard time suffering from stomatitis in the mouth, and this is a lot of stress for the young body, not to mention the fact that the disease worsens the child’s appetite and disrupts the child’s sleep pattern. Therefore, if you notice the formation of ulcers in the mouth of your daughter or son or identify other symptoms of stomatitis, immediately show your child to a doctor (dentist or therapist).
Studying pictures and photographs of other children with oral stomatitis on the Internet is pointless; you will only waste your time and may come to the wrong conclusions. The doctor will help you understand the reasons that provoked the development of stomatitis in the child’s mouth and prescribe effective treatment for stomatitis.
Symptoms of glossitis
- increased salivation;
- swelling and redness;
- pain and burning when eating;
- plaque on the tongue in the form of spots;
- bad breath;
- papillomas or warts on the tongue;
- speech disorder;
- foreign body sensation.
Prevention of glossitis - high-quality oral hygiene and no bad habits. It is important to undergo timely preventive examinations and also eat well. All these factors actively contribute to the development of the disease and bring a number of problems.
Prevention of inflammation of the floor of the mouth
To prevent diseases of the sublingual area, dentists give recommendations on proper oral care:
- take care of your gums;
- avoid the accumulation of bacterial plaque;
- visit the dentist 2 times a year;
- prevent the occurrence of caries;
- brush your teeth 2 times a day.
But if the patient has congenital or acquired anomalies in the development of the floor of the oral cavity, such as a shortened frenulum or structural asymmetry, then you will have to be more careful to prevent injury. Some abnormalities can be treated. Come to an appointment at Family Dentistry and experienced specialists will tell you how to get rid of defects, tumors and inflammations.
Treatment of glossitis
A specialist must make an accurate diagnosis and identify the cause of the disease. If you suspect that you have glossitis , and all symptoms indicate this, contact your dental clinic. This is the only way to create the right treatment plan and provide timely assistance. Quite often in such cases, doctors prescribe antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and rinsing the mouth with special antiseptic solutions. In advanced stages, glossitis is treated surgically. Deep abscesses must be opened in the maxillofacial department. Under no circumstances should you take medications without a doctor’s recommendation.
You can cure glossitis, caries or any other diseases of the oral cavity right in your sleep. Family Dentistry Center "Medexpert" provides dental treatment under medicinal sedation. Thanks to this approach, the patient falls into a healthy sleep, ceases to feel pain and discomfort, while the vital functions of the body remain unchanged. Sedation is widely used in pediatric dentistry and even helps fight dental phobia. Dental treatment can be comfortable and painless - tested for yourself.
How is the sublingual area treated?
Considering the above reasons, if you have the slightest pain in the sublingual space, you should immediately consult a doctor. The doctor will find out the source of the pain and determine a treatment regimen. In some cases, allergists and therapists provide treatment. But more often, pain in the floor of the mouth is treated by dentists.
In case of injury to the frenulum or the tissues of the area under the tongue, rinsing will be prescribed: with a solution of soda, romazulan, stomatophyte, hexoral, chlorophyllipt or iodinol. You should rinse your mouth according to the following schedule:
- morning and evening before bedtime;
- after meal.
The doctor also treats the area of injury with an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Inflammations caused by dental problems require immediate treatment - the specialists at Family Dentistry will get rid of caries, pulpitis or periodontitis and prescribe a course of anti-inflammatory drugs to cope with sublingual inflammation.
But one of the most dangerous diseases in the floor of the mouth is inflammation of the salivary glands. It is important to begin treatment before an abscess appears and complications develop. In this case, the doctor prescribes:
- antibacterial therapy - the doctor injects medicine into the gland and also prescribes a broader-spectrum antibiotic;
- drugs to activate saliva secretion - either a solution of potassium iodide or pilocarpine is used, sometimes regular lemon is used;
- hot dry compresses;
- physiotherapy course.
If the inflammation is advanced and pus appears or a stone has formed, the patient is sent to a surgeon, who cleans the gland cavity of pus and removes the stone.
Why do they appear?
As already mentioned, there are no sebaceous glands on the tongue, so “pimples” cannot appear on it in principle. After all, a pimple is an inflammation of the sebaceous gland. But the bumps and nodules that sometimes appear on the surface are very similar in appearance to pimples, which is why they got that name. Pimples under the tongue or on the tip cause a lot of trouble and are extremely painful. Let's consider the reasons for their appearance.
Mechanical damage
Often, in the process of chewing or biting food, we bite our tongue, resulting in a slight mechanical injury. The risk of surface damage increases when consuming hard foods with sharp edges (crackers, chips, seeds). A small painful swelling or bump forms at the site of the injury, which after some time turns into a white pimple. The pain intensifies while eating. With severe mechanical damage, slight swelling may occur.
You should exclude spicy and hot foods from your diet, carefully monitor oral hygiene, and after a few days the pimple will disappear on its own.
Allergic reaction
The appearance of pimples on the tongue may indicate an allergic reaction to food, medicine or toothpaste. In this case, small white pimples and sores form, which hurt and irritate when eating or drinking liquid.
If your doctor suspects an allergy, it is very important to identify the allergen and eliminate it from your diet. First of all, you should stop chewing gum, change toothpaste and tooth elixir - you may be allergic to oral hygiene products. If these measures do not bring the desired result, you need to analyze whether you have recently taken medications. Pimples on the tongue after antibiotics and other medications are a common occurrence. In this case, you should consult your doctor and stop taking the drug or try replacing it with another one.
If the cause of acne is a food allergy, you need to track what foods they appear after and eliminate these foods from your diet.
Stomatitis
Stomatitis is a common cause of white or red pimples on the surface of the tongue. The main cause of stomatitis is insufficient oral hygiene, exposure to pathogenic bacteria on the mucous membranes due to dirty hands, unwashed fruits and vegetables. Most often, children suffer from stomatitis, because they tend to put everything in their mouth.
With stomatitis, small white, pink or red pimples appear on the surface of the tongue and other mucous membranes of the mouth, which burn, irritate and hurt not only during eating, but also at rest. It is sometimes difficult not only to eat, but also to talk or simply swallow saliva. Small pimples under the tongue or at the root cause severe discomfort.
At the first suspicion of stomatitis, you should consult a doctor, he will prescribe medications that relieve itching and soreness of the tongue, as well as promote the speedy healing of ulcers and pimples.
Herpes
The herpes virus most often affects the area around the lips. However, this is not the only place where it is localized; herpes can affect all mucous surfaces of the human body, including the oral cavity. In this case, one or more watery pimples may appear on the tongue and inner surface of the cheeks. Many people do not pay enough attention to the herpes virus, believing that it will go away on its own. In fact, this is not such a harmless disease.
Without proper treatment, herpes can eventually affect the entire body, including the brain. Therefore, if you have a herpes virus, you should consult a doctor and undergo a course of antiherpetic therapy.
Poor nutrition
If you eat too much spicy and hot food, inflammation of the tongue, or glossitis, may occur. The papillae on the surface of the tongue are constantly irritated by hot or spicy foods, which leads to their inflammation. If your diet constantly contains spicy foods, inflammation can become chronic.
Drinking alcohol in large quantities, as well as smoking, can cause inflammation of the tongue. Therefore, when the first problems appear, you should immediately try to get rid of bad habits.
Pathologies of the patient's internal organs
Pimples on the surface of the tongue can be a manifestation of various diseases, including candidiasis or tuberculosis. Therefore, you should not take the appearance of small pimples lightly. Be sure to monitor their behavior. If a pimple does not go away for a long time, be sure to consult a doctor.
Weakened immunity
If the immune system is weakened as a result of a previous illness or due to a lack of vitamins and microelements, small painful pimples may appear on the surface of the tongue. If there are no other reasons for their appearance, you should contact an immunologist to check the state of the immune system. If malfunctions are detected in its functioning, it is necessary to take immunomodulators, as well as drugs with lactobacilli to normalize intestinal function and correct the activity of the immune system.
What to do
The human oral cavity is home to many bacteria, both beneficial and pathogenic. They have both negative and positive effects on the human body. Pathogenic bacteria cause inflammatory processes, including glossitis, or inflammation of the tongue. Often patients notice a white pimple that reacts with pain to every touch. In fact, this is not a pimple, but an inflamed nodule. In medicine, such inflamed nodules are called glossitis.
A transparent pimple under the tongue can occur as a result of mechanical damage or as an allergic reaction to chemical and food irritants.
You can get rid of glossitis only through comprehensive measures. The first step is to consult a doctor to determine the true cause of its occurrence. The oral cavity should be kept clean, preferably rinsed with a soda solution or a decoction of St. John's wort. It is also necessary to strengthen the immune system and limit the consumption of spicy and too hot foods so as not to irritate the inflamed nodule.
Types of stains
Spots on a child’s tongue can be different, both in shape and color. Depending on this, all the spots on the mucous membrane of the uvula can be divided into several groups.
Geographic language
In this case, the mucous membrane is very reminiscent of a map of countries and continents. This change can occur in children of all ages, including newborns. The tongue looks patchy and has areas of small bald patches that connect to each other. A similar type of mucous membrane is observed in the following pathologies:
- For diseases of a hormonal nature;
- With helminthic infestation;
- For diseases of the digestive system.
Geographic tongue spots can be of different shapes and sizes. In many cases, they are not a sign of a disease at all, and do not pose a danger to the child.
White spots
White spots on the mucous membrane are in most cases caused by fungi. Popularly, this pathology is called thrush. Candidiasis develops against the background of weakened immunity in children of different ages. Such spots have a cheesy appearance; they can cover not only the surface of the tongue, but also the cheeks and palate. When a fungal infection of the oral cavity occurs, the child cannot eat normally, he becomes moody and restless.
As first aid, the child’s oral cavity is treated with a soda solution. Prepare such a solution at the rate of 1 teaspoon of soda per glass of boiled water.
Red spots
Such spots almost always indicate an inflammatory or infectious disease of the oral cavity. The cause of red spots can be glossitis, stomatitis, herpes and bacterial dermatosis. The cause of this phenomenon may be an allergic reaction and consumption of red foods.
Quite often, the appearance of such spots is accompanied by pain and a burning sensation in the tongue. Due to pain, the child may refuse to eat and be capricious. Sometimes body temperature rises.
Depending on the cause, antifungal agents, antibiotics and antiviral drugs may be prescribed. It is recommended to treat areas of inflammation with antiseptic solutions such as Miramistin or Furacilin.
Dark spots
Often appear on the tongue after consuming certain foods. They are not dangerous and disappear after rinsing the mouth or brushing the tongue.
Black spots may appear as a result of prolonged treatment with antibacterial drugs. In this case, treatment comes down to normalizing the microflora of the digestive organs.
A very rare cause of dark spots are deep degenerative processes when areas of the mucous membrane die off. This condition requires urgent medical attention.
Yellow spots
Occurs when a child has problems with the digestive tract. Such spots densely cover the base of the tongue and the rest of its surface. Plaque consists of dead epithelium and is difficult to remove. This phenomenon is almost always accompanied by bad breath.
To eliminate the problem, you should undergo examination and treat diseases of the digestive tract. After treatment, the yellow plaque quickly disappears.
Blue spots
Blue spots on the tongue of children are extremely rare. They talk about problems with the cardiovascular system. To eliminate this phenomenon, sometimes it is simply necessary to normalize blood circulation in the vessels.
The cause of blue spots can be a hemangioma. In this case, there is most often one spot. Treatment in this case is always surgical.
Other spots
Normally, the tongue is covered with many taste buds, which give the mucous membrane a velvety appearance. With tongue injuries, burns and some inflammatory diseases, the taste buds die, forming smooth pink areas.
Such spots do not cause discomfort to the baby; his taste may only change slightly. This condition cannot be treated, since the taste buds are not restored.
When you see different spots on a child’s tongue, you should not panic, but you cannot ignore this phenomenon.
The baby should be shown to a doctor who will correctly diagnose and, if necessary, prescribe treatment. This article is for informational purposes only, please consult your doctor for details! Ask your doctor about contraindications and side effects.