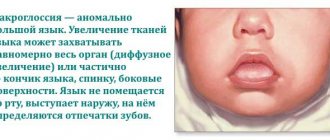
We are used to the fact that we need to go to the dentist if we have problems with our teeth or gums. What to do if you have inflammation of the tongue or glossitis? Dentists identify more than 10 types and subtypes of infection. The infection can be caused by both fungus and bacteria. Viral infection is less common. Inflammation can be caused by a lack of certain vitamins and minerals, or hormonal changes. There are many reasons for the disease, so it is important to identify what exactly caused the inflammatory process.
Causes of glossitis
- improper oral hygiene;
- bacterial infection;
- fungal infection;
- heavy metal poisoning;
- bad habits (smoking, alcoholism);
- congenital pathologies of the tongue (folded tongue);
- allergic reaction;
- tongue injury (often caused by malocclusion);
- oral infections;
- lack of iron in the body;
- burn of the mucous membrane (hot food or drinks);
- infectious diseases (AIDS, tuberculosis, scarlet fever, measles).
When to see a doctor
If this is not the first time a burning sensation in the mouth has occurred, and the culprit is NOT spicy food, then this is a reason to consult a doctor. Based on the above reasons, doctors of various specialties can deal with this problem. First of all, these are therapists. A general practitioner, based on the history taken, will be able to exclude a number of pathologies and refer the patient to the right specialist. Among them are dentists, endocrinologists, infectious disease specialists, gastroenterologists and others.
Important! During the interview, the doctor should tell you about all concomitant diseases, lifestyle and medications you are taking. This information will help the doctor rule out a number of diseases and quickly identify the cause of the symptom.
The most common types of glossitis
The most common occurrences in dental practice are:
- acute catarrhal glossitis;
- tongue abscess;
- desquamative glossitis.
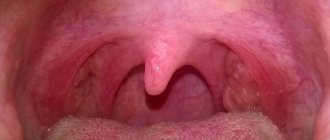
Acute catarrhal glossitis is the most common type of inflammation. Inflammation can be caused by microbes or mechanical damage to the tongue. The predominant symptoms are pain, redness and swelling.
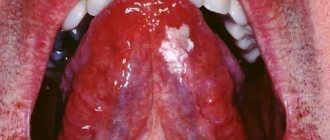
A tongue abscess is the appearance of an abscess in the tongue. The abscess can be superficial, under the mucous membrane, or maybe in the thickness of the tongue. Abscesses in the thickness of the tongue, in addition to pain in the tongue, can cause a disturbance in the general condition. A person develops a fever, a headache, and weakness. Most often occurs due to injury to the tongue.
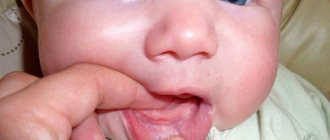
Desquamative glossitis, also known as “geographic tongue,” most often appears in children. It appears in the form of various spots on the tongue, which look like a white coating, alternating with areas of pink mucous membrane. There are no changes other than appearance. Scientists have identified a clear reason for it. The main factors are believed to be bacteria, allergic reactions and hormonal imbalances.
Diagnostics
The cause of the symptom is determined by the dentist. If there are indications, patients are referred for consultation to a gastroenterologist, therapist, neurologist, and other specialists. The doctor determines when the pain first appeared, what symptoms were accompanied, and how the disease developed. To clarify the diagnosis, the following procedures are performed:
- Inspection
. During the physical examination, general changes are sometimes detected (for example, pale and dry skin with anemia). When examining the tongue, swelling, hyperemia, discoloration, the presence of erosions, ulcers, and infiltrates may be detected. With neuralgia, areas of pain indicate damage to one or another nerve. During a dental examination, carious teeth, defects in dentures and orthodontic structures may be detected. - Instrumental techniques
. To exclude xerostomia and assess the condition of the salivary glands, sialography and ultrasonography are recommended. If gastrointestinal pathologies that provoke glossalgia are suspected, esophagogastroduodenoscopy and a contrast study of the stomach are performed. For neuralgia, electromyography is indicative. - Lab tests
. Confirm the presence of pernicious or iron deficiency anemia. As part of the differential diagnosis, saliva is examined. In case of candidiasis and bacterial lesions, the discharge is inoculated onto nutrient media. For viral infections, PCR is performed.
Symptoms of glossitis
- increased salivation;
- swelling and redness;
- pain and burning when eating;
- plaque on the tongue in the form of spots;
- bad breath;
- papillomas or warts on the tongue;
- speech disorder;
- foreign body sensation.
Prevention of glossitis - high-quality oral hygiene and no bad habits. It is important to undergo timely preventive examinations and also eat well. All these factors actively contribute to the development of the disease and bring a number of problems.
Features of pain
Pain that appears on any part of the tongue is called glossalgia. This pathological deviation is characterized by the appearance of signs of inflammation, when the mucous membrane acquires a reddish tint. Glossalgia is never an independent disease; it always acts as a secondary factor provoked by a certain pathology.
Most often, the appearance of discomfort on the tip of the tongue is not associated with the consumption of specific foods - spicy or salty foods. But inflammation of the mucous membrane may intensify if salty, sour or spicy foods come into contact with the injured area.
It is very difficult to determine the provoking factor of pathology without diagnostic studies.
Treatment of glossitis
A specialist must make an accurate diagnosis and identify the cause of the disease. If you suspect that you have glossitis , and all symptoms indicate this, contact your dental clinic. This is the only way to create the right treatment plan and provide timely assistance. Quite often in such cases, doctors prescribe antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and rinsing the mouth with special antiseptic solutions. In advanced stages, glossitis is treated surgically. Deep abscesses must be opened in the maxillofacial department. Under no circumstances should you take medications without a doctor’s recommendation.
You can cure glossitis, caries or any other diseases of the oral cavity right in your sleep. Family Dentistry Center "Medexpert" provides dental treatment under medicinal sedation. Thanks to this approach, the patient falls into a healthy sleep, ceases to feel pain and discomfort, while the vital functions of the body remain unchanged. Sedation is widely used in pediatric dentistry and even helps fight dental phobia. Dental treatment can be comfortable and painless - tested for yourself.
What to do if your tongue hurts?
If you experience pain in any area of the tongue, you should make an appointment with a dentist or otolaryngologist. Before going to the clinic, it is necessary to exclude the presence of minor injuries or accidental burns, for which it is important to leave time to heal. If the cause of the pain was a cosmetic puncture, you must strictly adhere to all recommendations and carefully monitor oral hygiene. If your tongue hurts without punctures or wounds, you should consider one of the following options:
- Carrying out dental procedures
with surgery: anesthesia and medical procedures cause swelling of the gums and a small area of the tongue. The discomfort usually goes away as the swelling decreases.
- Inflammatory and fungal diseases of the oral cavity
eliminated by taking antifungal agents and maintaining constant cleanliness in the mouth.
- Inflammatory and infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract
: sore throat, sore tongue - signs of inflammation of the tonsils or submandibular lymph nodes. The otolaryngologist will draw up a treatment regimen with the prescription of antiviral, painkillers and antihistamines.
Are you worried about short-term or constant pain in different areas of the tongue?
Try to find out the causes of discomfort, remember cases of injury or accidental burns. If pain continues to bother you, you should immediately consult a therapist, dentist or otolaryngologist. An experienced doctor will conduct all the necessary studies and take tests to accurately determine the diagnosis and create an effective treatment regimen. This article is for informational purposes only, please consult your doctor for details! Ask your doctor about contraindications and side effects.
Preventive measures
Preventive measures against a “burning” tongue include the following:
- Proper dental and oral hygiene.
- Clean your tongue daily with a special cleaner (but not with a brush!).
- Compliance with drinking regime.
- Avoiding allergens, in particular food ones.
- Controlling blood sugar levels.
- Timely treatment of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Compliance with the principles of balanced nutrition.
- Regular preventive examinations with a dentist (at least 2 times a year).
Prevention of pain in the tailbone
The main preventive measure in the fight against coccyx diseases is the correct posture when sitting, working on your posture; It is also not recommended to abuse sitting on upholstered furniture, placing pillows and poufs. With such factors, there is a serious risk of developing osteochondrosis and worsening existing diseases. It is also not recommended to wear clothes that compress the waist and waist area; it is highly advisable for pregnant women to wear a support bandage, which avoids deformation of the tailbone. Among other things, doctors recommend regular exercise, strengthening the muscle corset and muscles around the spinal column, and monitoring nutrition.
Glossalgia
This term describes the occurrence of pain in the tip of the tongue for no apparent reason. Often accompanied by a feeling of dry mouth, itching, tingling, burning. Appears against the background of various problems with blood vessels and circulation, hormones, gastrointestinal tract, and during menopause. Basically, this condition develops with psychological disorders, depression and stress.
Glossalgia
Maintenance therapy consists of rinsing with herbal decoctions, performing pain-relieving applications, and rinsing the tongue with special medications prescribed by the doctor. But at the same time, it is worth calming the nervous system, since most often glossalgia is a psychological problem.
Anatomy of the coccyx and coccygeal-sacral joint
The coccyx is the trailing, lowest part of the spine. The coccyx is a rudimentary part of the spinal column; it is formed from 3–5 fused vertebrae, each of which has a rudimentary body, transverse processes and joints. The shape of the coccyx is a small triangle or pyramid, which is inverted with the narrow part down. The sacrum is the penultimate section of the spine, which is connected to the coccyx by the sacrococcygeal joint (joint). There are differences between the male and female coccyx and the mobility in the area of the connection with the sacrum. The male coccyx has a curved shape, and, as a rule, it is motionless at the intersection with the sacrum. The female tailbone is not as curved and more mobile, that is, it can deviate towards the back. This physiological feature is necessary for a woman to give birth and for a child to pass through the birth canal.
Despite the fact that the coccyx is considered a vestigial remnant of the human tail and a seemingly unnecessary organ, its presence is nevertheless important:
- The coccyx is the junction of a large number of nerve endings, muscles, ligaments and tendons, which are necessary for the normal functioning of the organs of the genitourinary system and colon;
- the gluteus maximus muscle is attached to the coccyx;
- the nerve endings attached to the anterior surface of the coccyx are connected to the pelvic organs;
- The tailbone serves as an additional support point for a person when he bends back and forth - in this case, the tailbone is responsible for evenly distributing the load on the pelvic part of the spine.
Any injuries and pathologies of the coccyx lead to pain and require professional medical care.