According to antiplagiat.ru, the uniqueness of the text as of October 16, 2018 is 90.3%.
Key words, tags: tooth extraction, wisdom tooth, bone tissue, implant installation, augmentation, implantation.
Despite the rapid development of modern dentistry, tooth extraction is still a very common operation. When a doctor removes a tooth, be it a dystopic wisdom tooth or a severely rotted molar, in its place there remains a hole, a cavity, which is called the alveolar socket. Previously, the affected tooth was simply removed, and the resulting cavity, the socket, healed on its own, with a significant decrease in bone tissue. But today, when talking about qualified dental care, we should talk about preserving the alveoli in its original state, even in the absence of a tooth.
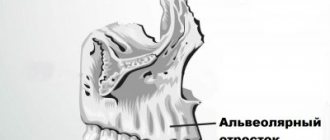
Anatomy of the alveolar process
The alveolar, or dental, process (from Latin - processus alveolaris) is the part of the upper and lower jaws that extends from their bodies and contains teeth. The development and normal functioning of this structure is ensured by the roots of the teeth located in it. The alveolar process appears only after teeth erupt and almost completely disappears with their loss. After a tooth is removed, the corresponding area undergoes resorption (resorption). Dental alveoli, or sockets, are individual cells of the alveolar process in which teeth are located. They are separated from each other by bony interdental (interalveolar) partitions. Inside the alveoli of multi-rooted teeth there are also internal (intra-alveolar) interradicular septa, which extend from the bottom of the alveoli and divide the alveoli into chambers (according to the number of roots). The alveolar socket of the tooth has clear, defined boundaries, and it has all the conditions for bone regeneration; you just need to help it maintain its contour.
Tooth tissue
- Enamel: The most durable tissue in the human body, covering the surface of the dental crown. In terms of hardness, enamel is equivalent to crystal, since 97% of this tissue is inorganic.
- Dentin: the main hard tissue of the tooth. It consists of 70% hydroxyapatite, as well as water and organic material, fibers consisting of collagen, and dentinal tubules.
- Cement: tissue that covers the surfaces of the root and neck of the tooth. It is similar in hardness to bone. Cementum connects the alveolar bone to the tooth via the periodontal ligament.
- Dental pulp: loose tissue consisting of connective tissue fibers located in the tooth cavity. Rich in nerves and vessels (lymphatic and circulatory). Supplies dentin with nutrients.
Considering how a tooth is structured, one cannot exclude nearby tissues that support and strengthen the tooth.
- Periodontal ligament: fibrous tissue connecting the tooth root and alveolar bone.
- Alveolar bone: The jawbone that supports the tooth - it contains the sockets where each tooth is seated.
- Gums: soft tissue covering the alveolar bone.
- Gingival sulcus: a small space between the tooth and gum, the depth of which is between 1 and 2 mm. If this space deepens due to inflammation, a gum pocket is formed.
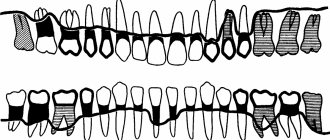
Based on their chewing function, teeth are classified into 4 types:
- The front teeth are incisors, used for cutting and grasping food.
- Fangs are cone-shaped teeth located next to the incisors, involved in holding and tearing food.
- The back teeth are small molars (premolars) and large molars (molars) that grind food.
Knowing the structural features of teeth, it is easier to find a common language with a dentist. You will feel confident and better understand the essence of the manipulations being performed.
Structure of the human tooth:
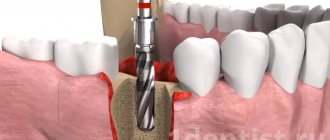
Hole preservation procedure
Preservation of the socket of an extracted tooth is a fairly simple and effective operation for preserving bone volume and maximizing the preservation of the natural contours of the alveolar socket. This surgical procedure is performed under local anesthesia and does not pose any risk.
Usually the operation is carried out in several stages:
- treatment of the hole after tooth extraction with special antiseptic compounds;
- installation of a membrane to protect the vestibular wall;
- filling the socket cavity with granular bone-forming substance;
- fixation of the operating surface by tensioning the free edges of the connective tissue;
- applying a bandage or a thin, neat suture.
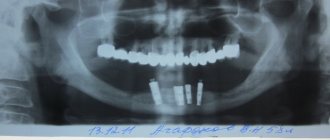
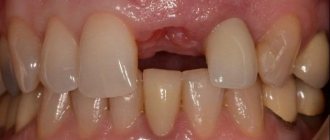
Complete healing of the postoperative area occurs by the fourth week, and after 3–4 months, in some cases 6 months, if the condition is satisfactory, this area can be used to install an implant.
Treatment quality criteria
The main criterion for the quality of an alveolar socket preservation operation is its independent complete healing and maximum preservation of bone tissue, preservation of the natural contour and volume of the alveolar ridge, improvement of the condition of soft tissues and simplification of further stages of treatment. If the operation is successful, there will be enough bone tissue in the socket to install a dental implant. Separately, it is worth highlighting the advantages of condomization for the doctor and the patient - this is improved long-term treatment results, more predictable aesthetics and, of course, saving time for the doctor and the patient.
Treatment of alveolar sockets
Treatment is carried out strictly by a dentist. Remember that when treating alveolitis yourself with rinsing and antibiotics, you will not get rid of it, all these measures are useless! The main treatment procedure can only be performed by a dentist. Treatment at the dentist goes something like this:
- Removal of the blood clot under anesthesia, removal of food debris and necrosis from the socket (if all this is not removed, any treatment will be null);
- The hole is disinfected and washed with an antiseptic; antiseptics are placed in it, which are changed from time to time by the dentist at separate appointments;
- The dentist will prescribe antiseptic baths and an antibiotic, and painkillers for pain;
Moscow metro station Zvezdnaya, Danube Avenue, 23
Indications for condom
Preservation of the socket of an extracted tooth is indicated for everyone who in the future wants to install a dental implant in its place. The process of loss and resorption of the jaw bone at the site of the extracted tooth begins immediately after the operation. In the first year, bone tissue resorption will be 25% in volume, and over the next 3 years the loss in width will be 40 - 60%. In the case of socket preservation after tooth extraction, a larger volume of bone tissue in the jaw and the most natural contours of the alveolar process are preserved. And then, subsequently, the likelihood of such a complex operation as alveolar bone augmentation when installing an implant will most likely not be required.
Main symptoms
Alveolitis that occurs after tooth extraction can be diagnosed especially quickly; the main thing is to know its symptoms and, of course, visit a doctor. A superficial inspection can determine the following:
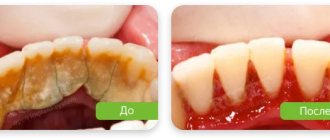
· a) the hole may turn out to be empty, but with a yellowish coating, especially on the walls of the hole, where traces of food remains remain, or it is completely filled with rot;
· b) the gums near the socket have their own color, usually bright red (swelling and severe pain);
· c) bone tissue begins to bulge.
Pain during alveolitis can sometimes be very strong, acute, and possibly mild. In this situation, a cutting pain in the head may appear. Bad breath occurs when a blood clot festers, as well as when an inflammatory process occurs in the orifice. In addition, the suppuration of this clot very often leads to poisoning of the human body, which is why the person’s general condition only worsens, this is accompanied by severe weakness, and the temperature rises.
Swelling in the area of the gums and cheeks sometimes goes away without any significant swelling of the person’s face, since at this moment the pus, as well as the infection, have a certain outflow that passes through the empty socket. But still, the suppuration of clots is particularly acute, with the appearance of a sharp tumor in the gums, as well as in the soft tissues of the face, the body temperature rises sharply, and severe pain appears.
Contraindications
Preservation surgery is subject to the same restrictions as any osteoplastic surgery. Separately, I would like to note that it is not recommended to preserve a hole after tooth extraction in a state of acute pain, since the risk of complications increases. But in each specific clinical case, the actions of a professional dentist are strictly individual. Sometimes situations arise when you have to take risks, but this is due solely to medical indications. In any case, it is necessary to understand that performing a tooth extraction operation and subsequent preservation on a planned basis is better than as part of emergency care.
Symptoms of alveolitis and dry socket
The diagnosis of “alveolitis” is made quite simply. With alveolitis, the following symptoms are observed:
- Outwardly, it may be empty, with a yellowish coating on the walls of the hole and traces of food debris, and festering blood clots are also visible. The gum next to the hole is usually inflamed, red, swollen, and hurts when touched.
- The pain associated with this disease varies and can be both acute and mild. Some people also experience pain in the head when the socket becomes inflamed.
- When a blood clot festers, it always begins to smell unpleasant, and the hole that is inflamed also has an unpleasant odor. It can be described as the smell of rotting, decay. A clot that festers leads to intoxication of the body, which is expressed in the person’s poor condition, as well as weakness and fever.
- In most cases, alveolitis occurs without swelling of the soft facial tissues due to the fact that the infection and pus come out through the sore hole. But there are cases when this does not happen, the facial tissues and gums swell, all this is accompanied by high fever and acute pain.
Restrictions
It is logical to perform a preservation operation after the removal of permanent molars, within the so-called sevens, second molars (except for wisdom teeth, eights), since when baby teeth fall out, bone tissue does not resorption. There is no upper age limit for performing an operation aimed at preserving the natural contours of the alveolar process.
Price
According to the classifier of surgical interventions in the oral cavity, condomation is not among the standard surgical interventions and this, of course, affects the cost of its implementation. In addition, the price of osteoplastic materials and related products is quite high. Some materials are used only in conjunction with a special membrane to avoid ingrowth of soft tissue into the alveolar socket. The price is also affected by the method of tooth extraction. Removal of a tooth or tooth root is sometimes still a traumatic procedure, leading to direct loss of alveolar bone and soft tissue. With atraumatic removal, the alveolar bone is preserved in a larger volume, which reduces the final cost of the operation.
Preservation of the socket after tooth extraction is an important procedure when planning the installation of an implant. Timely preservation of the socket will allow you to preserve such valuable bone tissue and avoid a much more complex and expensive operation to build it up - augmentation, as well as significantly reduce the overall treatment time. The cost of preserving the natural contours of the alveolar socket pays off, because you thereby provide the teeth surrounding it with a reliable position, and as a result, during implantation, you get an imitation of the removed tooth root. This procedure applies even to those patients who do not intend to restore or replace a lost tooth with an implant, because in this case the gingival contour will have the most aesthetic appearance, without failures, and will allow for the most aesthetic bridge prosthetics. Therefore, reservation is gaining increasing popularity in dental dentistry.
According to antiplagiat.ru, the uniqueness of the text as of October 16, 2018 is 90.3%.
Key words, tags: tooth extraction, wisdom tooth, bone tissue, implant installation, augmentation, implantation.
*Images: Astra Tech Dentsply Implants; Principles of hard tessue regeneration and implant therapy.
The main reasons for the appearance of alveolitis in the socket after tooth extraction
In many cases, alveolitis of the tooth socket occurs due to a doctor’s error. This is especially evident after the entire tooth has been removed, and in the meantime, a formation in the form of a small cyst remains in the depths of the socket hole, which will serve as the cause of infection in the future. On our website you can see + what alveolitis of the socket looks like in the photo.
Another reason may be a fragment of a tooth or root, which can sometimes remain after the next extraction. These same fragments also lead to infection of the blood clot. If there is a small piece of tooth left in the hole, you must immediately go to the doctor and have it removed, since if ignored, it leads to damage to the surface of the bone tissue and completely injures the entire blood clot.
With complex surgical removal, a fragment may also remain, especially if there was a slight inflammatory suppuration. But the doctor did not bother to prescribe an antibiotic to eliminate the inflammatory process. Especially often, the hole dries out after a tooth is removed, but the resulting hole is completely free of a blood clot and is not filled with blood. In the meantime, the doctor decided to send the patient home - this is a gross violation.
This article is for informational purposes only, please consult your doctor for details!