A fistula on the gum (also called a fistula) is an opening in the gum from which pus is released, often with blood. A fistula appears against the background of caries, periodontitis, and also due to poor-quality dental services. Over a long period, the fistula develops asymptomatically, but subsequently can lead to severe complications. Therefore, if a purulent formation appears on the gum, you should immediately contact your dentist.
Fistula on the gum: causes
A fistula on the gum is a hole that forms as a complication after inflammatory pathologies, including untreated ones. It can also occur after dental intervention (poorly provided services). Very often, a fistula is formed as a complication of long-term chronic periodontitis.
Also, the reasons for its appearance may be:
- damage to the tooth root;
- advanced caries;
- pulpitis;
- inflammatory processes of the cyst;
- problems with the growth of wisdom teeth;
- improper teething in children;
- granuloma - inflammatory processes in the tissues of the periosteum and the apical region of the tooth root (accompanied by an increase in temperature, enlarged lymph nodes and other signs).
How dangerous is a fistula? Consequences
The fistula itself does not pose a danger, since through it the pus is removed from the source of infection, and accordingly, the degree of tissue damage is reduced. But the presence of a fistula indicates that the process is serious, and various types of complications may arise, such as:
- Loss of teeth in the affected area;
- Attachment of a secondary infection - inflammation of the lymph nodes, ears;
- Sinusitis;
- Sinusitis;
- Damage to bone tissue;
- Sepsis as a result of infection entering the general circulatory system;
- The appearance of cystic formations at the roots of the tooth;
- Heart complications, bacterial endocarditis.
Sometimes it happens that the pus drains almost completely, the fistula heals, and the patient thinks that everything is gone. But in fact, the source of inflammation has not been eliminated, so relapse of the disease is inevitable. Repeated abscesses and fistulas are more difficult to treat.
How a fistula is formed
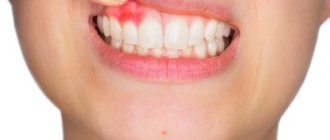
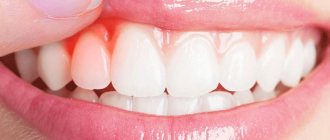
The process of fistula formation looks like this. A small hole appears in the gum near the base of the tooth. Its color stands out a little against the background of healthy tissues - the color is rich pink or red. At the same time, the remaining teeth remain healthy and do not hurt.
At first, the fistula looks like a small swelling, then it grows and resembles a pimple or an abscess. The last stage - the seal opens, after which mucus or pus comes out of it. Then the wound becomes covered with a scar, but does not disappear. In the future, the development of the fistula can become chronic - it will open several times a year and exude pus. During exacerbations, mild pain will be felt.
Reasons for appearance
In medicine, a hole in the gum is called a fistula. A fistula appears as a consequence of the activity of harmful microorganisms that are located in the area of the alveolar process. As a rule, the causative agents of pathology are coccus bacteria.
That is, the main reason for the formation of a fistula is a large amount of pathogenic microflora in the mouth. Lack of hygiene, the accumulation of soft plaque and the formation of tartar provoke the appearance of a fistula in the gums. Over time, tartar grows and begins to put pressure on the gums. In addition, soft dental deposits spoil the aesthetics of a smile; pigment spots may appear on the enamel.
Another reason for the appearance of a fistula near a tooth may be infectious inflammation. Diseases such as tonsillitis, ARVI, and whooping cough reduce immunity, creating all the conditions for the proliferation of bacteria.
Symptoms of a fistula: how dangerous is it?
Fistula manifests itself with a number of symptoms:
- unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- tooth mobility;
- feeling of foreign taste;
- mucous membrane is bluish or, conversely, pale in color;
- discharge of purulent mucus, often with blood;
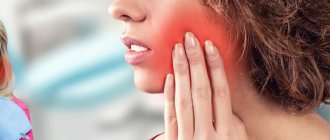
- painful sensations during mechanical contact (chewing food, drinking hot drinks, brushing teeth).
The disease may also be accompanied by symptoms not directly related to the oral cavity. It is manifested by such signs as apathy, general weakness, and fever.
Despite the small area affected, the fistula poses a certain health hazard. Thus, purulent discharge can penetrate the lymph or blood, which will lead to diseases of the internal organs, pathological processes in facial tissues and even loss of teeth. Therefore, even at the first relatively mild symptoms, it is important to consult a doctor.
It is worth keeping in mind that the disease is asymptomatic for a very long time. Moreover, if treatment is delayed, this can lead to partial death of the periosteum. And then the patient will have to remove not one, but several teeth at once.
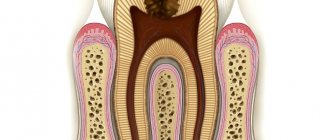
What is a fistula, what does it look like, symptoms
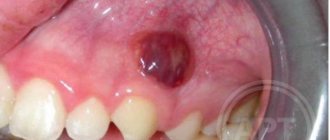
Externally, the fistula is a convex formation with a noticeable white spot on it. This means that the pathological process is accompanied by the formation of pus in large quantities.
There are two types of fistula:
- External, when the gum fistula comes to the surface;
- Internal, when the process remains hidden inside the gum, due to the fact that the fistula channel does not reach its surface. The inflammatory process can only be detected by x-ray examination.
Symptoms of a dental fistula are detected primarily by visual examination. There is a noticeable bulge on the gum, from where pus comes to the surface. There are other signs:
- The pain is cutting, stabbing, spasmodic. Becomes stronger with impact (for example, when chewing), weakens slightly after some of the purulent contents come to the surface;
- Putrid odor;
- Foreign tastes in the mouth;
- Tooth mobility with pathology;
- Swelling of the gums in the area of inflammation;
- Discharge of mucus with pus;
- Increased temperature, symptoms of intoxication of the body;
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes.
Diagnosis and treatment of fistula
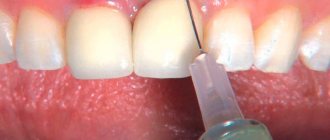
To carry out a diagnosis, you must contact your dentist. The doctor orders an x-ray and conducts a visual examination. Treatment is carried out in a clinical setting. Therapy depends on the cause of the fistula. For example, fillings are used to treat caries, and when an infection is detected, appropriate medications are used. The dentist can also perform treatment with ultrasonic waves or laser.
In some cases, a fistula appears due to poorly done filling of the canal. Then the patient is given an anesthetic, the filling is removed, the dental canal is cleaned and then a new high-quality filling is performed.
If the cause is a cyst, it is removed, which also requires the intervention of a dentist. For recovery, the use of antimicrobial agents, antibiotics, and antihistamines is indicated. If swelling occurs, the doctor may prescribe rinsing with a salt solution.
Diagnostics
First of all, this is a visual inspection. An external fistula is visible to the naked eye. If the fistula in the jaw is hidden, an x-ray is taken. With the help of X-ray examination, the focus of inflammation and the depth of the pathological process of damage to the periosteum are accurately identified. It is important to distinguish a fistula from gum tissue, purulent tissue inflammation and other pathologies.
Self-medication of such a disease at home and self-diagnosis are unacceptable. Treatment is carried out under the supervision of a doctor, which he prescribes based on the diagnostic results.
Is treatment possible at home?
A fistula can only be treated in a clinic. But if it is impossible to urgently visit the dentist, for example, the pain occurred at night, it is recommended to rinse the mouth with the following means:
- infusion of chamomile;
- infusion of oak bark (dry raw materials can be purchased at a pharmacy);
- if there is purulent discharge, the mouth should be rinsed with a solution of salt and soda or antibacterial agents.
The described measures help relieve pain, but do not eliminate the cause of the disease. Therefore, in any case, you need to see a dentist.
The appearance of a hole in the periodontium in a child
The formation of a hole in the gum near a tooth in a child can be due to reasons such as: periodontitis caused by complicated caries, or injury to the oral mucosa. With periodontitis, the lesion reaches the jaw bone. A cavity appears inside the periosteum, which is filled with pus. When there is an excess of pus, it breaks out through the fistulous tract, thereby bringing severe pain.
Frequent mechanical damage to the mucous membrane and gums causes infection to enter the oral cavity. Bacteria entering the periodontium cause inflammation and fistula formation.
Prevention of fistulas
The main measure for preventing fistulas is maintaining oral hygiene. It is necessary to undergo an annual examination by a dentist and, if necessary, begin treatment for caries and periodontitis in order to prevent the development of chronic diseases.
It is also advisable to be treated by experienced, qualified dentists, since poor-quality services can also lead to the formation of a fistula. After the intervention, you need to monitor your well-being to prevent the development of a fistula.
Fistula between tooth and gum
A hole between a tooth and periodontal tissue indicates the development of cervical caries or the complications it caused. Cervical caries can be located between the teeth and not be visible to the naked eye. Due to its inaccessible location, such caries often turns into pulpitis.
Pulpitis is an inflammation of the blood vessels and nerve endings located in the pulp chamber of the tooth. The chronic stage of the pathology may be accompanied by the formation of a purulent focus in the soft tissues. If pulpitis progresses to the next stage of periodontitis, several fistulas may appear at once.
Reasons for the formation of bumps on the gums
To find out why a lump appeared on the gum, you need to make a correct diagnosis; only a specialist can do this. There are several reasons why swelling appears, but none of them are harmless. When diagnosing, the nature of the formation, color, density, presence or absence of pain, purulent exudate is taken into account, and the nature of the disease is clarified - infectious or other.
Important! Basically, most dental problems are associated with poor oral care. As a result, mucosal pathology develops with its own symptoms.
The reasons why a lump appears between the gum and cheek may be the following:
- irregular and illiterate oral care, resulting in infection affecting periodontal tissues;
- complications of untreated caries - infectious lesions of the roots (fistula, periostitis);
- periodontitis;
- complications resulting from dental implantation;
- improper wearing or manufacturing of orthopedic structures;
- cystic formations;
- gingivitis;
- periodontal trauma (hematoma);
- benign neoplasms (epulis, fibropapilloma);
- malignant tumors.
There is another reason for the occurrence of periodontal compaction. If a child has a white bump on his gum, this may indicate the eruption of a new tooth. Short-term swelling is not terrible, but if after a long time the tooth does not appear, you should consult a surgeon.
Attention!
Many are in no hurry to go to the doctor, since the growth does not hurt. The absence of discomfort does not indicate the absence of disease. Remember: if a lump appears on your gum, only a doctor will determine what to do and how serious the consequences will be!
Diseases in which a lump on the gum does not hurt
There are diseases in which the resulting compaction does not bother the patient with pain. It is because of this that people are in no hurry to see a doctor, which can subsequently complicate treatment. In what diseases does a lump that appears on dental tissue not hurt?
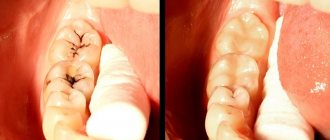
Fistula
If a lump with pus appears in the gum, for the flow of which there is a hole in the gum, we are talking about a fistula. The formation is a growth 3-5 mm in size with a white tip. When the outlet is not blocked by compacted exudate and pus flows freely, such compaction, as a rule, does not hurt. The reason for the formation of a fistula is a complication of periodontitis, in which the tissue grows and becomes infected by accumulated bacteria. Despite the fact that pus periodically flows out and does not accumulate in large quantities, if left untreated, an acute fistula becomes chronic. If the fistula is not treated, there is a risk of infection spreading through the periodontium and tooth loss.
Exostosis
Exostosis is a type of jaw abnormality when the bone protrudes slightly to the surface. Such a lump is hard and painless to the touch, since it is, in fact, a bone or osteocartilaginous growth of a benign nature. The causes of occurrence are hereditary predisposition, congenital pathology or consequences of injury. With such an anomaly, prosthetics are difficult or even impossible: the prosthesis will rub the skin on the bone growth, which can cause injury and infection.
Important! Exostosis is determined by x-rays. The decision to remove is made by the patient, but it is worth considering that such growths can become malignant over time.
Epulis
If a lump appears above the gum, shaped like a mushroom on a stalk, pale pink or red in color, we are talking about epulis - a pathological formation, common mainly in women, and also occurs in children when their first teeth erupt. The reasons for the appearance of epulis are often post-traumatic in nature (large filling, tartar, chips), however, a pathological growth can also appear due to malocclusion, hormonal disorders or wearing low-quality dentures. The symptoms of epulis are similar to those of gingivitis, so for an accurate diagnosis, the doctor uses radiography or a histological test.
Periodontitis
You should think about periodontitis if a lump has formed on the gum - hard to the touch, up to 10 mm in diameter. The causes of inflammation of the periodontal tissues are usually unsealed dental canals and their infection. An abscess forms at the root apex. A characteristic sign of the disease is that when you press vertically on a tooth, pain appears. If the pus has already drained, there may be no pain, but the disease cannot be ignored, as it can lead to tooth loss and further spread of infection.
Attention!
If a seal appears on the gum, under no circumstances should you apply a warm compress or hot rinses: this can aggravate the course of the disease!
Hematoma
A soft-to-touch swelling with watery contents – a hematoma – is formed as a result of tissue injury during tooth extraction. This bump, as a rule, does not require special treatment, dissolving a few days after its appearance.
Do not ignore preventive visits to the dentist.
It is enough to visit a specialist 1 – 2 times a year, which will allow you to promptly identify any dental problem at an early stage of development. This means that its elimination will be quick, easy and without complications.
By clicking the “request a call” button you agree to the personal data processing policy.
Why do ulcers appear on the gums, and is it always dangerous?
There are many possible reasons. To understand how dangerous the appearance of certain lesions on the gums is, you need to look at additional accompanying symptoms:
- in case it is trivial mechanical damage. The gums can be damaged by hard food, a toothbrush, or a foreign object. These lesions may resolve in 3-5 days. If a person does not brush his teeth, then infection is added to these damages, and healing may take several weeks.
- Sometimes ulcers can appear as a result of wearing orthodontic structures, braces or removable dentures.
Short description
If an inflammatory process, dental disease, or poor-quality therapy develops, a cavity appears that is filled with pus and blood. A canal connects it to the surface of the gum. It's called a fistula.
In other words, the hole is a kind of tube that helps release pus from the infectious focus. The shade of the fistula differs from the color of healthy gums; it is pinkish or reddish in color.
Healthy teeth do not become infected. The hole appears gradually, so even an early stage can be detected. Initially, the gums become swollen, after which an abscess begins to form.
Then the purulent or mucous contents come out, and tissue scarring begins. In this case, the disappearance of the channel is not observed, as a result of which relapse occurs periodically.
Prognosis and possible complications
If the fistula is detected and treated in a timely manner, the prognosis is favorable. If you follow all the specialist’s recommendations, within a week the resulting wound will completely heal and heal.
If proper treatment is not carried out, the following consequences are possible:
- abscess formation;
- phlegmon;
- osteomyelitis;
- tooth loss.
Preventive measures
- regular teeth cleaning;
- carrying out professional hygiene in the dental office;
- preventive examinations by a dentist every six months;
- daily consumption of fruits and vegetables.
Diagnosis of wisdom teeth
Any pathology associated with the problematic eruption of one or more wisdom teeth should always be investigated through x-ray diagnostics. To determine the position of the tooth in the jaw (inclination, shape, configuration, structure, how it grows), an orthopantomogram is used.
OPTG is a high-quality panoramic image of all teeth on both jaws. Another diagnostic method that will help you understand why your wisdom tooth hurts is visiography.
Causes of wounds in the gums
The main reasons why a hole forms in the gum:
- Incorrect treatment of caries. Pulpitis develops when purulent processes begin in the hard tissues of the tooth. As a result, an intradental cavity appears. As the disease progresses, the nerve will die and the infection will spread to the apex of the tooth root. If left untreated, periodontitis will begin to develop.
- Cyst. This is a capsule in which pus accumulates, which over time will seek a way out. This is how a hole appears. In most cases, when a cyst forms, there are no significant symptoms, which is why a person is in no hurry to visit a dental clinic. The appearance of a cyst is associated with untreated pulpitis.
- Improperly sealed tooth canals. The most common cause of a hole. Root canal filling is prescribed for pulpitis or periodontitis. If the procedure is carried out poorly, a void remains. An inflammatory process develops in it. The infection will then spread to the top of the tooth.
- Eruption of wisdom teeth. Often during this process, severe pain and inflammation appear, and swelling of the gums is observed. Inflammation can cause a purulent process, which will cause a hole to appear
- Perforation of the tooth root. When intervening in the root canal, a violation of its integrity may occur. Because of such an error, serious complications develop. A purulent process begins, which provokes the appearance of a wound in the gum.
Hole in the gum near the tooth
The main reason for the occurrence of a fistula in this place is pathogenic microflora of the oral cavity. With insufficient hygiene measures, mineralized dental deposits form more intensely, which can result in a hole appearing.
In addition, the appearance of a fistula is associated with an infectious disease (angina, scarlet fever, ARVI), due to which local and internal immunity decreases. This is favorable conditions in which pathogenic microorganisms will multiply.
- Fistula on the gum: treatment at home
Hole in gum after tooth extraction
After a tooth is removed, a hole remains. This intragingival space is normal. The resulting hole heals within 3-4 weeks after removal.
The hole in the gum after a wisdom tooth heals after 1.5-2 months. The healing time may increase if an infection occurs or the socket is frequently injured. Complications associated with tooth extraction can be prevented by following all medical recommendations.
Sometimes, after a tooth is removed, a gap appears, localized in the lateral part of the gum. In this case, the hole is tightened well. In such a situation, one may suspect that small parts of the tooth or dental material remain in the intragingival space.
The decomposition of the foreign body begins, resulting in the release of pathogenic bacteria to the outside. This creates a hole.
Hole between tooth and gum
The formation of a wound is associated with cervical caries and its complications. The carious lesion is located in a hard-to-reach place, not on the teeth, but between them, which is why it is often unnoticeable. Its development will cause pulpitis.
With pulpitis, the blood vessels and nerve bundles localized in the pulp chamber become inflamed. If the disease reaches a chronic stage, a purulent focus will appear. In the future, the purulent mass will seek a way out, resulting in the formation of a hole.
If you ignore pulpitis, you are more likely to develop periodontitis, which can cause several holes to appear in your gums.
Hole in a child's gum
The appearance of holes in the gums in children is associated with 2 reasons:
- periodontitis has developed;
- the mucous membrane was injured.
Mechanical trauma causes damage to the gum surface, resulting in infection.
- Consequences of a cyst in the gum of a tooth
Main treatment methods
The answer to the question of how to treat a fistula on the gum in a child is given by the dentist after a careful examination of the patient and collection of anamnesis. It is important that the doctor considers the process comprehensively, using not only medication, but also therapeutic methods. Sometimes proper local surgical intervention is also necessary. Let's talk about each of the listed measures in more detail.
First aid methods
When parents and a child visit the dentist, they need to answer questions about how long ago the first symptoms appeared and whether the child has other concomitant diseases. At the first stage, the symptoms of the disease are relieved, and then a deeper plan is drawn up to eliminate the root cause of poor health.
There are several basic first aid methods:
- Relieving pain syndrome. If the baby has a high fever and all signs of inflammation, you can give him antihistamines - Nurofen, Cifecon, paracetamol.
- Reducing swelling. It is best to use safe gels, such as Kalgel.
- Removal of pathogenic bacteria. Most often, this reduces inflammation. It is recommended to rinse or carefully treat the affected area with Miramistin or Chlorhexidine.
First aid helps to slow down the spread of the inflammatory process and reduce it. But you should take medications only with a clear understanding that the baby is not intolerant to them. It is best to consult a doctor.
Subsequent drug treatment will be based on taking properly selected antimicrobial drugs, antiseptics, anti-inflammatory and antihistamines.
Surgical intervention
Surgery is usually the last option to correct the situation. Doctors resort to it when other means are completely ineffective.
The main reason for prescribing such treatment is the widespread spread of soft tissue inflammation. The area becomes more and more extensive, and pus is actively flowing from the fistula.
In this case, the doctor removes the fistula and scrapes out the affected tissue. Today, laser processing is used for this purpose, which automatically seals small vessels. The likelihood of infection is minimal and the procedure itself is much faster and painless than using traditional surgical instruments.
Next, depending on the situation, the question of the need to remove the tooth is considered. Often it can be preserved and done with simple filling of the canals. A more detailed answer to the question about treatment methods can only be given after a careful examination of the patient.
Diagnostic methods
Typically, parents or a dentist detect fistulas at a very early stage. They are localized on the outer or inner side of the gums and reveal themselves by noticeable swelling and the appearance of a whitish lump.
It is very important not to self-treat when a problem is discovered. If your baby has baby teeth, improper treatment can pose a risk to the formation of the dentition. When the teeth are molars, there will also be a lot of problems, and there is a risk of needing extraction.
At the dentist's appointment, the doctor will carefully examine the child and take an x-ray. The location of the inflammation, its nature, and estimated depth are taken into account. Already at the first visit, the doctor begins to develop treatment methods to try to solve the problem without surgical intervention.
Symptoms
Signs of fistula formation include:
- aching pain that increases in the evening;
- burning and itching of gums;
- swelling in the affected area;
- gum hyperemia;
- increased body temperature;
- general weakness, chills;
- increased irritability;
- apathy.
The appearance of symptoms of pathology is individual for everyone. Some may experience very severe pain and discomfort in the mouth, while for others the symptoms may be almost invisible.
How to cure a hole in the gum
Before treatment, the doctor prescribes an x-ray examination to determine:
- hole position;
- condition of the roots;
- affected area.
Treatment is prescribed only by a qualified doctor. The therapeutic action plan is drawn up based on what caused the hole in the gum.
Drug therapy
To eliminate the inflammatory process and the source of infection, antibacterial drugs (tetracycline, metronidazole, lincomycin) are prescribed. If a hole in the gum is associated with caries or pulpitis, the tooth is treated. Regular external treatment of the inflamed area is also prescribed:
- Rinse your mouth with chlorhexidine. The solution has an anti-inflammatory, antiseptic effect. Pathogenic microflora is destroyed and the natural immunity of the mucous membrane is restored. Rinsing is carried out with undiluted preparation 2-3 times a day.
- Rinse your mouth with chamomile tincture. Fresh or dried flowers are used to prepare the decoction. Four tablespoons of raw material are poured into 0.5 liters of boiling water and left for 2 hours. Strain the solution using gauze. Rinse the mouth 2-3 times a day.
- Using Cholisal ointment. This is a special drug that is prescribed for gum diseases. Relieves the inflammatory process, eliminates painful syndrome. The drug is approved from the first months of life. The ointment is applied morning and evening. The duration of use is determined by the attending physician.
Surgery
Surgical intervention is prescribed when a hole appears in the gum due to periodontitis or an infectious source at the root. Local anesthesia is used. The fistula is opened using a dental scalpel, and the accumulated exudate is removed using drainage. The cleaned hole is treated with an antiseptic drug, then a medicated bandage is applied.
If the infection is present at the root, opening of not only the gums, but also the alveolar process is required. Surgical root treatment is performed using an open method. At the end of the surgical intervention and bone tissue augmentation, the wound is sutured. If the root is severely damaged and there is no possibility of its preservation, the tooth is removed.
- Fistula on the gum: treatment in a child
Folk recipes
If a fistula appears on the gum, in combination with drug treatment, the use of traditional healing methods may be prescribed. The most common and effective recipes:
- Herbal infusion. To prepare the decoction you need 2 tablespoons of St. John's wort, the same amount of calendula and chamomile. The herbs are poured with 0.5 liters of boiling water. Leave for 2 to 3 hours. Rinse the mouth with the strained infusion at least 4 times a day.
- Sage decoction. Used to disinfect and restore damaged areas in the oral cavity. It can be infused with yarrow or oak bark.
- Eucalyptus ointment. The leaves are crushed and sunflower oil is added. The infusion of the resulting mixture should last for at least 24 hours. After this, add a small finely chopped onion. The prepared composition is wrapped in gauze and applied to the hole in the gum. Eucalyptus ointment helps draw out purulent exudate and accelerates healing.
- Propolis. If surgery was performed, the use of bee propolis may be prescribed to disinfect the wound. It dissolves in the oral cavity until completely dissolved.
Prognosis and complications
If a hole in the gum is identified in a timely manner and treatment is started, the person will have a favorable prognosis with complete restoration of the mucous membranes. If you follow all medical recommendations, the elimination of the fistula occurs within 2 weeks.
If there is no treatment or a person self-medicates, the likelihood of developing dangerous complications increases:
- abscess;
- phlegmon;
- osteomyelitis;
- sinusitis;
- sepsis;
- tooth loss.
Signs of pus and purulent inflammation
- severe pain in the area of the wisdom tooth; when you press on the gum, pus is released;
- redness of the gums and swelling;
- a large carious cavity is filled with softened soft tissue;
- colored plaque on the tooth and tartar;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- change in facial contour. It becomes asymmetrical.
Treatment of gingival fistula
The treatment of fistulas on the gums is based on the principle of eliminating all factors that contribute to the formation of fistulas. Along with treatment of the underlying disease, the patient is prescribed a course of rehabilitation measures. In particular, the affected gum is treated with ultrasound or laser, cauterized with diathermic current, and antibacterial solutions, special gels, rinses and toothpastes are used to eliminate the inflammatory process. If necessary, the patient is prescribed antihistamines (suprastin, tavegil and others).
If complications develop, for example, if the pathological process spreads to the periosteal tissue, surgical removal of the fistula is performed. After completion of the operation, the patient is also prescribed a course of rehabilitation measures.
Treatment
Treatment is prescribed after a visual examination of the oral cavity and determination of the source of pus. Treatment of purulent inflammation can be:
- In a therapeutic way with the help of medicinal drugs.
- Physiotherapeutic.
- Surgery.
If purulent discharge does not stop after a course of therapeutic treatment, the doctor will prescribe surgery. Before the operation, plaque and tartar are cleaned and the mouth is disinfected.
An injection with a local anesthetic is injected into the gum and the gum is cut. The gum mucosa is cleaned of pus. If the fistula through which pus flowed is large, then a drainage is inserted. In the postoperative period, the patient is prescribed therapeutic treatment, which includes taking antibiotics and rinsing the mouth with a 0.05% chlorhexide solution, and is prescribed a complex of vitamins and minerals.
Every day, until complete healing, the patient must come to the dentist, where he is given an antibacterial application on the gum of the wisdom tooth. The patient must strictly follow all the dentist’s recommendations for oral care and consume only liquid foods.
What to do with it: remove or treat
Epulis on the gums is considered a serious pathology that requires specialist help as early as possible. Delaying a visit to the doctor can cause complications. What treatment will be carried out depends on the type of disease and clinical picture.
Treatment always begins with identifying and eliminating the provoking factor. If the cause lies in internal processes, then therapy is carried out simultaneously with the treatment of epulis. When a tumor is caused by orthopedic or orthodontic structures, tooth damage, poor-quality restoration, etc., the cause is first eliminated. Professional teeth cleaning using a gentle method is mandatory. The dentist may prescribe the use of local antiseptics, hormonal drugs, antibiotics and other types of medications depending on the cause of the pathology.
In most cases, angiomatous and fibromatous epulis of the gums can be cured conservatively. After the causes of the pathology are eliminated, the tumor may begin to decrease in size and even disappear completely. Giant cell epulis is an indication for surgical treatment.