Causes of caries of temporary teeth
Factors influencing the formation of caries on primary teeth can be divided into local and general
- Local factors:
- Pathogenic microflora in the oral cavity. This is the most common cause of caries in children. A change in one's own microflora can occur due to the ingress of foreign microflora. For example, a pathogenic environment can be transmitted to a child from parents or those who care for him. Therefore, it is important that parents' oral cavity is healthy.
- Poor hygiene. If the baby does not have oral hygiene, then bacteria accumulate on the teeth, which negatively affects tooth enamel and provokes the development of caries.
- Enamel hypoplasia. This pathology occurs even before the eruption of the first teeth directly in their rudiments. The cause of hypoplasia is a violation of metabolic processes, as well as protein and mineral metabolism in the body of a child or even a fetus. The defect provokes the development of caries, as tooth enamel loses its protective properties.
- Nutritional features. Diet greatly affects the condition of teeth. Foods containing large amounts of sugar (for example, baby juices and cereals) can trigger caries. If a child wakes up at night to eat, then the teeth are also subject to destruction, since food particles remain on them, which rot during sleep. At night, the production of saliva is reduced, which washes the oral cavity and provides protection to the teeth and mucous membranes.
- General factors:
- Weakened immunity. Children with weak immunity often suffer from viral and infectious diseases. During these periods, the composition of saliva changes: the level of protective substances in it decreases, which prevent the growth of bacteria. Therefore, children with weak immunity develop caries more often.
- Deficiency of vitamins and microelements. Typically, a deficiency state occurs due to improper and unbalanced nutrition, when the body does not receive enough nutrients. Because of this, saliva and, accordingly, tooth enamel have a low level of mineralization. The quality of complementary foods directly affects the condition of teeth. These should be not only sweet purees containing sugar, but also cottage cheese, vegetable purees and other foods containing vitamins and microelements.
- Chronic diseases. The presence of chronic diseases negatively affects not only the entire body, but also the condition of the teeth. These diseases include: frequent colds
- rickets
- dyspepsia (indigestion)
- exudative diathesis
- gastroenterocolitis
- dysfunction of the endocrine glands
- Iron-deficiency anemia
- measles, scarlet fever
- diphtheria
- dysentery
- pneumonia
- whooping cough, etc.
All these diseases affect the composition of saliva and make it pathogenic.
- The course of the mother's pregnancy. The rudiments of baby teeth are formed during the formation of the fetus in the womb. Therefore, it is important that the mother is healthy. One of the factors that negatively affects the development of a child’s teeth is toxicosis. According to statistics, mothers who have had late toxicosis are more likely to give birth to children who experience caries of primary teeth between the ages of 1 and 3 years.
- Mother's illnesses during pregnancy. Diseases such as rheumatism, heart defects, hypertension, arterial hypotension, endocrine diseases, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, blood, etc. negatively affect not only the formation of teeth, but also all other tissues of the unborn baby’s body.
- Bad habits of the mother during pregnancy. Alcoholic drinks, medications, tobacco smoke: all this affects the child. In the fetus, the rudiments of temporary and permanent teeth are affected, anomalies of the hard tissues of dental units are formed, and the mineralization of enamel is disrupted. All these disorders cause low resistance of teeth to caries.
Indications for tooth extraction for periodontitis
- Acute septic condition, intoxication of the body due to a tooth.
- The tooth became a source of periostitis or osteomyelitis.
- Formation of the tooth root to less than half its length.
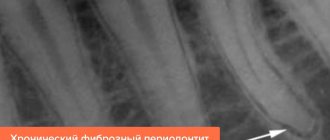
- Damage to the follicle plate (visible on x-ray).
- Root resorption by more than a third of the length, second or third degree of tooth mobility.
- Complete destruction of the crown (if the physiological change is less than one and a half years).
- Perforation of the wall of the tooth root or the bottom of the cavity.
- Internal root resorption.
- Ineffectiveness of conservative treatment.
- Aggravated general anamnesis.
- Retention of a tooth in the jaw during the eruption of a permanent tooth.
Conservative treatment of periodontitis in children is aimed at eliminating the source of infection, and then ensuring the normal course of physiological root resorption and preventing damage to the follicle of the permanent tooth.
Treatment depends on the etiology of the process (traumatic, infectious, toxic), on the stage of root development, on the form (acute or chronic), on the presence of a focus of periapical destruction and the condition of the young patient.
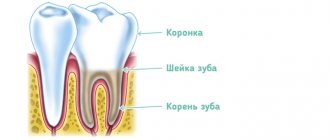
Symptoms of caries in primary teeth
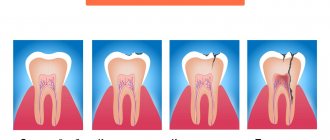
In children, caries is located mainly in the cervical region on the upper front teeth and in the grooves of the first and second molars. The infection quickly turns from a small spot into a large spot that covers the entire tooth. In an advanced state, the disease leads to the tooth simply breaking off.
In the early stages of caries, the disease is not accompanied by any symptoms. Sometimes children may complain of short-term pain and discomfort when eating sweet and sour foods, which quickly passes.
When the infection spreads to the contact surfaces, the teeth may feel like they are bursting, as if pieces of food are stuck between them. In addition, the gums become inflamed and bleed.
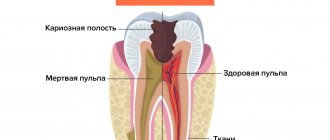
Deep carious lesions cause damage to the integrity of not only the enamel, but also the dentin of the teeth. The higher the activity of the infectious process, the greater the damage to dentin tissue.
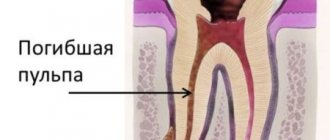
Caries may be limited to the front surface of the teeth, or may be localized on contact surfaces. In the latter case, the disease causes the tooth crown to break off. In this case, pulpitis often occurs - inflammation of the nerve bundle inside the tooth. These pathologies are accompanied by severe pain.
Dental treatment for children
The opinion of some parents that children’s baby teeth do not need treatment, since they will soon fall out anyway, is fundamentally wrong. A normal bite is formed on the basis of temporary teeth and, if caries progresses, the infection penetrates into the deep tissues and can damage the newly formed dentition.
Premature loss of baby teeth, destroyed by caries, leads to disorders that, even if they can be corrected, will cost a lot of time, money and nerves. The jaw develops with pathologies, permanent teeth grow out of place, often crowded. Subsequently, the child will have to wear braces for years in order to somehow straighten the teeth and achieve a normal smile.
Advanced caries causes pulpitis - inflammation of the dental nerve, periodontitis, and the formation of a cyst in the root area. To treat such consequences, you will have to fill the root canals. But the process does not stop there: periodontitis can turn into osteomyelitis and cause an abscess, and this is a problem on a completely different level. The disease reduces the overall immunity of the body and poses a threat to the very life of the child.
If you have any questions, doubts, etc., talk to your pediatric dentist, visit the clinic, sign up for a free consultation, find out how dental treatment for children is carried out, but do not leave your child alone with a problem he is not aware of. able to decide on my own.
Treatment methods for caries of temporary teeth
There are 2 groups of methods for treating caries of primary teeth:
- Non-invasive – techniques that do not involve surgical intervention. They are used in the initial stages of diseases with superficial caries. These include:
- Remineralization of teeth. The procedure is aimed at restoring the mineral composition of the hard tissues of the tooth and is carried out using preparations containing calcium and fluoride. Remineralization can be performed both in the clinic and at home.
- Deep fluoridation. It involves treating teeth with a special agent that provokes the formation of highly dispersed calcium fluoride. The latter, in turn, is a conductor of minerals that fill voids in tooth enamel, strengthening it. At home, it is possible to use calcium-containing gels, for example, Tooth Mousse, ROCS medical minerals, etc.
- Impregnation method (silvering) – filling of root canals. An alcohol solution of silver nitrate is used for the procedure. This product promotes the formation of albuminates, which form a protective film on the surface of enamel or dentin. The disadvantage of silver plating is that it temporarily turns the tooth black.
- Invasive – surgical methods used in the treatment of medium and deep caries.
- Infiltration of enamel with “Icon” material. This is a modern microinvasive technique for caries treatment. The main goal of the procedure is to restore the hard tissues of the tooth by filling voids in the enamel that can allow acids and minerals to pass through. The active ingredient is a 15% solution of hydrochloric acid. After it, the teeth are treated with synthetic resins, which penetrate into the cavities in which there was caries and fill them.
- Preparation of caries. This procedure involves mechanical removal of caries from the surface of the teeth using a drill. If the carious lesions are small, then you can get by with a hand tool - an excavator. If you need to treat a large number of teeth, it is better to do it under general anesthesia or sedation.
After removing the caries, the doctor performs a filling using the following materials:
- composite fillings;
- glass ionomer cements;
- compomers.
Primary teeth are usually filled with glass ionomer cements due to their good adhesive and anti-carious properties.
If most of the coronal part of the tooth is destroyed, then the unit is restored using a crown. The denture protects the tooth from plaque and bacteria, as well as the effects of other external factors (hot and cold food).
Therapy of acute toxic periodontitis of temporary teeth
A conservative approach is aimed at neutralizing the effect of a toxic substance and eliminating inflammation. After anesthesia and opening of the cavity, the dentist removes the devitalized pulp or turundas with an aggressive medicinal substance. Full instrumental processing of the channel is performed. Then, depending on the cause of periodontitis, a suitable antidote drug is selected for treatment. It will be different for arsenic periodontitis and disease caused by phenol. The drug is injected into the canal on the turunda and the cavity is hermetically closed for a day.
If the pain reaction is severe, the patient is prescribed analgesics. The child is examined every day. If the pain and soreness of percussion persist, the antidote treatment is repeated, and the intracanal dressing is left for another day, adding intracanal agents with an anti-inflammatory effect. After the symptoms disappear, the canal is completely obstructed.
Prevention of caries in baby teeth
When diagnosing caries of primary teeth at an early stage, the prognosis for treatment of the disease is favorable. If the disease was discovered when it was in an advanced form, then premature tooth loss or death of the molar tooth germ may occur. In any case, it is necessary to carry out treatment and follow-up monitoring. Preventive examinations by a specialist should be carried out once every 2-3 months.
For timely prevention of caries of primary teeth, it is necessary to eliminate risk factors for the development of the disease and control:
- Mother's health during pregnancy.
- The course of labor.
- The condition of the child after birth.
- Character and mode of feeding.
- Taking medications in a child.
To maintain the health of your child’s teeth, you must follow the following recommendations:
- Carry out the first examination by a pediatrician within a month after the birth of the child. A specialist will be able to assess risk factors for the development of pathologies in the body, including in the oral cavity. If any are identified, the doctor will give advice on preventing the development of dental diseases.
- When a child’s first teeth erupt, their hygiene should be carried out using special napkins or fabric rags soaked in boiled water. You can also use rubber finger brushes with polymer bristles.
- It is necessary to select toothpastes that are appropriate for the child’s age. They will not harm the body if swallowed and do not contain dyes or harmful chemicals.
- If your child has eaten sweets, you need to brush or wipe his teeth. Leftover sweet foods should not remain in the mouth for long, as refined carbohydrates have a negative effect on them, causing tooth decay.
- It is recommended to periodically treat baby teeth with gels containing calcium.
- On chewing teeth, you can close fissures (natural depressions on the surface of the enamel). This is an easy and painless procedure performed using dental sealants.
As you know, the best treatment is prevention. Therefore, it is important to visit pediatric dentists promptly and regularly. One of the best dental clinics in St. Petersburg is “World of Dentistry”. Experienced specialists work here who know how to find an approach to small patients and provide high-quality treatment in an atmosphere of absolute comfort.
Therapy of acute traumatic periodontitis of temporary teeth
Transapical removal of an endodontic instrument often ends in periodontal trauma, which is accompanied by infection. The tooth can be treated in a “closed” way due to the absence of exudation. Treatment is similar to the regimen for toxic periodontitis, but instead of antidotes, substances with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties are used.
If root formation has not yet completed, treatment requires special care so as not to damage the growth zone or permanent tooth germ with an instrument or irritating drug. In this case, the apical foramen is not opened.
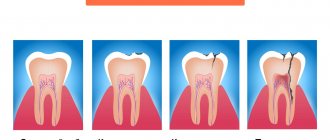
Superficial caries
If treatment is not carried out, the process progresses - the spot becomes soft and a small cavity forms under it - superficial caries. With superficial caries, pain occurs from chemical agents - sweet, salty or sour. Often this stage is asymptomatic, which makes it impossible to identify the process in the early stages. If the tooth is not treated in time, the carious cavity will increase and reach the dentin - medium caries or deep caries.