Unfortunately, some patients do not want to have their teeth treated, which often leads to serious complications, including gumboil or periostitis. The person experiences severe pain, cannot eat, drink, or sleep, the cheek swells, and the temperature rises. In this case, you will need prompt assistance from a professional from the Center for Modern Dentistry, who will provide treatment without pain and stress using modern techniques and anesthetics. In our article we will talk in detail about the causes of tooth flux, why it is dangerous to health, as well as methods of treatment and prevention of caries and periodontitis.
What is tooth flux
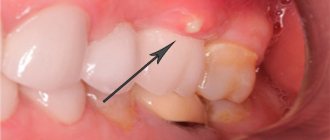
Tooth gumboil is usually an exacerbation of diseases such as periodontitis or periodontitis. An acute inflammatory process begins in the area of the tooth root, when the nerve has already died and an infection develops in the root canal.
Periostitis is a common disease among children and adults. The inflammatory process manifests itself as follows: a cavity filled with pus appears on the mucous membrane of the jaw - a purulent bubble. As a rule, flux is accompanied by severe swelling of the cheek, pain and increased body temperature.
In the absence of professional dental care, the inflammatory process will develop further. Tooth flux can cause serious complications: phlegmon and sepsis. The patient will need a lot of time to recover.
Forecast
If the patient strictly adheres to all recommendations and carefully monitors hygiene, then there is no need to fear relapses.
If treatment was started already in the acute stage of flux or interrupted in the middle, then the prognosis becomes less pleasant. Flux can become chronic, which increases the risk of re-development several times. If the patient does not seek qualified help on time, then the flux can even cause blood poisoning, which leads to death.
It is very important to use only proven treatment methods and consult with experienced specialists, since some consequences of self-medication can be even more unpleasant than the disease itself.
Symptoms of tooth flux
Among the first signs of periostitis are the formation of a painful infiltrate on the alveolar process, fluctuation, and swelling. The tooth itself usually doesn’t hurt anymore
If you discover symptoms of periostitis, we strongly recommend that you consult a doctor who will stop the spread of infection and remove inflammation. But if you haven’t decided or haven’t found the time to make an appointment with a dentist, then let’s figure out how the situation will develop further.
If the spread of infection is not stopped, then at the next stage the flux will manifest itself visually, as we wrote about earlier - a bubble appears on the gum, the cheek swells. In this case, urgently go to the Center for Modern Dentistry, otherwise you risk ending up in the hospital in a couple of days. Surgery will be complex and may last for a week or more.
Answers to frequently asked questions
- How to get rid of flux?
You should immediately contact a dental surgeon. He will administer anesthesia (local anesthesia), make an incision and/or remove the tooth. The choice of treatment method depends on the specific clinical situation and the stage of periostitis. In addition, the doctor will select the necessary medications and dosages to eliminate the infection and swelling.
- What means should I use to rinse so that the flux breaks through?
Here it is worth using antiseptic solutions, for example, Chlorhexidine, Miramistin. You can also use saline solutions (1 teaspoon of baking soda and 1 teaspoon of baking soda per glass of water). It is worth noting that if the flux has broken through, this does not mean that it has completely gone through. There will be some relief, but the pain and swelling will return, so you need to urgently consult a dentist.
- What to do after flux treatment?
If such a serious disease as periostitis (flux) has occurred in the oral cavity, this indicates that the condition of the remaining teeth is also extremely unsatisfactory. It is necessary to find out which teeth still need treatment. Examination and consultation are carried out by doctors in our clinic. The best prevention of gumboil development is timely treatment of caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, as well as regular professional oral hygiene.
Diagnosis of tooth flux
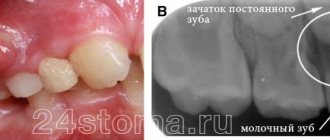
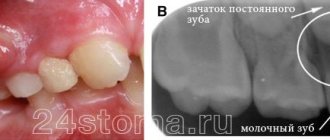
At the dentist's appointment, a thorough examination of the oral cavity and an X-ray examination - a targeted or panoramic image - is carried out. In some cases, two studies will be required to make an objective diagnosis.
As soon as the diagnosis is made - exacerbation of chronic periodontitis and the diseased tooth is identified, the doctor begins treatment.
Flux
3027 13 July
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Flux: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Flux, or periostitis, is an inflammation of the periosteum (periosteum) of the jaw. The root of the tooth is located in a special hole, which is called the alveolar process, if we are talking about the upper jaw, or the alveolar part, when we are talking about the lower jaw. With periostitis, inflammation spreads from the affected tooth to the alveolar processes or alveolar part, the body of the jaw and other surrounding tissues, for example, the gums.
Periostitis of the jaw is one of the most common complications of purulent inflammation of the tooth and accounts for 20 to 40% of their total number.
In approximately 60% of patients, periostitis occurs in the lower jaw and in 40% in the upper jaw. In 94-95% of cases the process is acute, and only in 5-6% the inflammation becomes chronic.
Reasons for the appearance of flux
The development of acute periostitis is most often associated with bacterial microflora. In most cases, the cause of flux development is untreated caries - destruction of hard tooth tissue. As caries progresses, the infection penetrates inside the tooth and affects the pulp, a soft connective tissue consisting of blood vessels and nerve plexuses. From the infected pulp, inflammation penetrates further through the tooth canal - into the bone and submandibular periosteum.
Other diseases can also lead to periostitis, for example, inflammation of the periodontium - the tissue surrounding the root of the tooth, gums (periodontitis), suppurating jaw cysts, alveolitis (an infectious-inflammatory process in the area of the tooth socket and its walls). In people with weakened immune systems, inflammation of the periosteum may develop after tooth extraction or oral surgery.
Chronic periostitis can be caused by acute purulent periostitis in case of a weak immune response, as well as suppuration of cysts, inflammatory processes in the maxillary sinuses, injuries when using removable dentures, and difficult teething in children.
Most often, chronicity of the process occurs in children, the elderly and in patients with weakened immune systems.
Classification of flux
According to
the clinical course
, acute and chronic periostitis are distinguished, while acute periostitis can be serous and purulent. In the classification of chronic periostitis, simple and ossifying periostitis, as well as its rarefied form, are distinguished. The ossifying form is characterized by hyperostosis - the proliferation of bone tissue. Referential periostitis usually occurs after injury; it is accompanied by restructuring of bone structures and pronounced symptoms of osteoporosis.
Flux symptoms
In case of acute flux, the patient complains of general weakness, weakness, loss of appetite, insomnia, fever up to 37.5-38.0°C (in rare cases - up to 38.5-39.0°C). On the affected side there is pronounced inflammatory swelling of the soft tissues. When the process is localized in the upper jaw, the swelling spreads to the infraorbital region, nasolabial fold, and upper lip. Swelling of the lower jaw extends to the submandibular region. Due to swelling of the soft tissues, the face becomes asymmetrical.
Acute diffuse pain in the jaw radiates to the ear, temple or eye, causing difficulty opening the mouth.
If the cause of the flux is a tooth disease, the pain intensifies when biting on the affected tooth or touching it with the tongue. As the disease progresses, the pain when pressing on the tooth may decrease, but the pain in the jaw area increases.
Purulent periostitis, localized in the transitional fold of the oral cavity, is characterized by painful limited swelling in the form of a roller, sometimes with fluctuation phenomena (sensation of iridescent liquid), indicating the accumulation of pus.
In the chronic course of the process, the pain is wave-like in nature - it is weak, aching, inflammatory infiltration of the surrounding soft tissues is poorly expressed, the configuration of the face is not changed or there is slight asymmetry, the submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged, compacted, and painless. Patients may complain of thickening of the jaw in the area of inflammation - both from the skin and from the oral cavity.
Flux diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, the doctor collects complaints and medical history, examines the maxillofacial area, palpates the lymph nodes, chewing muscles, and assesses the degree of mouth opening and pain.
Additionally, a general blood test and x-ray examination are prescribed to determine treatment tactics.
How is tooth flux treated?
If the cause of the inflammatory process is a diseased tooth, then at the first stage the question of the possibility of preserving it is resolved. Our experienced specialists will do everything to avoid removal.
Treatment usually involves five stages:
- first: the doctor, under local anesthesia, removes all tissues affected by caries, old fillings and creates direct access to the tooth canals
- second – removal of the nerve and determination of the length of the root canal
- third - expansion of the root canal of the tooth to gain access to its deeper areas
- fourth - installation of a paste containing calcium into the canal to stop acute inflammatory processes.
- fifth – temporary filling of the root canal
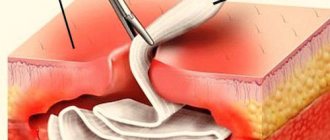
If necessary, an incision is made in the gum, the pus is removed and drainage is installed. For tooth flux in an adult, the doctor may also prescribe antibiotics or other drug therapy. In three to seven days you will need to come back for a follow-up appointment. If the doctor sees that there is no pus, the abscess is completely stopped, and the swelling of the cheek has subsided, he will seal the dental canal. The final stage of treatment will be the restoration of the crown of the tooth.
Treatment
It is important to understand that gumboil cannot be cured in one day. It is necessary to prepare for at least a week of treatment. It is very important to use only those treatment methods prescribed by a specialist, and not use dubious folk remedies and advice on forums on the Internet.
Self-medication is dangerous with complications!
Attention
Despite the fact that our articles are based on trusted sources and have been tested by practicing doctors, the same symptoms can be signs of different diseases, and the disease may not proceed according to the textbook.
Pros of seeing a doctor:
- Only a specialist will prescribe suitable medications.
- Recovery will be easier and faster.
- The doctor will monitor the course of the disease and help avoid complications.
find a doctor
Do not try to treat yourself - consult a specialist.
All treatment is divided into several main stages.
Visit to the dentist
This part is mandatory, since this is where the examination is carried out and further treatment is prescribed, even if it does not require surgical intervention. However, at some stages the flux must be opened.
In this case, the dentist cleans the gums and bone tissue. If the flux has already burst, the doctor cleans out the purulent masses through a special incision. If the abscess is still mature, then the pus is removed through drainage.
Drug treatment
One of the most important components of successful treatment is antibiotics. You should use only those medications prescribed by your doctor. In addition to antibiotics, anti-inflammatory, antihistamine and painkillers are prescribed.
External treatment
This method is auxiliary, but no less effective. Tissue treatment is necessary in order to relieve inflammation and destroy microbes.
Prevention
This is one of the most important parts of treatment and is especially effective in preventing relapses. In addition to careful oral hygiene, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of the primary disease.
If it was caries, then the affected tooth should be removed. If the flux is the result of a sore throat, then it is necessary to take a course of vitamins and immunomodulators that will help avoid this disease in the future. It is also necessary to visit the dentist several times a year solely for preventive purposes.
Tooth gumboil: what medications to take?
This is the most common question in Internet search engines when people try to deal with the problem on their own. Our answer: “Do not take anything before consulting a doctor!” Only the attending physician, taking into account the stage of the disease and your individual characteristics, can prescribe an antibiotic for tooth flux, which stops the inflammation process. The dentist will also advise which drug is best to use as an anesthetic.
Why does flux burst?
Above in the article it was said that pus is looking for a way out. So, when there is too much of it, the capsule in which the purulent masses are located becomes thinner, and the gum stretches, causing it to rupture and form a small hole through which the contents of the abscess come out. Very often, the gumboil breaks through on its own, after which the patient almost instantly experiences relief, the pain subsides, and the swelling of the gums goes away a little. But you shouldn’t assume that this problem is solved. In fact, only part of the pus came out, and a large number of microbes remained in the gum. This is very dangerous because it can cause flux to form again. To prevent this from happening, you need to visit a dentist who will treat the wound and cure the tooth.
Prevention of flux in adults and children
Since the main cause of gumboil in both adults and children is complications of caries, careful oral care and timely dental treatment at the Center for Modern Dentistry are necessary. We recommend brushing your teeth morning and evening, rinsing your mouth after meals, and using dental floss and irrigator.
In addition, once every six months you need to come for a preventive examination at the dentist, where the doctor will identify caries and immediately begin treatment. An effective method for preventing diseases of the teeth and gums is a professional hygiene procedure in the dentist’s office, during which a specialist will remove hard dental plaque from the teeth, which is simply impossible to get rid of at home.
The Center for Modern Dentistry employs experienced specialists who use progressive techniques to treat tooth flux, as well as modern anesthetics that will relieve you of the pain of stress. Therefore, if you feel pain, do not delay your visit to the doctor, put off work and any other activities. Your health is much more important.
Types of disease
Flux is classified according to its development into the following types:
- Odontogenic. Pathology occurs against the background of advanced diseases of teeth and gums,
- Hematogenous. The disease develops when infection penetrates through the circulatory system.
- Lymphogenic. The cause of the disease is pathogenic microorganisms in the lymphatic system.
- Traumatic. Flux occurs at the site of injury to the periosteum, often after unsuccessful dental procedures during dental treatment.
According to the degree of spread, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- An ordinary flux that does not affect the periosteum.
- Fibrous flux, characterized by the onset of inflammation in the tissues of the periosteum.
- Orthodogenic flux, which develops as a complication - osteomyelitis, which requires tooth extraction.
- Albuminous flux, characterized by a chronic course, subfertile temperature and the occurrence of suppuration.
Flux on the gums: treatment, causes
From this article you will learn:
- why does flux (abscess) occur?
- abscess on the gum: treatment, antibiotics,
- opening of a gum abscess: video.
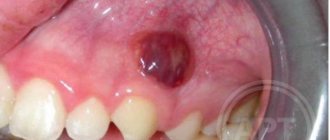
Flux on the gum is a swelling of the gums associated with the development of purulent inflammation. Dentists do not use the term gumboil or abscess (only patients say so), but use terms such as “gingival abscess” or “periostitis”.
Flux on the gum: photo
How to cure gumboil
With periostitis, there can be no talk of any home treatment. Prompt medical attention is required. At best, home treatments will briefly relieve symptoms; at worst, they will accelerate the course of inflammation. It is strictly forbidden to heat the affected area (as the pus spreads faster), take antibiotics and painkillers without a doctor’s prescription (there is a risk of bleeding). If you ignore the problem, you can achieve sepsis - blood poisoning - and even death.
At the clinic, the doctor conducts an examination, consultation, and, if necessary, prescribes x-rays and blood tests to determine the extent of the disease and the level of leukocytes. If the patient seeks help at an early stage of periostitis, the specialist prescribes therapeutic treatment. This is taking antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs that destroy pathogens. If the situation is advanced, the doctor removes the flux through surgery: administers anesthesia, makes an incision in the gum, cleans out the pus, disinfects the wound and installs drainage. Additionally, laser therapy or iontophoresis may be needed.
This is followed by a period of rehabilitation: taking antibiotics, immunomodulators, rinsing with antiseptics. Monitor the condition of the oral cavity for 3-4 days. If during this time the symptoms do not subside and the swelling does not go away, you should consult a doctor again. If the tooth crown is destroyed by more than 50%, as well as in case of relapse of periostitis, the tooth will have to be removed.
Simple means to speed up flux breakthrough
An abscess causes discomfort, is very painful and makes the patient nervous. But you cannot pierce the lump yourself to break through the pus. You can speed up the process of maturation of the abscess using medications and folk remedies.
At home, you can do the following: rinse your mouth with a disinfecting solution, make sure that there are no cracks, wounds, or open caries in the area of the abscess. Then the fingers are treated with alcohol or chlorhexidine. If the flux is well matured, lightly press on it. The walls should burst.
The resulting pus is spat out - if it penetrates the stomach, it can cause infection . Then the mouth is rinsed again with an antiseptic (Miramistin or chlorhexidine). Remember that decoctions of medicinal herbs will be useless in this case.
You need to rinse your mouth for another 1-2 days until the remaining wound heals. Make sure there is no new pus collecting in it. To prevent relapse, maintain good oral hygiene.
Herbal tincture for gumboil
To make the flux break through faster, you can make a solution from “Rotokan” - a tincture consisting of yarrow, calendula and chamomile:
- dilute 1 part product in 10 parts water;
- rinse your mouth;
- repeat 4-5 times a day.
The drug eliminates inflammation, destroys bacteria and relieves pain. Instead of Rotokan, they use a tincture of calendula in alcohol to break through the gumboil.
Aqueous infusions of herbs for flux
To make the abscess break faster, you can use other herbs. An infusion of sage and green tea is used to rinse the mouth.
When treating the disease, you should not heat a purulent abscess, since under the influence of heat the abscess spreads to nearby tissues and worsens the patient’s condition. If dental caries is not treated, the abscess will constantly return. The destruction of bone tissue continues for up to 20 years, and during this entire period a sluggish infection is present in the body, weakening the immune system.
Rinse solutions are prepared from some dry mixtures: take 1 part herb to 5 parts water and boil for 15 minutes over low heat. The following are suitable for this: plantain, coltsfoot, sage, chamomile, calendula, oak bark. You can make combined infusions:
Melissa . For 1 liter of water take 0.5 tbsp. dry grass. Pour boiling liquid over the mixture and cover with a warm towel. After an hour, filter, you can rinse every 2-3 hours so that the abscess breaks through faster.
Oak bark and sage . Take 1 part each of lemon balm, oak bark, and sage. Pour boiling water so that there is 3-4 times more of it than the mixture. Rinse your mouth 7-10 times during the day.
Hyssop herb . At 2 tbsp. l. dry composition, take 1 cup of boiling water, pour in for 2 hours. Strain and mix with 10 drops of table vinegar. You should rinse your mouth several times a day to quickly break through the lump.
Mint and birch buds . Mix 100 g of dry heel, 50 g of angelica, 50 g of birch buds and the same amount of periwinkle. Pour a liter of boiling water for 50 minutes. You should rinse every 3 hours.
Oak bark . Mix 0.5 liters of boiling water with 2 tbsp. l. dry composition for 30 minutes. You can rinse every hour to relieve pain and speed up the breakout of the lump.
The use of herbal infusions does not guarantee the desired result. They are prescribed to speed up the healing process, disinfect and relieve pain from the flux.
Other means
Here's what to do to make the gumboil break through faster using additional preparations:
- dilute 3 drops of iodine in a glass of water, rinse your mouth;
- take an aloe leaf , cut it in half, apply the mucous part to the damaged area (do not forget to remove the needles from the sides so that they do not injure the gums). After 4-6 hours or after eating, change the application;
- use of cabbage leaf - pour boiling water over the vegetable for 10-15 minutes, then cut out a small piece from the cabbage. It should be soft. Then the product is applied to the damaged area;
What to do if a child has flux
Flux is not common in children and occurs against a background of weakened immunity - for example, after illness. Since any infection spreads faster in children, the child should be seen by a doctor immediately. Moreover, if the baby’s age does not exceed 5 years, urgent hospitalization is indicated.
In older children, treatment is the same as in adults. Diseased teeth are treated or removed if they have no functional value. Local and general treatment is combined with physical and antimicrobial therapy.
It is important to stimulate increased immunity and strengthen the children's body. But this is the task of a pediatrician, not a dentist.