Types of flux
This pathology is characterized by several stages of its clinical development. At the first stage, minor pain appears. The second stage is characterized by swelling and redness of the gums in the area of infection.
During the third stage, pus appears, the temperature rises, and the cheek and gum area swell noticeably. At the fourth stage, a person feels a sharp throbbing pain, swelling intensifies, and an extensive inflammatory process may begin. The following types of flux exist:
- Ordinary.
The pathological process occurs without infiltration of the periosteum by pus;
- Fibrous.
With this type of periostitis, inflammation spreads to the periosteum tissue;
- Orthodogenic periostitis.
The disease manifests itself in the form of osteomyelitis, which is a serious complication requiring surgical tooth extraction;
- Albuminous flux.
Chronic pathology, which is characterized by a sluggish course, subfertile temperature and suppuration.
Only a dentist can determine the type of disease and prescribe proper treatment, but before visiting, it is necessary to stop the process.
What is tooth flux?
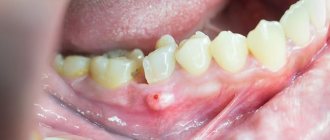
What is tooth flux? Flux, or odontogenic periostitis, is a purulent inflammatory process in the tissues surrounding the tooth, characterized by the formation of a purulent abscess. It can be an independent disease, but most often develops as a complication of dental diseases. It manifests itself as suppuration of the gums, swelling and redness of the gums and cheeks, pain, and fever.
It’s worth saying right away that such tooth flux is a disease that is almost impossible to cure at home, and self-medication in this case is simply dangerous. If the pus begins to spread into the intermuscular spaces on the face and down to the neck, purulent phlegmon develops, which in some cases leads to death. Therefore, there is no need to take risks - if you detect signs of gumboil, you should immediately go to the dentist.
What to do in case of tooth flux:
- Rinse your mouth with a baking soda-salt solution: add 1 teaspoon of baking soda and salt to a glass of boiling water, cool the solution and rinse your mouth thoroughly. Such rinses should be performed every 2-3 hours before visiting the dentist.
- Applying a cold compress to the painful area for a few minutes will help relieve pain and reduce swelling.
- At the first opportunity, go to the dental office for treatment of gumboil.
The dentist performs flux treatment under local anesthesia: if necessary, removes the tooth, opens the abscess and installs a special drainage to ensure the drainage of pus. In addition, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs - they should be used strictly as prescribed, without amateur activities.
But what to do in case of tooth flux is strictly prohibited:
- Applying warm compresses will only speed up the spread of pus through the soft tissues.
- Open a purulent abscess on the gum yourself.
- Apply homemade bandages.
- Take antibiotics at your own discretion, without a doctor's prescription.
- Before visiting the dentist, you should not take analgesics, as this will complicate the diagnosis.
- Aspirin should not be taken as a pain reliever, since it thins the blood and can cause bleeding when treating flux at the dentist.
And you should not rely on a wide variety of folk remedies - they do not provide a complete cure, but can only relieve pain and reduce tissue swelling. But often such drugs provoke complications of the disease. Therefore, entrust the treatment to specialists.
Rinse with flux
Rinse solutions have a regenerating and anti-inflammatory effect on the pathological focus. You can use a soda solution, which reduces pain and inflammation. Rinsing should be done every two hours. Two teaspoons of soda are dissolved in 200 ml of warm water and used throughout the day.
Manganese solution has good therapeutic efficacy. It will reduce swelling by eliminating pathogenic microorganisms. You can use the drug Rotokan, which includes chamomile, yarrow and calendula. To prepare the solution, just add one spoon of Rotokan to warm water. You should rinse your mouth at least 4-5 times a day.
Antiseptics such as Chlorhexedine and Miramistin are also used. They do not need to be dissolved in water. It is enough to irrigate the affected cavity in order to reduce swelling, pain and inflammation. Rinse products similar in their therapeutic effects to Miramistin and Chlorhexidine also include Furacilin, which is sold in tablets. A couple of tablets are enough to prepare 200 ml of solution for treating the oral cavity.
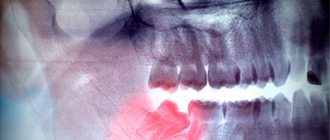
Flux diagnostics
The patient can recognize the first manifestations of flux himself. He will feel the characteristic symptoms described above. Regardless of the stage of the disease, you need to see a dentist for an appointment. The doctor will conduct an initial examination of the gums. If necessary, he will prescribe x-rays and tests to determine the stage of inflammation and possible complications. The dentist then selects an individual treatment.
Early contact with the dentist will help to quickly cure gumboil and avoid possible complications.
Compresses and lotions for periostitis
Compresses and lotions have a local anti-inflammatory and disinfecting effect, they destroy pathogenic microbes and will help get rid of swelling on the mucous membrane. You can use the drug Dimexide, which is diluted with water until a concentration of 20-30% is reached. The compress is applied to the area of inflammation and left for about an hour.
Soda lotions also help a lot. Baking soda is diluted in a volume of two teaspoons in 200 ml of water. You can moisten a cotton pad or several layers of gauze with the solution and then apply the lotion to the affected area of the gum.
Good therapeutic effectiveness is also observed when using salt compresses. It is enough to dissolve a couple of teaspoons in 100 ml of warm water. A gauze swab soaked in the solution should be applied to the inflamed area and held between the gum and cheek for at least half an hour.
Features of flux flow and the reasons for its appearance
Flux
Flux (periostitis) occurs when a very strong inflammation process develops. Reasons for its development:
- poor oral care, improper hygiene or lack thereof;
- tooth trauma;
- accumulation of microbes in dental pockets;
- infection of the pulp with advanced caries.
Soft plaque often accumulates on the gingival edges of teeth, which gradually hardens and turns into tartar. It is in such plaque and stones that millions of pathogenic bacteria live, the waste products of which lead to inflammation and ulcers.
Periostitis is accompanied by swelling of the gums and mucous membranes of the cheeks; often the outer side of the face also swells. Depending on where the center of the lesion is located, the eye, neck, and chin areas may swell. The lymph nodes under the jaw often become inflamed, causing pain. If the flux is not eliminated in time, the pus moves into the area of the periosteum, maxillary sinuses and jaw bones.
Self-medication for periostitis is dangerous. Correct treatment can only be prescribed by an experienced dentist, which may vary depending on the characteristics of the disease and its location.
If left untreated, pus accumulates at the top of the tooth root. It is because of this that flux occurs, swelling and pain appear. The infection then spreads to healthy tissue, bone tissue and periosteum. In this case, you cannot do without surgical intervention - removal of pus after an incision and extraction of the affected tooth.
Anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics
The use of antibiotics helps relieve pain and stop acute inflammation. You can use antibiotics such as Trichopolum, Lincomycin, Ciprofloxacin, Flemoxin, Biseptol, Amoxiclav, Tsiprolet. Antibacterial drugs should not be used for more than five days to avoid microbial resistance in the body.
To reduce swelling and redness, you can additionally take Diazolin, Nimesil or Diclofenac, which have a local anti-inflammatory and decongestant effect.
Why does pathological formation occur?
The main reason for the development of the pathological process is injury to the soft tissue of the gums. The disease also often develops against the background of:
- Caries.
- Inflammation of the gum pocket.
- Violation of the rules of oral hygiene.
- Infectious diseases: tonsillitis, furunculosis, etc.
Pathology is characterized by gradual development:
- The initial stage is characterized by the appearance of mild pain when touching the gums.
- In the second stage, swelling and redness of the gums develop, and the pain becomes intense.
- If left untreated, pus appears in the gum pocket, body temperature rises, and swelling spreads to the cheek.
- Next, an extensive inflammatory process develops, characterized by the appearance of acute throbbing pain and an increase in the area of edema. The patient's general condition deteriorates significantly.
Gels and ointments
Ointments are used for topical application. In particular, this is Vishnevsky’s ointment, which stops the development of the purulent process. The birch tar included in its composition increases blood circulation in tissues and accelerates their natural regeneration.
Among modern gels, it is recommended to use the drug Metrogyl Denta, which contains antibacterial components in the form of Chlorhexidine and Metronidazole.
This article is for informational purposes only, please consult your doctor for details! Ask your doctor about contraindications and side effects.
How to recognize periostitis
The most striking signs of gumboil are swelling and throbbing pain in the area of inflammation, which intensifies with pressure on the tooth. Over time, pain does not respond to painkillers, the cheek and jaw swell due to inflammation, the gums become red, pain can radiate to the eye, ear or throat (difficulty swallowing, turning the neck), body temperature rises, lymph nodes enlarge, weakness in the body is felt .
Causes of inflammation:
- neglected or untreated caries is the most common cause;
- dental intervention - flux after tooth extraction, poor quality treatment;
- sinusitis;
- angina;
- hypothermia;
- infections and injuries of teeth and gums;
- insufficient hygiene;
- Oral diseases - periodontitis, pulpitis, gingivitis and others.
Classification of periostitis
Like any inflammatory dental disease, periostitis can manifest itself in various forms. So, based on the cause of the development of pathology, it is customary to distinguish the following types:
- odontogenic: develops against the background of untreated diseases of the teeth and gums,
- hematogenous: occurs as a result of infection through the circulatory system,
- lymphogenous: becomes a consequence of the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the lymphatic system,
- traumatic: develops as a result of mechanical trauma to the periosteum, damage to the integrity of the jaw bone, or surgical intervention.
According to the degree of spread, limited and diffuse forms of the disease are distinguished. If in the first case the infection spreads to one or several teeth, then in the second it spreads to a large segment or the entire jaw (although this is less common).
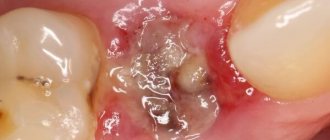
It is also customary to distinguish between acute and chronic periostitis. In this case, the acute form of the pathology can be serous or purulent. With serous periostitis, almost clear liquid accumulates in the periosteal tissues, which easily resolves with timely treatment. The purulent form is accompanied by the formation of a characteristic lump - the flux itself, which gradually increases in size.
Treatment of flux and removal of edema
Dental flux (odontogenic periostitis) is a purulent disease in the subgingival and subosseous jaw area. It occurs as a result of inflammation of the tooth root and manifests itself in the form of a purulent sac on the gum. If you do not consult a dentist in time with this diagnosis, then there is a very high probability that the tooth will have to be removed and dental implantation performed or dental prosthetics performed in another way. And this is not the worst option, because the infection can enter the circulatory system and then the whole body is in danger!
Causes of flux
The causes of the disease are varied. It can be a consequence of an advanced stage of caries and its complications, a tooth bruise, or an inflamed pocket between the tooth and the gum. It can also appear as a result of infection, when food debris that accumulates in the tooth cavity begins to rot. Pus makes channels in the bone tissue and looks for a way out. It is stopped by the periosteum or lower jaw. The inflammatory process is accompanied by pathological changes in tissue, a person’s temperature rises and severe toothache (often unbearable) is observed.
Flux treatment
Treatment tactics depend on the localization of the process, the location of the tooth, and the form of inflammation. At an early stage, swelling is relieved with the help of antibiotics and high-quality painkillers. But first, the specialist must assess the condition of the tooth root, after which he will decide on the advisability of removing or preserving it. Please note that specialists at our dental clinic in Perm make a decision to remove a tooth only in exceptional cases when the inflammatory process poses a threat of blood poisoning. The purulent form is treated with surgery. The dentist will remove the abscess and carry out a series of antiseptic actions in the area of inflammation. All manipulations are carried out under the influence of painkillers. The dentist will make a small incision near the diseased tooth through which the pus will be released. In some cases, to ensure complete outflow, drainage in the form of a rubber strip is left in the incision. This manipulation in combination with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents quickly relieves swelling.
For patients from other regions, our clinic offers such a popular service as dental tourism. You can undergo complex treatment, prosthetics, dental implantation and other procedures and still have a good rest! We provide: preferential accommodation and assistance in organizing leisure activities. To preliminary draw up a treatment plan remotely and estimate the cost, contact us in any way convenient for you: by email, by phone or via a widget (send a request or request a free call back).
How to relieve swelling at home?
If you have gumboil, only a dentist can remove the swelling. Especially if it is manifested by an increase in body temperature. If you are unable to see a doctor immediately, you can try rinsing with sage or green tea infusion (but this should only be done in exceptional cases). All folk remedies have a weak effect and practically do not relieve pain. In addition, they will not eliminate the cause of the flux. These are just temporary measures that can help disinfect your mouth. Rinsing will in no way cure periostitis, but will only slightly slow down the process, which will reduce the risk of unfortunate consequences while the patient is unable to get an appointment with the dentist. If you are within reach of a doctor, then treating periostitis at home is strictly prohibited, as this can lead to disastrous consequences. You should immediately contact a dental clinic at any time of the day or night. If pus is not removed in a timely manner, inflammation can quickly spread to adjacent tissues. The Kostamed dental clinic operates around the clock, so you can contact us at any time. The dentist on duty will diagnose the flux and relieve the swelling.
Folk remedies
For treatment, traditional medicine offers different recipes. Below are some of them:
- Alcohol tincture of calendula (1 tsp per glass of water).
- Hot infusion of Siberian or red elderberry (a handful of berries in three cups of boiling water, cook for 15 minutes, leave for 2 hours).
- Heat flaxseed, 3 tbsp. wrap in cotton cloth, then tie with thread and apply to the cheek.
- Brew a mixture of green tea and sage and add half a teaspoon of salt. Rinse your mouth with hot infusion.
- 4 tbsp. l. pour lemon balm leaves with two glasses of boiling water. After 4 hours, express and rinse.
There are also quite ridiculous recipes for “treatment”:
- Make “cigarettes” from the cat’s paw plant, smoke without inhaling the smoke into your lungs.
- Place a piece of salt-free lard between the gum and cheek and hold for 30 minutes.
- Chop the garlic and apply it to your wrist.
- Mix tar with sea buckthorn in equal proportions and apply as a compress.
- Burdock, radish and sorrel in the form of a compress.
Doctors at the Kostamed dental clinic will provide:
- maintaining the integrity and health of the oral cavity;
- prevention of dental diseases;
- creating a perfect smile;
- preventing serious complications;
- minimizing life-threatening risks;
- high aesthetics and beauty, and, consequently, higher success in career and personal life.
If you have the slightest symptoms of dental flux, then call us 24/7 as soon as possible and come to Costamed dentistry. We will definitely help you!