Chief editor of the site:
Snitkovsky Arkady Alexandrovich
Chief physician of the professorial dentistry “22 Century”, dentist, orthopedic dentist
Author of the article:
Scientific team of dentistry “22 Century”
Dentists, candidates and doctors of medical sciences, professors
Plate prosthesis
A plate prosthesis is the most common of the simple and affordable methods of removable prosthetics for complete or partial absence of teeth. Let's look at the materials and stages of its manufacture.
What is a plate prosthesis made of?
To begin with, let us recall the general requirements for the material:
- No impact on the oral mucosa and the body as a whole;
- Aesthetics;
- High strength, low abrasion;
- Preservation of shape during use;
- Easy to care for;
- No unpleasant taste or smell;
- Must be repairable;
- Must be technologically advanced.
Plate dentures consist of a base (foundation) and artificial teeth. Also, in case of partial absence of teeth, support-retaining elements (clasps) .
The base is made from:
Acrylic plastics
Plastics are polymers that represent a large group of high-molecular compounds obtained chemically from natural materials or by chemical synthesis from low-molecular compounds. One of the properties of polymers is their high manufacturability, the ability to be molded under heat and pressure and stably retain their given shape, which explains their widespread use in orthopedic dentistry. Plastics are made from powder and liquid.
Advantages:
- Affordable price;
- Simple manufacturing technology (various color and size combinations are possible);
- Short production time for the prosthesis;
- Easy to care for.
Flaws:
- With prolonged use of the structure, the material begins to release special substances that can cause a local allergic reaction;
- Acrylic plastics are porous compounds. With poor oral hygiene and poor-quality care of the prosthesis, it becomes contaminated with microorganisms, which helps to reduce local immunity. And this can cause the development of inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa;
- Possibility of injury to the soft tissues of the oral cavity.
Nylon
Nylon removable dentures
Nylon is an elastic material.
Advantages:
- Hypoallergenic;
- High aesthetics (complete imitation of natural teeth and gums);
- In case of partial absence of teeth, the supporting teeth are not treated;
- The flexibility of the material ensures a short adaptation period and also has the least mechanical impact on the soft tissues of the oral cavity;
- Easy care;
- When used carefully they last quite a long time.
Despite the significant positive qualities, nylon prostheses have their disadvantages :
- The fixing elements do not transfer the load to the remaining teeth. As a result, the mucous membrane takes on the chewing load, which leads to gradual periodontal damage and further inflammatory process;
- The absence of a rigid frame leads to the fact that chewing pressure is distributed unevenly. Subsequently, this leads to atrophy of the bone tissue of the jaws;
- For technological reasons, nylon prostheses are not polished. This design absorbs and retains foreign odors;
- Frequent adjustments are necessary;
- High price.
The material for the base is selected based on the individual characteristics of the body and the condition of the oral cavity.
Classification
It should be noted that in dentistry, removable dentures are divided into the following groups:
- Complete removable plate dentures;
- Partial removable dentures, which, in turn, are: plate dentures;
- immediate dentures;
- clasp dentures.
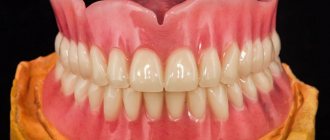
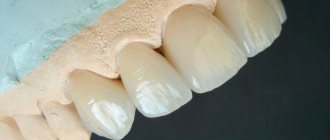
Complete removable dentures are used when it is necessary to restore completely missing teeth and are often the only alternative to prosthetics in the complete absence of teeth in both or one of the jaws. In this case, the full denture is attached due to the suction effect of the gums. An example of complete removable dentures is shown in the figure on the left.
Such dentures are made from imported dental acrylic plastics using the following methods:
- injection molding method;
- hot cold compression polymerization method;
- by cold compression polymerization.
Modern technologies make it possible to create dentures that vary in color, shape and size of teeth, depending on the individual characteristics and needs (wishes) of each patient.
We especially emphasize that artificial teeth have very high wear resistance and good aesthetic qualities. With proper use and good hygiene, they do not change their appearance, color, density for a very long time and can serve for a long time.
Complete removable dentures, as well as other removable orthopedic products, are quite acceptable to leave in the mouth overnight after evening hygiene procedures. If the owner of a removable orthopedic structure wants to take a break from the prosthesis while sleeping, then after hygienic cleaning, wipe it dry and, wrapped in a napkin or handkerchief, leave it until the morning.
Partial removable dentures are applicable in the following cases:
- in the absence of one tooth;
- in the absence of a number of teeth in one row;
- in the absence of chewing teeth;
- as a temporary prosthesis.
Thus, this type of removable dentures is often prescribed for the loss of the main chewing teeth, the presence of terminal defects in the dentition, when it is not possible to use adjacent teeth as a support for the bridge due to their absence or loosening in the jaw bone, and long-term defects in the dentition.
Partial removable dentures, as I already said, are divided into:
- plate prostheses;
- immediate dentures;
- clasp dentures.
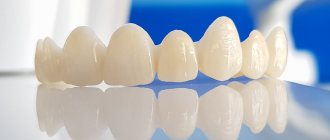
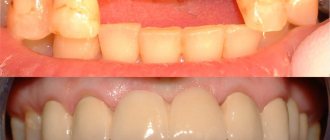
Acrylic plate dentures are used to restore a lost fragment of the dentition when the patient has few teeth left in the mouth or the remaining teeth are unreliable, which does not allow them to be used for prosthetics with fixed prostheses (crowns and bridges). The advantage of this type of prosthetics is its simplicity and affordability. Dentures made of acrylic plastic correctly distribute the load on the gums and allow full chewing. An example of partial plate removable prosthetics is shown in the figure:
It should be noted that the main disadvantage of this type of prosthetics is that the fixation of the prosthesis is not rigid enough, which leads to the need to frequently activate the clasps (tighten the hooks).
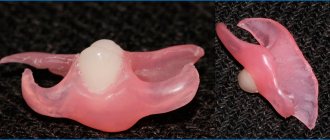
Immediate dentures are a temporary structure that is applied to the jaw immediately after tooth extraction or in preparation for prosthetics with a permanent denture. The goal of immediate prosthetics is to prevent teeth from moving and to keep them in place. Prosthetics with these removable dentures are short-lived and long-term use is not recommended. The figure shows an option for replacing a defect in a central tooth using an immediate prosthesis:
The adaptation period for plate dentures proceeds as follows: at first, of course, the sensations are quite unpleasant. The new design is foreign, intrusive, and may give the impression that there is very little room for the tongue. The main thing is not to be nervous - everyone without exception goes through these sensations. It’s hard to believe, but in a week or two or three you will already forget that the teeth are “not your own.” There are several phases of addiction:
- irritation (usually up to a day);
- partial inhibition (days 1-5, when chewing function and speech are gradually restored);
- complete inhibition (5-33 days, when you already begin to experience discomfort without a prosthesis).
The first thing you may encounter is a gag reflex to the prosthesis and increased salivation. The body’s normal reaction to a foreign object goes away on its own; psychotherapy and sucking on lollipops will help alleviate the condition.
At first, usually, marks form on the gums, so you have to grind the prosthesis. This is also absolutely normal, because a dense plaster model cannot perfectly replicate pliable living tissue. You need to adjust as many times as necessary. The same goes for rubbing or biting your cheek or tongue.
Over time, as a rule, the denture begins to fit less tightly and “walk” when chewing. This is a consequence of subsidence of the gums, or rather the jaw bone, which changes due to the absence of its own teeth. This is also quite easily corrected by adding plastic ( relining ) - this is a manipulation carried out in the patient’s mouth or in a laboratory way in the laboratory. The fact is that while wearing a removable denture under the base of the removable denture (the base is the part of the denture that is in direct contact with the oral mucosa), atrophy of the mucous and bone tissue occurs. As a result, a void appears between the prosthesis and the mucous membrane, and the prosthesis no longer fits tightly. To eliminate this discomfort, the prosthesis is relined, plastic is placed in place of the void formed due to atrophy, and a tight fit of the prosthesis is restored.
Let's consider clasp prosthetics as the most comfortable and at the same time complex design. The clasp prosthesis consists of several elements: a metal frame, including an arch (clasp) and fixing elements, as well as a saddle-shaped part with artificial gum on which artificial teeth are located.
This is the most reliable, convenient, but more expensive design. Its main difference and advantage is that the chewing load is distributed evenly between the gingival surface of the jaw and the remaining teeth, in contrast to partial plate dentures, where the entire load falls on the gum. In the manufacture of such prostheses, accurate calculations and modeling of all elements of the prosthesis are performed. Also, the clasp prosthesis is used as an immobilizing, splinting for periodontal disease and increased tooth mobility. Removable dental prosthetics using a clasp allows you to restore any areas of the teeth without creating discomfort, which is very important for the patient. This reduces the time it takes to get used to the prosthesis, phonetic disturbances are reduced to a minimum and disappear in the first stages of adaptation.
Artificial teeth
Laminar dentures
For laminar dentures, artificial teeth are made of plastic.
There are frontal (front) and chewing (root) groups, produced in sets in headsets.
Plastic teeth are very similar in appearance to the enamel of natural teeth. During production, you can vary the color and shade. Artificial teeth are firmly connected to the base due to the homogeneity of the material (their connection occurs during polymerization of the base plastic). They are also easy to adjust both by a technician in the laboratory and by a doctor when handing over the prosthesis. Headsets are available in several styles and shades, many combinations are possible. Due to this, it is possible to harmoniously select and manufacture a prosthesis according to the individual parameters of the face.
Over time, the technology for making artificial teeth has progressed.
proposed to produce acrylic artificial teeth using the injection-compression method (continuous injection of material during polymerization to compensate for its shrinkage, followed by compaction of the material to a homogeneous state). This makes them incredibly durable.
The Ukrainian company produces artificial teeth in the form of a set in Estedent, Estedent-02. They have the following positive properties: imitation of the anatomical shape and color of the tooth; high strength indicators; fluorescent effect (both in natural and artificial lighting). Estedent-D is used for prosthetics for children during the period of temporary and mixed dentition.
“Executive” artificial teeth (“Dentsply”, USA) have five distinct shade zones, which will allow you to imitate natural teeth as accurately as possible.
Also in our country, headsets “Megastar” (Great Britain), “Ivoclar” (Liechtenstein), etc. have found use.
When selecting artificial teeth, not only the color of natural teeth (if any) is taken into account, but also the shape of the patient’s face and constitution. Thanks to a wide selection of artificial teeth in color and shape, an individual approach to each clinical case is possible.
Caring for removable dentures
To maintain the functionality and presentable appearance of your removable denture for a long time, simple daily care is necessary. Dentures do not require special care. There is absolutely no need to take them off at night. For the first couple of months, dentures should be kept in a damp environment. Fresh plastic can continue to release monomer for a long time. In air, this process can lead to the formation of whitish stains inside the plastic, and the prosthesis takes on a somewhat “marbled” appearance. This does not happen in water. Therefore, at first the prosthesis should be in the mouth, or in a glass of water.
We recommend brushing your dentures at least twice a day, and preferably after each meal, or before bed, using the same movements as you would your teeth, using a soft toothbrush and toothpaste. All surfaces of the denture are important, but special attention should be paid to the inner surface of the denture, adjacent to the gum.
There are also special solutions for caring for dentures (and special tablets for their manufacture). The prosthesis is placed in it once a day for 15 minutes to rid the surface of the structure of germs, dyes, food debris and unpleasant odors - this way the prosthesis receives more durable protection. Even more serious tablets with a bioformula are used only once a week, but this is enough - penetrating into all the cracks, such a solution removes any plaque without causing harm to the materials from which the prosthesis is made.
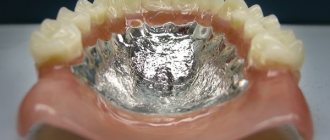
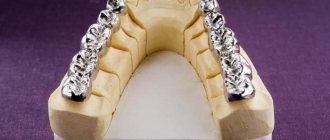
Clasps
Clasp denture with clasps
In case of partial absence of teeth, one of the ways to fix the prosthesis in the oral cavity is the presence of clasps. They are usually made of metal. They tightly cover the tooth, can only serve as a retaining element, and also act as a support, that is, transmit chewing pressure to the tooth. Noticeable when talking and smiling.
Clasps made of elastic material (nylon dentures) can only perform a retaining function. Excellent aesthetics, but unreliable and can become deformed and break.
Types of clasp dentures
Let's look at the different types of clasp prosthetics used in the Dentalika clinic.
The clasp clasp prosthesis is held in place using hooks (clasps) that tightly cover the tooth but do not harm the enamel (see picture):
Clasp prosthesis with locking fixation - the fixing element is hidden inside the prosthesis, and therefore, even with a wide smile, the removable structure is absolutely invisible:
Clasp prosthesis on telescopic crowns - is held on the tooth using a crown consisting of two parts: the first part is a removable metal-ceramic crown, the second is a metal cap with parallel walls, cemented to the tooth. The crowns fit one on top of the other, tightly fixing, the prosthesis is comfortable and is not perceived as removable.
Caring for a clasp prosthesis is simple: in the evening you need to remove and clean the prosthesis. You don’t have to remove the prosthesis at night, which is quite comfortable psychologically.
The clasp denture is a technologically complex design, which leads to the need for mandatory periodic monitoring by your attending physician in order to monitor the inevitable “gum shrinkage” under the prosthetic bed (to avoid the appearance of voids there) and the load on the supporting teeth. If necessary, relining (layering of plastic) of the prosthesis is carried out.
We recommend that our patients pay attention to full and partial removable dentures ACRI-FRI (see pictures) and Vertex , which have proven themselves in the practice of our clinic.
Stages of manufacturing a plate prosthesis
- Conversation with the patient (it is necessary to clarify complaints, the presence of chronic diseases, allergic reactions, etc.);
- Examination of the oral cavity, assessment of the condition of soft tissues and level of hygiene;
- Additional studies (radiography, tests, etc., if necessary);
- Selection of design;
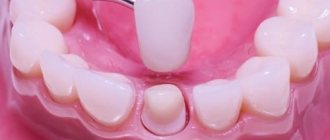
- Taking impressions from the upper and lower jaws;
- Making a plaster model, then a wax template with bite ridges;
- Trying on in the oral cavity, determining the relative position of the jaws, the color and shape of the teeth, choosing fixing elements (if there are preserved teeth);
- Strengthening models into an articulator, placing artificial teeth on a wax base, placing fixing elements in the base;
- Try-on in the oral cavity, correction if necessary;
- Replacement of wax with the final material, processing, polishing of the prosthesis;
- Fitting in the oral cavity, correction. Recommendations for care.
Plate dentures have proven themselves to be affordable, quick to manufacture and aesthetic designs.
Date of publication: September 20, 2020 Last update: September 22, 2022 © 2020 Professorial Dentistry “22 Century”. All rights reserved.
Features of the denture base
The denture base is attached to the human anatomical structures:
- on the upper jaw with the alveolar process and palate;
- on the lower jaw only with the alveolar process.
In addition to the function of attaching to the patient’s jaws, the elements perform a number of additional functions:
- basis for attaching the structural elements of a denture (guide plates, artificial teeth, frame, fastening);
- transfer of sensitivity during chewing to living human tissue;
- replacement of damaged gingival tissue, which forms a static function;
- support for tissues in case of operations on the face and mucous membranes.
The base is a frame for a denture, without which it is impossible to install them.