Treatment of caries of children's primary teeth
Caries of primary chewing and front teeth has long been treated without the slightest pain.
New modern techniques have reduced the use of drills and drilling to a minimum, and timely scheduled examinations make it possible to detect the disease at a very early stage. The doctors at Aza&Buka Pediatric Dentistry who work with young patients are distinguished by an amazing sense of tact and constant positivity. Knowledge of the child’s psychology allows doctors to build communication and dialogue in such a way that children sit in the dental chair without the slightest fear. If the child already has some dental phobia, then adaptation techniques can solve the problem.
Caries on baby teeth in children is treated using the following technologies:
Prevention of dental caries in children
How to avoid caries in a child? There are simple measures that can help reduce the likelihood of its occurrence.
- Brush your baby's teeth as soon as his first teeth emerge. You can first use oral sanitary wipes with xylitol.
- Do not lick baby's nipples or allow your child to eat from his spoon. This can pass bacteria from your mouth to your baby and increase the chance of developing tooth decay on newly erupted teeth.
- Avoid giving your baby sweet juice or formula at night or throughout the night. After your last meal, you should definitely brush your teeth! If the child is breastfed, after a year, reduce night feedings, remember that breast milk is also sweet and can provoke the development of caries.
- Starting from 1-1.5 years old, visit the pediatric dentist regularly (every 3-4 months).
- Don't forget about regular oral hygiene at least twice a day for 2-3 minutes.
- Brush your child’s teeth on your own until he is 4-5 years old, then be sure to help him with brushing. Until the age of 8-9 years, a child cannot yet brush all his teeth well, even if he knows how to do it correctly.
- Let your child's diet be rich in microelements. Teach your child to chew carrots and apples - this reduces soft plaque and strengthens the gums.
- Professional oral hygiene is not a luxury, but an extremely useful procedure, since hard plaque can only be removed by a dentist. Also, if possible, go through with your child the procedures of enamel mineralization and fissure sealing on young permanent teeth. These measures are good prevention of caries in children.
Classic filling
requires a special approach when treating young patients, since the doctor has to use dental equipment, which often causes fear in children.
Aza&Buka dentistry uses both traditional and modern methods of treating caries of primary teeth, selecting a method taking into account the age of the child and the degree of neglect of the process.
Plaksina Margarita
“Modern parents are great! They themselves are not afraid of dentists, and children are taught the same thing: to come on time for preventive appointments and examinations. In such cases, doctors can intercept the very beginning of a cavity infection and prevent tooth decay without drilling.”
Prevention of childhood caries
How to protect children from caries? Dental procedures are not cheap, so not everyone can afford to have their teeth treated in paid clinics, and making an appointment for a free appointment is problematic. In addition, children are afraid of doctors, which greatly complicates treatment. The best way to avoid these problems is to prevent the development of caries in baby teeth.
Prevention of childhood dental diseases includes:
- Individual oral hygiene. Children should get used to brushing their teeth from early childhood. Otherwise, they will constantly suffer from caries. Carry out hygiene procedures with him in the format of a game, interest the child in this process so that he enjoys cleaning himself. Buy him a beautiful children's toothbrush, stylized as cartoon characters. Don't forget that young children's teeth are very vulnerable. Therefore, the means of caring for them must be appropriate to the age of the child.
- Proper nutrition. There is no need to put your child on a diet to prevent tooth decay, but you should limit your intake of sweets. It is advisable that he get used to good products from childhood. The diet must include dairy products, which are rich in calcium. The condition of the enamel depends on this element.
- Professional hygiene. Bring your child to the dentist for teeth cleaning 2-3 times a year. He will also help you choose a suitable toothbrush for your baby and teach you how to use it.
At the first symptoms of caries, take your child to the doctor. Caries does not go away on its own, folk remedies do not help, so there is no point in delaying a visit to the clinic.
Milk caries: initial, superficial, medium, deep
Doctors distinguish 4 stages of the formation of carious areas:
- Initial caries - tooth enamel becomes covered with small spots of white or yellowish tint.
- Superficial caries - the enamel begins to deteriorate, small and light cavities are observed.
- Medium – the layer of tooth enamel is destroyed, the affected area extends deeper.
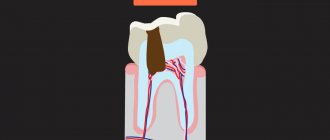
- Deep - the layers of dentin have already been affected, and the pulp is under threat.
It is necessary to treat milk caries at the very first stage, although it does not cause any discomfort in the child. The fact is that the enamel and crowns of temporary teeth are subject to rapid destruction, and the development of caries occurs very quickly. Deep caries often provokes irreversible changes, which leads to premature removal of the baby tooth.
Rodikova Tatyana
“Medium and deep caries most often occurs in schoolchildren, almost teenagers. Children brush their teeth poorly, and they talk about problems only when caries has already affected the pulp. In this case, the treatment turns out to be more unpleasant, since removal of the pulp cannot be avoided. That’s why I always ask parents to carefully monitor their teenagers’ hygiene and bring them to appointments on time.”
Caries of permanent teeth in children
Newly erupted teeth have lower mineralization, which is finally completed only by 4-5 years after eruption. Young permanent teeth are especially vulnerable in the first year of development. The enamel on them is easily permeable to caries bacteria, so a junior schoolchild should be helped to brush his teeth and be sure to consult with a dentist about the need to seal the fissures and make a protective coating for the enamel.
Meet our tooth fairies and check prices.
Reasons for the development of caries in temporary teeth
When visiting a dentist, parents are invariably interested in the reasons for the appearance of such an unpleasant disease. This is important because it helps prevent damage to new teeth. Sometimes it is enough to change eating habits and hygiene patterns so that the child forgets about fillings for a long time, and only comes to the dentist for examinations.
Causes of caries:
- Poor or insufficient oral hygiene. Food remains in the interdental space and on the enamel are an excellent environment for the development of carious bacteria.
- An unbalanced diet with a preponderance of sweets and carbohydrates - during the fermentation of simple carbohydrates, acids are formed that provoke the destruction of enamel.
- The lack of solid foods in the menu leads to a decrease in the frequency of chewing, reduces salivation and becomes a common cause of caries of primary teeth in young children.
- Long-term use of nipples, including on bottles and sippy cups, increases the risk of developing single or multiple bottle caries of the anterior milk teeth in children.
- Rickets is a pathology that provokes the destruction of dental tissues.
- Genetic predisposition of the child.
- Problems with bite – various anomalies in the formation of the dentition.
- Decreased natural immunity due to frequent acute respiratory viral infections, chronic diseases, and taking various medications.
- Damage to tooth germs in the prenatal period - due to maternal illness or neglect of health in the first trimester.
Possible causes of caries in children
- Poor dental hygiene.
- Poor nutrition. Bacteria multiply more actively in the mouth of people who prefer foods with a high content of easily digestible carbohydrates and sugars.
- Insufficient production of saliva, its increased viscosity.
- Lack of solid foods in the diet, which helps remove soft plaque.
- Lack of calcium and phosphorus in food.
- Lack of fluoride in water (below 1.5 mg/l).
- Crowding of teeth, since it is impossible to clean plaque from the interdental space in this case.
- Some diseases predispose to increased activity of the carious process: diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease.
Type 3: multiple
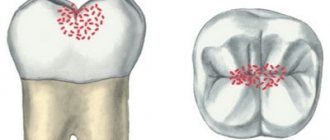
Multiple childhood caries of primary teeth is very common. To understand what it looks like, look at the photo.
The photo shows multiple caries
A disease that consistently affects 8-10, or even all 20 teeth located in the primary occlusion is considered multiple. Multiple is also usually called a pathology that can destroy several surfaces of one tooth at once.
Experts give this anomaly different names: blooming caries, acute, galloping. The pathology can develop immediately after eruption, quickly corrodes the coronal part, leads to necrotization of the pulp and can leave the child without teeth by the age of 3-4 years.
Why does the disease appear? Most often, it develops against the background of severe infectious, chronic and genetic diseases: measles, tonsillitis, tonsillitis, rickets, Down syndrome, damage to the bronchopulmonary system. The same cervical and circular varieties, if left untreated, quickly become multiple, that is, they spread to adjacent elements and spread throughout the entire row.
Why is caries treated for young children?
There is a myth that baby teeth with caries do not need to be treated, as they will fall out anyway. In fact, dentists unanimously say that treatment of childhood caries at any age, both on milk and permanent teeth, is mandatory.
There are several reasons why caries of baby teeth should be treated before the age of 5-6:
- The baby tooth preserves space for the permanent tooth and stimulates its growth.
- It takes part in the chewing function and, therefore, in the digestion process.
- Baby teeth affected by caries are a source of chronic infection in the child’s body. In addition, the root of the baby tooth is located next to the germ of the permanent tooth. If caries in children is not treated, the inflammatory process can affect permanent teeth even before they erupt.
- Healthy baby teeth are necessary for a child to develop high-quality speech skills and correct pronunciation of sounds.
- If parents do not treat their child's caries, this can lead to untimely loss of baby teeth. Because of this, other teeth in the row shift, permanent teeth begin to cut in the wrong place, which leads to malocclusion.
- Early loss of a baby tooth can delay the eruption of a permanent one.
This is why it is so important to preserve baby teeth until they fall out naturally. And this can only be done if baby teeth are treated properly in a timely manner.
How will caries be treated for a one-year-old child?
For young patients, the most gentle, gentle treatment is usually selected. In modern clinics, when treating young children, doctors try to ensure that the appointment time does not exceed 30 minutes.
If anesthesia is necessary, application is mainly used; in rare cases, an anesthetic injection is given. For babies under one year of age, it is preferable to treat caries using non-invasive methods, without drilling. But such therapy is justified and effective only if caries is detected early at the spot stage.
The most popular methods of treating caries in children.
- Remineralization.
Remineralizing therapy at the carious stain stage helps restore the mineral composition of the enamel, restore its strength and prevent the destruction of dental tissues. The essence of the method is that gels and pastes containing phosphorus, calcium and other components beneficial to dental health are applied to the surface of the enamel. Remineralization can be carried out both in a dental clinic and at home, using products recommended by the doctor. Home treatment is preferable for one-year-old children, because the mother or another family member will treat the teeth, and the baby will feel comfortable.
- Silvering.
Today this technique is considered outdated, although in some clinics it is still used to treat caries in children under three years of age. The essence of the method is that the enamel is coated with a 30% solution of silver nitrate, which neutralizes the activity of bacteria and stops the process of tooth decay. Among the main disadvantages of the method is a decrease in the aesthetics of the smile, because after silvering, white teeth turn black.
- Ozone therapy.
A modern non-contact method of caries treatment that is suitable for children of any age. It is based on the antibacterial effect of ozone, which neutralizes carious lesions at an early stage and disinfects the tooth. Usually ozone therapy is combined with remineralization. First, the affected area is cleaned with ozone, and then the enamel is coated with strengthening compounds.
Which treatment method to choose for a particular child is determined by the dentist after the first appointment.
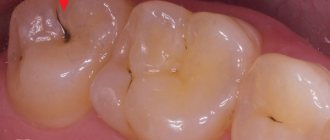
Type 1: cervical variety
It is formed at the point of contact of the crown with the gum - it is in this area that the enamel is very thin, and in children it is also weakly mineralized.
When the first milk and permanent teeth erupt, they have weak hard tissues in which mineralization processes have not yet been completed. Usually only after a few years1 the enamel naturally strengthens and increases its resistance to external irritants. And if during this period of life there are unfavorable factors (poor hygiene, the presence of sweets and soft foods in the diet, vitamin deficiency, various chronic, infectious and viral diseases), then the child most often develops cervical caries.
The photo shows cervical caries
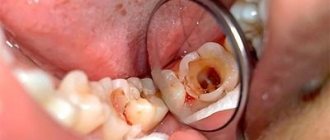
Caries in children, regardless of the type, goes through the same stages (superficial, initial, medium, deep) as in adults. True, it progresses faster and can be almost asymptomatic, accompanied by severe pain only with the development of pulpitis and periodontitis. It all starts with the appearance of white matte spots on the surface of the enamel, then their color changes to yellow and brown, and deep pits form on hard tissues. Next comes first short-term, then long-lasting discomfort.
Symptoms of the disease
A child cannot always point out the source of pain and discomfort, so parents need to be especially attentive to their child’s behavior and monitor the condition of the oral cavity. The following symptoms should alert you:
- Refusal to eat, tearfulness while eating;
- Chewing food on only one side of the jaw;
- Painful sensations from hot, cold and sweet;
- Yellow or white spots, dark streaks on tooth enamel;
- Bad breath.
If you observe one or more of the signs listed above in your child, contact your dentist immediately.