Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
The taste of blood in the mouth is quite common. However, this symptom should never be ignored. Of course, the reasons for its appearance can be quite harmless, for example, a slight injury to the gums or eating food from clay dishes. However, an unpleasant taste can also indicate very dangerous pathologies. Let's figure out why a metallic taste may appear in the mouth and what to do to eliminate it as soon as possible, and most importantly, remove the reasons for its appearance.
Conventionally, all the causes of a pronounced metallic taste can be divided into three groups:
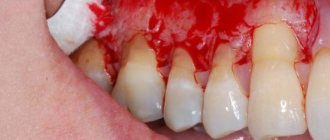
- Dental problems are usually associated with increased bleeding of the gums.
- Oral injuries.
- Internal pathologies.
Taking various medications often leads to a taste of blood in the mouth.
Oral injuries
If the mucous membrane is damaged, a little blood may enter the taste buds and, accordingly, a metallic taste appears in the mouth.
The causes of mucosal injury may be:
- tartar in the mouth;
- improper dental care, for example, using a brush that is too hard;
- incorrectly installed dentures;
- incorrectly installed braces.
Often the cause of the taste of blood in the mouth is a more significant injury, such as to the esophagus or throat. For example, a strong cough often leads to mucosal injuries. After an injury, a small amount of blood enters the mouth and causes an unpleasant taste.
Diagnostic methods in Medscan
Diagnosis for hemoptysis includes:
- Taking anamnesis - it is important to establish the history of the symptom and the presence of chronic diseases that could cause it.
- Physical examination - allows you to detect accompanying symptoms.
- Laboratory tests - Abnormalities in blood and urine values may be clinically significant.
- Computed tomography - in Medscan CT allows you to identify inflammatory processes, pulmonary neoplasms, determine their nature, stage of development and the presence of metastases.
- Bronchoscopy - this method makes it possible to assess the condition of the bronchi and take a sample of lung tissue for histological examination. Based on it, the doctor judges the presence of a tumor, its benignity or malignancy.
Internal pathologies
The most common diseases of internal organs that lead to the taste of blood in the mouth include:
- bronchitis;
- pneumonia (pneumonia);
- lung abscess;
- lungs' cancer;
- cystic fibrosis;
- tuberculosis;
- dysfunction of the heart;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT);
- diseases of the ENT organs.
Neurological diseases can also cause the taste of blood in the mouth. A signal travels through the nerve fibers of the brain to the taste buds; if its transmission is disrupted, an unusual taste may appear in the mouth.
However, neurological problems accompanied by a blood taste usually have other unpleasant manifestations. For example, they may be accompanied by headaches, hearing problems, hand tremors, trembling eyelids, and lumbago in certain areas of the face.
In very rare cases, the taste of blood in the mouth is caused by heavy metal poisoning. A similar problem often awaits workers in chemical laboratories and metal processing plants. Intoxication of the body is accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms - attacks of dry cough, nausea, aching limbs, swelling of the gums, and lack of appetite. Dysbacteriosis is also rarely the cause.
Provoking factors
Patients can accurately detect the taste of blood in their mouth. The biological fluid contains a large amount of iron, so in pathology there is a pronounced metallic taste.
The reasons leading to the development of pathology are conventionally divided into 2 main groups:
- dental problems associated with increased bleeding gums;
- internal pathologies.
In addition to the above, there are other factors that contribute to the occurrence of a metallic taste in the mouth. Among them: oral injuries, taking certain groups of medications, as well as causes not related to the disease.
Injuries to the oral mucosa
When the mucous membranes of the mouth are damaged, a small amount of blood enters the taste buds . Injuries may occur:
- due to the presence of tartar in the oral cavity;
- with improper dental care, for example, using a brush that is too hard;
- when the inner surface of the cheek is damaged by the sharp edge of a tooth;
- due to incorrectly installed braces or dentures.
A person may accidentally bite their cheek while sleeping or eating. Due to damage to the surface of the mucous membranes, the taste of blood is felt in the mouth.
Injuries to other organs
The taste of blood in the mouth is also observed with more significant injuries:
- Bleeding from the nose . In this case, the symptom can be observed for a long time.
- Blood from the throat . During severe coughing attacks, the mucous membranes are injured, and blood clots enter the mouth, causing an unpleasant taste.
- Damage to the respiratory system.
Diseases of internal organs
The taste of blood in the mouth appears as the only sign of damage to internal organs or is accompanied by other symptoms. Among the pathologies leading to the occurrence of an abnormal condition are:
- Bronchitis . Additionally, the disease is accompanied by difficulty breathing and a rise in temperature. In the chronic type of the disease, blood is present in the saliva.
- Pneumonia.
- Lung abscess . Due to the accumulation of necrotic masses in the respiratory organs, an unpleasant odor emanates from the patient’s mouth.
- Lungs' cancer . Characterized by rapid weight loss, fatigue, and lack of oxygen.
- Bronchiectasis . In addition to the metallic taste in the mouth, the patient is bothered by a severe paroxysmal cough, weakness and high fever.
- Cystic fibrosis.
- Pulmonary embolism.
- Tuberculosis.
- Cardiac dysfunction . The taste of blood is associated with increased fragility of the organ’s blood vessels and is more common in the morning.
- Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract . The taste occurs due to inflammation of the pancreas, dilation of the esophageal veins or cholecystitis.
The listed diseases lead to both minor and heavy bleeding from the mouth.
Pathologies of the oral cavity
© Zsolt Bota Finna / Fotolia
The most common cause of the problem is dental disease and lip damage. Pathologies are easily recognized by their characteristic clinical picture:
- staining of saliva in reddish shades;
- inflammation of the oral mucosa;
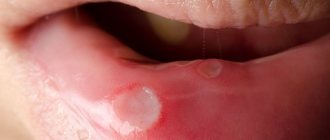
- the appearance of ulcers and erosions.
The taste of blood in the mouth occurs due to:
- gingivitis - inflammation of the gums;
- cheilitis – damage to the lips;
- stomatitis – damage to the mucous membranes of the mouth;
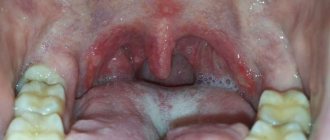
- periodontitis – inflammation of the tissues responsible for fixing the teeth.
The diseases provoke bleeding in the mouth due to damage to soft tissues. At the same time, a person feels a constant taste of metal.
Gingivitis and periodontitis are discussed in more detail in the following video:
Poisoning
A metallic taste in the mouth indicates poisoning by toxic substances of heavy metals. People working in chemical laboratories and metal processing plants are at risk for the disease.
Intoxication of the body is accompanied not only by the appearance of a taste of blood in the mouth, but also by other symptoms:
- nausea;
- attacks of dry cough;
- swelling of the gums;
- aching limbs;
- problems with stool;
- poor appetite.
What is necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis and why is it dangerous?
Our article discusses pericoronitis.
We talk about the treatment of hypertrophic gingivitis https://www.vash-dentist.ru/lechenie/desnyi/gingivit/gipertroficheskiy-prichinyi-vozniknoveniya-terapiya.html at the link.
Inflammation of ENT organs
A common cause of the taste of blood in the mouth is damage to the paranasal sinuses by fungal pathogens . The pathology first affects one side of the nose, and then spreads to neighboring organs, as a result of which all ENT organs suffer.
During the inflammatory process, increased blood supply to the infected areas occurs. Some of the blood may be released into the oral cavity.
Neurological problems
The pathological condition can develop due to neurological diseases. The signal to taste buds comes from the brain through nerve fibers. When signal transmission is disrupted, a taste of blood occurs in the mouth, and the disease is accompanied by a number of symptoms:
- lumbago in certain areas of the face;
- trembling of eyelids and hands;
- headaches;
- hearing problems.
The taste of blood in the mouth is one of the first signs of Alzheimer's disease, multiple sclerosis and tumors in the nervous system.
Taking medications
A person can also feel this taste after taking medications. A problem that arises as a result of illiterate or too long-term use of medications indicates the need to discontinue them.
The following medications cause this reaction:
- antibacterial drugs – Augmentin, Aipicillin, Vilprafen;
- antihistamines - Suprastin, Claritin, Diazolin;
- vitamins for pregnant women – Amway, Materna;
- ganglion blockers – Pyrilene;
- food supplements containing iron - Fenyuls, Matltofer, Actifferin.
All of these drugs lead to changes in the composition of saliva and the appearance of a blood taste in the mouth.
Anemia and hypovitaminosis
© abhijith3747 / Fotolia
An imbalance of microelements in the body leads to a distortion of taste perception. In addition to the taste in the mouth, patients experience:
- loss of appetite;
- sleep disturbance;
- increased irritability;
- decrease in intelligence and physical abilities.
The condition can also be caused by anemia - a lack of iron in the body. The disease manifests itself:
- drowsiness;
- frequent headaches;
- rapid fatigue.
Severe forms of anemia are accompanied by dizziness, aching joints, and heart rhythm disturbances.
We will discuss the symptoms and treatment of gingivitis at home in a separate review.
We will tell you here why the gum has moved away from the tooth.
The link describes methods https://www.vash-dentist.ru/lechenie/desnyi/gingivit/opisanie-kataralnogo.html for treating catarrhal gingivitis.
Dental diseases
The most common cause of the taste of blood in the mouth remains dental diseases and lip lesions. Diseases are easily recognized by reddish-colored saliva, inflamed oral mucosa, and the presence of ulcers and erosions.
The main dental problems that cause the taste of blood in the mouth are:
- gingivitis - inflammation of the gums;
- stomatitis - damage to the mucous membranes;
- cheilitis - lip injuries;
- periodontitis is inflammation of the periodontal tissues.
What does vomiting blood look like?
The blood in the vomit may be scarlet or just coagulated. The presence of such blood in the vomit in significant quantities indicates heavy gastric bleeding. In small quantities, the presence of blood can be explained by Melory-Weiss syndrome, that is, rupture of the mucous membrane of the lower third of the esophagus with strong vomiting.
If blood remains in the stomach for any length of time, it reacts with gastric juice, oxidizes and turns brown; such blood in the vomit will resemble coffee grounds.
What to do if you taste blood in your mouth?
First, you should contact your dentist. The doctor will confirm or deny dental diseases, prescribe effective gum treatment or refer you to another specialist.
If the taste of blood in the mouth appears for a short time, you can eliminate it using traditional methods of treatment. For example, rinse your mouth with water and lemon juice or a water-salt solution. You can also get rid of the unpleasant taste using a chamomile solution. To prepare it, you need to pour 5 g of dried flowers into 500 ml of water and cook for 7-10 minutes in an enamel bowl. The product must be infused for an hour.
A decoction of oak bark will also help get rid of the taste of blood in your mouth. To prepare it, 10 grams of raw material should be steamed with boiling water and left for about an hour.
An effective means of treating gum inflammation and eliminating such unpleasant symptoms as the taste of blood in the mouth is ASEPTA Active mouth rinse. This combined action remedy is used for infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, and also quickly relieves bleeding and inflammation of the gums. The rinse has an antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect, does not contain alcohol, fluorine and dyes, so it is perfect for treating even those with the most sensitive tissues.
Preventive measures
To avoid gum problems, you must follow a number of simple rules:
- Perform high-quality and correct hygiene procedures aimed at oral health. It is necessary to select care products that will not injure the mucous membrane. You should brush your teeth morning and evening. Use dental floss with caution. Instead, you can use an irrigator, which will help effectively remove food debris. Your toothbrush should be changed every three months.
- Balance your diet. The body must receive all the necessary vitamins and minerals. To strengthen teeth and gums, it is important to eat solid plant foods, such as apples and carrots.
- Give up bad habits, in particular smoking. Toothpicks should be used with caution.
- Regularly undergo preventive examinations at the dentist - at least twice a year. This will allow timely detection of oral diseases.
Paying close attention to your oral health will help you maintain a beautiful and healthy smile for many years.
Clinical researches
The effectiveness of various ASEPTA mouth rinses has been repeatedly proven clinically.
For example, it has been clinically proven that the two-component mouth rinse ASEPTA ACTIVE more effectively combats the causes of inflammation and bleeding compared to single-component rinses - it reduces inflammation by 41% and reduces bleeding gums by 43%.
Sources:
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- The effectiveness of the use of Asept “adhesive balm” and Asept “gel with propolis” in the treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis and gingivitis in the acute stage (Municipal Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk, Kaminskaya T. M. Head of the therapeutic department Kaminskaya Tatyana Mikhailovna MUZ City Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk
- The effectiveness of complex therapy in the treatment of periodontal diseases. (Department of Periodontology of the SF State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education MGMSUIM.A.I. Evdokimova. Moscow.) Nemeryuk D.A. - Associate Professor, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Dikinova B.S. - Postgraduate Student of the Department of Periodontology of the SF Tsargasova M.O. - Postgraduate Student of the Department periodontology SF Yashkova V.V. - postgraduate student of the Department of Periodontology of the SF Department of Periodontology of the SF State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education MGMSUIM.A.I.Evdokimova. Moscow
Physiological conditions as a cause of metallic taste
Piercing as a cause of metallic taste in the mouth
If you do not pay enough attention to oral hygiene, you can soon experience this unpleasant symptom. Tartar, bleeding gums, periodontitis, plaque on the teeth and tongue - all these problems affect the appearance of distorted taste sensations.
The use of high-quality toothpaste and mouth rinse, the use of dental floss, and timely sanitation of teeth and gums can eliminate this problem. Hormonal changes in a woman’s life are certainly reflected in changes in the chemical composition of certain environments in her body.
In particular, menopause, pregnancy, and lactation change some positions of the blood formula. This is why sometimes a metallic taste appears in the mouth of women, especially often during pregnancy. Working in hazardous industries, accidents involving exposure to chemical compounds, and unfavorable environmental conditions can cause poisoning, one of the symptoms of which is the taste of metal in the mouth. Mercury, zinc, lead, copper, and arsenic are especially dangerous in this regard.
If poisoning with these chemicals occurs, then the metallic taste is accompanied by symptoms such as:
- Intense thirst.
- Continuous headache.
- Confusion.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Dizziness.
- Pain in the abdomen and muscles throughout the body.
Without seeking medical help, a person with similar symptoms of poisoning may die or become disabled. A condition that is not as dangerous, but still very unpleasant and also accompanied by a metallic taste in the mouth, can be anemia, or iron deficiency. You can find out about its presence by donating blood for hemoglobin. Anemia can manifest itself with the following symptoms:
- Loss of strength, drowsiness.
- Headaches and dizziness.
- Dry skin, hair, brittle nails.
- Pale skin.
- Cardiopalmus.
- Cracks, or “jams” in the corners of the lips.
- Dry mouth, taste disturbances.
Although there is not enough iron in the body in this condition, it is its taste that becomes a frequent companion to anemia. It can be caused by an unbalanced diet, an increased need for iron compounds during pregnancy and lactation, and rapid growth of children and adolescents.
In addition to iron deficiency, the same reasons can lead to hypovitaminosis - a lack of individual vitamins or their groups. And just as with anemia, the taste of metal in the mouth can be a companion to this condition. Hypovitaminosis may cause irritability, drowsiness or insomnia, and decreased physical and intellectual potential. Taking vitamin complexes and enriching your diet with healthy foods will solve this problem.
Causes of hepatosis in pregnant women
Doctors turned their attention to this disease relatively recently, so experts are still arguing about what causes its appearance. Most medical minds agree that hepatosis in pregnant women is caused by certain genetic characteristics or disorders and can be transmitted through the female line. These genetic abnormalities may not manifest themselves in any way throughout life. But sometimes pregnancy, which brings with it an increase in body weight, hormonal imbalances and an increased load on the body in general and on the liver in particular, gives impetus to the development of hepatosis. The liver is also very susceptible to the influence of pregnancy hormones. For example, estrogen.
The main factors that increase the risk of this disease include:
- Incorrect intake of vitamins. Vitamins are always an additional burden on the liver. Many vitamin complexes contain increased amounts of various components, which cause liver dysfunction, so they need to be taken correctly, taking into account age, body weight, dosage and stage of pregnancy.
- Dietary disorder. Overeating and eating salty, fried, smoked, fatty foods, as well as foods rich in chemical additives, overload the liver and impair its functioning.
- Insufficient physical activity. If the expectant mother moves little, then little energy obtained from food is consumed, and the metabolism, which is already slowed down by pregnancy, slows down.
Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!
What measures need to be taken
If the taste of blood occurs as a result of pathological changes in internal organs, the doctor will prescribe inpatient drug treatment depending on the disease. Drug treatment of the oral mucosa involves the use of antimicrobial solutions (Chlorhexidine, Miramistin), dental gels (Metrogil Denta, Cholisal, Kalgel), drugs that stimulate the process of tissue regeneration (Solcoseryl dental adhesive paste).
There are contraindications, you need to consult a specialist!
If suppuration occurs, you can use antibiotics, previously crushed into powder.
To quickly remove the unpleasant taste and smell, you can eat a slice of lemon or other citrus fruit. Tea with cardamom or ginger effectively copes with the metallic taste.
In order not only to get rid of the taste, but also to promote the healing of the wound surface, rinses made from plant materials are used:
- chamomile flowers;
- Oak bark;
- calendula officinalis;
- peppermint leaves;
- Salvia officinalis leaves.
Related posts:
- Treatment of fear in children Fear is a feeling that arises in response to influence...
- Ingrown toenails on both big toes. How I overcame the disease after 12 years of suffering. Ingrown toenail...the mere mention of this seemingly harmless ailment prompts...
- You don’t take the city as a seat, or what a sedentary lifestyle can lead to At the beginning of the last century, it was rare to see something falling out…
- Signs You're Eating Too Much Sugar Many people are unaware of their sugar addiction. Sugar…