Content
- Causes of bleeding
- Possible complications
- Treatment regimens
- Prevention
If your tooth is bleeding, gum disease may be the cause. Inflammatory processes develop as a result of gingivitis and periodontitis, in the absence of proper oral hygiene. If there is pathology, bleeding can be caused even by regular brushing of teeth.
To fix a problem, you need to understand the cause of its occurrence. In some cases, it will be enough to eliminate the source of the problem; sometimes the approach to treatment should be complex, using medications.
PROMOTION
Dental restoration, installation of fillings
from 2200 rub.
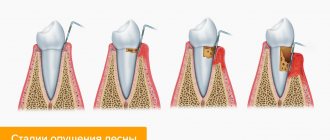
Types of bleeding
Mild: Localized bleeding in one or two areas of the mouth, usually between teeth, when dental floss is not used correctly.
Moderate: More widespread bleeding in the mouth. Most areas bleed when flossing.
Severe: Rapid bleeding when brushing with a toothbrush. Often too strong, so it takes a few minutes for it to stop.
Severe periodontitis
Smoking prevents bleeding, the main symptom of gingivitis and severe gum disease. In this way, it is possible to mask the presence of a very serious disease, which will ultimately lead to maximum deterioration of the condition of the oral cavity.
Main causes of bleeding
Lack of proper oral hygiene. Injury to the gums and the formation of bruises can be caused by a hard toothbrush. Improper flossing can also cause injury.
Plaque and tartar, the accumulation of many microorganisms contribute to the rejection of teeth from the gums. The resulting gap fills with blood. In order not to provoke such a problem, you should brush your teeth thoroughly and regularly visit the dentist for preventive purposes.
A risk factor is changes in hormonal levels, including during pregnancy, disruption of the internal systems of the body, or simply with age. The result is looseness of the walls of blood vessels and their slight injury.
Infectious diseases of the oral cavity that develop as a result of the accumulation of harmful microorganisms and bacteria. The reason is poor oral hygiene, lack of timely treatment and professional cleaning. The result is bleeding from the tooth canal.
Swelling of the gums due to periodontitis -
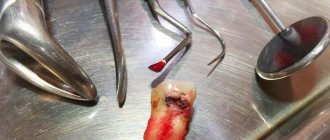
In case of poor-quality root canal treatment, due to tooth trauma, or in the absence of timely treatment of caries and pulpitis, inflammation occurs at the apex of the tooth root, which dentists call “periodontitis.” Sometimes the terms “granuloma” or “cyst” are used to refer to periodontitis, which you may well have heard. Such names are due to the fact that the focus of inflammation at the apex of the tooth root in these cases has the appearance of a purulent sac.
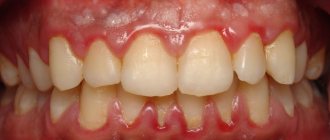
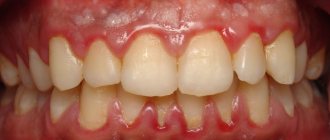
Symptoms - usually periodontitis has a chronic asymptomatic course, or there is only slight pain when biting on this tooth. But sometimes periods of exacerbation of inflammation occur, and in this case, acute pain may first occur in the causative tooth (especially when biting on it), and a little later, swelling of the gums usually appears in the projection of the causative tooth. But sometimes pain may be completely absent, and patients complain solely that the gums near the tooth are swollen (Fig. 1-3, 7-9).
Please note that with periodontitis, the source of inflammation is located at the apex of the tooth root, i.e. quite deep in the bone tissue. Therefore, swelling of the gums during periodontitis usually develops not just in the projection of the causative tooth, but most often in the projection of the apex of the root of the causative tooth. And in multi-rooted chewing teeth - no less often in the projection of the bone interradicular septum. But periodontitis is not characterized by swelling of the interdental papilla or the gingival margin adjacent to the neck of the tooth.
In general, if you have swelling on the gum in one of your teeth, pain occurs when you bite on it, and there is a crown, filling or carious destruction on the tooth, and also if, in addition to swelling on your gums, you also have swelling of soft tissues face (again in the projection of the causative tooth) - you can definitely make a diagnosis of “Exacerbation of chronic periodontitis.” An X-ray of this tooth will allow you to accurately determine the cause of periodontitis and the required amount of treatment.
What treatment may be required -
As we said above, if the gums are swollen and painful, then in most cases the reasons are poor-quality filling of the canals, or the lack of timely treatment of dental caries and pulpitis. Only according to official statistics, root canal fillings are performed poorly by dentists in at least 60-70% of cases. The main errors during treatment are underfilling of root canals, poor obturation of root canals with filling substances, breakage of instruments, perforation of the tooth root...
As a result of this treatment, a focus of purulent inflammation appears at the apex of the tooth root. Moreover, in the absence of timely treatment of the tooth for caries and pulpitis, exactly the same focus of inflammation will appear at the apex of the tooth root, but only against the background of unsealed root canals. In Fig. 10-12 you can see how the inflammation at the apex of the tooth root looks like during periodontitis (on the diagram, x-ray and on the root of the extracted tooth) -
Below we describe several treatment options that may be possible for patients with gum swelling due to dental periodontitis. In any case, the doctor will first be forced to take an x-ray. The image will allow us to determine whether this tooth can be saved at all, the size of the inflammatory focus at the apex of the root, and whether root canals have been filled in this tooth previously. The treatment tactics will depend on the latter, and below we will tell you how to cure a tooth and remove swelling from the gums so that it does not appear again.
1) If the channels are not sealed -
If root canal treatment has not previously been carried out on this tooth, then standard treatment of periodontitis is carried out with mechanical treatment of the root canals and treatment of the source of inflammation behind the root apex. On your first visit, they will open your tooth, expand the root canals to allow pus to drain out through them, and leave the tooth open for several days, prescribing antibiotics and anti-inflammatory therapy.
If necessary, your dentist may then refer you to an oral surgeon to make a small incision in the gum to allow additional drainage of pus. After about 3-5 days, the doctor makes an appointment for a second appointment and, if the inflammation subsides, completes the mechanical treatment of the root canals and seals them - either first with a temporary medicinal paste, or immediately with gutta-percha (the latter depends on the size of the source of inflammation at the apex of the tooth root). You can read more about the treatment of periodontitis at the link above.
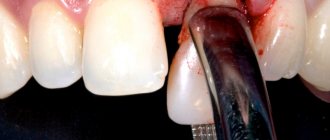
How the gum incision is made - significant swelling of the gums, or if your gums and cheek are swollen at the same time - indicates the formation of a large purulent abscess, which will require not only opening the root canals of the causative tooth, but also making an incision in the gums to release the pus. The incision is made under local anesthesia, the wound is then washed with antiseptics and a drain is inserted into it (see video below).
2) If the channels are sealed poorly -
If an x-ray shows that canal treatment has already been carried out previously and the cause of inflammation was incomplete filling of the root canals to the apex of the tooth root, then there are 2 treatment options: either standard conservative therapeutic treatment, or an option associated with resection of the root apex.
- Conservative therapeutic treatment - on the first visit, the filling/artificial crown is removed from the tooth, poorly filled root canals are unsealed, washed with antiseptics, and antibiotics are prescribed.
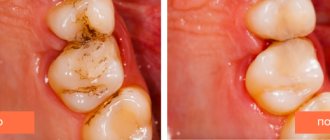
If necessary, the patient is referred to a dental surgeon to make an incision along the gum. Thus, to the treatment we described in the previous section, only 1 point was added here (unsealing the root canals). Then everything is the same - after the inflammation subsides, temporary or permanent filling of the root canals is carried out. If the source of inflammation is small, the canals are usually filled immediately and permanently with gutta-percha, and a permanent filling is placed at the next visit. If the inflammation is large, the canals are sealed with temporary medicinal paste for 1-3 months, and a temporary filling is placed. And only after this time the canals are filled with gutta-percha + a permanent filling or crown is placed. - Resection of the root apex (Fig. 13) –
This surgical method is much simpler and much cheaper than conventional therapeutic treatment, and it allows you to avoid removing the crown from the causative tooth in order to unfill and reseal the root canals.
However, this method is only suitable for those teeth in which the root canal was poorly filled only at the very apex of the root (and throughout the rest of the length the canal should be filled normally). This simple surgical operation is carried out within 25-35 minutes and consists of cutting off the apex of the root with the unfilled part of the root canal using a drill. To do this, an incision is made along the gum and a flap of the mucous membrane is moved back to give access to the bone tissue in the projection of the apex of the tooth root. Next, a small hole is made in the bone with a drill, through which the apex of the root is cut off and removed from the wound along with the granuloma/cyst at the apex. The wound is sutured and antibiotics are prescribed. Pros: cheap, simple, no need to remove the crown and re-treat the tooth.→ How is root resection surgery performed?
What complications are possible?
When, in addition to bleeding, there is an unpleasant odor coming from the mouth, you should immediately visit the dentist. At home, you can only rinse your mouth with an antiseptic. If such symptoms are not followed by treatment, complications will not be long in coming.
Many bacteria increase the risk of cyst formation; cystic formations can only be removed surgically.
The pathological process will cause destruction of the filling and crown, inflammation of the gum tissue. Treatment includes the use of medications and surgical removal of the infection.
The lack of timely treatment of pulpitis and caries aggravates the situation and ongoing inflammation completely destroys the teeth.
To eliminate the risk of complications, it is necessary to carry out a course of treatment in a timely manner.
Folk remedies
They are sometimes included in the overall treatment strategy, and sometimes used as a temporary measure before going to the dentist.
If your gums bleed, the following folk remedies are usually used:
- Oak bark decoction. They rinse the mouth with it several times a day, as it strengthens the gums and helps eliminate the inflammatory process. The preparation is simple - you need to brew 1 tbsp. l. crushed oak bark in 1 glass of water. The product should be allowed to brew until it cools, decant, and then you can use it;
- Camomile tea. This plant is an effective antiseptic with healing and anti-inflammatory effects. Pour 1 tsp into a glass of boiling water. plants, after which the infusion should be left to cool. Next, it is expressed and used to rinse the mouth. The procedure must be performed several times/day;
- Sage tea. The plant is an excellent antiseptic that has a healing, anti-inflammatory effect. It is brewed at the rate of 1 tsp. for 1 cup boiling water. Cooled to room temperature and strained, the infusion is used for rinsing;
- Water pepper infusion. This is something you can rinse your mouth with to reduce bleeding. The plant helps strengthen the walls of blood vessels, thereby normalizing blood clotting processes. To prepare the product, add 1 tsp. raw materials 1 cup boiling water, let it brew. It is then expressed and used as a mouthwash;
- Horseradish or black radish juice. It must be freshly squeezed, and its properties are that it helps eliminate plaque and tartar. You need to mix 2 tsp. juice of one of the vegetables with wine (200 ml). You can not only rinse your mouth with it, but also use it as an immunomodulator, taking it orally in small portions.
Traditional medicine suggests using sauerkraut and freshly squeezed carrot juice as ways to combat the problem. Please note that the methods listed above only help eliminate the symptom, but do not help cope with the cause of its occurrence. Therefore, visit your dentist, and only with his permission, use or discard them.
The treatment regimen includes:
- systematic professional teeth cleaning – removal of plaque and tartar;
- a course of physiotherapeutic procedures to relieve inflammation;
- sanitation of the oral cavity.
The next stage of treatment is home therapy: rinsing with disinfecting solutions (salt and soda, chlorhexidine).
For a purulent infection, the patient is prescribed antibiotics.
At home, you can independently use traditional medicine methods, including decoctions and infusions of medicinal plants:
- oak bark;
- chamomile flowers;
- sage herbs.
You can use these decoctions and calendula tincture as lotions on problem areas of the mouth.
Use of pharmaceutical products:
- fluoridated toothpastes with the addition of medicinal herbal extracts;
- dental anti-inflammatory gels (Cholisal);
- vitamin complexes.
How to treat bleeding gums
Depending on the severity of the oral infection, treatment takes two weeks. If the cause of the bleeding is a serious infection, then more aggressive intervention will be required.
Table. Remedies for bleeding gums.
- Do gums bleed during pregnancy: a problem or normal?
| Medicines | What is | What is it used for? | How is it used? |
| Antimicrobial rinse | A mouthwash that contains the antimicrobial chlorhexidine. | To control the amount of anaerobes when treating gums after surgery, as well as against gingivitis. | Like a traditional mouth rinse. |
| Antiseptic | A small piece of gelatin containing chlorhexidine. | To kill bacteria and reduce gum pockets. | Releases slowly in pockets. |
| Antibiotic gel | The main ingredient is doxycycline. | To kill bacteria and reduce gum pockets. | Releases slowly in pockets. This usually takes a week. |
| Antibiotic microspheres | Small particles containing minocycline. | To fight bacteria and reduce gum pockets. | Minocycline is released slowly into the pockets. |
| Medicine to suppress enzymes | A small amount of doxycycline, which controls the release of enzymes. | To inhibit the body's response to enzymes, otherwise some of them will destroy the gum tissue. | Available in tablet form and used during dental procedures. |
| Oral antibiotics | They come in the form of tablets and capsules. | To treat acute or locally persistent periodontal infection. | Used orally. |