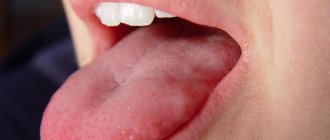
The presence of a pip on the tongue indicates the development of a pathology of infectious etiology, requiring immediate treatment.
The material in this article consists of basic concepts, classification, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, methods of therapy and prevention of this pathology. This article also describes the features of treatment of glossitis in children and during pregnancy.
What kind of disease is this?
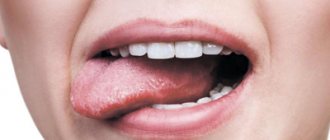
In medical terminology, a tip on the tongue is called glossitis. This is an inflammation of the soft tissues of the tongue of infectious and non-infectious origin, which develops as a result of the presence of bacterial or viral microflora in the oral cavity.
A characteristic difference of this pathology is a change in its structure and color, both on the surface and in the deep layers of the organ.
Important ! Pipun are inflamed papillae of the tongue that look like small ulcers or pimples that may contain fluid inside. If they appear, you should immediately seek medical help. This will eliminate the development of a chronic form of pathology, which subsequently cannot be treated.
Pipun does not belong to the category of independent diseases. Most often, glossitis is a manifestation of certain pathologies associated with the development of inflammatory processes.
Therefore, it is impossible to accurately determine whether tongue glossitis is contagious. If the etiology of the disease is non-infectious, then there is no point in talking about the transmission of pathology.
Pipun are inflamed papillae of the tongue that look like small ulcers or pimples that may contain fluid inside.
Causes of pip on the tongue
The etiology of the development of glossitis is very diverse. First of all, it is associated with the growth of various pathogens in the oral cavity, which, after damage to the tongue, penetrate into the wounds and provoke the development of the inflammatory process.
Against the background of a weakened immune system, a pip appears on the affected area.
Why and what causes the pip on the tongue?
The most popular causes of pip include:
- Against the background of a weakened immune system, a pip appears on the affected area
Violation of the integrity of the epithelium of the tongue.
- Dysfunctions of the human immune system.
- Vitamin deficiency, primarily B vitamins, retinol and ascorbic acid.
- Thermal or chemical injury to the tongue.
- Piercing.
- Dental pathologies: abnormal bite, stomatitis, wearing braces, improper installation of implants, acute periodontitis.
- The presence of bad habits: smoking, drug and alcohol abuse, onychophagia, addiction to highly seasoned and highly saturated foods.
- Individual intolerance to the components of oral care products.
Also, pip can be a characteristic sign of more dangerous pathologies: diphtheria, stomatitis, tuberculosis, helminth infestation, anemia, measles, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Often its appearance is observed in women during pregnancy.
Important! Correct determination of the etiology of glossitis will allow the disease to be cured in the shortest possible time, eliminating the main cause of its development.
Fighting methods
- Avoid coarse, spicy, salty foods and carbonated drinks that irritate the tongue.
- Eat more fruits, berries and vegetables, especially rich in vitamin C. For example, beets are an inexpensive, accessible vegetable that has a good effect on the immune system and enriches the body with vitamins.
- If the cause of the tip is a crown or prosthesis that injures the tongue, this defect must be corrected by a dentist.
- Forget about cigarettes and alcohol.
- Treat comprehensively with folk and/or medications by rinsing and applying applications.
- Strengthen the immune system with Imupret, Immudon, Immunal.
- Balance your diet. Reduce flour, sweet and salty foods in your diet. Try to eat foods that are compatible with each other.
Symptoms
The symptoms of glossitis are directly related to the degree of development of the pathology.
At the initial stage, the presence of pip is accompanied by the following external manifestations:
- In addition to the external manifestations of the pathology, discomfort, burning and pain are felt when eating or talking.
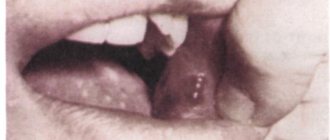
The surface of the tongue is covered with single or numerous pimples.
- The area around the tip is inflamed and red.
- Swelling is observed in the affected area of the muscular organ.
- Salivation increases.
- The surface of the tongue may become covered with a whitish coating.
In addition to the external manifestations of the pathology, discomfort, burning and pain are felt when eating or talking. The patient's sense of taste becomes dull or completely disappears.
The advanced stage of the disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Persistent and dense swelling of the tongue.
- Hyperplastic changes in the structure of the organ.
- The presence of mushroom-shaped growths.
- With a viral etiology of the pip, erosion subsequently forms in its place.
- A local increase in temperature is observed.
Important! When the first symptoms appear, treatment should be started immediately. The advanced stage of glossitis is complicated by abscesses, and when the pathology becomes more complicated, phlegmon of the soft tissues of the mouth and neck develops.
Kinds
The International Classification of Diseases defines the following types of glossitis:
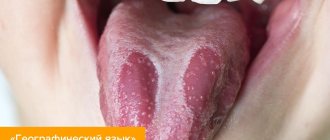
- Wandering (desquamatous). The pathogenesis of the pathology is associated with focal destruction of the epithelium, forming red areas of a pronounced red color on the surface of the tongue and its sides.
- Atrophic. A characteristic feature is a reduction in the size of the tongue. The etiology of this form of the disease is associated with infection of the body of any etiology, as well as the development of oncology of the organ and its injury.
- Diamond-shaped. As it develops in the central part of the tongue, the papillae atrophy and visually form a small lesion. It has three forms: flat, tubercular, hyperplastic.
- Black tongue (villous tip). It manifests itself as the growth of papillae in the form of threads over the surface of the tongue, followed by their keratinization.
- Folded. These are congenital deviations from the norm in the structure of language. It is characterized by the presence of folds on the back of the muscular organ, of which the deepest is located longitudinally in the center.
- Gunterovsky. Refers to the consequences of pernicious anemia. A distinctive feature of this form of pathology is the complete absence of ulcers and pimples on the surface of the tongue. Its surface is smooth, shiny and has a rich crimson color.
Forms of manifestation and localization
In medical practice, glossitis is classified taking into account the etiology and clinical course of the disease. Depending on the type of pathology, the focus of inflammation in the form of a tip is located in different parts of the tongue (root, tip, etc.).
In primary localization, taste buds and tubercles are affected. As the tip progresses, it spreads over the entire surface of the tongue and can affect other mucous and soft tissues of the oral cavity.
The table shows the forms and description:
| Form | Description |
| Catarrhal | A characteristic feature is the absence of inflammation in the deep layers of the tongue. It develops against the background of many dental, hematological and gastroenterological pathologies. Catarrhal form can also be provoked by bacterial, viral infections, helminthic infestation and injury to the tongue. It manifests itself as a intense feeling of burning and discomfort. The back of the tongue swells, the color of the organ becomes bright red, salivation increases and taste is dulled, and the mobility of the tongue is limited. White or gray spots may appear. |
| Ulcerative | It develops against the background of complications of the catarrhal form of glossitis or is the result of advanced stages of pathologies of internal organs or the oral cavity. Clinical manifestations are caused by the localization of single or multiple ulcers on the surface of the tongue. Their development is accompanied by pronounced pain, bleeding and severe swelling. There is often a deterioration in general health. |
| Purulent-phlegmous | Defined as the most severe form of pathology. When it develops, it affects: the deep layer of the tongue, tissues of the oral cavity, and nearby lymph nodes. Manifests itself as intoxication, hyperthermia, and severe malaise. Surgery and antibacterial drugs are recommended as effective therapy. |
Catarrhal
Purulent-phlegmonous
Ulcerative
Diagnostics
A dentist can determine the presence of glossitis. At the initial appointment, he determines the presence of pathology and prescribes a comprehensive examination in order to establish an accurate diagnosis and etiology of the disease.
This complex includes:
- At the initial appointment, the doctor determines the presence of pathology and prescribes a comprehensive examination in order to establish an accurate diagnosis and etiology of the disease
Physical examination by the dentist.
- Clinical blood test.
- General urine analysis.
- Blood chemistry.
- Examination of stool for helminths.
- Oral smear for microflora.
- Examination of tissues for the presence of pathogenic microflora in the oral cavity.
- Histological examination of tissues.
- PCR diagnostics.
If indicated, the diagnostic complex can be supplemented by other studies, such as ultrasound of internal organs, fluorography of the lungs, fibrogastroscopy, bacteriological blood test, blood donation for torchinosis and syphilis.
Important! The primary diagnosis of glossitis is carried out by a dentist. An examination by specialized specialists is necessary to differentiate glossitis and prescribe appropriate treatment for the pathology.
Treatment
In medical practice, two main therapeutic methods are used in the treatment of pipun:
- Conservative;
- Traditional medicine.
Conservative or medicinal treatment involves the use of certified pharmacological drugs.
The most effective medications:
- Furacilin and Iodinol. Used for irrigation of the oral cavity.
- Stomatophyte and Oxolinic ointment. These products lubricate the surface of the tipun.
- Tretinol acetate. The solution from the ampoule is applied to the site of inflammation.
- Hexaspray. The surface of the tongue is treated.
Among folk remedies, treatment is particularly effective when using:
- Herbal decoctions based on chamomile, sage, calendula and St. John's wort.
- Compress of grated potatoes with vegetable oil.
- Applications and rinsing with propolis.
- Irrigation of the oral cavity with soda solution.
When treating pipuna, medications with analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, decongestant and antifungal effects are used. The therapeutic complex may be supplemented with other medications depending on the accompanying pathologies.
Important! When treating pipun, all drugs enter the oral cavity and can penetrate into the body. Therefore, any type of tongue tip therapy should only be prescribed by a doctor.
Poisoning
Poisoning in birds ends in mortality, either within a few hours or within a few days. The cause of poisoning can be poisonous plants that come across in the hay or while the bird is grazing, as well as seeds of poisonous plants, food susceptible to putrefactive bacteria, mold, as well as pesticides and fertilizers.
Common symptoms are cramps, diarrhea, vomiting, thirst, and sudden death.
- Poisoning can occur due to poor disinfection, namely slaked lime or caustic soda. Symptoms of poisoning include swelling of the head and inflammation or swelling of the eyelids. In such cases, the bird is given vinegar diluted in three times the amount of water, and the eyes are washed with warm water.
- If forage grasses have been stored without proper technology, nitrile glycosides accumulate in them and strong acid is released. The bird experiences drooling, rapid breathing, convulsions, and suffocation.
- After consuming a large amount of salt, or poorly mixed salt in the mash, salt poisoning occurs in the bird. Death occurs within 10–12 hours. Timely rescue of the bird will yield results, for example, pouring cold water on the bird, and if this does not help, then give mucous decoctions, vegetable oil and vodka (10 g per head).
- Red beets are the most dangerous; you should not feed the bird rotten beetroots.
- Potato poisoning often occurs in the spring, when solanine accumulates in the tubers. Potatoes that have turned green and wilted are not recommended for feeding to poultry. In case of poisoning, they give a mucous decoction, as well as charcoal from burnt bones (3 g per head).
- Non-contagious diseases in poultry arise as a result of errors in feeding, and, of course, in violation of the maintenance regime - when using dirty water and low-quality feed.
How to get rid of it as quickly as possible and prevent its occurrence?
To achieve a rapid therapeutic effect and reduce symptoms, as well as to prevent relapse, it is necessary to follow a number of medical recommendations.
What to do:
- It is necessary to treat the affected area of the tongue with sea buckthorn oil every half hour
Eliminate solid foods from your diet.
- Consume dishes with rare and liquid consistency.
- Do not drink hot or strong drinks.
- Avoid drinking alcohol.
- Reduce or quit smoking.
- Do not eat hot and spicy foods.
- Enrich your diet with fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Brush your teeth with toothpaste twice a day.
- Rinse your mouth after every meal.
- Apply toothpaste to the tip and leave it until the burning stops completely.
- Cauterize the pimple with ethyl alcohol or iodine.
- Treat the affected area of the tongue with sea buckthorn oil every half hour.
- For allergic etiology of glossitis, take an antihistamine.
Important! If emergency treatment methods at home are unsuccessful, you should immediately consult a doctor. This will prevent the development of a chronic form of pathology and its complications.
Methods of therapy
The course of therapy is prescribed by a therapist or dentist. Treatment will be meaningless if the causative factor of the disease is not identified and eliminated. The injury will be repeated, which means that the ulcer will appear periodically.
If damage to the mucous membrane occurs due to a dental problem, then you must first examine and tidy up the teeth, polish the edges and remove chips.
If the cause of the appearance of pipun is general diseases of the body or infections, then it is important to accompany the therapy with the treatment of these diseases.
Find out reviews about the treatment of pulpitis of primary teeth in children. This article contains all the information about the action of Solcoseryl dental adhesive paste.
At this address you are offered information about the treatment of rotten teeth.
What medications are prescribed
Glossitis is quickly and easily treated, but only if therapy is started in a timely manner. Modern medicine has enough means that can save a patient from pipun.
- Iodinol, chlorhexidine , solutions of potassium permanganate, furatsilin - are used for rinsing the mouth.
- Stomatophyte or oxolinic ointments are prescribed to lubricate the affected area of the tongue.
- Retinol acetate - applied to a gauze pad and applied to the wound.
- Tetracycline antibiotics are prescribed by a doctor for severe glossitis.
- Antifungal drugs (for example, hexaspray) are prescribed if the appearance of pip was caused by stomatitis.
- Antiseptics - used topically to relieve pain and relieve inflammation.
- Decongestants – prescribed for severe swelling of the tongue.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs - used if the disease is accompanied by malaise and fever.
- Painkillers – prescribed to reduce pain symptoms, used medicinally or topically. A solution of lidocaine and Kamistad is prescribed for rinsing.
- Antiviral agents - use is justified if the appearance of glossitis is caused by infectious or viral diseases.
If the cause of glossitis is a weakened immune system, vitamin-mineral complexes are prescribed to increase the body’s protective properties.
If thickening and growth of glossitis is observed, surgery is recommended for patients after additional examination. This method of treatment is necessary in case of degeneration of the pip into a malignant neoplasm.
Each drug should be prescribed only by a doctor after examining the patient and identifying the cause of the appearance of pipun. It’s impossible not to treat glossitis, but you shouldn’t self-medicate either!
Home and folk recipes
Most experts recommend accompanying drug treatment with the use of traditional recipes. Medicinal plants, having healing properties, help cope with the disease.
Infusions for rinsing are prepared from medicinal plants:
- Celandine and St. John's wort : 1 tbsp. l. mixture of herbs is poured with 1 tbsp. boiling water, infuse for 20 - 25 minutes, strain.
- Oak bark : 2 tbsp. l. bark is poured with 1 tbsp. boiling water and incubate for 10 minutes in a water bath. The prepared infusion is covered with a lid for 20 minutes, after which it is filtered and used for its intended purpose.
- Basil, sage : 1 tbsp. l. Pour water over each herb, simmer over low heat for 10 minutes, cool and strain.
- Raspberry, mallow, coltsfoot leaves: the mixture is poured into 3 tbsp. water, boil for about 10 minutes, then infuse for another 30 minutes and filter.
Chamomile, St. John's wort, calendula, horseradish leaves, coriander, nettle . Infusions prepared from these herbs will help relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and speed up the healing of the mucous membrane.
It is recommended to rinse your mouth with this infusion every 3 hours. For the procedure, you can use a solution of baking soda (1 tablespoon of soda per 1 tablespoon of water) with the addition of iodine (3 drops of iodine per 1 tablespoon of solution).
Propolis can be used in treatment . A small piece should be kept in the mouth for up to 30 - 40 minutes. It promotes rapid wound healing and the death of pathogenic bacteria.
An ointment made from mashed raw potatoes with the addition of any vegetable oil will give a good result. The resulting mixture is placed on a napkin and applied to the affected area. An alternative to grated potatoes is their juice. You can rinse your mouth with it.
Compresses can be applied to the affected surface of the tongue based on:
- liquid honey;
- oils: peach, sea buckthorn, burdock, rosehip, eucalyptus;
- toothpaste containing propolis and calcium;
These products are applied to a sterile gauze pad and applied to the tip for 3 to 5 minutes.
During treatment, you should change your usual diet, that is, give up sour, salty, spicy, fried, smoked foods. Such products will only irritate the mucous membrane, preventing its healing. There is no need to drink hot and carbonated drinks, but strong warm tea will be very useful.
Whichever of these remedies is used in the treatment of glossitis, each has a healing effect and is not harmful to health.
What to do and how to treat it in children?
In pediatrics, gentle drugs are used to treat glossitis. It is important in this treatment to determine the reasons for the appearance of pip on the tongue. The choice of drugs is based on the etiology of the disease and the age of the patient.
An effective therapeutic course includes a complex of drugs aimed at stopping inflammatory processes and eliminating the source of inflammation.
If a pip has jumped up, when treating children, gentle medications are used to treat the affected area and the entire oral cavity. They can take the form of a spray, gel, ointment or rinse.
Natural preparations and traditional medicine are allowed only as adjuvant therapy. Their use helps speed up the dynamics of recovery.
Important! Avoid self-medication. Strictly follow the treatment regimen prescribed by the doctor and do not interrupt the therapeutic course on your own.
The meaning of phraseology
This phraseological unit is used when they are afraid that a frightening or unpleasant thought expressed by someone will come true.
Nowadays, of course, no one wants something to actually jump out of the speaker’s tongue, but in the not-too-distant past the expression had a very direct and specific meaning: “Let a sore appear in your mouth so that you don’t talk all sorts of things.” nonsense!
In what cases is it appropriate to use an idiom? Well, for example, when a neighbor makes unfavorable predictions about the future of your children: “Your children are so tame. Never mind, in ten years you’ll be running around looking for them all over the city.”
Or when an envious competitor predicts the collapse of a well-started business. Both the predictors want to say: “Tip your tongue! Keep quiet, don’t croak, otherwise it will really come true.”
Treatment during pregnancy
In parallel, in agreement with the leading gynecologist, a therapeutic course begins to remove the tip on the tongue
In most cases, the appearance of a pip on the tongue is caused by the presence of natural physiological changes and the development of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
Therefore, treatment must begin with eliminating the cause.
In parallel, in agreement with the leading gynecologist, a therapeutic course begins to remove the tip on the tongue.
Local funds may be used for these purposes.
How to treat:
- Dissolving tablets.
- Pastilles.
- Spray.
- Tinctures for irrigation of the oral cavity.
- Treatment of pipun with ointment.
Important! The selection of drugs and the duration of their use are prescribed exclusively by a doctor. If the slightest side effects occur or if the clinical picture of the disease worsens, you must immediately consult a doctor to correct the therapeutic course.
Pasteurrelosis disease (cholera)
This is also an infectious disease. Mainly characterized by severe nasal discharge and high mortality. The source of infection includes sick or ill birds, insects, rodents, and contaminated food. And the main thing is that the virus is transmitted through contact.
When the disease occurs in an acute form, the bird is depressed, eats poorly, has a characteristically pronounced nasal discharge, wheezing, difficulty breathing, diarrhea, which leads to the bird’s death as general weakness increases within 18–72 hours.
The virus is bactericidal by a solution containing 3% formaldehyde and 3% sodium hydroxide, 10% iodine monochloride, as well as a clarified solution of bleach containing 5% active chlorine, and a 20% suspension of bleach.
For any illness, we advise you to consult a veterinarian.
Preventive measures
You can prevent the appearance of pip on the tongue, prolong the period of remission and avoid relapse of the disease by adhering to simple preventive rules:
- It is necessary to carefully carry out oral hygiene
Maintain a proper diet.
- Avoid consuming foods and drinks that irritate or injure the oral mucosa.
- Systematically take vitamin complexes and immunomodulators to strengthen the immune system.
- Completely give up bad habits.
- Regularly undergo dental examinations to ensure the integrity of dentures and implants.
- Carry out oral hygiene carefully.
- Use professional antibacterial rinses daily.
Despite its small size, a pip on the tongue brings discomfort and a lot of trouble. The insidiousness of this pathology lies in the fact that if left untreated, pipun can take the form of a malignant neoplasm or lead to the appearance of serious concomitant diseases.
Therefore, when the first signs of pathology appear, you must immediately consult a doctor and undergo the prescribed therapeutic course without delay.
Other phraseological units
Fully
Thoroughly, very detailed.
Foundation stone
An element of the whole that lies at the base, foundation, support, basis.
Pandora's Box
An object or phenomenon that contains a threat and can lead to irreversible consequences.
The cat cried
Something very little or not at all.
All phraseological units
A book from the authors of this article!
Collection: “100 popular phraseological units of the Russian language”
More details