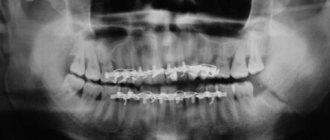
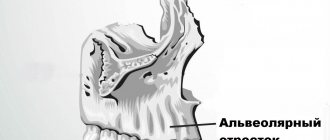
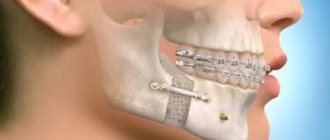
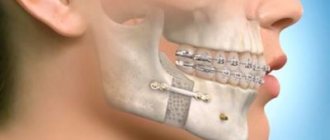
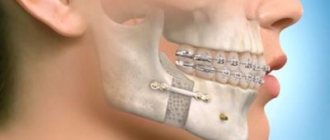
The most important condition for successful dental implantation is a sufficient amount of bone tissue. If there is not enough for reliable installation of the implant, then an operation called bone grafting is used to increase the volume. If indicated, such an operation is also performed in CELT dentistry.
Many patients are afraid of this procedure - it seems risky to them. Often, having learned that bone tissue augmentation is necessary, they refuse implantation in favor of less comfortable and reliable methods of prosthetics. We will look at the features of bone grafting, make sure that grafting is not dangerous, and find out in which cases it cannot be done without it.
Consultation with an implantologist (when conducting or OPTG studies at CELT - free of charge) - 1,500 rubles.
Taking an autograft - 10,000 rubles.
Plastic surgery of complex hard tissues (membrane) - RUB 20,000.
Complex hard tissue plastic surgery (veneer) - RUB 35,000.
Complex hard tissue plastic surgery (block) - RUB 35,000.
Simple plastic surgery of hard tissues (minor regeneration) - RUB 7,500.
Complex soft tissue plastic surgery for 2-3 teeth - 15,000 rubles.
Simple soft tissue plastic surgery in the area of 1 tooth - 10,000 rubles.
Bone material BIO-OSS - RUB 11,000.
Osteomatrix bone material - RUB 5,000.
Membrane BIO-GUIDE PERIO - RUB 15,000.
Osteomatrix membrane — RUB 7,500.
At CELT you can get advice from a dental specialist.
- Cost of consultation with an implantologist (when performing CT or OPTG in CELT - free) - 1,500
- Consultation with a dental surgeon – 1,000
Make an appointment
Implantation and bone volume
Dental implantation has many advantages over classical prosthetic methods. One of the things that is not very obvious to people far from medicine is the preservation of bone volume around the implant (implant) due to the stimulating load during chewing, while with removable dentures or simply a long-term absence of a tooth, a gradual decrease in the thickness and height of the bone is observed. This is due to the fact that when installing dentures that rest on teeth, the bone tissue does not receive the necessary load. The bone plate gradually becomes thinner as it does not receive sufficient stimulation.
This is not the best consequence of removable prosthetics; over time it can cause a lot of inconvenience. Resorption of tissue is fraught with weakening of the gums and a decrease in the strength of the remaining teeth. The thinning of bone tissue can be stopped using bone grafting followed by implantation. After installation of the implant, the tissue receives a normal natural load, which means that pathological thinning does not occur. In addition, the implant looks much more aesthetically pleasing than a removable denture and looks more natural.
How does the procedure work?
The first stage is careful cleansing and makeup removal. Next, an anesthetic gel is applied to the area of the upcoming treatment (it minimizes discomfort at the time of punctures). Then, using special ultra-thin needles, the doctor injects gel filler into pre-designated areas. Usually, to work with the lower jaw, you need to make two punctures - one on each side.
It should be noted that in addition to improving the contour, the introduction of filler also provides other beneficial effects - under the influence of hyaluronic acid, the tissues are saturated with useful substances. deep hydration occurs, the production of your own collagen and elastin is activated. That is, the procedure not only corrects the angles of the lower jaw, but also has a positive effect on the condition of the skin as a whole, rejuvenating it.
When is bone grafting needed?
When implanting teeth, there is often a need for bone grafting. This is an operation to augment bone tissue using synthetic material or bone material, either animal or obtained directly from the patient.
After tooth loss, the process of bone atrophy begins at the site of the missing tooth. This can be avoided by carrying out so-called socket preservation, or a set of measures aimed at preserving the anatomy of the bone and soft tissue in the area of the extracted tooth. That is, how exactly the tooth was removed is of great importance. Unfortunately, when a tooth is removed, such a complex is not always carried out. The first changes in the alveolar ridge (bone) are visible after 3-4 months. Pronounced thinning is observed a year after tooth loss and then only increases. Therefore, it is important to contact an implantologist in a timely manner. According to our statistics, few patients install an implant immediately after tooth loss. Some people take a long time to heal after removal, some have no time, some need to prepare mentally, others need to save up the necessary amount. As a result, when a patient comes to have implants installed, it often turns out that he does not have enough bone tissue - which means that a augmentation procedure is required first, and maybe only then implantation.
Sometimes bone grafting is prevented by serious contraindications. There are some cases when the bone tissue does not thin out and is preserved in full. Each case should be considered individually with the implantologist you contacted. It is important to choose a competent specialist - the doctor must objectively assess the condition of the bone tissue, the feasibility of implantation and offer the patient the most profitable and reliable procedure.
The volume and need for bone grafting can be most accurately assessed only with the use of computed tomography and 3D modeling - which is successfully used in our clinic at an expert level.
In most cases, bone grafting is still needed during implantation. Without it, tissue thinning can cause further bone atrophy, which will affect the stability of the implant.
Plastic surgery is also used if implantation is not planned - sometimes bone atrophy can lead to teeth shifting towards the lost tooth. Then dental correction of this pathological condition is required.
How much does surgical treatment cost?
The cost of surgery to restore gums starts from 15,000 rubles. For creating an ideal contour around one tooth.
In case of significant bone deficiency, additional bone grafting may be performed. The decision to use this treatment method is made by the doctor based on the results of computer diagnostics.
The specialists of Dr. Lemberg Dental Clinic are waiting for you for a consultation, where you can see all the equipment used, get answers to all your questions and undergo a comprehensive diagnosis to draw up a comprehensive treatment plan. Doctors will make every effort to make your smile perfect.
Types of bone grafting
Plastic surgery can be performed in different parts of the jaw:
- Plastic surgery of the lateral sections of the lower jaw. Correction of the lateral sections of the lower jaw is required if there is a pronounced decrease in the volume of the alveolar process and a decrease in the distance to the canal of the lower jaw.
- Frontal plastic surgery on both jaws. As for the anterior section, plastic surgery is necessary due to bone resorption. During thinning, a modified alveolar ridge, thin and sharp, is formed. And the front teeth bear an increased load when they dislocate forward, so it is important to return the normal volume of bone tissue to install implants adequate to the load. Plastic surgery in this area is complicated by the fact that the result must be not only functional, but also aesthetic. Any problems with the front teeth are conspicuous to others and can seriously damage self-esteem.
- Lateral sections of the upper jaw - this procedure has a special name, sinus lift. Sinus lifting is so called because the operation involves penetration into the bony volumes of the skull occupied by the sinuses or, as they are also called, the maxillary sinuses. It is important to understand that this is not an operation associated with penetration into the cavity of the maxillary sinus itself, but the release of bone volume for the introduction of replacement material WITHOUT perforation of the nasal mucosa. Currently, two types of surgery are used: open sinus lift and closed sinus lift. They differ in the surgical technique and the method of access to the sinuses.
What is gum grafting?
When problems with gums appear, the patient first notices bleeding. This is the simplest disease called gingivitis. And in difficult cases with periodontitis and periodontal disease, when inflammation affects not only the gums, but also the bone, you can also see external changes in the gums, it rises and the roots of the teeth are exposed. Such situations cause great discomfort to patients and reduce the quality of life.
The problem of gum recession can best be dealt with by a surgeon. Treatment with surgical methods brings positive long-term results and helps get rid of the problem.
Flap operations for periodontitis help cover exposed necks and roots of teeth. Thus, the volume of missing soft tissues is restored, and with it a protective function appears.
Materials used
The material used to make the bone plate can be natural or synthetic. They are similar in their ability to replenish bone tissue and have comparable engraftment rates. Synthetic materials are powder or shavings and are currently used by dentists in all developed countries of the world.
But better than synthetic is material of animal origin (xenograft) or your own bone material. Synthetic takes root well, but materials from animals or your own (autogenous material) have a lower risk of rejection, a lower degree of resorption, and the body accepts them better. To produce materials of animal origin, biomaterial from cows and bulls is used, which goes through several degrees of purification and sterilization. In fact, in terms of purity, this material corresponds to synthetic, but depending on the manufacturer, it can give better results than synthetics. Natural material is taken from the donor area, usually the chin or bone tissue near the wisdom teeth. The only difficulty in using your own bone material is that its collection requires additional intervention (in fact, harvesting an autograft is an operation not much different from removing a wisdom tooth and in some cases even simpler). Another type is xenotransplantation.
There is no specific standard, so the material is selected by the doctor together with the patients. The final cost of bone grafting may depend on the material chosen. The use of artificial biocompatible osteoplastic material or sampling from the patient himself is considered more justified and popular. If necessary, you can select material from extraoral areas without damaging the gum tissue.
If bone grafting is carried out correctly and in full, then subsequently the installed implant will hold securely, regardless of the complexity of installation and healing.
Postoperative recovery
After gingivoplasty, the doctor will tell you what needs to be done during the period of soft tissue restoration. Healing lasts from several days to 2-3 weeks. During the postoperative period, patients at our clinic are recommended to:
- take painkillers as prescribed by your doctor;
- reduce physical activity;
- eat warm crushed food;
- exclude spicy foods from the diet;
- rinse the mouth with an antiseptic solution;
- Do not use a toothbrush to clean the suture site.
After the procedure, the swelling lasts up to 5 days, then it begins to subside. If the swelling does not disappear, or complications arise, you should immediately consult a doctor.
To correct a smile using soft tissue, gingivoplasty is the optimal procedure. It is absolutely safe, but there are risks, as with any surgical procedure.
This could be an allergic reaction to the anesthesia (which is extremely rare when using modern anesthetics) or a recurrence of gum recession. In case of relapse, re-treatment is carried out after six months. To avoid this, immediately inform your dentist about any existing diseases.
Benefits of bone grafting
During implantation, bone loss occurs, which can be avoided with plastic surgery.
After surgery, the body experiences stress, and most importantly, it begins to work differently. While eating, there is no load on the jaw, so the bone tissue gradually disappears. Standard dentures do not solve the problem, but only create unnecessary stress on neighboring teeth. To solve the problem 100%, you need to install an implant. It will improve your smile, maintain your health, and also prevent the development of complications after tooth loss. Bone grafting completely eliminates atrophy of the jaw bones even in adulthood.
Microsurgical operations of maxillofacial surgery
Microsurgery is a universal method used in almost all surgical disciplines to eliminate a defect in a particular tissue. In the human body, there are more than 400 donor sites with an axial type of blood supply, from which taking tissue does not cause any harm to the further blood supply of the entire organ. In the reconstruction of the jaws, the main place is played by the property of the flap with the presence of such a quantity and quality of bone that will make it possible to recreate the anatomical integrity of hard tissues and in the future the possibility of use for dental implantation and prosthetics .
For total and subtotal defects of the mandible, a fibular skin-bone flap . The fibula has sufficiently large supporting properties, having a fairly large amount of cortical component, and can be easily modeled to recreate anatomical contours. An iliac or otherwise inguinal skin-bone flap is optimal for the reconstruction of small defects of the lower jaw; in the latter cases, it is sometimes possible to use a free iliac bone.
For total and subtotal defects of the upper jaw, radial skin-bone and fibular skin-bone flaps are optimal. In cases where the defect covers the zygomaticomaxillary buttress in combination with a defect in the alveolar process, it is possible to fill the bone defect with corticocancellous parietal grafts and mandibular grafts taken from the ramus and mental region with free grafts of mesenchymal origin, which is optimal for reconstruction of the middle zone faces.
Of course, the dominant algorithm remains aimed at engrafting the flap on a vascular pedicle. If you have to choose between convenience for subsequent dental implantation in the form of the presence of a cortical plate of the bone component of the autograft in the area of the recreated alveolar process for subsequent implantation and this somehow reduces the reliability of the vascular anastomosis, it is necessary to choose the reliability of engraftment. Disputes often arise between implant surgeons and reconstructive surgeons about how the iliac bone should be positioned in the defect area, but experience shows that there can be no compromises, since in case of thrombosis of the vascular anastomosis, the entire flap is lost. It is also necessary to understand that the location of the spongy component in the area of the alveolar process does not interfere with subsequent implantation, since a new one is formed within 6 months.
To return and normalize chewing function and the ability to eat, it is necessary to have:
- 1. Lips and complex of swallowing organs.
- 2. Presence of jaws.
- 3. The presence of teeth and a bite that provides adequate chewing.
- 4. Presence of buttresses.
- 5. Stabilization of the TMJ.
- 6. Synchronicity of the masticatory muscles.
- 7. Mental balance of the patient.
In the literature, we did not find a specific algorithm or approaches aimed at returning such vital abilities as sucking and swallowing, chewing and normalization of speech function. To normalize the patient's nutrition, the presence of lips is necessary, otherwise salivation occurs, followed by maceration of the skin and the inability to receive and send food into the esophagus. Patients with defects of the soft tissues of the perioral area constantly suffer from gastritis, inflammation of the oropharynx, since the vacuum property of food evacuation into the esophagus is reduced, many adapt to swallow with an open mouth, throwing their head back; in the latter, the absorption of carbohydrates is impaired, since saliva takes part in cleansing the oral cavity from food residues, plaque and bacteria, thanks to its buffering properties, it neutralizes the negative effects of strong acids and alkalis within the buffer capacity, provides the supply of ions necessary for the remineralization of teeth, and has antibacterial, antifungal and antiviral properties. Claude Bernard proved that we recognize the functions of an organ by identifying the consequences of its absence. From the point of view of the functional return of the ability to eat, the second place in our algorithm is the presence of jaws. To eliminate defects in part or the entire jaw, we use preoperative planning.
Preoperative planning of the jaws is carried out using 3D visualization programs that allow modeling the sizes and shapes of autografts, taking into account the positioning of the condylar processes of the lower jaw in the temporal fossae (in the anterior-superior position in the articular cavities) according to CT scans. Despite the fact that we perform reconstruction in the previous bite, most often we have to deal with an already remodeled TMJ and a broken bite. Therefore, planning is necessary taking into account the subsequent achievement of centric occlusion in the centric relation. A functional study of occlusion consists of comparing central occlusion (CO-occlusion in which there is maximum contact between the teeth of the upper and lower jaw) and the central ratio (CO-condition in which the heads of the lower jaw occupy an anterior-superior position in the articular sockets). If there is a significant difference, a description of the differences is required. Thus, a significant difference between these conditions is more common with asymmetric deformations and with Angle class II deformities. Determining the CA is important for correctly drawing up an operational plan.
When planning the elimination of maxillary defects, we take into account the need to restore the buttresses, as well as the air supply of the upper jaw. Buttresses are the most important component for supporting the alveolar process, otherwise mobility of the upper jaw occurs after prosthetics.
Although restoration of the lost maxillary cavity and mucous lining is not possible, restoration of anatomical proximity is necessary, therefore filling the zygomaticomaxillary buttress with ilium is incorrect. It is optimal to use free split mandibular or parietal auto-bone blocks in shape in combination with bone with vascular nutrition. In the future, perhaps with the development of technologies for the use of stem cells, we will learn to restore the true mucous lining of the maxillary or paranasal sinuses.
In the reconstruction of the upper jaw, we use a fibular autograft for the reconstruction of total defects and a radial one for subtotal defects. When a radial skin-bone flap is subsequently used to place dental implants, it becomes necessary to reconstruct the second cortical-spongy layer of the alveolar process on the lingual side, which can be done using parietal or mandibular free autoblocks.
In maxillofacial microsurgery , when it is necessary to recreate bone curves, in the choice of grafts with bone, we are limited to iliac, fibular, and radial flaps, since only the latter allow 3D modeling of the bone component congruent with the defect.
of one-stage reconstruction after resection still remains open in the country . It is necessary to understand that if the reconstruction is not performed simultaneously with the resection of the jaw and even a temporary titanium structure is not applied to maintain the bite, remodeling of the temporomandibular joint occurs, both from the healthy and from the pathological side, and a violation of the trophism of the masticatory muscles. In these cases, before placing dental implants and before prosthetics of the implant, orthodontic fixation of the bite is performed in the form of braces and mini-implants, as well as muscle relaxation of the masticatory muscles on the part of the healthy jaw using Botex therapy or myotronic.
HISTORY OF THE PROBLEM
In our opinion, microsurgical autotransplantation for the purpose of jaw reconstruction has gone through several stages in its development:
Stage 1 – high-quality autograft collection, minimal modeling, and transfer to the recipient area. The main objective of this stage was to ensure graft engraftment (from 1978 to 1990).
Stage 2 included better modeling of autografts using conventional radiographs and wax templates. The main task of this stage was to restore facial aesthetics. The impaired function of the lower jaw was restored after a series of additional corrective operations and removable dental prosthetics (from 1990-1995). Stage 3 - computer modeling of the lower jaw and restoration of chewing function using prosthetics using dental implants. The main goal of this stage is to restore facial aesthetics and chewing function of the lower jaw without the use of additional corrective surgeries (from 1995 to 2011). Stage 4 - restoration of not only an ideal bite and stabilization of the TMJ, but also elimination of the imbalance of the masticatory muscles (in fact, this article opens the 4th stage in the history of maxillofacial microsurgery).
We have developed an algorithm for treating patients with jaw defects: 1. Preoperative 3D planning and production of stereolithographic and bite templates. Planning taking into account subsequent dental implantation and prosthetics. Selecting the optimal flap. 2. Restoration of buttresses, if possible, and the anatomical contours of the alveolar process of the jaws using free and pedunculated bone grafts. 3. Remodeling of the TMJ when eliminating subtotal defects of the lower jaw. 4. Dental implantation and prosthetics.
Microsurgical operation: resection of the lower jaw affected by the tumor with simultaneous reconstruction with a fibular graft on a vascular pedicle
| 1. Resection of the lower jaw affected by the tumor within healthy tissues | ||
| 2. Stage of control of resection according to the preoperative template | ||
| 3. Harvesting the fibula on a vascular pedicle | ||
| 4. Stage of modeling the harvested transplant using the author's device Karayan A.S. and Nazaryan D.N. | ||
| 5. Control of the simulated transplant on the preoperative template | ||
| 6. Fixation of the graft on the vascular pedicle to the remaining healthy fragments of the lower jaw | ||
| 7. Microsurgical stage: under a microscope, the vessels from the lower leg and the external carotid artery, jugular vein are sutured, after suturing the vessels, the clips are removed and the tissue taken from the leg is filled with blood, i.e. the flap becomes alive, but on the jaw. | ||
| 8. Control of blood supply - the final stage of microscopic surgery | Watch the video | |
| 9. The patient’s appearance before and after the operation will be practically unchanged; thanks to one-stage reconstruction, after 6 months the person will be completely rehabilitated | ||
In the scientific and clinical department of maxillofacial and plastic surgery of the Federal State Budgetary Institution NCCO FMBA of Russia under the leadership of Professor Karayan A.S. and Ph.D. Nazaryan D.N. Unique surgeries are performed to eliminate jaw defects. Such operations are performed only in 3 medical centers in Russia.
Disadvantages of bone grafting
The main disadvantage is that excellent results can only be achieved by a real expert.
Any errors at the diagnostic stage or during surgery can lead to serious consequences: rejection of the bone block, formation of pus, inflammation and infection. After surgery, swelling often occurs, but it goes away on its own within 3-4 days. Hematomas often appear. Swelling and hematomas occur during any procedure. Therefore, it is necessary to inform the client in advance about the possible consequences.
What results does soft tissue grafting provide?
Flap surgery in the oral cavity helps:
- Increase gum volume
- Close up exposed necks of teeth
- Form the anatomical shape of the gums
- Correct the contour of the gingival margin
A positive result can be assessed after 3-6 months of follow-up. After complete healing, some more time passes, during which the gums take root and acquire the desired volume.
Complications of bone grafting
There is a risk of complications in any surgical operation and bone grafting is no exception. The complexity of bone grafting greatly depends on the volume of the operation - preparation for implantation of one or more teeth will differ significantly in volume. Naturally, the risk of complications is reduced if you turn to a professional who performs such operations on a regular basis and if you strictly follow all postoperative recommendations.
The most serious complications known from bone grafting are:
- Inflammatory process in the wound.
- Suppuration, infection of the wound.
- Rejection of osteoplastic material.
These complications can be either a consequence of the doctor’s lack of competence or the result of the patient’s neglect of rehabilitation recommendations. It is important to follow all your doctor's instructions regarding the recovery period. Complications are not irreversible with proper treatment, but can lead to complete rejection of the material and the return of the original bone volume.
In addition to complications, there are natural consequences of plastic surgery - tissue swelling and slight bleeding. These symptoms appear immediately after the intervention and persist for 2-3 days. If symptoms last longer, you should consult your doctor. Sometimes hematomas appear, which can be visible on the skin of the face (especially when working with the lateral parts of the jaw and double-sided plastic surgery).
What to do after the procedure
No special rehabilitation is required after such an intervention. The result is noticeable immediately; there are usually no traces left after the injections. In the first couple of days after the session, you need to protect your face as much as possible, try not to touch it unless necessary (so as not to cause an infection). You cannot use foundation and powder. For 2 weeks after the procedure, it is not recommended to sunbathe on the beach or in the solarium, or visit the bathhouse or sauna.
After this time, you can return to your normal life and enjoy the results.
To make an appointment for correction of jaw angles in Moscow, just call us or use the form on the website. We are located in the very center of Moscow, next to the Baumanskaya metro station and 1905 Goda Street. Our specialists will select the optimal solution for your case and help you achieve the best aesthetic result.
Is it possible to perform bone augmentation at the same time as dental implantation?
New implantation technologies make it possible to perform two processes at once in one procedure, but first you need to determine the feasibility of this approach. Professionals often divide the work into several stages:
- Removal of a tooth.
- Bone grafting.
- Implantation.
But there are two pitfalls here. Firstly, not all clients are ready to go through the operation 3 times. Secondly, dividing the process into several stages is advisable only in cases of severe bone loss. To determine the appropriate method of performing the procedure, it is necessary to take into account the individual characteristics of the client and conduct competent diagnostics.
Indications and contraindications
The absolute indication for the extension procedure is implantation in case of tissue atrophy, tooth extraction, or rejection of the installed implant.
The procedure has some contraindications:
- oncology;
- infectious, systemic, immune diseases;
- inflammatory processes of ENT organs;
- drug intolerance, allergies;
- blood clotting disorder;
- mental disorders.
A relative contraindication is pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Alternatives to Bone Grafting
There are 2 technologies in dentistry that do not involve building up bone tissue for implantation:
- The All-on-4 protocol is recommended for fixed prosthetics in edentulous clients. It is possible to carry out work even with minimal bone height, since all implants are installed at different angles. The technology is performed without bone grafting in 99% of cases.
- Basal implantation is carried out using a complex technology that involves fixing implants in the basal layers of bone tissue at the maximum depth. This layer has enormous strength and rarely atrophies over time. The technology is universal and suitable for installing a bridge or local missing teeth
As a rule, both technologies are implemented in one visit to a specialist. The use of the All-on-4 protocol makes it possible to fix a horseshoe-shaped bridge consisting of 12-14 teeth on 4-6 implants.
Comprehensive correction of face shape for dysgnathia class III according to Engle
View as an album on VK
I think that with specific examples it will be easier for me to explain, and for you to understand , what changes and through what operations can be achieved for various facial deformities . In this case, the patient has class III dysgnathia according to the Engle classification . What does it mean? This means that the upper jaw is “lag behind” the lower jaw in its development . And now the teeth are closing incorrectly . But we are more interested in understanding how improper development of the jaws affects the appearance of the face . So, let's start the analysis.
Correction of the midface (moving the upper jaw forward), chin reduction
| As we have already understood, the cause of deformation of the midface in this case is the too “backward” position of the upper jaw (retroposition). Accordingly, to solve the problem, you need to move the jaw anteriorly , which was done. Through incisions inside the mouth, the upper jaw was cut and moved by 6 mm. anteriorly and fixed in the new position with titanium plates. In addition, the chin was reduced. What happened: | ||
| As a result of the operation, the middle area of the face was “straightened” and “filled out” . This is especially noticeable in the side shot. Also pay attention to how the position of the lips has changed - they have received the correct support . The chin became smaller and also changed shape. But one more problem still remained unresolved. |
Improved bite
| Well a few words about the bite. After all, these operations were originally conceived to solve such problems. To obtain the correct bite, first orthodontic preparation was carried out, which consisted of aligning the dentition and creating a gap between the upper and lower incisors, which I needed as a surgeon for maximum advancement of the upper jaw forward. As a result of the operation, the bite became correct and the smile became beautiful. Many thanks to orthodontist Elena Nailievna Ismagilova! |