Why do papillomas occur in children?
Once inside the body, the virus peacefully coexists with other microorganisms and does not manifest itself in any way until a certain point - when the child’s immunity weakens, benign growths may appear. The reasons for the appearance of papillomas in children are due to a decrease in natural protection in the case of:
- previous bacterial, viral and fungal infections;
- frequent colds;
- allergies;
- autoimmune pathologies;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- immunodeficiency;
- long-term drug therapy;
- injuries, surgeries and burns;
- vitamin deficiency
Any attack on children's immunity can provoke virus activity. Sometimes the starting point is mental and physical overexertion, stress, and nervous shock.
HPV is highly contagious and can be transmitted even through short-term contact with a carrier. In children, 3 routes of infection with the human papillomavirus are most relevant.
- Perinatal. Passing through the vaginal canal during childbirth, the baby comes into contact with the physiological secretions of the mother, receiving a viral load. Another option for this method of infection is the transmission of HPV from the expectant mother to the fetus through the placental bloodstream during pregnancy.
- Domestic. This method is the most common reason for the appearance of papillomas on a child’s body. The virus is transmitted through surfaces and objects touched by an infected person. Common sources are towels, combs, general hygiene products, and clothing, from which HPV enters the child’s body through abrasions and small wounds.
- Contact. Transmission of the virus occurs when a healthy person comes into contact with the skin, hair or other parts of the carrier’s body. The simplest example of such an infection is playing and interacting with children who have rashes.
The incubation period lasts from 2–4 weeks to 3–6 months, less often up to 2–4 years. The optimal conditions for the development of HPV are a humid and warm environment. In the fresh air without contact with human skin, the virus quickly dies.
Causes of papillomas on the inside of the lip
The cause of the appearance of papillomas on the inside of the lip is a human papillomavirus infection. The viral agent penetrates into the deep layers of the epithelial layer of the oral cavity through microwounds and cracks and leads to disruption of the process of cell division in the lower layers of the mucosa. Penetrating into chromosomes, the virus provokes the proliferation of cylindrical cells. As a result of this effect, the epithelium grows and specific growths appear on the surface.
When it comes into contact with the oral mucosa, the virus can enter the body and remain latent for a long time. The strain is activated by a confluence of factors favorable to it. On average, the incubation period lasts 1-6 months. Infection with the subsequent appearance of papillomas on the lips of the mouth can occur as a result of oral sex, through personal hygiene items (toothbrush), shared dishes with a sick person, lipstick, kisses. Children are often infected with HPV. Especially at risk are children who attend children's groups and public places.
It is worth noting that there are over 100 strains of HPV, but not all are able to penetrate the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. There are approximately 6 known strains of the pathogen that cause papillomas on the inner lips. All of these viruses are considered non-oncogenic, which means that there is an extremely low probability of transformation of these neoplasms in the mouth into malignant tumors.
HPV can become active for various reasons. Among the most common: a general decrease in immunity, long-term antibiotic therapy, severe stress, overwork, hormonal imbalances, and the presence of bad habits.
- See also the reasons for the appearance of warts on the inside of the lip
HPV symptoms
The papilloma virus infects the skin and mucous membranes, causing the proliferation of the epidermis and the appearance of pathological neoplasms:
- papillomas;
- warts;
- condylomas.
They look like small skin growths ranging in size from 1 to 5–8 mm, sometimes there are growths reaching 1–2 cm. Basically, such formations imitate healthy skin in color, but there are elements of dark brown and white shades.
The main places of distribution of papillomas:
- face and neck;
- external genitalia and groin area;
- the inner surface of the elbow and knee bends;
- soles of feet;
- fingers and skin around nails.
On the mucous membranes, elements can appear in the larynx, nasal passages; in girls, sometimes there are formations localized on the cervix.
Types of formations
There are several types of papillomas.
- Vulgar (common) warts. They are the most common type of neoplasm. They have a “leg”, rise noticeably above the surface of healthy skin, reaching a diameter of up to 1–2 cm. Sometimes hair grows from the central part of the wart. Such formations do not bother the child with pain or itching and appear on the arms, back or legs.
- Flat or juvenile papillomas. They look like small pigmented plaques of a fuzzy round shape, do not extend beyond the skin and form in groups. Such elements are characterized by a smooth surface and selectivity: they appear on the face, neck, legs, sometimes hands, but never in the armpits, genitals or skin folds. Occurs in children older than 5–6 years.
- Condylomas or genital papillomas. These elements resemble small papillae. They are pink in color and form in areas with thin skin: in the genital area, on the mucous membranes.
- Plantar warts. They affect the feet, occur under the big toes and visually resemble small round calluses.
Another variant of formations is filamentous warts or acrochords. They are similar to regular ones, but differ in elasticity and more compact sizes up to 5–6 mm. They prefer to appear under the mammary glands, in the groin, armpits, and are found on the neck and face.
The dangers of human papillomavirus
Some of the representatives of these microorganisms are harmless to humans, while others can provoke the growth of cancer cells. HPV is classified into two main types:
- Strains with high oncogenic risk. Such variants of the virus provoke the development of condylomas on the mucous membranes and in the genital area. Under unfavorable circumstances, they can cause an oncogenic mutation.
- Strains with low oncogenic risk. Viruses of this type cause warts, plantar lesions and juvenile papillomas. The risk of cell degeneration is minimal.
The greatest danger lies in girls: studies conducted in the USA have proven that 98% of cases of cervical cancer are associated with this virus. There is also a risk of developing cancer of the vagina, ovaries, anal canal, larynx, pharynx, and in boys, the genitals. Papillomas located in the anus and genital area require special attention.
Diagnosis of HPV
The main clinical sign of papillomatous infection is formation on the skin. Therefore, in most cases, an examination by a doctor is sufficient to make a correct diagnosis. Additional examination methods are:
- biopsy or scraping - taking biological material for further research;
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction);
- General and biochemical blood test.
These laboratory diagnostic methods help:
- detect the presence of papilloma virus in the child’s body (if there are no growths on the skin);
- accurately determine the HPV strain;
- understand the form of the infection (acute or chronic).
These data are necessary for assessing oncogenic risk and timely further examination.
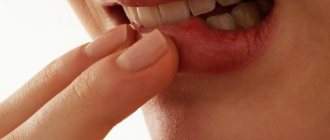
What do papillomas look like on the inside of the lip?
Photo of papillomas on the inside of the lip
As a rule, a person is not aware of the presence of the papilloma virus in the blood until visual evidence of this appears in the form of neoplasms on the skin or mucous membranes.
Papillomas on the lips of the mouth look like rough growths that resemble miniature papillae, round or oblong. They have a flat base or thin stem. In color they practically do not differ from healthy mucous membranes of the mouth and lips; they may have a whitish coating. The size usually does not exceed 12 mm.
Neoplasms can be isolated or form groups. In the latter case, they resemble a cockscomb or a broccoli floret.
Such growths do not cause pain unless they are injured. They are soft and mobile, elastic. However, if we are talking about pointed papillomas, then they are easy to injure. This can lead to an inflammatory process, suppuration, and the addition of an additional infection.
Papillomas on the inside of the lip are reactive and neoplastic. Reactive ones can grow due to regular irritation or injury, which is inevitably present in the oral cavity (food, teeth, sharp objects). Neoplastic papillomas are a collection of nodular growths that merge and form a large tumor.
Often, papillomas on the lip mucosa can form in children. The larger the tumor, the more problems it causes for babies. Thus, children cannot pronounce certain sounds due to discomfort in the oral cavity, the correct growth of molars may be disrupted, papillomas sometimes grow and affect the throat, tonsils, vocal cords, which poses a real threat to life.
Treatment of HPV in children
Unfortunately, there are no effective medications for the treatment of papillomavirus in children, as well as in adults.
In most cases, the body copes on its own, and action is only necessary in situations where there is a risk of oncological processes or tumors interfere with the child’s daily life. What do they do if children develop papillomas?
- Do not panic. In the vast majority of cases, warts and other growths go away on their own within 2–3 years. The human papillomavirus is not only easily transmitted, but also quickly “leaves” the child’s body without any consequences or external help.
- Do not try to remove the growths at home, do not tear off or cut off under any circumstances. This is fraught with infection and the extensive appearance of new rashes.
- Contact a dermatologist if any suspicious elements appear on your child’s skin. During the consultation, the doctor will examine and give recommendations, and, if necessary, prescribe removal.
Medical care for manifestations of HPV is limited to the removal of formations that affect the quality of life or are located in places where they are often injured and cause discomfort (on the eyelid, in the genital area, in the larynx).
An extraordinary inspection is needed if:
- the color of the papilloma changes;
- the wart begins to grow or change shape;
- blood or other fluid is released from the formation;
- papilloma is subject to constant friction due to clothing;
- the rashes are on the face or mucous membranes.
It is advisable not to delay a visit to a dermatologist if the formation itches, hurts, causes other physical discomfort, or has been injured. In other cases, it is recommended to observe the “behavior” of the papilloma virus and control the elements on the child’s body.
Options for removing papillomas
There are 5 modern and proven methods, each of which has its own limitations, features and advantages.
- Electrocoagulation. The method is based on the influence of high-frequency electric current. It literally “burns out” the neoplasm, leaving in its place only a dry crust, which eventually falls off on its own.
- Radio wave surgery. This method allows you to remove warts and other elements without contact with the skin, which eliminates the risk of thermal damage to tissue.
- Laser therapy. It involves treating the affected area with light waves of a certain length.
- Cryodestruction. It involves “freezing” new growths with liquid nitrogen.
- Surgical excision. It is performed under local anesthesia using a scalpel.
It is strictly not recommended in childhood to resort to traditional methods of removing warts and to use medications from the pharmacy on your own without the supervision of a doctor. After removal of papillomas, children should not:
- tear off the crust;
- sunbathe;
- visit the baths;
- cover the treatment area with a plaster;
- scratch and rub the removal site.
You should not use creams and ointments without a dermatologist's prescription. In the first 1–4 days, it is advisable to refrain from walking in direct sunlight, swimming in public bodies of water and activities that can injure the treated area of skin.
Treatment methods for papillomas on the lip mucosa
Treatment of this pathology is prescribed individually. The best results are observed with combination therapy of papilloma on the lip mucosa. Drug treatment and physical destruction of the tumor are used. Sometimes traditional medicine methods can be used additionally. However, the latter cannot be the main treatment.
Medicines for papillomas on the lips inside the mouth
In the photo there are preparations for papillomas on the inside of the lip
Papillomas on the inside of the lip are essentially just a symptom of a viral infection that has affected the body. In addition, these tumors often recur, so for maximum treatment effectiveness, care should be taken to strengthen the body and strengthen its protective functions. For this purpose, antiviral and immunomodulatory therapy is used.
Let's consider the most popular drugs that are used in the treatment of papillomas on the inner lips:
- Antiviral agents . Good results are demonstrated by the following drugs: Isoprinosin (from 600 rubles), Panavir (about 1500-2000 rubles), as well as their analogues Groprinosin (from 600 rubles), Allokin-Alpha (from 3400 rubles). These medications help suppress the papillomavirus and reduce the viral load in the body.
- Immunomodulators . Strengthen the body's protective functions and help the immune system fight the pathogen. When treating human papillomavirus infection, the following drugs can be prescribed: Amiksin (about 650 rubles), Likopid (from 300 rubles) and their analogue Derinat (from 350 rubles).
Also, as part of general restorative drug therapy, multivitamin complexes and various dietary supplements can be prescribed.
In addition, before treating papillomas on the inside of the lip, you should review your diet and give preference to healthy and vitamin-rich foods so that the immune system works smoothly.
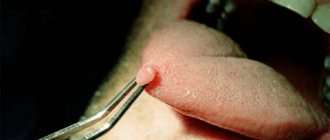
Methods for removing papillomas on the inner lips
Modern methods of destruction of tumors on the lips and mucous membranes are low-traumatic and quite effective. Currently, the following methods are used to remove papillomas on the lips of the mouth:
- Laser coagulation . A semiconductor laser is used, which evaporates unhealthy cells and, at the same time, cauterizes the capillaries to avoid blood loss and the spread of the viral agent. The removal procedure lasts several minutes under local anesthesia. After a few days, the crust disappears and no trace remains of the papilloma. The cost of laser removal of papilloma from the lip mucosa is 1550-2600 rubles in Russia and 370-700 hryvnia in Ukraine.
- Cryoremoval . This procedure uses liquid nitrogen, which is applied using applications or a special device to the pathologically altered area of the mucosa. The substance acts quickly and effectively, but the problem is that even a specialist can find it difficult to track the depth of penetration of liquid nitrogen into tissues. Therefore, burns are possible or there is a need for a repeat procedure. The price of cryoremoval of papilloma on the inner lips is 650-1650 rubles in Russia and 270-470 hryvnia in Ukraine.
- Electrocoagulation . A heating element is used that produces an electric current. Removal of the growth is carried out under local anesthesia, as this is a rather painful process. Suitable for eliminating neoplasms on a flat base or small papillomas on the inside of the lip. The cost of electrocoagulation is 1250-2500 rubles in Russia and 350-650 hryvnia in Ukraine.
- Radiosurgery . In this case, special radioknives or loops are used, which act pointwise, directly at the place where the growth attaches to the mucosa. A very precise and minimally invasive method of removal, rarely leads to recurrence and complications. Its cost is the highest. The price for radioremoval of papillomas on the lips of the mouth is 2500-3450 rubles in Russia and 650-1300 hryvnia in Ukraine.
In addition, various cauterizing chemicals , for example, acids, alkalis. However, these drugs should also be used only under the supervision of a physician, since the risk of burns and tissue necrosis is high.
- See also removal of papillomas by radio wave method or laser - which is better
HPV prevention
The most effective method of preventing infections and complications caused by the human papillomavirus is vaccination. It is carried out before the onset of full puberty and before the start of sexual relations. The optimal age is from 9 to 11 years.
Other preventive measures are:
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- balanced healthy diet;
- timely treatment of abrasions, scratches and other skin damage;
- informing children and adolescents about the dangers of smoking, since tobacco use increases the risk of oncogenic mutations of the virus;
- regular preventive examinations.
It is very important to monitor the child’s health and support immunity in accessible ways. Active physical activity, hardening, and outdoor games are encouraged, allowing the formation of an adequate immune response to environmental factors. It is advisable to abandon home self-medication and uncontrolled use of medications, since incorrect actions can reduce the natural defenses of the child’s body and lead to the activation of HPV.