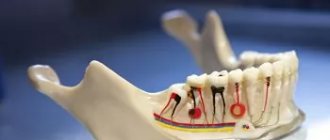
Dental modeling is a set of manipulations to prepare for the installation of orthopedic structures. Used to visually demonstrate the potential appearance of an artificial smile model and check the comfort of wearing a denture. At this stage, the doctor reproduces with wax the external aesthetic shape of the complete dentition and individual units.
The second name for modeling is the Wax-up technique. It is carried out during dentures and implantation by taking a personal impression of the oral cavity.
The wax sample is used as a base for the production of a permanent orthopedic product. To obtain an ideal impression, carious and destroyed units are reconstructed with liquid wax. The technician begins further manipulations after the composition has completely hardened. The specialist determines the accuracy of the connection between the created model and the tooth and determines the correct distribution of the chewing load.
There should be no pain during fitting. After receiving data on the anatomical structure of the visitor’s dental system, the physician determines the tactics of further treatment and begins restoration.
Features of the procedure
Wax-up for aesthetic restoration is popular among orthopedists. Wax is a malleable compound that can be molded. With its help, an accurate impression of the tooth is created, taking into account the anatomical features.
The accuracy of manipulation affects the comfort of the artificial prosthesis. Following the technology will relieve the patient from pain when talking and eating.
The Wax-up technique is safe and does not cause discomfort. This is due to the absence of violation of the integrity of the oral mucosa. There is a risk of cross-reaction in those who suffer from allergic reactions to bee products. In this case, replace the composition.
Classic modeling of crowns and bridges for metal-ceramics of the frontal and chewing group
A huge amount of materials is used in the professional work of a dental technician. The final result of its work depends on their quality and performance characteristics. Dental waxes are also important materials.
The main requirements for waxes are:
- Low shrinkage
- Good ductility
- No delamination during application and processing
- Sufficient hardness to ensure stability of the wax structure
- Ashless
For the last two decades, in my work I have been using waxes from a German manufacturer, so I will compare Denest wax with them.
We will test using the example of modeling anterior and chewing teeth for metal-ceramics. The design also provides for one-piece crowns. Collapsible models were prepared and plaster dies were made. Heat up the dipping wax in the wax furnace. We will not dwell on operating temperatures, since both wax melters and electric spatulas work differently for everyone - depending on the attachment used, the quality and age of the device. In general, it’s not difficult to adjust intuitively.
Dipping wax is yellow in color and quite transparent. The thickness of the initial structure is well controlled. When adjusted with a modeling tool, it does not crack and scrapes well. When cooled, it is quite hard and durable.
Green modeling wax
Easy to apply. At the correct temperature, the spatula has predictable fluidity; chips are easily blown off the model and do not stick to it. A little softer than the German wax I use, but I liked this one better. It polishes better with a brush. Let's evaluate this when modeling solid crowns. Also perfect for modeling intermediate parts of bridges.
Red cervical wax
It also has good fluidity and is easily applied to the cervical part of the stump. Combines well with dipping and modeling wax.
When adjusting with a modeling tool, I noticed that it was a little softer than the German one I was used to. This is not a negative, just an observation. It is better to polish with a brush. A little work was left for a day before casting the frame.
No visible shrinkage processes were detected. At one time, I had an incident with cervical wax from a respected well-known German manufacturer: the shrinkage of the cervical wax in a few hours reached almost half a millimeter, as a result of which the work did not have time to reach the foundry laboratory. Perhaps it was a defective batch.
The modeled crowns are removed from the dies easily, without any cracks or deformations. The junctions of different waxes are monolithic, without delamination.
Bonding blue wax
It is easy to apply, has the necessary fluidity, forms well, and ensures the stability of the connecting elements. Very similar to the bonding wax of the German manufacturer, only a little more transparent.
conclusions
Having worked with Denest waxes, I concluded that these waxes are of high quality and in no way inferior to their foreign analogues.
- Nice, contrasting colors where required
- Necessary transparency
- Good, predictable fluidity at correctly selected instrument temperatures
Waxes are flexible, easy to process and polish. When heated, they hold their shape.
I would like to pay special attention to the packaging in a sealed tin jar with a convenient lid. It’s more convenient than its foreign counterparts, which made their packaging out of plastic (the lids break, are accidentally burned with a spatula, and so on) or the wax itself is made in the shape of a tooth, and it’s so beautifully modeled that it’s a pity to immerse a hot spatula in such beauty.
To summarize, I will say that with a clear conscience I can recommend Denest wax as a high-quality material that is not inferior to foreign analogues. At least the waxes that I have tried from their wide range have excellent characteristics. I think the others are not inferior in quality and ease of use.
Author: Dental technician (Municipal clinic, Novosibirsk, highest category, work experience - 28 years).
Purpose of application
The need for Wax-up is due to the following factors:
- Reproduction of dental units from wax is the starting stage of restoration work. It is required for planning future work of dentists. Wax impressions help to track the individual characteristics of the structure of teeth and avoid errors during implantation.
- Calculation of the cost of upcoming dental procedures.
- Temporary prosthetics. The specialist takes samples for the production of intermediate prosthetic restorations made of plastic. The technology is used when additional time is needed to create fixed prostheses.
Indications and contraindications
The orthodontist prescribes dental diagnostics after a clinical examination if there are indications:
- Abrasion of units due to malocclusion and other pathologies.
- Destruction of the supragingival area due to advanced forms of caries.
- Distinctive color.
- All that remains of the units is the root base.
- Edentia.
- Multiple pathologies.
Contraindications:
- dental pathologies in acute form;
- recovery after radiation therapy;
- drug addiction;
- diseases of the jaw tissue;
- inflammation of various etiologies.
Modeling methods
Dentists use two methods of diagnostic modeling.
- Indirect
This technique is based on modeling a plaster model. Does not require prolonged presence of the visitor in the clinic. The orthodontist takes an impression of the oral cavity and passes it on to the technician to form the structure in the laboratory.
Precise finishing of the sample edges is carried out for user comfort. This method is chosen by the dentist to work with teeth located in hard-to-reach places.
- Straight
It is a combination of two technologies - Wax-up and Mock-up. Modeling is carried out directly in the patient’s mouth. Suitable for working on single structures.
The specialist fills the tooth cavity with liquid wax or a plastic mass. Reproduction and pinning are then performed, after which the resulting model is retrieved. Based on the resulting layout, a composite sample is created.
A person walks with the installed temporary system for a short time to evaluate its convenience and correct manufacture. The method is suitable for people who want to improve their bite or suffer from increased enamel wear.
Material characteristics
When carrying out the procedure, two types of beeswax are used:
- 1 type Found application in direct modeling.
- Type 2 Used with indirect technology. The wax is of lower quality, but the result of the work is at a decent level.
Recommendations must be followed when selecting, storing and using the material:
- the use of colored waxes allows you to achieve clear contrast;
- the frozen forming composition is rigid and does not crumble;
- absence of crumbs and impurities in the heated mass;
- absence of chips and cracks when scraping;
- compliance with storage periods;
- competent selection of the type of material depending on the technique;
- selection of soft types of material.
Preparatory stage
Before starting to reproduce the dentition, the following recommendations are followed:
- inspection is carried out;
- CT and X-ray diagnostics of the jaw are performed;
- treatment of dental diseases;
- compliance with hygiene rules, sanitation of the oral cavity.
The manipulation is carried out after a full examination and dental therapy.
Step-by-step algorithm
Stages of the procedure:
- taking a plaster (silicone) impression of the patient’s jaw at the site of future placement and on the opposite side;
- preventing jaw closure using silicone bite pads;
- determining the relationship between the upper jaw and the skull using a facebow;
- transferring samples onto a gypsum base;
- fixing the model on the articulator;
- modeling a wax cast on plaster models;
- Demonstration of the layout to the client.
The Mock-up technique involves transferring the mock-up to the mouth. Algorithm of the doctor’s actions:
- obtaining silicone keys;
- gentle removal of deposits;
- fixing the layout with special glue;
- placing composite or polyurethane into impressions, fixation;
- impression taking, grinding and polishing;
- assessment of work quality.
The duration of making a model depends on the specific structure and development of the jaw and location.
Pros and cons
Making wax models is a painstaking and technologically complex process. The popularity of the procedure among dental technicians and orthodontists is due to its advantages:
- adjustment of nuances;
- no need to get used to wearing permanent orthopedic structures;
- absence of discomfort, pain;
- gentle preparation process;
- patient participation in the process of adjusting the model using the indirect method.
The disadvantages include reduced accuracy with the indirect method. The volume of the material changes as it hardens.
Short or overactive upper lip
If a patient with excessive visualization of the maxillary gums has a short upper lip (compared to the norm) (Fig. 4 and 5), then this is most likely the cause of aesthetic imbalances. If the length of the facial contour, gums, lips and central incisors is normal, then in a patient with excessive visualization of gingival tissue, the likely cause of this condition will be an overactive upper lip. In young women, with a calm state of the facial muscles, 3-4 mm of the central incisors of the upper jaw are usually visualized, and with a wide smile, the crown of the teeth 10-11 mm long is completely visible. Accordingly, the upper lip should usually rise 6-8 mm during the transition from a relaxed state of the facial muscles to a wide smile. However, in a patient with a hyperactive upper lip, these parameters may be 1.5-2 times higher. At the moment, there are no methods for dental correction of a short or overactive upper lip, however, plastic surgery is possible. However, it is important to make this diagnosis when planning restorative treatment of anterior teeth. The patient should be informed that treatment may not only fail to correct, but may even worsen excessive gingival visualization.