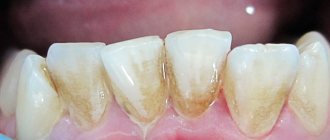
To answer the question: why there is a yellow palate in the mouth (see photo), you should study the subject of attention in more detail.
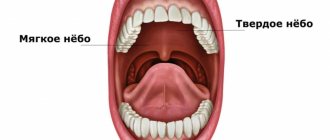
When examining the mouth, in addition to the tongue, gums with teeth and the inner surfaces of the cheeks, a concave dome-shaped surface is also visible, limiting the oral cavity from above.
This palate is a mucous membrane-covered bony structure formed by the palatine processes of the two halves of the upper jaw.
The main purpose of the palate is to be a partition separating the oral cavity from the nasal cavity.
The palate performs the following functions:
- prevents saliva and food from entering the area responsible for breathing and smell recognition;
- ensures unhindered movement of inhaled and exhaled air;
- is responsible for the separate participation of the oral and nasal cavities in the function of sound formation.
In addition to the fixed bone (hard) part of the palate, there is also a soft part. This is a duplication of the mucous membrane (a fold that looks like tissue folded in half), moved up and down by a special muscle: when it contracts, the soft palate rises, and when it relaxes, it lowers.
In a calm state, the soft palate hangs down, allowing free passage of the air stream. But when swallowing, straining and blocking access from behind, from the nasopharynx, it absolutely hermetically separates the two largest cranial cavities from each other, preventing food from entering the nasal space.
Why did the sky turn yellow?
The palate area, like all areas of the skin and mucous membranes on and inside the head, has an abundant blood supply due to a dense network of capillaries.
The palate owes its normal color to the color of the blood flowing through them: in hard ones it is pale pink, in soft ones it is also pink, but of a more saturated dark tone. When inflamed, the color may become flaming crimson or bluish with a purplish tint. If the palate turns red and the throat hurts, this is considered normal, but the palate should not be yellow. For what reason does its color change?
The first thing that comes to mind is smoking. Indeed, the resins contained in tobacco and released when it burns stain the oral mucosa, giving it various shades of yellow and cause the formation of plaque on the palate.
But in addition to direct coloring, smoking:
- causes disorders of blood microcirculation in tissues;
- changes the composition and properties of blood.
Blood cells that contain minimal oxygen become paler, as does the area they supply. At the same time, in the region poorly supplied by them, fatigue and aging of cells increase due to chronic oxygen starvation.
And finally, once the transformations begin, they become irreversible, leading to changes in the biochemistry of tissues and the loss of their original color.
Therefore, the palate in a smoker’s mouth becomes covered with yellow spots with red dots and veins - a picture of capillary paresis.
Causes
The palate area, like other areas of the skin and mucous membranes, is characterized by a strong blood supply, which is due to the presence of a dense network of capillaries.
The normal color formed on the surface indicates the absence of an inflammatory process in the body and other serious disorders. A change in the color of the palate is a manifestation of the symptoms of the disease, which is determined after the study.
The reasons that provoke the formation of yellowness can be found in the table:
| Reasons for the formation of yellow plaque on the palate | ||
| Reason name | Description | Additional symptoms |
| Liver diseases | The most common liver diseases, recognized by the yellowness of the palate, are: jaundice, cirrhosis, cholecystitis, cholelithiasis and syphilis. When an organ is damaged, disruptions in the functioning of all systems and metabolic processes occur: protein, carbohydrate, fat, pigment, etc. Depending on the disease, the corners of the palate and the boundaries between soft and hard tissue (with cholecystitis, bile stones) or the entire surface of the mucous membrane turn yellow. (for hepatitis). |
|
| Pancreas problems | The organ regulates energy exchange and biochemical processes occurring in the human body. If there are problems with the pancreas, one of the main signs appears - the soft palate acquires a bronze tone. If malfunctions occur in the biliary system, the color is combined with pronounced jaundice. |
|
| Intestinal inflammation (large/small) | Yellowness on the upper palate with intestinal dysfunction appears due to the morphofunctional unity of the oral mucosa and the gastrointestinal tract. The color of the palate changes to yellowish both in individual zones and over its entire surface. The neglect of the disease is reflected in the intensity and structure of plaque. |
|
| Kidney failure | The main provocateurs of renal failure: urolithiasis, diabetes mellitus, pyelonephritis, neoplasms, lipid metabolism disorders. As a result of a failure of metabolic and biochemical processes, yellowness appears on the hard palate. Additional symptoms help determine whether the kidneys are involved in the problem. |
|
| Cholesterol and fat metabolism disorders | Cholesterol metabolism disorders are accompanied by a change in the color of the soft palate from pink to yellow. At the same time, gray lumpy spots are clearly visible on the surface of the mucosa. Failures in fat metabolism are recognized by a pale icteric coating on the palate. The main provocateurs of metabolic disorders are: tuberculosis, diabetes, oncology. |
|
| Smoking | The color of the palate changes under the influence of resins, which are included in tobacco in high concentrations. A bad habit provokes disruption of blood circulation and biochemical processes in tissues associated with disruption of metabolic and other processes. The mucous membrane loses its pink color and becomes yellow. |
|
Diagram of the oral cavity
What diseases can there be?
In addition to smoking, the following diseases can cause a yellow palate in the mouth:
- liver;
- kidney;
- gastrointestinal organs.
Or lipid metabolism disorders lead to the same result.
Liver diseases
Disorders of intrahepatic metabolism lead to profound disorders in the biochemistry of all organs and systems of the body and disorders of all types of metabolism:
- protein;
- fat (lipid);
- carbohydrate;
- microelement;
- pigmented.
There is a disruption in the formation of vitamins and hormones, blood parameters change (viscosity, etc.), which leads to tissue hypoxia, which is fraught with biochemical changes on a local scale. In relation to the upper soft and hard palate, this can be either pallor and loosening of the mucous membrane, or a change in its color to yellow.
In case of liver diseases, the appearance of the palate will be particularly diverse, namely:
- yellowish corners of the anterior part of the soft palate with lines in the middle are characteristic of chronic cholecystitis and gallstones;
- Liver cirrhosis is characterized by the appearance of yellow spots in areas of dying tissue;
- viral hepatitis in the icteric phase also leads to staining of the palate.
Kidney diseases
Kidney diseases threaten the body not only with edema and dangerous blood thinning due to impaired water excretion, but also with the accumulation of many toxic substances in the blood: uric acid, creatinine, heavy metal salts and others, which also affect the biochemistry and color of tissues.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
A change in the properties of the digestive juice, bile, which has a pronounced yellow color, during inflammation, which occurs in parallel in the liver and pancreas, leads to the deposition of bile salts in the tissues of the skin and mucous membranes. The skin responds to this process not only with itching, but also with a change in color. The same is observed in the mucous membranes lining various cavities.
With pathology characteristic of the liver-pancreas system, a bronze-icteric color appears exclusively on the soft palate.
The palate may turn yellow due to chronic inflammation in the small and large intestines with frequent constipation.
Blood diseases rarely have an independent character; most often they are a reaction to metabolic disorders in the liver or other organ systems. But its properties determine not only the level of tissue chemistry, but also their color.
It is for this reason that the skin of patients not only due to liver diseases (malaria, hepatitis), but also due to anemia-anemia, looks icteric, as well as the mucous membranes. In addition, the phenomenon of hemolysis is inherent in blood, and the transition of the initial “bruises” to yellow is a common thing for hemoglobin.
A yellow color to the body can also be given by “bronze disease” - a pathology of the adrenal glands, also called Addison’s disease.
Why is there a problem?
The causes of yellowing of the palate in the mouth in patients over 50 years of age are directly or indirectly related to liver failure. In representatives of other age groups, this phenomenon is explained by other factors:
- acute, chronic liver diseases of any nature;
- catarrhal jaundice;
- cholecystitis, cholelithiasis (inflammatory processes or the presence of stones in the gall bladder);
- syphilis;
- pancreatitis and other disorders of the pancreas;
- inflammation of the large and small intestines;
- chronic renal failure;
- violation of cholesterol or fat metabolism in the body.
No Ads
Important! Exacerbation of any diseases of the gastrointestinal tract in most cases leads to a change in the color of the palatal mucosa (due to blood flow to the capillaries of the oral cavity).
Oral candidiasis is a known “provocateur” of discoloration of the palatal mucosa
The yellowed soft palate is a “faithful companion” of smokers (the impact of nicotine affects). In some cases, dental diseases become the “culprits” of the problem - in particular, fungal infection of the mucous membrane (candidiasis), gingivitis, periodontitis and other infectious and inflammatory processes.
Associated symptoms
In addition to staining the palate yellow, the diseases that cause it also have other characteristic accompanying symptoms. So, this is when:
- kidney pathologies - swelling and urinary disorders;
- blood diseases - symptoms of insufficient blood supply to organs (up to the development of trophic disorders or enlarged lymph nodes);
- changes in the liver - digestive disorders and all types of metabolism.
But if, with diseases of the digestive system, metabolism also suffers and body weight changes, then Addison's disease is characterized by crises. Caused by acute adrenal and vascular insufficiency, they are expressed:
- sudden sharp pain in the lower back, legs, abdomen;
- a sharp decrease in the ability to move (adynamia);
- severe (hectic) fever;
- intense diarrhea and vomiting, quickly leading to dehydration and shock;
- sharply developing arterial hypotension (drop in blood pressure);
- loss of consciousness occurring after a previous short acute psychosis with confusion or delirium;
- violation of water-salt metabolism due to low levels of adrenal hormones in the blood, detected by laboratory tests.
Considering the formation (due to hemolysis) of brown plaque on the teeth and tongue, there is a very high probability that the first doctor a patient with “bronze disease” will visit will be a dentist.
Liver pathologies
When it comes to changing the appearance of the mucous membranes, first of all, suspicion falls on a disruption in the functioning of this particular vital organ. The liver performs many functions, including the regulation of fat and carbohydrate metabolism and the digestion process. It removes harmful substances from the body and takes a hit when affected by various viruses.
Common liver problems that affect the color of the sky include:
Jaundice
Jaundice, in which the concentration of the hormone bilirubin in the blood of an adult or child is exceeded. The mucous membranes become yellow. This phenomenon is considered a sign of damage by hepatitis viruses, liver cirrhosis, and obstruction of the biliary tract. The patient also complains of nausea, vomiting, belching and problems with bowel movements.
Treatment is prescribed after diagnostic measures have been carried out and the virus that has caused the change in pigmentation has been identified.
Syphilis
Syphilis is in the second stage, lasting from 2 to 5 years, which is characterized by a wave-like course, when symptoms appear and disappear from time to time. The main signs of this pathology with liver damage are the appearance of yellow spots in the mouth. The patient feels weakness and aching muscles, like during a cold. Hair begins to actively fall out.
A patient with syphilis can avoid unpleasant symptoms and further damage to all vital organs if treatment is started in a timely manner. The venereologist selects therapy for the patient depending on individual characteristics.
Most often, penicillin or antibiotics with a different composition are used if there is intolerance to the first component. Additionally, measures are taken to strengthen the immune system.
The degree of recovery is determined by laboratory tests. The patient and those in close contact with him are treated until blood tests show the complete absence of spirochema pallidum in the body.
Cholelithiasis
Cholelithiasis or cholelithiasis, leading to a yellow tint to the palate. Its cause is considered to be the filling of the gallbladder with stones formed as a result of the accumulation of cholesterol, salts and other elements. Cholelithiasis is accompanied by disruption of the normal circulation of bile and its stagnation.
To eliminate this problem, various methods of breaking stones are used. In advanced cases, it is necessary to remove the gallbladder through surgery.
Cholecystitis
Cholecystitis or chronic inflammation of the gallbladder, accompanied by pronounced yellowness at the junction of the hard palate and the soft palate. Additional symptoms include a bitter taste in the mouth, nausea, vomiting and pain in the right hypochondrium. The gastroenterologist prescribes therapy to the patient who has been diagnosed with antibiotics, drugs to normalize digestion and detoxification.
Problems with the liver and gall bladder are quite serious pathologies that require mandatory monitoring by an appropriate specialist. The longer the patient ignores the alarming symptoms and treats himself, the more difficult it is to get rid of the consequences of the disease.
Diagnostic methods
You should begin studying the problem with a visit to the dental office, because only a dentist is able to conduct the most complete and competent examination of the oral cavity.
When treating a patient, the dentist will pay attention not only to the palate - he will examine and examine the entire oral cavity, including the spaces between the cheeks, gums, and lips and the area under the tongue.
Because it is in these hidden places that something that does not catch the eye at a quick glance can be discovered, for example, the first signs of thrush-candidiasis.
Considering that pigmentation of the palate is rarely an independent condition, in addition to a dental examination, the help of other medical specialists may be required to diagnose the problem:
- therapist;
- ENT doctor;
- oncologist;
- allergist.
A mandatory part of diagnosis is laboratory studies of the internal environment of the body in the form of biological fluids: blood, urine, bile, and feces.
It may be necessary to perform allergy tests and study the body’s immune system using instrumental (ultrasound, MRI, CT, radiography) and laboratory methods.
Treatment methods
The data obtained after completing all the necessary studies provides an answer to the question: what is the patient dealing with?
If a therapeutic pathology is detected (diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, etc.), treatment is carried out by a general practitioner or a specialist with a narrower profile:
- gastroenterologist;
- urologist:
- nephrologist.
In the case where there is a systemic disease of the category rheumatism, syphilis, HIV, treatment is necessary in a specialized medical institution.
The presence of oncological pathology may require joint treatment by an oncologist, a surgeon and consultant doctors of various profiles: a neurologist, an ophthalmologist and others.
If there is a local microbial-viral nature of the lesion in the oral cavity, antiseptics and antibiotics recommended by the dentist can be used.
After the process subsides or during it, professional cleaning of the oral cavity is often required, without which one cannot count on the success of treatment. It may be necessary to repair or replace existing orthodontic structures in the mouth.
Personal hygiene should be ensured by the patient himself, who is interested in resolving the problem as quickly as possible.
Treatment with traditional methods
The general principles of treatment with traditional methods do not differ from those in medicine and dentistry:
- the use of antiseptics (teas, infusions) for oral hygiene;
- increasing the level of health with the help of traditional, proven means (honey and bee products and the like).
The use of traditional medicine methods should in no way contradict the requirements of official science; proposals to use unstudied or questionable treatment methods should be categorically rejected.
The use of any form of rinse or other treatment method must be approved by the patient's attending physician.
Yellow palate in the mouth of an adult
In people over 50 years of age, the appearance of a yellow coating on the palate is considered a physiological process
If the sky has turned yellow, you should see a dentist. During the examination, the specialist will determine whether the yellowness of the mucous membrane is a sign of any disease, or indicates a lack of proper oral hygiene.
The patient’s attitude towards bad habits is also taken into account. Yellowness with a pronounced network of veins is often formed as a result of regular smoking.
When conducting diagnostics, the patient's age is taken into account. In people over 50 years of age, the appearance of yellow plaque on the palate is considered a physiological process, so serious health problems are not always detected.
The child has
A yellowed sky appears not only in adults, but also in children. In addition to dental problems, this sign may indicate other diseases, so the child should be shown to a gastroenterologist, ENT specialist, pediatrician, infectious disease specialist, or hepatologist.
Often, young patients with this symptom are diagnosed with thrush. If there is any doubt in determining the problem, it is recommended to undergo a full examination, including donating blood to check bilirubin levels.
Prevention measures
Preventive measures include the following:
- careful and attentive care of teeth and oral cavity in general;
- visiting the dentist in a timely manner and following his recommendations, and if problems arise, providing professional assistance;
- preventing possible diseases by fully increasing the body’s defenses (maintaining a consciously healthy lifestyle), and in the event of an acute pathology, its timely treatment.
As a conclusion from what has been said: a person needs to be constantly engaged in maintaining health, but if problems arise, be sure to consult a specialist doctor.
Folk remedies
The symptom itself in the form of yellowing of the palate, tongue or mucous membrane cannot be eliminated only by improvised methods. You should definitely consult a doctor and make a diagnosis, determine what exactly caused the pathology. Self-medication in this case can be very dangerous.
But after undergoing diagnostics and choosing an effective method of therapy, you can further eliminate certain unpleasant symptoms in the oral cavity and speed up healing. For this we recommend:
- Prepare antiseptic infusions or decoctions from medicinal herbs (chamomile, sage, calendula, oak bark). After making a light solution and cooling it to a warm state, you can rinse the mouth. They are good at eliminating various pathogenic microorganisms from the surface, thereby accelerating healing.
- Beekeeping products also help a lot - honey, propolis, etc. By consuming them in small quantities, you can relieve the inflammatory process, heal wounds, ulcers, normalize blood supply, etc.
In order not to harm yourself, it is better to first consult with your doctor what folk remedies are allowed to be used in your case.
Video: three warning signs in the mouth.