Candidal stomatitis (or oral thrush , or fungal stomatitis ) is a fungal infection of the oral mucosa and in some cases can even affect muscle tissue. The patient not only sees a white coating in the mouth of various structures, but also experiences unpleasant and sometimes painful sensations throughout the entire oral cavity. The disease can appear at any age, but most often in early childhood (20% of children under one year old) or in older people (10% after 60 years). If thrush is left untreated, the fungal infection can spread to the surface of the throat and esophagus.
Causes of candidal stomatitis
The most common cause of candidiasis stomatitis is a fungus of the Candida albicans group. It is worth noting that these fungi are always present on the mucous membranes of the mouth, and do not cause any harm to the body until they begin to multiply.
The causes of the development of candidal stomatitis are the following factors and diseases:
- Weak immunity;
- People with Sjögren's syndrome;
- Neglect of general rules of oral hygiene;
- Constant stress;
- Various diseases of the oral cavity;
- Taking antibiotics or corticosteroids;
- Having a disease such as diabetes. This is all due to the fact that the blood contains a large amount of sugar, and this serves as an excellent environment for the development of fungus of the genus Candida.
It is also worth noting that adults who suffer from excessive dry mouth can get candidal stomatitis. The most common cause of such dryness is the abuse of dental elixirs.
Another factor that can cause the development of candidal stomatitis is pregnancy. After all, it’s no secret that it is during this period that significant hormonal changes occur in a woman’s body, which, in turn, greatly affect the bacterial balance in the mouth.
Predisposing factors and risk groups
It is known that 50% of people are carriers of fungal microflora, and under normal conditions it can be in a kind of “dormant” or suppressed state in the form of chlamydospores, resistant to the external environment. This is why fungal microflora can be transmitted from person to person (i.e., it is contagious). However, under certain conditions, the fungus can begin to multiply rapidly, form colonies and lead to thrush in the mouth (candidal stomatitis). Moreover, under certain conditions, this disease can recur in both children and adults (chronic candidal stomatitis). There are many factors that predispose to this disease and form risk groups for candidal stomatitis in adults and children.
General decrease in immune defense. Can be caused by pregnancy, general diseases (diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, diabetes mellitus, tuberculosis, immunodeficiency states), long-term use of medications (especially antibiotics, corticosteroids, cytostics), dysbacteriosis, avitaminosis (lack of vitamins B, C, PP) , bad habits (alcohol, smoking).
Infants and elderly people. Children, up to about the seventh month of life, and the elderly, due to imperfect or reduced immune defense, are especially susceptible to this disease. Moreover, when diagnosed with chronic candidal stomatitis, a thorough immunological examination is necessary.
Local factors. For example, injuries to the oral mucosa (due to malocclusion of the dentition, chipped tooth enamel). Another common case is removable dentures, which, with insufficient hygiene, contribute to the proliferation of fungal microflora or injure the mucous membrane. Local factors include allergic reactions to dental materials, when allergic stomatitis initiates the appearance of fungal stomatitis.
Symptoms
A number of symptoms are characteristic of candidal stomatitis:
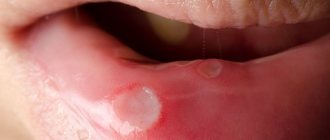
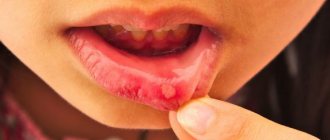
- The appearance of a white or yellowish coating on the tongue, cheeks or palate. When trying to eliminate it, bleeding wounds may appear on the mucous membrane.
- Constant metallic taste.
- Feeling of heartburn on the tongue.
- Painful sensations from touching plaque.
- Later, as plaque spreads, difficulty swallowing occurs.
- Deterioration of tongue sensitivity and poor taste perception.
How to treat herpetic stomatitis?
Herpetic stomatitis
The form develops against the background of cold complications, gingivitis and other inflammatory processes in the body. The symptom is the appearance of multiple small rashes on the tongue, gums and inner surface of the cheeks. The pain, as a rule, is much stronger than from aphthous ulcers, but it is not the discomfort itself that is scary, but the consequences - fever and weakness.
Herpes lesions are primarily treated with a course of medications:
- Acyclovir - from 1 to 3 tablets per day.
- Viferon-gel - topically, twice a day, and only after the approval of the attending physician.
- Solcoseryl - temporary pain relief, 15 minutes before and immediately after meals.
- Rinsing with soda creates an additional alkaline environment in the mouth against bacteria.
Forms of the disease
Candidal stomatitis is a fairly common disease that manifests itself in various forms. The symptoms can determine how much it is progressing. Treatment depends on the severity of the disease.
In the earliest stages, a mild form of the disease appears. It is characterized by the formation of single small white spots on the tongue or cheeks.
In the next middle stage, ulcers may form, and white spots themselves cover most of the tongue and mouth.
And at the most severe stages, plaque cannot be removed - it completely covers the entire oral cavity and forms a white film. Also, candidal stomatitis is classified separately depending on the location:
- Candidal stomatitis of the corners of the mouth. Very small cracks appear at the corners of the mouth, which cause pain. This is especially evident when opening the mouth.
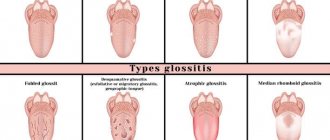
- Yeast glossitis usually occurs on the surface of the tongue. It is characterized by a white coating and even swelling of the tongue.
- Thrush - the so-called yeast stomatitis - is a disease in which plaque forms on the cheeks and gums. The mucous membrane itself becomes reddened.
Types and forms of pathology
In practice, acute and chronic oral candidiasis occurs. The first develops rapidly, the second is characterized by a sluggish course and vague symptoms, periodic relapses and inflammation.
Acute fungal candidal stomatitis can be pseudomembranous (white plaque is easily removed and reveals reddened areas) and atrophic (there is no plaque, the mucosal surface dries, turns red and becomes painful).
Chronic thrush can be hyperplastic (white or grayish cheesy plaques form on the soft tissues) and atrophic (the oral mucosa dries out, becomes thinner, the patient complains of pain and discomfort).
Treatment
First of all, when treating candidal stomatitis, you need to determine and eliminate the cause, adhere to the principles of proper nutrition and strengthen the body's immune system. And, of course, it is necessary to monitor oral hygiene. In most cases, this is quite enough for recovery.
If the disease is in a moderate or severe stage, the doctor often prescribes special medications for oral administration and antifungal ointments. Taking medications continues until the symptoms in the oral cavity are completely eliminated, in order to exclude possible relapses.
Treatment of mild forms of candidal stomatitis is carried out at home and does not require special conditions. Antifungal elixirs and lozenges are used. On average, the treatment course takes no more than two weeks.
More severe forms are characterized by the fact that the infection enters the digestive tract. Antifungal drugs are used to combat the disease. The course of treatment lasts from 2 to 4 weeks.
Recurrent forms of candidal stomatitis require much more time and money. Treatment is carried out until all symptoms disappear completely. Various antifungal agents are used.
Treatment of candidal stomatitis must be combined with a special diet. First of all, you should stop eating foods that are rich in starch and various confectionery products, minimize the consumption of cereals, baked goods, potatoes, etc.
When treating candidal stomatitis, other concomitant diseases should be eliminated, in particular:
- Caries;
- Periodontal disease;
- Chronic diseases of internal organs.
Candidal stomatitis in children
Candida albicans is often activated in children's bodies. The risk of disease is highest in infants and children in the first days of life. The ways the fungus enters the baby’s body can be different:
- Through the mother's breast during feeding
- During childbirth when passing through the birth canal
- Through a pacifier, bottle
- Through care items or toys5
The causes of candidal (fungal) stomatitis are also associated with improper or insufficient hygiene, especially in children from three to ten years old. Children attending kindergartens and nurseries are at risk, since the infection can be transmitted to healthy people through joint games, tactile contact or through shared utensils.
Unlike adults, in children the disease is often severe, with high fever and signs of intoxication. Ulcers that appear in the mouth interfere with normal food intake, causing severe discomfort to the child.
Symptoms of candidal (fungal) stomatitis in children:
- Redness of the tongue, gums, inner lips
- The appearance of a cheesy coating in the form of grains - occurs two to three days after redness
- A sharp decrease in appetite, due to the inflamed mucous membrane, the baby cannot normally take the breast and make sucking movements
- Anxiety, refusal to eat
- Fever6
If signs of candidiasis appear, you should immediately see a pediatrician, who will select effective treatment.
Prevention
To ensure that candidal stomatitis never bothers you, you should follow a few simple but very useful rules:
- Follow basic hygiene rules. Namely: wash your hands well with soap, especially when returning from the street, brush your teeth, use dental floss at least once a day, and also rinse your mouth with special means.
- You should definitely buy a new toothbrush. For those who have dentures, it is recommended to place them in a disinfectant solution overnight.
- After consuming liquid antibiotics, you should immediately rinse your mouth with water.
- When using spray corticosteroid drugs, you should wear a special nozzle.
What is oral candidiasis?
Oral candidiasis (also called oral thrush) is an infection of the mouth caused by the yeast-like fungus Candida. These microorganisms are part of a healthy microflora, but under certain circumstances their reproduction disrupts the favorable environment and becomes a source of disease processes. Inflammation and plaque on the tongue, ulcers on the mucous membrane and discomfort in the mouth - this disease is called oral candidiasis.
Infants are most susceptible to this disease, but at this age it is treated faster and is tolerated almost painlessly. Oral thrush is often observed in adults after 50 years of age, when the immune system is already weakened. Oral candidiasis is less common in men than in women. Recently, the percentage of cases has increased significantly, which is associated with uncontrolled use of medications: weakening of cellular immunity increases the risk of oral candidiasis after antibiotics, or rather their improper use. Microbiology, the science of microorganisms, studies the essence of oral candidiasis. And she successfully copes with her task, at the moment this disease has been studied in detail, and doctors know all the methods of treating and preventing infection.
Prevention of oral candidiasis
The occurrence of this disease is a very unpleasant and painful phenomenon, fortunately, it is quite easy to avoid by following the recommendations. One of the main causes of infection is weakened immunity, so the basic rule for preventing the disease is to treat any disease at the right time and take medications strictly as prescribed by the doctor. To avoid candidiasis of the oral cavity, pharynx and larynx, hygiene, visiting a good dentist, professional ultrasonic cleaning and other preventive measures will help. Oral candidiasis in women is often due to hormonal imbalance; if you have symptoms of the disease, you should pay attention not only to the affected area, but also to the condition of the body as a whole.