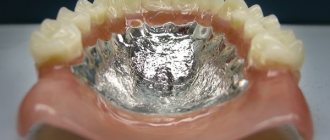
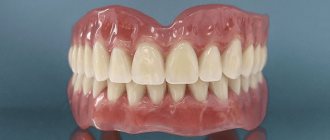
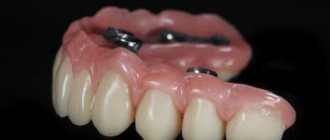
Acrylic removable dentures
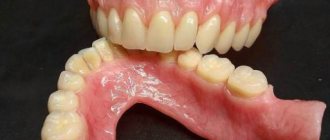
Acrylic dentures have been used in dentistry for a long time; they are light and unnoticeable, but at the same time bulky and rigid, which causes discomfort when using them.
The advantages of such prostheses are their weight and inconspicuousness to others. They are easy to repair or change the design if the gums shrink over time.
The disadvantage of acrylic dentures, in addition to some discomfort in use, is a rather long period of adaptation, during which there is salivation, problems with diction, a change in taste sensitivity, and sometimes allergies. It is not advisable to chew hard food, chewing gum, or sticky sweets with such dentures. A significant disadvantage of acrylic dentures is their base. Acrylic, reacting with saliva, releases toxic substances that can cause poor health.
The price of this type of prosthesis is affordable for almost everyone and is a good replacement for fixed prosthetics if it is impossible for some reason.
Nylon or silicone dentures
This type of prosthesis is similar to acrylic, but made from more modern and safe materials. Nylon is softer and more elastic, the prosthesis looks better than acrylic ones, but they are also fixed - not quite reliably. Due to the softness of the system, these dentures will not allow you to chew food well; in addition, they load the gums in this way, which over time leads to atrophy of the jaw bone tissue.
Nylon dentures have the following advantages: the absence of allergic reactions, due to the absence of pores in the material, they do not absorb moisture and odors, getting used to them is faster than acrylic ones, they do not rub the gums, are practically invisible to others and have antimicrobial properties.
The disadvantages include: uneven load distribution, short lifespan (3-4 years) and impossibility of repair, high price compared to acrylic ones. Another disadvantage is the problem of a massive base, which, covering the entire palate, causes problems with diction. The elasticity of the nylon prosthesis material is also its disadvantage. Due to the flexible base, the load during chewing is transferred only to the area where food is currently being chewed, this leads to accelerated atrophy of bone tissue.
Why do you need to restore your teeth?
Edentia is not only discomfort, but also early aging. The absence of teeth leads to changes in facial features, sunken cheeks, and the appearance of deep wrinkles. The person looks older, his appearance becomes sickly. In addition to visible imbalances in proportions and a deterioration in the quality of life, when there are no teeth at all, health problems
:
- The diet is reduced, the body does not receive the required amount of vitamins and minerals. The immune system suffers, metabolic processes are disrupted, and cells do not receive enough nutrients.
- Gastrointestinal diseases are provoked. Food is chopped poorly, making digestion difficult. Sometimes patients switch to eating pureed food or pureed food - this method also contributes to the appearance of dysfunction of the stomach and intestines.
- The absence of teeth in the jaws leads to improper distribution of the load on the gums and bone. Tissues atrophy and become thinner.
The bite also changes, diction is impaired - speech is slurred, most sounds are distorted. The absence of teeth affects the emotional state, lowers self-esteem, and the circle of friends narrows. Researchers have also established a direct connection with the presence of teeth and the state of intelligence and activity of older people.
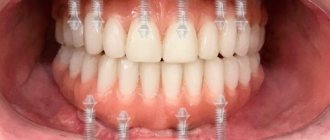
Fixed dentures on implants
Classic implantation. This method of restoring teeth in the absence of teeth makes it possible to reproduce functionally and aesthetically natural teeth as closely as possible.
This procedure occurs in 2 stages. During the first stage, implants are installed. The second stage is carried out after about 3 - 6 months - the time for the implants to engraft into the bone. The second stage is the installation of dentures on implants. Single crowns (more expensive) or bridge structures (cheaper) can be used as prostheses. These dentures are similar to conventional ceramic ones; they are simply installed on implants.
The frame material of the structure can be an alloy of chromium and cobalt or the more expensive zirconium dioxide. And for patients with allergies to metals, zirconium dioxide is the only option for implant prosthetics.
The use of such prostheses is comfortable, does not cover the gums and palate, and does not require getting used to. They are also more aesthetically pleasing and do not attract the attention of others.
Advantages: durability, lightness of construction, preservation of taste sensations, absence of a gag reflex, complete uniform chewing, and restoration of dental function by 90%.
The disadvantages are high cost, duration of treatment, and sometimes the need for bone grafting.
Treatment of adentia in children
It is important for parents of such children with identified pathological loss of teeth to have a good understanding of the need for treatment. Thus, if there is a lack of milk units in the frontal and lateral sections at a young age, during the eruption of permanent units, a pathological bite will form.
The disease in childhood is characterized by:
- delay and asymmetry in the eruption of radical units;
- preservation of milk units on one side only;
- the rudiments of permanent structures are not formed.
If at least one of these signs is detected in a small patient, you should immediately see an orthodontist to determine treatment with plates or a brace system.
The choice of an orthopedic device (plate) depends on the number of missing units and the child’s level of hygiene. Most often, non-removable devices are offered - solid or with a sliding mechanism, using special rings or crowns for support. Adaptation to new devices is quick.
With early change of units and in primary occlusion, removable plates are used that do not retard the growth of the bone structures of the jaws.
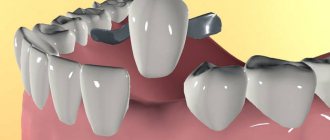
Clasp structures supported by implants
Due to the fact that clasp prosthetics requires support, in the case of complete edentia, the clasp can be installed only after implantation. Thanks to the metal frame in the form of an arc, strength and uniform distribution of the load when chewing are ensured. Artificial teeth and a plastic base that imitates gums are attached to the frame. There are several types of fastening: hooks, clasps and crowns.
The “All-on-4x” design is also a variant of the clasp on implants.
Diagnosis: complete absence of teeth
Partial edentia means that the patient is missing several teeth. Multiple edentia is a condition in which more than 10 teeth are missing. If the patient has lost the entire dentition - on one or both jaws, then the doctor diagnoses “complete edentia”. As a rule, people in adulthood face this problem, but in exceptional cases, this diagnosis can occur in young people and even children.
There are two types of edentia.
- With primary adentia,
a person is born with dead/undeveloped tooth rudiments. Even partial primary adentia occurs in only 1% of cases of all dental anomalies, and complete primary adentia is an extremely rare diagnosis. The congenital absence of tooth buds is caused by various hereditary factors or diseases that provoke disturbances in the development of the dental plate. Thus, the cause of congenital adentia can be ichthyosis, hypothyroidism, pituitary dwarfism, and infectious diseases. - Secondary complete adentia
is most common in adulthood, affecting about 20% of people over 65 years of age. This form is considered acquired; it is provoked by:
- metabolic disorders;
- age-related changes;
- injuries to teeth and jaw;
- gum disease;
- caries and its complications.
Periodontitis, periodontal disease, periostitis, pulpitis, periodontitis without high-quality and timely treatment can lead to complete or partial adentia even at a young age.
All-on-4 design. Prostheses with bar fixation
The essence of this prosthetics is in its name. It involves the installation of a complete denture on one jaw on 4 implant supports. Implants are implanted in an inclined plane; the prosthetic process does not take much time. This prosthesis does not affect changes in taste sensations or diction.
The advantages of such a prosthesis are high aesthetics, second only to classical implantation, reliable fixation, uniform load distribution, a short period of adaptation, the ability to choose a convenient design, and no need for bone grafting.
Disadvantages: high cost compared to removable dentures; the prosthesis still feels more like a prosthesis, and not like your own teeth.
Prices
| Service | Price |
| Removable acrylic (plate) dentures | from 15,200 rub. |
| Dental bridges | from 25,800 rub. |
| Nylon dentures | from 34,900 rub. |
| Clasp dentures | from 48,500 rub. |
| Complete dental prosthetics on implants | from 215,000 rub. |
| All-on-6 prosthetics | from 221,000 rub. |
To avoid possible misunderstandings, please clarify the cost of services in clinics with the administrator or during a consultation with a doctor. Prices on the website are not a public offer.
Sign up for a consultation
Mini-implantation and overdentures
Mini-implants are designed to improve the fixation of removable nylon dentures on the patient's jaw. Such dentures are sometimes called overlay dentures. This method refers to conditionally removable prosthetic methods.
Mini-implants serve as support for overdentures, and fixation (clicking) is carried out using silicone matrices. The simplest and most convenient is the spherical (push-button) fastening, which requires the implantation of at least 2-4 implants. The greater the number of supports, the more reliable the fixation will be, the less likelihood of bone tissue atrophy, but the higher the overall cost of prosthetics.
The main advantages of mini implantation are reliable fixation of the prosthesis, the ability to install implants without incisions, the ability to install a covering prosthesis immediately after, no need for bone grafting, and the cost is lower when compared with classical implantation.
The main disadvantages are that the plastic base cannot cope with loads like real teeth, the load is still not distributed evenly enough, and fixed prosthetics are not feasible.
Disease prevention
The best prevention of pathology will be high-quality care for teeth and gums: complete teeth cleaning, prof. examinations by a specialist once every 6 months, smoking cessation, proper nutrition.
If you or your family members are faced with this pathology, contact the specialists at West Dental. Experienced doctors at the branches in Yanino-1 and Vsevolozhsk will help you choose high-quality therapy.
Call and make an appointment by phone: +7 (812) 450-00-07. Our clinics are open every day from 9 am to 9 pm.
Basal implantation
This method comes to the rescue when the patient’s oral cavity does not have the conditions for classical dental implantation - this is a high degree of thinning of the bone tissue and the impossibility of bone grafting. Implants are placed in the basal bone of the jaw, which is largely free from atrophy. Such implants are individually selected depending on the size of the bone and its quality. Metal roots are attached at a certain angle, deep into the bone. The installation of implants and prosthetics takes one week.
There is no need to talk about aesthetics in this case; basal implantation is used if there are no other options for restoring teeth.
The main advantages of basal implantation are lower cost, the possibility of implantation even in the absence of alveolar bone, no need to build up atrophied bone, low cost and short treatment time.
The disadvantages of basal implantation are poor aesthetics and the impossibility of installing a single implant. In addition, if the doctor acts ineptly, there is a risk of harming the patient more than helping him. The qualifications of the doctor play a decisive role when choosing this method of prosthetics.
Diagnostic methods at the dentist
For an orthopedic dentist, even a primary external examination of the face can indicate a pathological condition - adentia. Symptoms and treatment of the disease are interconnected, so correct diagnostic measures are important.
The main technique is X-ray images of HF and LF. When identifying a congenital form of the disease, to determine the rudiments.
Patients under 18 years of age should choose OPTG - a panoramic Rg image to see the full development of bone structures and the TMJ.
It is also necessary to determine the likely limitations to the implementation of therapy - inflammation/neoplastic growths in the mouth, roots of damaged units, periodontal tissue diseases.
- Edentia of the upper jaw
On the bone structures of the upper jaw, there are more often various anomalies than on the lower jaw (symmetrical deficiency of two units - mainly the second incisors of the “twos”). The frontal group of teeth takes part in sound production and pronunciation.
- Edentia of the lower jaw
There is not much space in the lower jaw for a denture, so in the absence of teeth, the tongue will take up all the free space, which means a deterioration in speech and food consumption.
How to choose a prosthesis?
It is quite obvious that the aesthetic characteristics of more expensive designs will obviously be higher, even taking into account everyone’s subjective assessment. Of the objective factors that will help you choose a prosthesis in the absence of teeth, there are two:
The first is medical indications. If the bone is very thin, it may not be possible to place implants without bone grafting. If the patient is aged, then such operations are carried out solely with an eye to the state of health. Mini implantations and conventional prostheses are often used.
The second is the patient’s requirements for the cost of treatment. This factor plays the greatest role in drawing up the final treatment plan.
Bite with complete absence of teeth
With complete edentia, the jaw looks unaesthetic, and the shape of the patient’s face changes significantly. In this situation, specialists need to recreate the correct bite so that the prosthesis does not protrude or sink.
In order for the prosthesis to fit correctly, correcting aesthetic and functional problems caused by edentia, it is necessary:
- calculate the occlusal height of the upper jaw;
- form a prosthetic plane;
- determine the height of the lower facial region;
- determine the central relationship of the jaws and fix it with notches.
To determine central occlusion, the doctor holds the corners of the patient's mouth. After the patient swallows saliva, the jaws close correctly.