Acute herpetic stomatitis
This is an infectious viral disease that occurs in response to primary contact with the herpes simplex virus.
Infection occurs
- by airborne droplets;
- through contact and household means (through toys, dishes, etc.);
- from persons suffering from recurrent herpes.
Children aged 6 months to 3 years are most often affected.
Main signs of the disease:
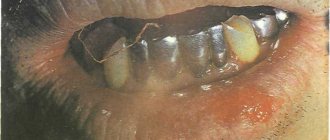
redness of the oral mucosa and blisters appear, which quickly open and form multiple painful round ulcers (erosions), bleeding gums; increased body temperature, general weakness, intoxication; the child eats and sleeps poorly.
To prevent the spread of infection
a child with acute herpetic stomatitis is not allowed to visit a child care facility, even if the disease occurs in a very mild form.
Prevention of infection with the herpes simplex virus upon contact with sick people involves lubricating the mucous membrane of the nose and mouth with 0.25% oxolinic ointment for 5 days.
If there are signs of disease, you should consult a pediatric dentist!
Chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis
This is a chronic inflammatory disease of the oral mucosa of a non-infectious nature, characterized by periodic exacerbations and remissions.
Causes of the disease:
- allergic reactions in a child;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- respiratory infections;
- functional disorders of the central and autonomic nervous system;
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the nasopharynx (otitis, sinusitis, etc.)
School-age children and adolescents are more often affected.
Main signs of the disease:
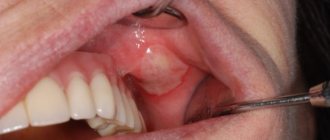
on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity (usually lips, cheeks, transitional folds of the upper and lower jaws, the lateral surface and back of the tongue) one or several areas of redness with rounded painful aphthae covered with a yellowish coating appear; the child’s general condition may deteriorate, the child refuses to eat; healing occurs with adequate treatment after 5-7 days without a scar.
In order to prevent exacerbations of the disease, it is necessary:
- regular visits to the dentist (at least 2 times a year);
- elimination of foci of chronic infection in the oral cavity (treatment of carious teeth and periodontal diseases);
- systematic hygienic oral care.
If there are signs of disease, you should consult a pediatric dentist!
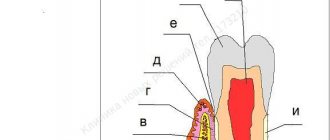
Prevention of diseases of the oral mucosa
The oral mucosa is the site of exposure to both external and internal factors and the manifestation of various somatic diseases.
Diseases of the oral mucosa are defined by:
- External factors
These include various microorganisms, mechanical, physical, chemical influences;
- Systemic internal factors
This is the reactivity of the body, depending on age, genetic characteristics, state of immunity, concomitant diseases.
Prevention of diseases of the oral mucosa is aimed at eliminating or reducing the influence of these factors. Individual prevention should be carried out at an outpatient dental appointment.
Knowledge of the etiology and pathogenetic mechanisms of the occurrence of diseases of the oral mucosa allows, to one degree or another, to carry out preventive measures, which are mainly aimed at eliminating risk factors and causes of the development of this pathology.
Prevention of mechanical damage to the oral mucosa is the removal of decayed teeth, timely filling of carious cavities, grinding of sharp edges of teeth, fillings, elimination of bad habits (biting the mucous membrane of the cheeks, lips, tongue), making new and correcting old dentures.
In the oral cavity, electric currents can occur between dissimilar metals, which are accompanied by various symptoms from the oral mucosa. Prevention of this complication is the manufacture of dentures and fillings from homogeneous metal.
Particular attention should be paid to persons who, during work, come into contact with substances harmful to the body, which causes corresponding changes in the oral mucosa.
Prevention of these diseases is the improvement of working conditions, as well as individual prevention (constant and thorough oral care, thorough hand washing before eating) and regular medical and preventive examinations by a dentist.
Candidiasis (thrush) is one of the most common diseases of the oral mucosa. The disease can affect both infants and adults. Among the local factors contributing to the development of candidiasis, poor oral hygiene, the presence of carious teeth, periodontal diseases, and prolonged wearing of plastic dentures without proper care are important. Therefore, to prevent the disease, it is necessary to carry out rational oral hygiene, treat carious teeth and inflamed gums.
The materials used in dentistry can cause the development of allergic contact stomatitis. Allergens are organic and inorganic components of acrylic prostheses. Intolerance increases in individuals with a history of allergies and as the time elapses since the manufacture of the prostheses increases.
Prevention of diseases of the oral mucosa with an autoimmune component is difficult, since their etiology and pathogenesis have not been fully identified. Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and various intoxications play a role in the occurrence of chronic aphthous stomatitis and exudative erythema multiforme. In these patients, examination may reveal the presence of bacterial sensitization, as well as disturbances in the blood T-lymphocyte system. Some authors note the hereditary nature of the disease. Based on the above, the identification and treatment of concomitant pathologies is important for the prevention of diseases. Careful sanitation of the oral cavity is necessary to eliminate foci of chronic infection. During the period of remission, drugs are used that increase the specific and nonspecific reactivity of the body.
Preventive measures to prevent changes in the oral mucosa due to pathology of internal organs include early detection and treatment of the underlying disease, rational hygiene and thorough sanitation of the oral cavity.
Particular attention in the prevention of diseases of the oral mucosa, red border of the lips and tongue should be paid to precancerous diseases, which more often occur in older men.
Primary prevention of cancer and precancer is based on the prevention and elimination of risk factors: chronic mechanical, physical and chemical injuries to the oral mucosa, occupational hazards, excess solar radiation, galvanism, hypovitaminosis, hormonal disorders, etc.
The most common in clinical practice are leukoplakia, the warty form of precancer, and abrasive precancerous cheilitis of Manganotti.
Of the risk factors for leukoplakia, exposure to tobacco smoke comes first. When burning tobacco, in addition to the thermal effect, various chemicals are formed, which, when they enter the oral cavity with smoke, irritate the mucous membrane. In the development of local lesions caused by smoking, pipe smoking is the most harmful. The risk of the disease increases if patients who smoke or abuse alcohol have dentures and do not regularly visit the dentist.
Chronic injury, as one of the risk factors, can be caused by sharp edges of teeth, roots, poorly made dentures, and tartar. Excessively hot and spicy foods, strong alcoholic drinks and drugs can also lead to leukoplakia. Lack of vitamin A in the body, hormonal disorders, anemia, etc. are factors contributing to the occurrence of leukoplakia.
Ways to prevent cancer and precancer of the oral mucosa and red border are based on knowledge of etiological factors. In this regard, it is necessary to promote cessation of tobacco use and, first of all, smoking of pipes, cigarettes and unfiltered cigarettes, frequent consumption of alcohol, hot and irritating foods, as well as the inclusion in the diet of foods rich in vitamins A, C, IN.
Regular visits to the dentist for the purpose of timely treatment of carious teeth, removal of dental plaque, rational prosthetics and compliance with the rules of hygienic oral care will significantly reduce the risk of diseases of the mucous membrane.
Institution "14th city dental clinic" Dentist N.N. Rybchenko
Candidiasis (thrush)
This is a fungal disease that occurs as a result of the proliferation of fungi of the genus Candida on the oral mucosa.
Transmission of a fungal infection to a child is possible:
- during passage through the birth canal of a mother suffering from candidomycosis;
- through contact and household means (through pacifiers, underwear and other items for caring for the newborn).
Weak children in the first weeks of life are more likely to get sick.
Main signs of the disease:
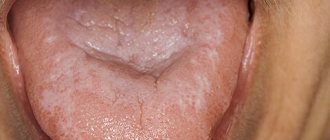
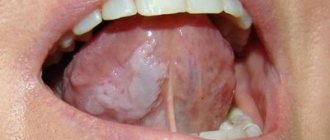
the disease begins asymptomatically, and then the child becomes restless, eats and sleeps poorly. Regional lymph nodes may be enlarged, body temperature is normal, but may also be elevated, a plaque in the form of white dots appears in the oral cavity on the mucous membrane of the cheeks along the line where the teeth meet; on the palate, lips, and tongue; As the fungus multiplies, the plaque increases in size, forming a film resembling curdled milk.
In order to prevent the occurrence of the disease, it is necessary to promptly treat thrush in women during pregnancy and maintain a healthy gastrointestinal tract in a young mother; observe sanitary and hygienic measures in maternity hospitals and at home, sterilize pacifiers and bottle nipples.
Prevention
in children is the timely detection and treatment of dysbiosis, and with long-term prescription of antibiotics - timely administration of probiotics.
If there are signs of disease, you should consult a pediatric dentist!
Motor function of the gastrointestinal tract in young children
The motor function of the gastrointestinal tract in young children also has a number of features. The peristaltic wave of the esophagus and mechanical irritation of its lower section with a bolus of food cause a reflex opening of the entrance to the stomach. Gastric motility consists of peristalsis (rhythmic waves of contraction from the cardiac region to the pylorus), peristole (resistance exerted by the walls of the stomach to the stretching effect of food) and fluctuations in the tone of the stomach wall, which appears 2-3 hours after eating.
Motility of the small intestine includes pendulum-like movement (rhythmic oscillations that mix intestinal contents with intestinal secretions and create favorable conditions for absorption), fluctuations in the tone of the intestinal wall and peristalsis (worm-like movements along the intestine, promoting the movement of food).
In the large intestine, pendulum-like and peristaltic movements are also observed, and in the proximal sections - antiperistalsis, which promotes the formation of feces. The time it takes for food gruel to pass through the intestines in children is shorter than in adults: in newborns - from 4 to 18 hours, in older ones - about a day. It should be noted that with artificial feeding this period is extended.
Afta Bednara
This is an inflammatory disease of the oral mucosa of a non-infectious nature, occurring in weak, bottle-fed infants in the first months of life.
Causes of the disease:
- permanent mechanical injury to the mucous membrane of the palate due to a nipple that is too long and too hard;
- may occur in breastfed children if the mother's nipple is very rough.
Main signs of the disease:
round or oval erosions, covered with loose plaque and located symmetrically at the border of the hard and soft palate, redness of the surrounding mucous membrane. The child becomes restless, eats and sleeps poorly.
In order to prevent the occurrence of the disease, it is necessary
promptly replace the pacifier or pacifier if irritation occurs on the oral mucosa.
If there are signs of disease, you should consult a pediatric dentist!
If any changes appear on the oral mucosa, you should visit a pediatric dentist to avoid complications and conduct a comprehensive examination and treatment!!!