The current state of affairs and the rapid development of dentistry and plastic maxillofacial surgery require detailed knowledge of the blood supply to the face, including the upper and lower jaws (HF, LF). In the literature over the past 40 years, we have not found any works devoted to the study of blood supply to the HF and LF. Meanwhile, this knowledge is necessary for various surgical interventions on the jaws, fractures, wounds, to interpret the paths of spread of purulent-inflammatory processes on the face.
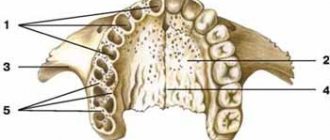
The HF is supplied with blood by a large number of large arteries, which widely anastomose with each other [2, 4]. As for the sources of blood supply to the NP, expert opinions differ. Some authors [5] consider the inferior alveolar artery to be the main and only source of blood supply to the NP. According to others [1-3], in addition to the inferior alveolar artery, additional arteries are involved in the blood supply to the NP.
The LF is supplied with blood from a number of additional extraosseous (extraosseous) arteries: the temporal, arteries of the pterygoid muscles, masticatory, facial, lingual and mylohyoid. The main arteries supplying blood to the NP are considered to be 6 intraosseous (intraosseous) arteries: maxillary, inferior alveolar, lingual, transverse facial artery, masticatory and facial.
The purpose of the study is to study the main and additional sources of blood supply to the HF and LF - extraosseous and intraosseous arteries, to study their participation in the blood supply of the jaws and their relationship with facial tissues.
Material and methods
The work is based on the study of 130 isolated NP preparations removed from corpses in Tver morgues, and 20 embalmed corpses of people aged 20 to 70 years, studied at the Department of Topographic Anatomy and Operative Surgery of the TSMA.
The following methods were used: morphometric measurements, contrast radiography, decalcification, preparation, recording and photography. Using 16 NP preparations, experimental ligations of the inferior alveolar artery in the initial part of the mandibular canal were performed to identify additional intraosseous arteries involved in the blood supply to the NP.
For contrast angiography, injections were made through the external carotid or inferior alveolar artery of lead, diluted in petroleum jelly and turpentine in the following ratio: lead - 60 g, petroleum jelly - 15 g, turpentine - 15 g.
Arteries, veins and nerves of the upper and lower jaw
This article describes the following anatomical landmarks and their relationship to oral implant surgery: external carotid artery, maxillary artery, pterygopalatine fossa, capitis veins, and trigeminal nerve.
External carotid artery
The arteries supplying the face, upper and lower jaw mainly originate from the external carotid artery. However, branches of the ophthalmic artery (a branch of the internal carotid artery) supply blood to the forehead, scalp, upper eyelid and nose. The external and internal carotid arteries (Figures 1-1 and 1-2) arise from the common carotid artery at the level of the superior border of the thyroid cartilage. The external carotid artery has eight branches:
- Three anterior branches: superior thyroid artery, lingual artery and facial artery.
- Two terminal branches: the maxillary artery and the superficial temporal artery.
- Two posterior branches: the occipital auricular artery and the posterior auricular artery.
- One medial branch: ascending pharyngeal artery.
Figure 1-1 Main branches of the aortic arch
Fig 1-2 Main branches of the external carotid artery
Maxillary artery
The maxillary artery (Figure 1-3) arises from the external carotid artery in the parotid gland as a terminal branch. The branches of the maxillary artery can be divided into three parts:
- Part I or mandibular part (located within the parotid salivary gland and in front of the external auditory meatus): In this part, the maxillary artery gives off branches to the ear, dura mater, temporomandibular joint, mandibular teeth, and mylohyoid muscle.
- Part II or pterygoid part (located in the infratemporal fossa): The branches here mainly go to the muscles involved in the process of mastication, the skin and mucous membrane of the cheek, and also to the buccal muscle through the buccal artery.
- Part III or pterygopalatine part (branches in the pterygopalatine fossa after entering through the pterygomaxillary fissure): the branches here mainly go to the hard and soft palate through the descending palatine artery, to the molars and premolars of the maxilla through the posterior superior alveolar artery, to the upper part of the pharynx and the tympanic cavity through the artery of the pterygoid canal, to the nasopharynx and sphenoid sinus through the pharyngeal artery and to the anterior teeth of the upper jaw through the infraorbital artery.
Figure 1-3 Course of the maxillary artery
The maxillary artery ends with the sphenopalatine artery on the nasal septum after dividing into nasal branches. Figure 1-4 shows in detail the branches of all three parts of the maxillary artery.
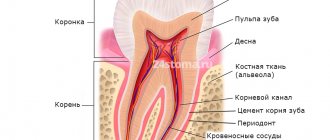
Internal composition of teeth
These organs are a solid hollow formation.
In the section you can see:
- internal cavity, which is filled with pulp;
- hard tissues, which are represented by dentin, enamel and cement.
Pulp, dentin and enamel
Structural differences between dentin and bone tissue
A significant difference between the hard tissues of teeth and bone is the complete absence of cell bodies - osteoclasts and osteocytes, which take part in the growth and development of bone tissue. The formation of new layers of dentin occurs due to dentinoblasts located in the pulp.
And the processes of these cells pass through the thickness of dentin, the structure of which also includes collagen fibers and a special adhesive substance.
Internal structure of dentin
In the crown part, the tooth is covered on the outside with enamel, and in the root area - with cement.
Enamel
The histological structure of tooth enamel contains 97-98% mineral salts. The molecular part of this outer shell is the so-called fibrillar protein, which forms special cells for fixing minerals.
Enamel structure
The surface layers of enamel contain an increased amount of fluoride compounds, which gives it increased strength.
The main structural elements of enamel are enamel prisms, which have an S-shaped bend in the direction from the tooth surface to the pulp. Histology indicates that the thickness of these elements ranges from 3 to 7 microns.
Cement
In dentistry, cement is the name given to the coarse fibrous tissue that covers the tooth root. From a biological point of view, this structure consists of collagen fibers compacted with calcium salts.
Microscopic image of root cement
Pulp
The internal cavities of teeth in children and adults are filled with pulp in the form of loose connective tissue, nerve endings, blood vessels and dentinoblasts.
Pulp extracted from a tooth
The main function of this organ is to counteract inflammatory and infectious lesions. Thanks to the branched blood network, the pulp provides nutrition and growth of tooth dentin.
Periodontium
The complex of ligamentous apparatus, which is located in the space between the bone alveolus and the root, is called periodontium. This tissue includes collagen fibers, cells of the immune system, osteoblasts and osteoclasts.
Retaining apparatus
The main components of the periodontium are connective tissue bundles that are stretched between the alveolar wall and the root cement. Collagen fibers are tightly intertwined with each other by anastomoses, which ensures reliable fixation of the root. All teeth and their structure also have slight mobility and this is normal.
Direction of periodontal fibers
Regeneration of dental tissues
Restoration of enamel, dentin, pulp and cement is possible, but not in all clinical cases.
Regeneration of the anterior and chewing teeth, as a rule, occurs due to the following processes:
- replenishment of enamel with minerals, which is carried out both from saliva and through the blood vessels of the pulp;
- in the pulp chamber, cellular elements form a special connective tissue capsule around the inflammatory focus, thereby preventing further spread of infection;
Some features of the structure of teeth
Normally, a person’s dental structure looks like this:
- central and lateral incisors, which have one root and one root canal;
- fangs with one pronounced and massive root;
- small molars, the first of which are distinguished by a double root and two canals, and the structure of the 25th tooth is already characterized by a single root with the same number of root canals;
- large molars - the upper group has three roots and the same number of canals, and the lower group includes two roots and three canals.
Removed 25th tooth
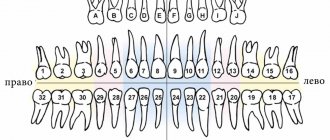
Classification of teeth
Among permanent human teeth, experts distinguish the following groups:
- incisors for cutting food;
- fangs, the function of which is to tear off individual food particles;
- premolars that crush food;
- molars, which serve for final grinding of food.
| Functional group | Clinical picture |
| Incisors |
|
| Fangs |
|
| Premolars | Small molars |
| Molars |
|
Such varieties indicate the development of a mixed type of nutrition in a person.
From an anatomical point of view, the tooth structure diagram includes the following parts:
- crown - the main visible part that rises above the surface of the gum;
- neck – the gingival area of the transition of the crown to the root;
- root - a fixing element located in the thickness of bone tissue and gums.
Teeth structure
Functions of dental pulp –
The functions of the dental pulp stem from its morphology (structure). Below we list its main functions:
- Trophic function - we have already said that the pulp has a well-developed network of blood and lymphatic capillaries.
The main intercellular substance of the pulp serves as an intermediate medium through which metabolism occurs. Thus, oxygen and nutrients from the blood enter the cellular elements of the pulp precisely through the intercellular substance, and metabolic products are excreted through it into the venous or lymphatic systems. But the trophic function of the pulp is not only to nourish its own structures. The dentin and enamel of the crown part of the tooth receive nutrients and calcium salts - almost exclusively from the dental pulp (the processes of odontoblasts play a major role here). But as for the nutrition of the hard tissues of the tooth root, it occurs not only through the pulp, but also due to the process of diffusion of nutrients from the pericementum.
- Plastic function is realized thanks to odontoblasts, which throughout a person’s life participate in the formation of secondary and tertiary dentin. For example, in teeth there is a constant deposition of secondary dentin on the side of the pulp chamber, which leads to a gradual decrease in its volume. The deposition of denser tertiary dentin, as well as the obliteration of dentinal tubules, also occurs due to odontoblasts, and protects the pulp from external irritants and the penetration of bacteria into it.
- The protective function - the function of phagocytosis and disposal of dead cells is provided by neutrophil granulocytes and macrophages. Lymphocytes (plasma cells) - participate in the synthesis of antibodies. Fibroblasts participate in the formation of a fibrous capsule around the inflammatory focus. In addition, the pulp is also a biological barrier that prevents the penetration of pathogenic bacteria from the carious cavity into the periodontium. The protective function also includes the processes of formation of tertiary dentin and obliteration of dentinal tubules that we have voiced.
- Sensory function - carried out due to the presence of a large number of nerve endings.
Age-related changes in dentogingival tissues
Over time, the human dentofacial system undergoes the following changes:
- reduction in the height of the enamel layer due to abrasion of the enamel;
- the formation of microcracks, which provokes gradual staining of teeth yellow and brown;
- active formation of secondary dentin and, accordingly, a decrease in the volume of dental pulp;
- age-related thickening of the walls of blood vessels also causes a narrowing of the pulp cavity;
- an increase in the amount of cement, which is observed both with an increase in chewing load and without it;
- thickening of periodontal bundles in the area of teeth that serve as support for bridges.
Age-related microcracks and darkening of enamel