Treatment of gums in children is a common reason for visiting a dentist. The susceptibility of delicate gums to inflammatory processes is explained by their sensitivity to all kinds of damage and poor hygiene. The remaining soft plaque on the teeth eventually turns into hard deposits in the form of tartar. Inflammation can also be caused by an infection that enters the oral cavity through dirty toys, for example. Unfortunately, parents are not always able to monitor the regularity and quality of brushing their children’s teeth or protect them from licking dirty surfaces.
Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the gums or gingivitis must be detected as early as possible and treatment begun. This is why regular scheduled examinations are so important. A delay in making a visit can result in a complication - there is a risk of transition to a chronic form, after which - to the ulcerative-necrotic stage, and, as a result, damage to surrounding tissues. Periodontitis is one of the most serious stages of gum disease.
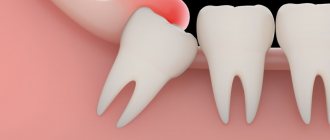
Teething in infants is not only a painful process, but also provokes inflammation of the gums, as well as injuries, as a result of diligently sucking a rattle or a cracker offered by the mother...
Causes of gum inflammation in children
- Skipping or poor quality teeth brushing;
- Sucking dirty objects;
- Errors when installing seals;
- Pathologies of the dentition;
- Carious cavities with sharp edges;
- Bite correction;
- Breathing through the mouth;
- Abnormal structure of the oral cavity organs (attachment of the frenulum of the tongue and lips);
- Problems with the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- Disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Infectious diseases (ARVI, influenza);
- Hormonal abnormalities;
- Hereditary anomalies.
Vincent's ulcerative necrotizing stomatitis
Mostly young people (17-30 years old), mostly men, are affected. A provoking factor in the development of necrotizing ulcerative stomatitis
Vincent's disease is often caused by hypothermia, which explains the highest frequency of its occurrence in autumn and winter. The maximum incidence of cases occurs from October to December.
Clinically, acute and chronic forms are distinguished, and according to severity - mild, moderate and severe forms of Vincent's ulcerative-necrotizing stomatitis.
The disease begins acutely with an increase in body temperature to 37.5-38 °C. Regional lymph nodes enlarge, become denser, become painful on palpation, and remain mobile. Patients are bothered by headaches, general weakness, soreness of the oral mucosa, which intensifies when eating or talking; bleeding gums, hypersalivation, putrid breath. There is pallor of the facial skin with a grayish tint due to severe intoxication of the body.
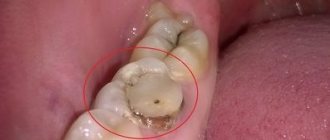
Catarrhal phenomena on the oral mucosa quickly turn into ulcerative ones. The process most often begins on the gums, and then moves to other areas of the mucous membrane. The gums become swollen, hyperemic, sharply painful and bleed when touched. The epithelium of the gum margin and interdental papillae becomes cloudy and then necrotic. As a result, the gingival margin looks as if it were cut off, with uneven jagged edges; its surface is covered with an easily removable grayish-yellow coating. Subsequently, the affected gum edge is not completely restored and remains deformed.
The area near the lower eighth teeth is most often and to a greater extent affected. Necrosis from the alveolar process quickly spreads to the buccal mucosa and retromolar region, causing in some cases trismus and pain when swallowing. Ulcers on the mucous membrane of the cheeks can reach large sizes (up to 5-6 cm in diameter) and depth. Their edges are uneven and soft. The bottom is covered with a thick grayish-greenish necrotic coating, which has a putrid, fetid odor. After removing the plaque, the bleeding bottom of the ulcer is exposed. There is no compaction in the area of the base and edges of the ulcer. The mucous membrane around the ulcer is swollen and hyperemic. If there are local traumatic factors in the oral cavity (roots of decayed teeth, sharp edges of teeth or dentures), other areas of the mucous membrane (hard and soft palate, arches, tonsils, tongue) may also be affected.
Oral ulcers can be single or multiple. When the ulcer is localized on the hard palate, necrosis of all layers of the mucous membrane develops quite quickly and the bone is exposed. Isolated lesion of the pharynx (Simanovsky-Plaut-Vincent angina), as a rule, is unilateral, and is rare in dental practice. 2-3 weeks after the onset of ulcerative necrotic stomatitis, the process usually resolves with complete epithelization of the ulcerative surfaces.
In rare cases, when treatment is not carried out or is ineffective, a chronic form of Vincent's ulcerative-necrotizing stomatitis develops, in which there are no general symptoms. Patients are concerned about constant bleeding and sore gums, as well as bad breath. The clinical picture of the disease is blurred. The gum is stagnant, hyperemic, edematous, its ulcerated edge is often compacted, necrotic areas are located mainly in the interdental spaces and can be visible during a cursory examination. Upon careful examination and probing of the gingival margin, exposed bone tissue is determined. Only some teeth have affected areas. Lymph nodes (submandibular, submental) are compacted, slightly painful and, when the disease lasts 4-8 months, acquire a cartilage-like consistency.
During pathohistological examination of areas of ulcerated gum edges, two zones are identified: superficial - necrotic and deep - inflammatory.
In the surface layers of necrotic gum tissue, an abundant diverse microflora is found (cocci, rods, fusobacteria, spirochetes, etc.). Fusobacteria and spirochetes predominate in the deeper layers). The underlying layers of connective tissue are inflamed, swollen, and the blood vessels are dilated. Blood cells are found in the perivascular inflammatory infiltrate. Inside the intact tissue in the same zone of inflammation, only spirochetes that have penetrated between the epithelial cells are detected.
The cytological picture of scrapings from the ulcerative surfaces of the mucous membrane in patients with Vincent's ulcerative necrotic stomatitis corresponds to that of a nonspecific inflammatory process. At the onset of the disease, an abundance of structureless masses, a sharp predominance of neutrophils, mainly in a state of decay, and erythrocytes (due to severe bleeding) are determined. In the second period of the disease, when healing begins, along with decayed neutrophils, full-fledged phagocytic cells and many macrophages appear. During the period of beginning epithelization, layers of young epithelial cells are found, the number of fusobacteria and spirochetes decreases.
In the chronic course of Vincent's ulcerative-necrotizing stomatitis, the relative amount of fusobacteria and spirochetes decreases and the number of cocci increases, but fusospirochetes still predominate.
Types of inflammatory processes
Gingivitis
Inflammation of the gums at the initial stage, that is, not yet spreading to the bone tissue, is called gingivitis.
Treatment of gingivitis in children follows the same principle as in adults, with the only difference being that children are prescribed more gentle medications. When starting the procedure, the hygienist performs professional cleaning, removing plaque and stone, after which he teaches the little patient proper hygiene techniques. Helps you navigate the selection of toothpaste and brush.
Periodontitis
Inflammation of the gums and periodontal tissues - periodontitis - is an advanced stage of gum disease. If left untreated, its progression may result in one or more teeth having to be removed.
Treatment includes occupational hygiene and physical therapy. If the process is advanced, surgical intervention may be required.
Periodontal disease in children
The defeat of all periodontal tissues, in this case, is called childhood periodontal disease. This degree is quite rare. Progression can be triggered by weakened immunity and vitamin deficiency.
An effective option in this case is surgical intervention, as well as strengthening the general condition of the body.
Stomatitis in children
Infectious inflammation of the mucous membrane of the gums, or stomatitis, is characterized by increased sensitivity and discomfort while eating. Therefore, you should show it to a dentist as soon as possible. A dental clinic specialist will examine the baby and prescribe appropriate procedures.
What causes bleeding?
Bleeding is often considered the main symptom of periodontitis and stomatitis. The disease occurs when brushing teeth, intensive chewing, or intense pressure on the jaw. But it can also happen during sleep. Along with this, with stomatitis, bleeding occurs due to infection of the mouth by bacteria and viruses. It appears in conjunction with the following diseases:
- For Vincent's stomatitis (ulcerative-necrotic)
- Herpetic stomatitis
- Aphthous stomatitis
Dentists say that stomatitis, which has progressed to the stage of gingivostomatitis and is characterized by the presence of ulcers, aphthae, and necrotic tissue, provokes severe bleeding. In addition, it is necessary to take into account traumatic stomatitis. This is explained by the fact that the factor affects the mucous membrane and can injure the gums. This also provokes bleeding and the occurrence of gingivitis.
This is interesting: X-ray of a child’s teeth: how to prepare for the procedure and when is an X-ray of the jaw prescribed?
Gum atrophy
A rather unique and rare disease - gum atrophy or exposing atrophic gingivitis manifests itself as itching in the area of 2, less often 4 and 6 symmetrically located milk teeth. A child experiencing discomfort constantly rubs the area of inflammation. At night, the itching usually intensifies.
The interdental papillae and other areas of the gums do not change in any way during gingival atrophy. Slight deposits of tartar are often observed on the unprotected root surface.
The manifestation of itching can be a consequence of measles or influenza, despite the fact that in most young patients such a relationship is not observed. The process of teething is also one of the factors causing itching in infants.
What causes the disease?
Parents can make a general diagnosis.
You can touch the area under the jaw with your own hands:
- Stomatitis provokes inflammation in the area of the lymph nodes. Touching can be painful or painless.
- Redness, plaque, and ulcers appear in the mouth. The microbial type of disease is characterized by the appearance of a yellow crust. It forms on the mouth and lips.
- Stomatitis occurs approximately on the fifth to eighth day of infection.
- Trauma to the mouth can later lead to bacterial stomatitis. Timely treatment can eliminate this.
- Parents often confuse stomatitis with infectious and viral diseases. Under no circumstances should you voluntarily prescribe antibiotics to your child, confusing stomatitis with sore throat. Such treatment will not bring any benefit, but can cause great harm.
- When stomatitis appears in childhood, the likelihood of recurrence of the disease increases.
Stomatitis often occurs in infants and preschool children. This is due to the fact that their mucous membrane is vulnerable to damage and infection. Removing ulcers is not so difficult; it will be more difficult to remove the cause of stomatitis.
Bleeding gums due to stomatitis
Most often, children suffer from herpetic stomatitis. They are vulnerable to herpes, especially at an early age, before three years of age.
The virus itself is transmitted in different ways, for example through household items, clothing, and by airborne droplets. It is also transmitted from adults, who may be carriers of this virus. In addition to the virus, the cause of stomatitis can be a complication from allergies and other diseases, such as otitis media and tonsillitis.
Stomatitis also appears from physical damage to the mucous membrane. This could be hot tea, soup, damage to the tongue and cheeks. The oral cavity is also damaged by toys, pacifiers, and pacifiers. Parents need to watch this closely.
When stomatitis occurs on the gums of a baby, you should definitely consult a doctor. Left untreated, it can lead to gingivitis.
It can also provoke other diseases of the teeth and oral cavity. Correct treatment instructions will reduce the risk of recurrence of the disease and its transformation into a chronic form.
Diagnosis of gum disease in children
A routine oral examination should be performed by a pediatric dentist every six months. And as necessary, if a small patient exhibits any deviations in the development of teeth or symptoms of disease of the oral mucosa. Since it is advisable to diagnose the inflammatory process at the earliest stage.
If redness, swelling and bleeding are detected, the cause of which is an excessive amount of soft plaque or food debris on the teeth, the dentist will make a diagnosis and prescribe procedures.
If a bacterial infection is suspected, a clinic specialist can take biomaterial from the inflamed areas of the gums for clinical tests. Based on the results of the analysis, the specialist prescribes a treatment plan and the date of the next appointment to ensure the final recovery of the little patient.
How does the treatment work?
If a child has stomatitis or bleeding gums, you should immediately consult a doctor. You should not contact your pediatrician. They cannot always determine the form of stomatitis.
The further success of the treatment process depends on a correct diagnosis. It is important to strictly follow all doctor's instructions. Incorrect treatment can cause complications.
Pediatric herpetic stomatitis
There are different types of stomatitis, so it can be difficult to make a diagnosis on your own. Some symptoms can only be seen by a professional.
Depending on the type of stomatitis, the doctor prescribes different medications. Their price depends on the type of treatment and the degree of the disease. To avoid significant expenses on medications, you need to diagnose the disease as early as possible.
Mild forms of stomatitis can be treated quickly and rarely lead to complications. For more information, you can watch the video in this article.
Treatment of gums in children
Medicines prescribed by a doctor have analgesic, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects. They help restore the proper condition of the mucous membrane. Methods of using drugs are different, but the principle is the same: rinsing, irrigation.
For gum disease in infants, the dentist will prescribe special gels to relieve symptoms, namely itching and pain. Parents should pay special attention to cleaning their mouths from food debris.
Antibiotics are prescribed by a dentist in rare cases. Indications for the use of antibiotics is a form that reaches a complex (ulcerative-necrotizing gingivitis) or chronic stage. Antibacterial or antifungal drugs are prescribed when the problem is caused by an infectious process, and the goal is to eliminate its causative agent.
Diagnosis of stomatitis
An experienced specialist can determine this pathology visually. This can be done due to the manifestation of symptoms of the disease such as redness of the mouth, inflammation and swelling.
And, of course, it’s hard not to notice the white ulcers with a red border. Their size and quantity are different.
As for special, narrowly targeted tests for diagnosing stomatitis, they do not exist in modern medicine.
However, before prescribing a medicine to a person with such a clinical picture, it is necessary to determine the type of bacteria/fungus that provoked it.
This is possible by taking a swab from the patient's mouth. The smear is sent to a laboratory where specialists study it.
Only after this the doctor determines the treatment strategy.
Which doctor should I go to?
If signs of the disease are detected, you should visit a dentist who will conduct the necessary examination. If symptoms of related diseases are identified, you may need to consult a dermatologist, venereologist, therapist, immunologist or pediatrician.
Preventive actions
The best prevention of inflammation of the mucous membrane is daily and high-quality hygiene from an early age and proper nutrition.
Hygiene
The concept of “quality hygiene” includes brushing your teeth at least twice: in the morning and in the evening, in conjunction with cleaning the palate and tongue.
Parents should take a very responsible approach to hygiene from the day the first tooth appears. And after he grows up a little, learn the rules of brushing his teeth: regularly and efficiently. The toothbrush and toothpaste should be selected according to the age of the small patient.
Nutrition
In addition to hygiene, parents need to approach the diet wisely: it should be balanced and include vitamins and minerals. Sweets and carbonated drinks should be consumed by the child in limited quantities. In addition, after finishing eating sweets, the baby should rinse his mouth with water and, if possible, brush his teeth. Note that a diet that promotes the proper development of a growing body includes nutritious and timely meals. Snacking and disordered eating should be kept to a minimum.
Bleeding stomatitis: how to treat?
Is it possible to cure bleeding gums and stomatitis at the same time? Because the methods of treating stomatitis and gingivitis are identical, they can be combined. As soon as the doctor establishes the causes of stomatitis on the gums, the form, then gingivitis should be treated in parallel.
The following methods are excellent for treating stomatitis:
- Rinse with antiseptic, effective anti-inflammatory drugs
- It is imperative to perform antifungal and antibacterial treatment of the mouth
- The use of hemostatic drugs, astringents
- You can get rid of unpleasant odors using special products using lemon balm, mint and lime.
- It is imperative to get rid of plaque, dangerous tartar, which only aggravates the course of the disease.
- Elimination of traumatic factors
- Relief from pain using lidocaine
Drugs that relieve stomatitis and associated bleeding
You can choose an effective remedy for a disease, but it is important to know what properties it has. So, to get rid of bleeding, you should choose drugs that solve a complex of problems at once, and not just one. Thus, the remedy must have a complex effect to treat related problems.
Recent innovative advances have shown that the best remedy for bleeding is phytotherapeutic agents designed for a long service life. And it is important that addiction is not provoked.
Experts noted that the best remedy for the disease is the rinse drug Stomatofit , its analogue Stomatofit A. The drugs were created using the latest innovative achievements with the participation of Polish pharmacists. The product is created from 7 healing and miraculous plants.
It is adjusted in accordance with the nature and level of gum damage. Bleeding is treated with antiseptics and herbal decoctions, which help reduce inflammation and heal the mucous membrane faster. To get test results, the doctor needs to prescribe symptomatic therapy.
If it is not possible to eat as before, then you need to start using local anesthetics. Such drugs are used immediately before eating. The best, proven drugs include:
- Benzocaine - anesthetic effect
- Chlorhexidine – gives an antiseptic effect
- Lidochlor, lidocaine
If we talk about products of natural origin, then you need to opt for chamomile, sage, and calendula.
Make it a habit to rinse your mouth with these herbs every 2 hours. If possible, then in the first days, preferably more often. If we talk about children, then they should take a soda solution.
Ointments and gels
Dental ointments and gels are used after preliminary rinsing 2-4 times a day, depending on the severity of the lesion.
Products with anti-inflammatory and restorative effects are used:
- Metrogil Denta;
- Solcoseryl;
- Dental;
- Holisal;
- Asepta;
- Gengigel;
- Actovegin.
Compresses
One of the treatment methods that destroy bacteria at the cellular level is the use of immunomodulatory drugs. The most effective means are Viferon, Interferon, Lafarobin.
Iodinol, or “blue iodine,” works well for treating the oral cavity with stomatitis on the gums.
Some experts advise using brilliant green. This is a rather painful method, but it will get rid of rashes in 1-2 applications.
To treat rashes in a child, brilliant green should be mixed with honey in a 1:1 ratio, then moisten a cotton swab and apply it to the ulcer. If there are a lot of rashes, you can lubricate the surface completely.
Rinse
Rinsing with antiseptic solutions is carried out 3-4 times a day after meals until the signs of the disease completely disappear.
The use of drugs with antiseptic properties is recommended:
- Chlorhexidine;
- Miramistin;
- Furacilin;
- Chlorophyllipt;
- Hydrogen peroxide;
- soda solution;
- potassium permanganate solution.
Nutrition and other factors
Child nutrition becomes a big problem. This process is accompanied by unpleasant and painful sensations. These can be reduced by using painkillers prescribed by your doctor.
As for the food itself, you can give your child dairy products. They should be low-fat. This is due to the fact that fat may not be absorbed and cause digestive problems. You can give your child soft-boiled eggs, omelettes, and liquid porridge. Decoctions of vegetables and fruits are also good.
It will be useful to include various soups and purees in your diet. If fish and meat are present in the diet, they should be well boiled and ground.
What should be excluded?
It is also important not to give your child very cold or hot food. It should be warm to reduce discomfort. It is imperative to remove salty and sour foods. Spicy foods are also excluded.
You also need to reduce the amount of sweets. This will speed up the healing process and help the medications work properly. You should not feed your baby more than four times a day. Eating in between is excluded.
This is interesting: How to recognize pulpitis in a child?
The general recommendation would be to structure the diet in such a way as to reduce the impact on the oral mucosa and not injure it further. Honey is also excluded.
Doctors say that it can provoke the appearance of a fungus, which leads to the onset of the disease. It’s also a good idea to give your child juices and rosehip infusion.
It is important to note that citrus juices can negatively affect the healing process. Therefore, the best solution would be carrot juice. Decoctions of sage, chamomile, oak bark, calendula and eucalyptus will be useful. It is also important to drink plenty of water. It should be warm. Rinsing your mouth also helps.
How else can you speed up the healing process?
To prevent the disease from progressing, the child must remain at home. Therefore, parents need to make sure that he does not go to school or kindergarten.
You need to provide him with a separate towel and dishes. The room in which the child is located must be frequently ventilated and wet cleaned.
If a child has stomatitis on the gum, then the teeth should be brushed with a synthetic brush. This will reduce the traumatic effect on the gums and oral cavity in general. Under no circumstances should this be done with someone else’s brush, because the likelihood of spreading the disease is high.
Folk remedies
To get rid of the disease at home, remedies are used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. They are used in addition to the main therapy.
The following remedies will help relieve symptoms:
- Freshly squeezed carrot or cabbage juice has regenerating and healing properties. In addition, they strengthen overall immunity.
- Applications made from finely grated potatoes mixed with olive oil.
- Cinquefoil erect root, bergenia and several clove buds are ground in a coffee grinder and mixed with tooth powder. The composition is applied to the gums twice a day using a toothbrush. The course of treatment is 10 days.
- Melt 75 grams of beeswax in a water bath, mix with two tablespoons of honey and a few drops of mint oil. After cooling, form small balls that should be chewed throughout the day.
- Dissolve a pin-head piece of mummy in a glass of warm boiled water and use for rinsing in the morning and evening.
Treatment of children at RAIDEN
In the RAIDEN network of dental clinics, the treatment and prevention of oral diseases of young patients is treated with the utmost attention and reverence - the health of the younger generation is very important to us!
All medications used in our clinic meet the highest quality requirements. Before using them, we conduct a blood test of the baby to determine drug tolerance. The safety of your children, our little patients, is paramount to us.
Symptoms
- redness of a local area of the mucosa (at the very beginning of the inflammatory process);
- swelling of the reddened area, burning and itching;
- the appearance of a round ulcer in the bacterial form (occurs within a day), the formation of a white coating in the fungal form or small blisters in the case of a viral infection;
- salivation gradually increases;
- the appearance of bleeding gums;
- unpleasant odor;
- increased discomfort, pain or burning sensation;
- Without treatment, your health may deteriorate and your temperature may rise.
If these symptoms appear, doctors at the Dentospas clinic recommend planning a visit to the dentist.