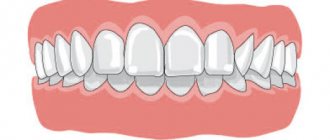
A physiological, that is, correct, bite in dentistry is considered to be one that allows the teeth to perform all functions efficiently. Normally, the antagonist teeth of the upper and lower jaws should touch, located almost opposite each other. In this case, the upper jaw should be slightly pushed forward to ensure slight overlap of the lower teeth with the upper ones. With a correct bite, the upper dental arch has the shape of half an ellipse, and the lower one has the shape of a parabola; the teeth themselves are located at a slight inclination towards the oral cavity.
In practice, correct dentition, a striking example of which is demonstrated by the ideal Hollywood smile formed by a dentist, is rare. Therefore, several types of physiological occlusion are considered to be the norm, to which some experts include a straight bite.
What is a straight bite
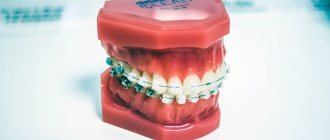
Direct bite refers to the closure of the dentition, in which the lower edges of the upper and lower teeth touch.
If a person has straight teeth, then such a smile seems flawless. Often such a bite appears in advertisements for toothpastes or chewing gum, which misleads viewers. In fact, direct bite is a variant of pathology, despite the above advantages. If you find your child's teeth are closing in this way, you should contact your dentist as soon as possible. Otherwise, serious complications will arise.
Formation of malocclusion
The bite is formed at the stage of fetal development, and here in many respects everything directly depends on the mother and her lifestyle: drinking alcohol or smoking, severe and difficult to treat diseases, injuring the fetus due to tight clothing, blows, falls, etc., a large number of stressful situations, radiation. Also, the bite of the unborn child is influenced by heredity on the part of both parents.
In a newborn, primary occlusion is formed between six months and one year, when the position of the upper and lower jaws, the time of eruption of baby teeth and the tone of the facial muscles are determined. You can notice the first signs of a deviation from the norm in a child by how often the child involuntarily opens his mouth and breathes exclusively through it, despite the fact that there are no symptoms of a cold. Or if the baby strongly strains his facial muscles during feeding, begins to suck his finger, bite his cheeks and sleeps with an unnatural head position.
A qualified pediatric dentist is able to identify problems in the first months after the formation of the bite, that is, when the baby is between six and eight months old. Most often, even for mothers of healthy babies, doctors recommend limiting the use of a pacifier for longer than fifteen minutes, not using nipples with a diameter of more than 35 millimeters, and not allowing the child to put foreign objects in his mouth.
At a later age, from two to ten years, the symptoms of dental anomaly are not very different, only noticeable unevenness of the teeth and even postural disturbances are added. To prevent further development of the disease, it is recommended to visit an orthodontist annually starting from two years of age or more often if necessary.
Is a straight bite normal?
If we are talking about a physiological bite, then in this case the upper row of teeth slightly covers the lower one. This does not happen with a straight bite.
Such occlusion cannot be considered normal, since it is fraught with the appearance of a number of defects and disorders, despite a visually ideal smile (if the person has straight teeth).
Important: straight bite is bad . Here are some problems that people with a straight bite experience:
- With a direct bite, the lower jaw gradually moves forward, which is why the bite becomes progenic.
- The enamel wears off at an accelerated rate due to heavy loads on the teeth.
- The jaw also experiences heavy loads, which is fraught with pain and problems in the functioning of the temporomandibular temple.
- Increased risk of developing caries and periodontal disease.
Diagnostic measures
Clinical examination (examination of the face and oral cavity) is the main type of diagnosis for direct bite. To establish hereditary causes, it is important to confirm or refute the presence or absence of this type in the parents.
In second place in importance are the methods of radiographic examination:
- Orthopantomography (OPTG) .
Panoramic photography with synchronous movement of the beam tube and film around the head, through which a complete image of the teeth, jaws, paranasal sinuses and TMJ is obtained in one picture. OPTG is a basic study that allows you to assess the general condition of the dentofacial apparatus. - Teleradiography . Frontal and lateral photographs of the face, showing the relationship of the jaws and dental arches in the sagittal, transversal and vertical directions, as well as compare the skeletal bones of the face with soft tissues.
- Occlusionography .
Study of occlusal contacts left on thin wax plates when teeth are closed. In this case, there are point contacts in the area of the lateral teeth and linear contacts in the anterior teeth. Excessive contacts manifest themselves as holes in the occlusiogram. If there are no dental contacts, there are no imprints on the wax. - Electromyography .
A diagnostic method that evaluates the electrical activity of the jaw muscles. It is performed using an electromyograph, the electrodes of which react to the electrical potential of the muscles and display its image on the screen. If the potential parameters go beyond the normal limits, this indicates a malfunction of either the muscle itself or the nerves.
Features of direct bite
The main feature of a direct bite is the parallel closure of the jaws, in which the upper incisors do not overlap the lower ones. Other features of a straight bite include:
- increased load on the front teeth;
- violation of the proportions of the lower part of the face (occurs over time if the bite is not corrected);
- clicks when opening and closing the mouth associated with dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint;
- pain in the cervical region and headaches arising from problems with the jaw joints.
Characteristics
The main and only feature of a direct bite is that with it the lower and upper incisors close with their cutting edges.
In all other respects, the orthogenic type does not differ from the orthognathic type and has the following characteristics:
- The midlines between the maxillary and mandibular incisors coincide.
- There are no facial disproportions (the midline of the face coincides with the line between the first and second incisors).
- Speech is clear.
- The chewing process is not disturbed.
- There are no gaps between the teeth.
The contact of teeth with the orthogenic type fully meets the norm:
- The upper canines, with their tubercles, fit between the first premolars and the lower canines.
- The first upper molars have mesiobuccal cusps located in the transverse grooves of the first lower molars.
- The upper lateral teeth overlap the buccal cusps of the lower ones with their buccal cusps, and their palatal cusps fall between the lingual and buccal cusps of the lower antagonists.
- The dental arches of the HF and LF are symmetrical.
- There is a tight occlusion between all teeth except those that have not erupted.
- Physiological rest is characterized by a 2 mm occlusal space.
Causes of direct bite
The main reasons for direct closure of the dentition include:
- Heredity . The position of the jaws and the placement of teeth in a straight bite are often determined by hereditary factors. This type of pathology is more difficult to correct than others.
- Disorders of intrauterine development . Much depends on the condition of the pregnant woman. Bad habits, hypovitaminosis, stress and other unfavorable factors negatively affect the health of the fetus, including the condition of the dental system.
- Artificial feeding and pacifiers . Often, a child develops malocclusion when using pacifiers for a long time.
- Bad habits in a child . Habits such as thumb sucking and other objects negatively affect bite formation. It is important to wean your child off this as early as possible.
Treatment of progenia
Treatment of pathology at a young age
In the early stages of the disease, it is much easier to stop the development of the pathological process.
Treatment of progeny in young children comes down to the following measures in dentistry:
- eliminating factors influencing the formation of malocclusion;
- massage of the anterior zone of the alveolar process located on the upper jaw;
- correction of a shortened frenulum of the tongue;
- combating bad habits (through the use of the vestibular plate);
- normalizing the functions of swallowing, chewing, breathing and speech (using labial activators, training the orbicularis oris muscle);
- artificially establishing the child’s incisors in marginal closure by grinding their cutting edges (the technique is used to treat children under 4 years of age with a slight reverse overlap);
- the use of the Bruckle device and a cap with a chin sling and an extraoral rubber rod to displace the lower jaw (advisable for deep incisal reverse overlap);
- the use of plates with protracting springs located on the vestibular or palatal surface of the central incisors during the eruption of the latter;
- the use of occlusal pads in the presence of incisal reverse overlap not exceeding 2 mm;
- the use of the Wunderer activator, the Bashirova apparatus, the Hoffman activator, the Schwarz double plate, the Andersen-Goipl activator, the functional Boule apparatus and the Frenkel clasp activator for the treatment of severe dentoalveolar types of pathology.
Treatment of pathology in adolescents
Treatment of progenia in persons with a formed permanent dentition requires much more effort and time than treatment of this pathology in children. At the same time, to correct the bite in adolescents in orthodontics, the same devices are most often used as in the period of temporary occlusion, however, dentists in this case opt for the use of fixed devices.
Treatment of the disease in adults
In case of severe progeny in adults, the Brückle apparatus, arc devices with intermaxillary traction and brace systems can be used.
In this case, orthopedic treatment of pathology is reduced to the following measures:
- displacement of the lower jaw teeth lingually, and the upper jaw labially (using a wire ligature, protraction springs and devices operating on the principle of an inclined plane);
- reducing the length of the lower row of teeth by removing some teeth or eliminating spaces between them, as well as lengthening the upper row by moving the front teeth forward;
- sagittal displacement of both dentitions in the required directions.
If necessary, the fight against progeny can be carried out using a combined hardware-surgical method.
Diagnosis of direct bite
Typically, an orthodontist can make a diagnosis based on an external examination alone. However, to clarify the diagnosis and select a treatment method, the patient undergoes additional instrumental studies:
- Occlusiogram - determination of areas of contact between the edges of the teeth. It is performed using special wax plates.
- X-ray of the facial part of the head . Performed in frontal and lateral projection.
- Panoramic radiography (orthopantomography).
- Electromyography is a study of the muscular system.
Types of bite correction in adults
The decision on how the bite will be corrected is made by the attending orthodontist based on data from an orthopantomogram or computed tomography of the jaws. The most common and effective methods of correction are treatment with braces and surgical correction of the bite. When choosing a treatment method, an important role is played by the patient’s age, the complexity of the pathology and concomitant diseases. Depending on this, prices for bite correction also vary.
Correcting overbite with braces
Patients over the age of 30 are most often convinced that in their case, correcting the bite with aligners and braces is impossible. However, this opinion is erroneous; teeth remain mobile throughout life. In adults, bite correction with braces is just as successful. However, an adult patient should be prepared for the fact that orthodontic treatment may take 2-3 years. At the preparatory stage, the doctor can calculate the duration of the correction based on the fact that the teeth of the upper jaw move 0.8 mm per month, the lower jaw - 0.3 mm per month.
Before installing braces, the orthodontist examines the condition of the oral cavity, the structure of the jaws, and specifies the type of bite. It is advisable to install braces in the following situations:
- the presence of individual abnormal units in the dentition;
- pathological bite;
- disproportionately wide interdental spaces;
- presence of impacted teeth;
- change in the line of teeth after the loss of some of them.
Correction of dental deformities takes place in several stages. After a comprehensive diagnosis, complete sanitation of the oral cavity is carried out: treatment of caries, elimination of inflammatory foci, professional cleaning with removal of tartar. Next, the actual installation of the bracket system occurs by attaching clasps to the surface of the teeth and passing arches through them.
The patient is required to regularly visit a specialist to monitor the condition of the dentition, perform cleaning and corrective procedures. As a rule, it takes about 1-1.5 years to correct the teeth line, in severe cases - up to 3 years.
Surgical correction of bite
In orthodontics, as a rule, non-surgical methods are used to eliminate dental defects. However, in some cases, surgery may be required before installing braces. For example, surgical correction of malocclusion is indicated in the following cases:
- pronounced facial asymmetry;
- post-traumatic bone deformities of the jaw;
- congenital pathologies, cross position of the jaws;
- articulation disorders;
- abnormalities of the alveolar processes;
- open bite that cannot be restored in any other way;
- elimination of errors made as a result of other operations.
After surgery, the orthodontist conducts a follow-up examination of the oral cavity and begins further planning and treatment of the patient using braces.
Treatment of direct bite
Straight bite is a problem that can be successfully treated. Modern dentistry has a solid arsenal of techniques for correcting all types of non-physiological bites, including direct bites. Today, treatment of direct bite in adults and children is carried out using special orthodontic structures:
- Braces . This is the main method of correction, allowing you to achieve the desired result relatively quickly. Treatment with braces is recommended to begin in adolescence, when the dental system is not yet fully formed. The type of braces, as well as the duration of wearing them, is selected by the doctor.
- Mouth guards and retainers. Retainers are worn after braces. These designs allow you to consolidate the results achieved with braces. However, both mouthguards and retainers help avoid the severe consequences of a direct bite. In particular, this is excessive wear of teeth.
Prices
| Name of service | price, rub. |
| Preliminary orthodontic analysis: taking an impression from one row of teeth, making a working model, orthopantomogram analysis, photographic examination | from 4000 |
| Correction of malocclusions and tooth position using a simple plate | from 19600 |
| Fixed appliance (braces) for correcting the position of the front teeth | from 40000 |
| Standardized positioners (Myobrace, LM-activator) | from 14000 |
| Vestibular plates (Dr. Hinz Dental) | from 7000 |
| Repeated (control) visits during treatment with removable devices | from 890 |
| Repeated (control) visits during treatment with fixed devices | from 1740 |
| Repairing a removable device | from 2620 |
Consequences
The main danger of a direct bite is accelerated wear of teeth. This happens despite the fact that enamel is considered one of the strongest biological materials. With constant contact between the cutting surfaces of the teeth, hard tissues are quickly destroyed, unable to withstand the load.
Let's look at the typical consequences of a straight bite:
- Toothache . With the destruction of hard tissues, teeth begin to hurt over time. It is advisable not to let it get to this point, but to consult a doctor as soon as a defect is discovered.
- Tooth decay . Sometimes people with a straight bite refuse to acknowledge the problem until their teeth are completely destroyed. In this case, the only way to help is with prosthetics.
- Aesthetic problems . Initially, a straight bite really looks beautiful. However, as teeth wear down, the smile deteriorates. The length of teeth can be reduced by 35-40%, which leads to aesthetic defects.
- Caries . Destruction of hard tooth tissues significantly increases the risk of developing caries. In turn, caries only accelerates the process of destruction due to the action of organic acids secreted by bacteria.
- Periodontal disease . The addition of an infection is fraught with the development of gum disease. Against the background of tooth wear and caries, periodontal disease often develops.
- Disorders of the temporomandibular joint . This leads to characteristic clicking sounds when opening and closing the mouth. Later, when working with the jaws, pain occurs. In addition, dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint leads to deterioration of hearing and diction.
Important . It is difficult to predict the above complications. In this regard, doctors strongly recommend correcting malocclusion as soon as possible.
Bite pathologies are present in approximately 80% of the world's population. For some people, incorrect alignment of the dentition causes serious functional (difficulty in chewing, pain when opening the mouth, clicking in the temporomandibular joint) and aesthetic disorders, while for others the problem is less pronounced. In any case, an incorrect bite not only contributes to the disruption of the beauty of a smile, but also has a detrimental effect on health. Incorrect position of the teeth triggers a restructuring of the musculoskeletal system, slowly adapting muscles and ligaments to the changed “comfortable” position of the dentofacial apparatus. In addition, bite pathologies in most cases disrupt the processes of chewing food, so patients with dental anomalies often experience problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
Incorrect bite leads to a large number of problems in the oral cavity. Inflammatory periodontal diseases, the appearance of increased tooth sensitivity, abrasion, chipped restorations - all this can occur if the teeth occupy an incorrect position in the dental arch.
To correct imperfections in your smile and straighten your teeth, contact orthodontist Irina Butorina.
What kind of bite should a person have?
Occlusion is the nature of the juxtaposition of the dentition during the habitual closure of the jaws.
There are physiological and pathological types of occlusion. Physiological:
- Orthognathic is the most correct bite, in which there are close contacts between the teeth and dentition, as well as 1/3 of the crowns overlap the lower dentition with the upper one.
- Progenic – a bite in which the lower jaw is slightly pushed forward.
- Straight bite - a bite in which the teeth of the upper and lower jaws touch the cutting edges and cusps in the usual occlusion.
- Biprognathic - a bite characterized by an inclination of the crowns of the teeth towards the vestibule of the mouth.
Physiological types of occlusion are not capable of leading to disturbances in the dental system, therefore they are considered as a variant of the norm.
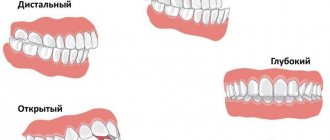
Pathological:
- Deep – a type of bite in which the upper teeth overlap the lower teeth by more than 1/3 of the crown;
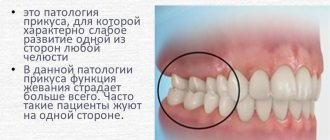
- Crossbite – a bite in which the upper teeth overlap the lower teeth in one segment, and vice versa in the other.
- Open bite – characterized by non-occlusion of the teeth in the position of central occlusion.
- Distal – a bite characterized by a large upper jaw.
- Mesial - a bite in which the lower jaw moves forward.
Pathological types of bite can cause serious disturbances in the functioning of the masticatory apparatus, as well as spoil the aesthetics of a smile.
Is it possible to determine the type of bite yourself? In most cases, this is very difficult to do, so it is better to consult a qualified orthodontist.
Butorina Irina Aleksandrovna is an orthodontist with more than 14 years of experience. The doctor has more than 1000 grateful reviews from patients who have already entrusted the specialist with transforming their smile!
Causes of dental deformities
Dental deformations are violations of the location of teeth in the dental arch, which lead to improper distribution of chewing pressure and worsening oral health.
The main causes of dental deformation in childhood are:
- Hereditary predisposition. In some cases, if parents have an incorrect bite, it is genetically passed on to the child.
- Using the wrong pacifiers and nipples for feeding. The feeding hole of the bottle should be at the bottom so that the baby can keep his tongue in a natural position while sucking. Pacifiers should be very thin at the base so that the baby's teeth are in a closed position.
- Using pacifiers after one year/Breastfeeding after one year. Prolonged sucking can lead to the formation of an infantile type of swallowing. In this case, the tongue “gets used” to resting on the teeth and gradually pushing them out.
- Poor oral hygiene. The accumulation of large amounts of plaque in the oral cavity contributes to the formation of caries. In childhood, all carious processes develop rapidly, so they very quickly turn into complicated forms. Unfortunately, some forms of complicated caries cannot be cured conservatively, so teeth have to be removed long before the physiological change. Early removal of baby teeth can lead to crowding of permanent teeth.
- Caries of milk teeth. If the caries of a temporary tooth is not treated in time, the infection can spread to the permanent tooth. This will manifest itself as a change in the shape, shade or size of the permanent tooth.
- Mouth breathing.
- Diseases of the ENT organs.
- Bad habits (finger sucking, holding foreign objects in the mouth, biting cheeks and lips, etc.).
- Postponed rickets.
- Diseases of the nervous system.
- Mother's illnesses during pregnancy.
The main causes of dental deformation in adulthood:
- Bad habits (biting a pen, biting a thread, etc.).
- Traumatic injuries.
- Long-term absence of one or more teeth in the oral cavity.
- Increased tooth wear.
- Impaired bone density.
- Diseases of periodontal tissues.
- Eruption of wisdom teeth.
What are crooked teeth?
For most people, crooked teeth are teeth of irregular shape, size, or those that are very different in position in the dentition.
But the curvature of teeth can be different. There are three main groups of deformations: dental anomalies, dentition anomalies, and dentition relationship anomalies. The first group includes individual teeth that differ in shape, size or shade from the rest of the dentition. The second group includes deformations formed during the eruption of several teeth at once, which violate the aesthetics of the entire dentition. The third group is deformations that occurred at the level of the jaws and entail their incorrect closure. Bite pathologies can appear at any age, so the process involves both permanent and temporary teeth.
Temporary teeth Often temporary teeth erupt with some curvature, but gradually take the correct position in the jaw. This feature is associated with intensive growth and development of the jaw bones in childhood. Unfortunately, in some cases, temporary occlusion is subject to the following defects: crowding of teeth, delayed eruption, early tooth loss, open bite, etc. All this can be avoided if you consult an orthodontist in time. The first visit for the purpose of prevention can be made at the age of 2 years.
Permanent teeth The eruption of permanent teeth largely depends on the condition of the temporary occlusion. In order to correct the condition of permanent occlusion in a timely manner, it is important to consult an orthodontist for a consultation.
Do I need to correct crooked teeth?
It is necessary to correct uneven teeth for the following reasons:
- An incorrect bite creates a functional overload on certain groups of teeth, which entails their rapid destruction;
- Deformations of the dentition lead to disruption of the normal functioning of the temporomandibular joint, hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles and overload of periodontal tissues;
- Crooked teeth are more susceptible to caries than others, and they are difficult to treat due to their incorrect position in the dental arch;
- An incorrect bite can cause problems in the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory system.
Orthodontist Irina Aleksandrovna Butorina will help correct the position of the teeth. You can make an appointment with a specialist by calling 8 926 203 32 32.
Up to what age is correction possible?
Many people believe that bite correction can only be done in childhood.
This opinion is not entirely correct. Modern orthodontics allows you to correct the condition of the dentofacial apparatus at any age, so there is no longer a time period for acquiring a beautiful smile! However, it should be understood that different age groups require completely different approaches to treatment. For example, in children, orthodontic treatment is faster and easier, since the dentofacial apparatus is at the stage of formation. Adult patients require longer treatment because their jaws have finished growing.
Overview of correction methods
You can correct crooked teeth using the following methods:
- Removable/fixed orthodontic structures (braces, aligners, plates, mouth guards, trainers, etc.);
- Surgery;
- Restoration of dental defects.
But how not to make a mistake when choosing a treatment method?
The orthodontist chooses methods for correcting malocclusion individually in each case. The choice depends on the patient’s age, as well as the growth characteristics of the components of the dentofacial apparatus. For example, in childhood, the facial part of the skeleton has not yet completed its growth, so all stages of orthodontic treatment should be aimed at stimulating the correct development of the jaws. For these purposes, the orthodontist may prescribe wearing special removable or non-removable structures, as well as performing certain exercises to strengthen the muscles of the oral cavity.
The teenage period is characterized not only by hormonal changes in the body, but also by a change in bite. Jaw growth continues, so it is important to properly influence the structures of the maxillofacial apparatus. During this period, plates can be fixed to temporary teeth, and braces can be placed on permanent teeth.
Gradually, jaw growth stops. This usually happens by age 21. The condition of a permanently formed bite can be corrected with the help of braces, aligners or surgical operations (in more complex cases). Sometimes for effective treatment it is necessary to combine surgery with wearing an orthodontic appliance.
For minor tooth curvatures that do not cause functional impairment, orthodontic treatment can be avoided. In this case, it is necessary to restore the tooth using veneers, crowns or filling material.
How long does it take to straighten teeth?
Only a specialist can establish specific terms for orthodontic treatment after examining the oral cavity and carrying out diagnostic measures. On average, the duration of therapy with an orthodontist lasts from one to three years.
Prevention of crooked teeth
It is important to prevent the appearance of crooked teeth from a very early age. Parents should follow the following recommendations:
- Visit an orthodontist for preventive examinations from the age of 2-3 years at least once a year.
- Avoid pacifiers/pacifiers/breastfeeding if the child is over a year old. For up to a year, use only orthodontic pacifiers and pacifiers.
- Perform lip and tongue frenuloplasty in a timely manner on the recommendation of an orthodontist and pediatrician.
- Attend preventive dental examinations, as well as professional oral hygiene procedures at least once every six months.
- Treat caries and its complications in a timely manner.
- Eliminate bad habits (chewing a pen, biting threads, etc.).
- Gradually introduce solid foods into complementary foods.
- Learn to use a sippy cup.
- Starting from the first tooth, brush your teeth with a brush and toothpaste in the morning and evening. Hygiene products should be selected according to age.
- Rinse your mouth after every meal.
- Perform myogymnastics exercises (as recommended by the orthodontist).
- Treat diseases of the ENT organs in a timely manner.
- Follow a balanced diet, which will be dominated by fresh fruits and vegetables.
Conclusions. Expert advice
Bite defects can appear at any age for a huge number of reasons.
Currently, such imperfections can be eliminated if you consult an orthodontist in time. The specialist will draw up an individual treatment plan and restore the beauty and charm to your smile! An orthodontist in Moscow, Butorina Irina Aleksandrovna, has been correcting malocclusion for more than 14 years. The specialist has a large number of positive reviews from patients who have already entrusted their health to her!
You can make an appointment for a consultation with Irina Alexandrovna by calling 8, 8 926 203 32 32.
The specialist conducts consultations at the address: metro Botanical Garden, Lazorevy proezd 3, DentalArt Clinic
Prevention
We can talk about preventive measures regarding direct bite if the child does not have a genetic predisposition to this anomaly. You can reduce the likelihood of developing an abnormal bite by adhering to the following recommendations:
- Adequate nutrition for a woman during pregnancy . It is important that a woman consumes enough calcium. This element is found in broccoli, dairy products, and sesame. A sufficient amount of calcium is important for the health of your baby's bones and teeth.
- Natural feeding. Keep your baby breastfed for as long as possible.
- No bad habits. These include thumb sucking or an obsession with pacifiers and bottles with pacifiers. Often against this background, children develop mouth breathing, which changes their bite.
- Balanced nutrition for a child . The child’s menu should have enough protein, vitamins and minerals. Try to minimize the consumption of simple carbohydrates (sugar, sweets, flour).
- Regular examinations with a doctor . Take your child to see a doctor twice a year.
Factors in the development of anomalies
The circumstances contributing to the formation of orthogenic occlusion at an early age include the following factors:
- Genetic predisposition of the body, caused by heredity;
- Unfavorable conditions accompanying gestation and the birth process;
- A long period of artificial feeding, with the formation of a pacifier habit;
- A shift in emphasis to mouth breathing due to frequent illness;
- Development of bad habits typical of young children;
- Mechanical damage that disrupts the natural structure of the jaw.
Practice shows that treatment of direct bite is not a prerequisite, since this form is not considered as an immediate pathology. However, with such a development, strict monitoring of the condition of the oral cavity and dentition is recommended, eliminating the likelihood of anomalies. Possible complications associated with orthogenic malocclusion include:
- Destruction of the structure of the enamel layer, leading to increased tooth sensitivity;
- Excessive load on the dentition, leading to bleeding, pain, development of pathologies and inflammatory processes;
- Reduction in the length of the frontal units, caused by abrasion of the crowns, disrupting the aesthetics of the smile, as well as distorting facial features;
- TMJ dysfunction, requiring special complex treatment.
Regular hardware diagnostics, including orthopantomogram, radiographic examination, as well as occlusal and electromyography, allow you to avoid dental problems characteristic of direct bite.
Treatment of direct bite at the CIS clinic
At the Israeli Dentistry Center, straight bites are treated by experienced orthodontists. Our clinics on the Left Bank (Kyiv) are equipped with modern diagnostic equipment that allows us to establish an accurate diagnosis. Based on the data obtained, we select individual treatment for each patient.
Treatment with braces for direct bite: before and after
Correcting dental malocclusion with aligners
At the patient's request, we will provide treatment with Damon braces, but we will always offer a worthy alternative - removable Invisalign aligners. Only they guarantee truly invisible and comfortable correction of bites of any complexity.
Using Invisalign aligners, PROBLICUS orthodontists successfully treat all bite pathologies that can be corrected with braces. We were the first in Russia to work with aligners.
The results and timing of treatment with aligners are always predictable: our patients know on what day the bite correction will be completed. Even before treatment begins, the orthodontist shows the patient what his ideal smile will look like.
FAQ
Is it possible to correct a straight bite on your own?
On the Internet you can find various massage techniques and exercises that supposedly will help correct your bite. Such methods are not only ineffective, but also harmful. Under no circumstances should you resort to self-medication, especially when you do not know the exact diagnosis. To identify the problem and solve it, be sure to consult a doctor.
Is it possible to live with an incorrect bite?
It's possible, but not necessary. Above we have provided a list of complications and adverse consequences of direct bite. Any other malocclusion is also fraught with the development of complications. Correct bite is the key to healthy not only teeth, but also other organs and systems.
How does your bite affect your appearance?
It all depends on what kind of bite we are talking about. For example, a shortened upper jaw or a massive lower jaw makes the face angry and disproportionate.
How much does straight bite treatment cost?
The price depends on the volume and complexity of the treatment. As a rule, the cost of treatment is discussed in detail after diagnosis, when doctors understand the patient’s treatment strategy.
Advantages of treatment with us
| Traditional approach | Our (integrated) approach |
| The goal of treatment is “to turn a malocclusion into a correct one” | The goal of treatment is not simply to “correct the bite.” The art of an orthodontist is to correctly close the “aligned” teeth, taking into account all the characteristics of the patient’s body (posture, etc.). After all, a bite (closing of teeth) is essentially a kind of “lock”. And in this regard, it is important - which patient (with what posture, for example) we will “clog” with a new bite.” |
| Relying on the fact that the device (for example, braces) will correct the bite itself | We don't rely only on equipment. It is not she who treats, but the doctor (braces are just a tool). |
| The work is most often done “by eye”, without proper diagnostics. And without a diagnosis (“bad bite” is not a diagnosis, it is a consequence of the problem). | We always find out the cause; we have a well-established diagnostic algorithm. And we always know what we are ultimately treating (there is a clearly formulated diagnosis). |
| Often there is no treatment plan. | Treatment planning. |
| Working according to the “template”: “put braces on, wear them for a year or two, get results”, in essence, work with the investigation (bad bite). | We work not with the consequence, but with the cause of the problem (anomaly). The cause is always insufficient jaw size. Insufficient jaw size is a consequence of problems with the skull. |
| The root cause remains unidentified and unresolved. High percentage of relapse (the anomaly returns). | Before correcting the bite, we always eliminate the root cause of the problem - we work with the skull and jaws. Therefore, there are no relapses (the problem is eliminated at the root). |
| Work with one device: either a plate or braces. | We are not limited by any limits in the field of hardware treatment. We have a full range of the most modern orthodontic devices in our arsenal. We practice multi-stage treatment. And for each stage there is its own apparatus. |
| Treatment involves the removal of teeth (usually premolars), which often leads to complications. | We do not correct bites with tooth extraction (the percentage of treatment with tooth extraction in our clinic is 0.01%). And not because we are “kind”, we just know how to find an alternative to treatment that involves removing teeth. |
| A large percentage of patients are sent for surgery (orthodontists often do not see a “way out”). | We know how to look for an alternative to surgery (success in 99% of cases). |
| If surgical treatment is necessary, the patient often undergoes surgery without proper preparation, which is fraught with complications. | If surgical intervention is necessary, careful preparation for it (stabilization of the TMJ, development of dentition, support after surgery, etc.). |
| Large prepayments for treatment (the popular scheme is 50% prepayment). No installment payments. | Small prepayments. Each stage (the entire treatment is divided into stages) is paid in installments. A successful treatment access program. |
| Lack of differentiation based on treatment complexity. The cost of treatment depends only on the type of equipment (for example, what kind of braces to treat - metal or aesthetic). | Different amounts of work (treatment) cannot cost the same. Clear differentiation of the cost of treatment depending on the complexity of the treatment and the type of device. |
| Providing “one-time services”: gluing and removing braces, changing the arch, etc. For this reason, it is difficult to predict the cost (no one knows how many and what services will be provided during treatment). | We do not provide “one-off” services. Therefore, do not ask us “how much does it cost to put braces on your teeth” or “how much does it cost to correct a bite in adults?” We don’t “install” - we treat. From and to. We have “package” offers. And the patient always knows the cost of treatment (treatment stage), which is convenient for budget planning. |
| Often there is a lack of prevention: “Come when your teeth grow in, we’ll put on braces and fix it.” And wasting time can be costly. | Prevention (it’s easier to prevent than to fix later). We don’t have a goal to “deliver” anything. We identify the cause of malocclusion and eliminate it at any age. |