Varieties
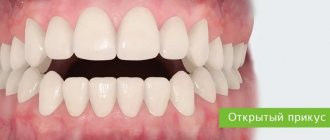
Incisal disocclusion is a general concept. It combines various phenomena in which the dentition in the frontal part does not close correctly.
Orthodontists distinguish the following types of incisal anomalies in the sagittal plane (divided into right and left sides):
- sagittal disocclusion – there is no contact between surfaces, this can occur due to abrasion or a change in the angle of inclination;
- direct occlusion - contact of the incisors of the lower and upper jaws with their cutting surfaces;
- reverse occlusion - the lower incisors are pushed forward, but the contact between the upper and lower dentition in the frontal zone is maintained;
- reverse disocclusion - the lower incisors are pushed forward so much that they do not contact the upper ones.
Incisal closure anomaly in the vertical plane:
- vertical disocclusion - the upper incisors are pushed forward, there is no contact between the antagonist teeth;
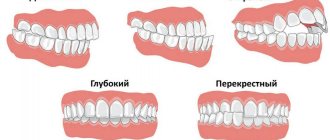
- deep occlusion – vertical overlap in the frontal area is more than 1/3;
- deep disocclusion - the overlap is the same as in the previous case, but there is an open gap.
In addition, there is the so-called false incisal disocclusion. It occurs due to injury, loss of teeth during an accident, etc.
How to fix an open bite
To prevent deformation of the dentition, their destruction due to mechanical pressure on each other, the appearance of caries and diction disorders, it is recommended to correct the bite from early childhood. Many patients experience fear due to discomfort when wearing braces. These structures are uncomfortable and require regular correction. Not many people know about a painless alternative to braces - aligners.
Sign up for free 3D modeling of your future smile!
Make an appointment
*By making an appointment you consent to the processing of your data
Essentially, this is a therapeutic mouthguard used for a corrective and fixing effect. They are made from soft polymers that are safe for humans. Aligners help move teeth in the desired direction. The patient is recommended to wear the device for up to 20 hours a day, removing it only for hygiene procedures and while eating. The product is easy to put on and take off. Another advantage of aligners over braces is that they are completely transparent and invisible to others. The average correction period is 3-6 months; to correct complex violations it will take up to a year. During long-term treatment, the aligners are replaced with a new set every 2-3 months.
Symptoms
The orthodontist sees all of the above anomalies during a visual examination of the patient’s oral cavity. The absence of normal closure in the frontal or lateral region is determined; a vertical gap may be observed.
Anatomical features cause various functional abnormalities. Patients with incisal disocclusion experience a number of symptoms:
- Violation of the parameters of the lower third of the face. Disproportions can be noticeable both in profile and in frontal view, but in profile they are usually more pronounced. The lower third of the face can be significantly reduced, an effect that makes the supramental fold appear enlarged. The nasolabial folds are smoothed out, and the angle of the lower jaw becomes larger, sometimes approaching 90°.
- Various diction disorders. The most strongly distorted dental consonants are hissing and whistling sounds. If the occlusion is maintained, speech is less affected.
- The process of swallowing saliva and food is disrupted, so overstrain of the muscles involved in lowering and raising the corners of the mouth develops; the orbicularis oris muscle becomes enlarged due to the constantly increasing load.
The stronger the degree of pathology and the larger the size of the vertical gap, the more pronounced all of the listed signs are. Even if they are not developed at the initial stage, over time all symptoms gradually worsen.
Signs
Visual signs of an open bite:
- a downwardly displaced chin and an enlarged lower part of the face;
- half-open mouth;
- the upper lip is narrow and tense at the moment of closure;
- the sky is shifted down and back;
- the nasolabial fold is smoothed.
Intraoral symptoms:
- vertical interdental gap;
- the first molars close in their normal position, but the incisors do not;
- trapezoidal shape of the lower jaw;
- the jaw arches narrow;
- crowding of the lower incisors due to lack of space;
- the height of the lateral parts of the jaw is greater than usual;
- the mucous membrane is often inflamed, the gingival papillae are deformed;
- macroglossia (enlarged tongue).
Lisp and slurred speech are also one of the signs of pathology. The patient breathes frequently through his mouth. Swallowing is infantile. It is difficult for him to bite off due to a violation of the closure of the teeth and chew food.
Causes
The appearance of malocclusion in the incisal zone occurs due to an increase in the angle of incisor inclination, reduction of one jaw in the frontal zone, lengthening of the lateral sections of the dentition, as well as due to protrusion of the lower or upper teeth.
All causes of these disorders are divided into primary and secondary. Primary ones are those that appeared at the time of fetal development, and secondary ones develop after birth.
Primary reasons:
- Hereditary factor - inheritance from one of the relatives or arising due to an unsuccessful combination of characteristics (for example, having a small jaw, like mom, and a large slope of teeth, like dad).
- Disruption of the formation of dental buds due to chromosomal mutations or unfavorable pregnancy - maternal illness, the effects of heavy medications, unfavorable environmental conditions, certain diseases during gestation, etc.
- Macroglossia is an increase in the size of the tongue.
- Shortened lip frenulum or short tongue frenulum.
Secondary causes:
- Bad habits - sucking fingers, sucking various objects, biting the upper or lower lip, etc. In preschoolers, the presence of such bad habits can lead to the development of pathology in record time, starting from one month.
- Mouth breathing, which becomes constant due to adenoids, chronic nasal diseases, allergic reactions, aggravated by rhinitis.
- Incorrect placement of the tongue in the oral cavity, which displaces the floor of the mouth and leads to impaired load on the muscles.
- Deep or multiple caries of the incisors, which leads to tooth protrusion.
- Metabolic disruptions – disturbance of mineral metabolism, rickets, osteomyelitis, etc.
- Hypovitaminosis.
- Weakened immunity due to frequent or chronic diseases - dyspepsia, exudative diathesis, staphylococcal infection, etc.
Diagnostics
Despite the fact that incisive disocclusion is determined by the dentist even during a routine examination, it requires detailed diagnosis. This need is necessary in order to identify the causes of the pathology and prescribe an effective course of treatment.
During diagnosis, the patient may be prescribed:
- X-ray of the frontal zone to detect unerupted teeth or other anomalies hidden in the mucous layer or in bone tissue.
- Orthopantomogram images allowing to assess the condition of the dentition in all areas.
- Profile and frontal photographs to measure the patient’s anthropometric parameters.
- Casts of the dentofacial apparatus. On the model, which is manufactured in a technical laboratory, more accurate measurements of all the necessary parameters are performed.
Measurements of the size and length of the gap between the upper and lower teeth are of decisive importance, since these parameters indicate the severity of the disorder.
FAQ
Why is an open bite dangerous?
This anomaly is dangerous not only due to the presence of an aesthetic defect, but is also a threat to the general health of a person. Gastrointestinal disorders, respiratory diseases, pain in the jaw joints - this is not the entire list of complications that abnormal bites lead to.
What happens if an open bite is not treated?
Abnormal bites will not correct themselves. The situation will only get worse. Teeth under increased stress will deteriorate until they are completely lost. In this case, the problem can be solved with prosthetics, but this can also be problematic until the bite is corrected. Therefore, you should not delay correcting abnormal bites. And it is advisable to do this as early as possible. In children and adolescents, the dentofacial apparatus is not yet fully formed, which increases the chances of doing without surgery.
How long does it take to treat an open bite?
It all depends on the severity of the disease and what treatment methods were chosen. If we are talking about orthodontic treatment, then this is 1.5-2.5 years. It is possible to increase the treatment period if the dynamics of changes lag behind those expected. Remember that after braces there comes a retention stage during which you need to wear retainers.
How much does open bite treatment cost?
The cost of open bite correction is influenced by the following factors: severity of the disease, type of treatment (orthodontics and/or surgery), dental clinic and others. As a rule, the price for treatment is announced to the patient only after diagnosis.
Treatment
The course of treatment is prescribed based on the clinical picture and age of the patient. The approach differs at the time of primary, replacement and permanent set of teeth.
Temporary kit
Often, to completely restore the physiological state of the dentition and eliminate incisal disocclusion, it is enough to eliminate bad habits. A return to normal may occur within four months or six months.
In almost all cases, treatment in children includes myogymnastics, which, when used temporarily, demonstrates the highest effectiveness. It is based on performing individual exercises that tone the facial and chewing muscles. This technique can significantly change the proportions of the dentofacial apparatus. Myogymnastics can be prescribed as an independent remedy or in combination with other methods.
If the cause of the pathology is shortening of the frenulum of the lips or tongue, its plastic surgery is performed. This surgical treatment is not considered difficult and is performed under local anesthesia. After the procedure, the patient is immediately sent home and his condition is monitored on an outpatient basis.
For incisive adentia, the use of therapeutic and prophylactic children's dentures is indicated. An automatic sliding prosthesis can be used, which increases as the child grows. Fixed structures must be changed at intervals determined by the doctor.
If the cause of the incisal closure anomaly is protrusion, the damaged teeth are restored. Sometimes silicone mouth guards are prescribed, which activate the development of the jaw and palate, while simultaneously leveling the angle of the teeth.
Replacement kit
During the replacement set period, disocclusion is eliminated relatively quickly. There are several most common treatment methods:
- Katz plate with bite pad in the incisal area. The base rests on the palate, and clasps are attached to it. The size, angle and thickness of the bite pad are determined by the orthodontist. Its function is to increase pressure and load on the alveolar process of the jaw.
- Muleman Propulsor . This is a two-jaw functional appliance that combines the functions of a vestibular plate for the upper jaw and an activator for the lower jaw. The support falls on the teeth and alveolar processes. The Muleman Propulsor is a removable device. Most often recommended for ages 7-9 years for use during nighttime sleep. In addition to normalizing the condition of the dental system, it helps to get rid of bad habits - finger sucking, lip biting and mouth breathing, and forms the correct position of the tongue.
- Frenkel function regulator . Types I and III designs are used. They are complex devices based on a rigid metal frame and plastic shields. In most cases, it involves use at night plus a few hours during the day.
- Functional apparatus Myobrace . Constructed from a rigid inner frame and soft outer silicone. Using Myobrace eliminates the need for braces. The advantage is comfort and convenience, gums and soft tissues are not chafed or irritated. The devices are available in standard sizes, from which the orthodontist selects the appropriate ones.
Permanent kit
During this period, restoration of occlusion lasts longer than at a younger age. It can be performed using orthodontic, orthopedic or surgical methods.
The most commonly used orthodontic treatment is wearing braces. This approach is aimed at gradually returning the physiological position to the incisors of the upper or lower jaw. The doctor determines the force with which the arch should press on the teeth. Braces are made according to individual parameters and can be worn from six months to three years. After removal, a retention period follows, during which the result is secured using silicone retainers.
In the case of the traumatic nature of the pathology, prosthetics are necessary - the installation of prostheses or implants is prescribed.
In severe cases, surgery is necessary to enlarge or reduce the palate or eliminate pathologies of the alveolar process. Such operations are performed in a maxillofacial surgery hospital under general anesthesia. Surgeries of this type are quite serious, so after them the patient must remain in the hospital for some time. Sometimes these operations precede the wearing of braces. Surgical methods can also be used to remove an impacted tooth.
Result
Photos before and after correction of the anomaly illustrate the possibilities of modern orthodontics. In most cases, it is possible to correct the bite, change facial features, and get rid of functional disorders. A competent orthodontist will select the optimal correction method. The patient must strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations and come for examination on time. The results of treatment last a lifetime. To consolidate the effect, after removing orthodontic appliances, retainers are installed on the inner surface of the teeth to prevent the incisors from returning to the wrong position.
Refusal of treatment
Malocclusion in the incisal region leads to various complications. First of all, conversational speech is disrupted, which entails the appearance of complexes in a child or an adult. The compensatory mechanism causes the facial muscles to be in constant overstrain, which causes myalgia or inflammation of the facial nerves.
Due to poor quality of biting and chewing food, various digestive disorders are possible. Dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint may develop, which causes blocking of the movements of the lower jaw. This phenomenon causes frequent or even constant headaches.
The periodontium in the frontal group is constantly under overload, so it begins to quickly wear out. Improper load distribution leads to injuries to the soft tissues of the upper palate.
To prevent the development of all these complications, treatment should be carried out at the initial stages of the development of the anomaly.