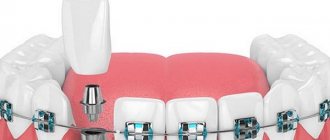
Braces allow you to correct your bite not only for children, but also for adults. It is much easier for the younger generation to straighten their teeth and form a beautiful smile, since their jaws are still growing and their teeth move quite quickly. And children and teenagers have fewer problems getting used to braces.
Adults have to spend more time and make significant efforts to form an attractive set of teeth and finally begin to smile openly and without embarrassment. Therefore, very often, during a consultation with a dentist, patients who need a quick and inexpensive bite correction ask the question: “Is it possible to straighten teeth using metal-ceramics?”
Is it possible to correct a bite without orthodontic systems?
Orthodontic treatment is aimed at correcting serious deficiencies: straightening protruding or misaligned teeth, reducing interdental spaces, and ultimately correcting all types of malocclusions. To do this, braces change the position of teeth in three planes at once, simultaneously affecting bone tissue and dental ligaments.
Patients who do not want to spend a lot of time wearing braces can indeed undergo dental prosthetics in Moscow . At the same time, the attractiveness of the dentition will be restored, since the teeth will look even and beautiful, and the gaps between them will be hidden by dentures. But it will not be possible to eliminate all the consequences of an incorrect bite, since a denture does not allow changing the incorrect location of the tooth roots, and therefore does not eliminate the root cause of the anomaly.
In this case, it is more correct to talk not about bite correction with dentures, but about the prompt restoration of the natural dentition and the correction of its individual defects. There is a special name for the corresponding technologies in dentistry - microprosthetics.
Basis of construction
Determining the height of the bite is based on assessing the distance between the jaws when fully closed, which makes it possible to determine the correct development and location of the elements of the dentition. The presence of defects leads to a displacement of the main anatomical components of the jaw region - the lips recede, the facial folds increase, the chin protrudes, and the height of the lower part of the face decreases. Increasing the height of the bite restores aesthetics and facilitates further therapeutic measures.
Veneers and inlays - modern types of dental prosthetics
A partial alternative to orthodontic structures can be elements made from high-tech ceramics, which allow:
- restore the integrity and functionality of the tooth;
- change its shape or “turn” around its axis;
- eliminate chips on its surface;
- visually reduce the large gap between the front teeth;
- restore the dentition when one or two teeth are lost (adhesive prosthetics).
The cost of microprosthetics is quite affordable, considering that along with the rapid restoration of the aesthetics of the dentition, the chewing ability of the teeth is also restored. Modern technologies make it possible to produce ceramic inlays and veneers that are indistinguishable in color and shape from the patient’s healthy teeth. Microprostheses are made by a dental technician using an individual impression, so they fit tightly to the surface of the teeth and have a long service life. It is also important that when microprosthetics is applied to a tooth, its healthy neighbors are not subjected to treatment and do not experience additional stress.
Quick appointment Free consultation
Reasons for the development of anomalies
Factors that have a negative impact include:
- Pathological changes in the structure of tooth enamel, leading to accelerated abrasion and loss of tissue density;
- Uncontrollable grinding of teeth during sleep (bruxism);
- Incorrect distribution of chewing load, leading to displacement of units;
- Partial edentia on one or both jaws;
- Metabolic failure, causing a deficiency of useful minerals, primarily calcium and phosphorus;
- Long-term wearing of low-quality replacement structures.
Correct production of dentures requires modern equipment and a comprehensive examination carried out under conditions that ensure complete physiological rest of the jaw apparatus.
Ceramic inlay - microinsert that replaces a filling
As you know, before filling a tooth affected by caries, the doctor first excises its non-viable tissue. Therefore, in case of secondary caries, when the filling has to be re-placed, due to the significant size of the cavity, the tooth is already practically destroyed. The patient is recommended to undergo depulpation and cover it with a crown.
Recurrence of caries occurs due to the lack of proper sealing between the walls of the tooth and the composite filling, which decreases in volume during polymerization. The ceramic inlay is free of this drawback; it is manufactured individually with high precision and therefore fits tightly to the tooth. The ceramic material of the inlay does not shrink and does not change color or shape during use.
Microprosthetics with inlays is performed on teeth whose defects make up up to 30% of the volume of their coronal part, and allows you to create exact copies of teeth with the correct shape of the chewing surface.
Treatment
On the first visit, a minimally invasive preparation of 9 teeth of the upper jaw was carried out, which took no more than 60 minutes, that is, about 7 minutes per tooth, which, in our opinion, is a lot, since the preparation was minimally invasive (Fig. 4). The bite is fixed in the usual occlusion with the first layer of silicone impression material. In the frontal region, the impression mass is removed before it hardens, which allows for visual control of the position of the lower jaw in relation to the upper jaw and subsequent optical registration of the bite (Fig. 4).
Rice. 4.
A light-curing composite was used to directly restore the lost tissue of the two central maxillary teeth, after which the patient was asked to close his mouth. The lower jaw teeth were inserted into the grooves of the impression material until the composite contacted the lower teeth, and the new position of the jaws was registered virtually. Thus, the position of the lower jaw in relation to the upper jaw remained stable, without deviation from the usual occlusion, and the height increased by the size of the temporary restorations (Fig. 5).
Rice. 5.
Virtual modeling of teeth is a simple procedure, since everything happens automatically and only in some cases does a doctor’s intervention be required. In this case, modeling of 9 teeth took no more than an hour, milling of 9 restorations took just over two hours, glaze firing took two times for 15 minutes, fixation, occlusal correction and polishing of the occlusal surface took just over two hours: total time was six seconds. half an hour, if you add one hour for preparation. But the patient’s appointment time is reduced due to the fact that all stages, except preparation, occur not sequentially, but in parallel; The fact that the dentist has two well-trained assistants further reduces the appointment time.
For example, the 26th tooth is virtually modeled, a ceramic block of the required size and color is inserted into the milling machine, and the milling process begins. And at this time, teeth 25 and 24 are modeled (Fig. 6), after milling the 26th tooth, its fitting is carried out, the approximal and distal contacts are checked, and the restoration of the 25th tooth is milled in parallel.
Rice. 6.
When 3-4 restorations are ready, with verified approximal contacts, glaze is applied, and these restorations are sent for glaze firing. At the same time, the stages of virtual modeling, milling, fitting and fixation of the remaining restorations continue (Fig. 7).
Rice. 7.
After the glaze firing, the restorations are cemented with DUO CEMENT VITA. After fixing all restorations, the teeth are ground according to occlusion and the areas to be corrected are polished.
Thus, in this clinical case, the total time of the first appointment was 4 hours 45 minutes (Fig. 8). To control the parallelism of the line of occlusion and the line of the pupils, the “smile design” option was used (Fig. 9, 10).
Rice. 8.
Rice. 9.
Rice. 10.
VITABLOCS TriLuxe forte 2M2 was chosen for the restoration. These blocks consist of four layers that differ in color intensity. In this clinical case, this made it possible to create natural color shades, as in the structure of a natural tooth, due to a subtle color transition from the enamel to the cervical layer with a more emphasized color in the lower part of the dentin and neck (Fig. 11, 12).
Rice. eleven.
Rice. 12.
At the second visit, it was planned to complete the prosthetics, but when the appointment time exceeded 5 hours, it was decided to postpone the restoration of the two remaining teeth, 32 and 33, to the next appointment. The preparation was also minimally invasive (Fig. 13-15). On the third visit, the work was completed (Fig. 16, 17).
Rice. 13.
Rice. 14.
Rice. 15.
Rice. 16.
Rice. 17.
Conclusion
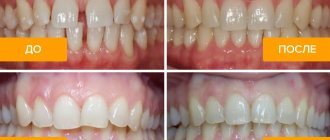
Rapid patient recovery is not the primary criterion for the CEREC technique. The precision quality of the fit of the restorations, minimally invasiveness and information content still remain in the foreground: the dentist constantly sees a virtual model of the tooth being restored with high magnification and can promptly prevent his mistakes, because the patient is sitting in a chair. Dentistry today is aggressive, often the patient is offered to remove all teeth or completely dissect the remaining ones. In my opinion, dentistry more often harms than helps, the patient loses money, but does not gain health. The CEREC technique changes the main thing: the patient still loses money, but gains health for many years.
Veneers - surgical correction of tooth defects
When it is necessary in the shortest possible time to correct the position of a deployed, protruded or creeping onto an adjacent tooth, to eliminate the gap between teeth or to disguise extensive fillings, wedge-shaped defects and restorations, microprosthetics with veneers . A miniature, thin ceramic plate is also made from an impression and applied to the front surface of the tooth using a special adhesive composition. The surface of the veneer is indistinguishable from tooth enamel in color and other characteristics.
The possibility of dental treatment and prosthetics under general anesthesia allows you to restore the integrity of teeth with inlays and veneers with minimal discomfort for the patient.
Materials and methods
CEREC Omnicam, Trilux Forte Vita ceramic blocks, Duo Cement Kit.
Clinical case
Smile design, a virtual articulator and the ability to virtually mark tooth contacts make total bite reconstruction an exciting task
The patient complained of abrasion of the teeth of the upper jaw and, accordingly, a decrease in the height of the upper incisors to such an extent that they were no longer visible when smiling. As a result of a clinical examination of the maxillofacial area, no muscular-fascial tension was detected, the movements of the lower jaw were full, symmetrical, and no pathological changes in the TMJ joint were detected. The bite is straight (Fig. 1). On the frontal teeth of the upper jaw 13-23, occlusal abrasion facets and wedge-shaped defects in the area of 24 and 25 teeth are determined (Fig. 1, 2). It was not planned to change the height of the lower teeth, although they also had occlusal abrasion facets, but with a slight loss of tissue (Fig. 3, 15), so the bite increased without transversal and sagittal movements of the lower jaw, namely, in the usual occlusion only due to an increase height of the upper teeth.
Rice. 1.
Rice. 2.
Rice. 3.
Treatment plan
Total prosthetics and increased bite by increasing the height of the teeth in the upper jaw. The first visit includes the manufacture and fixation of ceramic restorations for 9 teeth in the upper jaw. In subsequent appointments, it was planned to complete the prosthetics of the remaining teeth, and in fact it took the following two visits: on the second visit - 11 teeth, 3 teeth of the upper jaw: 15, 16, 27 - and 7 teeth of the lower jaw: 44-31 and 34-36. On the third visit - the remaining two teeth of the lower jaw, 32 and 33.
What is overbite
The bite is the relative position of the lower and upper rows of teeth when they are closed. A less common name is occlusion.
If it is correct, the upper teeth slightly cover the lower teeth (less than a third). This allows the chewing load to be distributed evenly and looks aesthetically pleasing.
The bite takes more than one year to form. The process includes 5 time periods:
- 0–6 months (the upper jaw is larger than the lower jaw, which is corrected through the baby’s active efforts during feeding);
- 6 months - 3 years (baby teeth erupt, temporary bite is formed);
- 3 years - 6 years (active jaw growth occurs, the body prepares for the appearance of permanent teeth);
- 6–12 years (jaws continue to grow, permanent teeth erupt);
- 12–16 years (the final bite is formed).
Deviations from the norm at least at one of the stages can lead to anomalies of the dental system.
So, if when talking, eating, or in a free state, closure defects are observed, they speak of a malocclusion.
Causes of malocclusion
There are several factors for the development of the anomaly; they can be both external and internal:
- If a child’s parents have an abnormal bite or teeth of irregular shape or size, there is a high probability that the pathology will be passed on to him, since the main factor in its occurrence is hereditary predisposition.
- Another internal factor includes intrauterine development disorders, pregnancy pathologies (maternal anemia, intrauterine infection of the fetus, and so on).
- A common cause of pathology is birth trauma.
- Parental care for newborns in the first months of life also affects the formation of occlusion. According to research, the lack of natural feeding becomes a prerequisite for the development of the defect, as well as non-compliance with the rules of artificial feeding. The hole in the nipple should be small so that the child makes efforts and makes chewing and sucking movements.
- It is important to ensure that during sleep the baby, and in the future the grown child, does not place a fist or toy under his cheek. This habit can provoke incorrect one-sided development of the dentition.
- A baby's tense sleeping position, in which the muscles of the entire body, including the jaws, do not relax, can also cause malocclusion.
- The child’s habit of constantly holding a finger, pacifier, or other objects in the mouth, as well as breathing through the mouth, also negatively affects the bite.
- You need to monitor your child's nutrition. It must be balanced and complete, maintaining optimal levels of fluorine, calcium, and other substances in the body. Disorders of their metabolism require treatment by a doctor.
- Incorrect posture of a schoolchild, in which the head moves forward, can lead to excessive development of the upper and insufficient development of the lower jaw.
- Impaired nasal breathing in combination with other factors leads to abnormalities in the development of the jaws.
It is also important to treat caries in a timely manner, to avoid injuries and serious diseases of the dental system.
If the bite was correct in childhood, it can be spoiled by a jaw injury, untimely restoration of lost teeth, or prosthetic errors.
What consequences are possible?
In some cases, a specialist may refuse to correct a bite with braces due to certain complications:
- The material from which the crown is made may not withstand constant pressure and the outer layers may crumble or even completely.
- The root of the tooth may move in the wrong direction.
- After aligning the units, the artificial tooth may not look aesthetically pleasing.
Each case is individual, so the final decision on the installation of orthodontic structures is made by the doctor.
Indications and contraindications
Installation of crowns for bite correction is advisable if the patient has certain pathologies:
- Reduced or enlarged elements.
- The presence of defects on the surface of the teeth (chips, damage).
- Curvature or rotation of clinical crowns.
- Increased interdental spaces.
- The top of the unit is completely or partially destroyed.
- Implantation of an implant instead of a removed element.
- Unit divergence.
Covering with crowns does not correct every malocclusion. To eliminate some defects, it is necessary to use other methods that do not require grinding of the support unit.
Prosthetics cannot correct pronounced defects in which the shape and position of the clinical crown and root are disrupted. In such situations, alternative correction methods are used.
It is prohibited to use crowns if the wall thickness of the element is insufficient due to the risk of thermal burn of the pulp.