The main criteria for the treatment of gingivitis are:
- Complexity
Each specific case requires a number of therapeutic procedures. Both local and general treatment are necessary. Therapy should be aimed not only at relieving symptoms, but also at the causative factors.
- Individuality
The features of the clinical course, associated problems (their presence and nature), as well as factors of local and general defense of the patient’s body (the state of the immune system) must be taken into account.
- Systematicity
Chronic forms of the disease require regular courses of maintenance therapy to bring the disease into stable remission.
Treatment tactics depend, first of all, on the form of the disease. Let us consider in detail the specifics of treatment of three forms of gingivitis. This will help you understand the basic principles of therapy and roughly explain how your dentist will treat gingivitis.
Forms of gingivitis
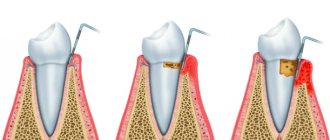
Catarrhal gingivitis
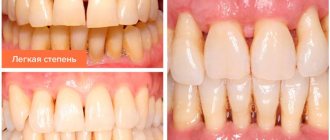
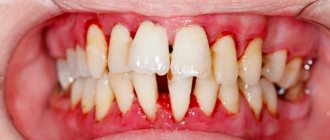
The most common form of gingivitis is the classic form. Many people encounter it at school, but do not pay attention. If you experience even slight bleeding while brushing your teeth, you should immediately consult a doctor. In addition to bleeding, symptoms such as bad breath, itching, and burning may occur.
Hypertrophic gingivitis
With this form of the disease, the gum increases in size and can cover half of the tooth or more. This form of gingivitis can be caused by hormonal changes in pregnant women and adolescents, as well as by taking medications.
Ulcerative gingivitis
The most dangerous and difficult to tolerate form of gingivitis, it causes necrosis (death) of the gums, severe pain, and a very sharp and unpleasant odor from the mouth. Sometimes it is painful for a person suffering from ulcerative gingivitis to even eat and speak, and the general condition is also disturbed. This form of gingivitis affects people with weakened immune systems.
Desquamative gingivitis
It manifests itself as swelling, bleeding and pain in the gums. The gums become bright red, “glazed”, and are easily injured.5
Atrophic gingivitis
It is characterized by a decrease in the size of the gums: it becomes thin, easily injured, and the roots of the teeth are exposed. The teeth seem longer, pain appears from cold or hot things. This form of the disease is rare.
Treatment of chronic catarrhal gingivitis
- The first and mandatory step in therapy is professional teeth cleaning - removing tartar and smoothing the surface of the teeth using ultrasonic and sandblasting devices. The steps of the procedure are shown in the figure below.
- Training in proper individual oral hygiene.
- Elimination of local factors that contribute to the formation of plaque - treatment of caries, correction of orthodontic and orthopedic structures.
- Relief of a problem that aggravates the effect of a microbial factor - elimination of injuries, treatment of pathology of the attachment of the frenulum (plastic surgery to enlarge the frenulum).
- Antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of oral baths, applications, irrigations are used for gingivitis at the stage of a pronounced inflammatory process.
- To improve the process of tissue regeneration, keratolytic agents are used (sea buckthorn and rose hip oil, solcoseryl, vitamins A and E).
- General strengthening therapy is necessary - the use of vitamins, adaptogens, antioxidant therapy, and means to normalize metabolism.
Diagnosis of gingivitis
It is always important to collect a complete history of the disease, because gingivitis is often a chronic disease that occurs in childhood.6
It is also worth paying attention to the general condition of the body; the dentist may refer you to other specialists.
Consultation with an endocrinologist – in diseases of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus, hyperfunction of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands), gum inflammation is more active.
Consultation with a hematologist – in case of blood diseases, gum inflammation is only a symptom of the underlying disease. Consultation with a hematologist is required for differential diagnosis and comprehensive treatment.
Consultation with a gastroenterologist – gingivitis is usually accompanied by chronic diseases of the digestive system.
Related doctors, in turn, prescribe a number of other tests to treat pathology, for example, a general blood test, biochemical blood test, gastroscopy, ultrasound, etc.
The dental office conducts diagnostic tests such as:
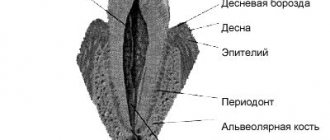
- Probing is a diagnostic method in which the characteristics of the attachment of the gums to the teeth are determined.
- Staining the gums with iodine-containing solutions: this shows whether the gums are inflamed. With gingivitis, the gums turn shades of brown.
- Determining the level of hygiene, that is, how well a person brushes his teeth.
- Panoramic X-ray of the teeth: This is necessary to see whether the inflammation has affected the bone or not, and also shows the condition of all teeth, fillings and crowns.
Treatment of ulcerative gingivitis
Therapeutic measures should be aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process, increasing the patient’s body’s resistance to microbes, and preventing the influence of local factors that provoke necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis. Let's consider the main stages and principles of the treatment.
- Professional oral hygiene.
- Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy.
- One of the features of the treatment of necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis is the removal of necrotic areas of tissue; Hydrogen peroxide and chlorhexidine are usually used.
- The use of keratolytic agents, vitamins, adaptogens.
- Training in the rules of proper oral hygiene, as well as monitoring hygienic skills.
- One of the features of the ulcerative form of the disease is severe pain, therefore the treatment of gingivitis, due to the difficulty of carrying out normal hygienic care, is accompanied by the use of antiseptics and anti-plaque agents.
- Elimination of factors contributing to the formation of plaque on the surface of teeth.
- Elimination of the problem that aggravates the proliferation of microorganisms and their pathogenic effects.
Vincent's ulcerative-necrotizing gingivitis -
Vincent's ulcerative-necrotizing gingivitis is one of the most severe forms of gingivitis, and its development is accompanied by quite serious symptoms of intoxication of the body. Sometimes the terms “Vincent gingivostomatitis” or simply “ulcerative gingivitis” are also used to refer to it. There are acute and chronic forms of this disease (Fig. 12-15).
Causes of occurrence: critically poor oral hygiene plays a significant role in the development, when there is a significant increase in the mass of microbial plaque on the teeth (especially fusobacteria and spirochetes). Under these conditions, the local immunity of the oral mucosa is no longer able to cope with large amounts of toxins released by pathogenic bacteria. As a result, foci of mucosal necrosis and ulceration occur.
The triggering factor that initiates the development of necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis against the background of poor oral hygiene can be a sharp decrease in immunity or an exacerbation of severe concomitant chronic diseases of the body. But these factors are only predisposing; the main reason is poor hygiene and the accumulation of microbial plaque and/or tartar.
Acute ulcerative-necrotizing gingivitis: photo
Chronic ulcerative-necrotizing gingivitis: photo
Necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis: symptoms and treatment in adults, upon visual examination, you can find that the gums are covered with a whitish or yellowish coating, there are areas of gum ulceration, and some of the gingival papillae are necrotic. In the acute course of the disease, patients complain of high fever, loss of appetite, headaches, putrid breath, bleeding and pain in the gums (Fig. 12-13). In the chronic course of Vincent's gingivitis, the symptoms are less pronounced (Fig. 14-15).
How to cure ulcerative necrotizing gingivitis - treatment is carried out exclusively by a dentist, and urgently. The basis of treatment is the removal of dental plaque, including mandatory scraping of necrotic plaque. Plaque along with dental deposits can be easily removed using a conventional ultrasonic tip (scaler), followed by removal of plaque residues with a curettage spoon. Next, antibiotics, antiseptic rinses, and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
- Antibiotic therapy - prescribed antibiotics must be effective against fusobacteria and spirochetes, therefore a combination drug of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid, Amoxiclav, is usually prescribed in a tablet.
(for adults - tablets of 500 mg amoxicillin + 125 mg clavulanic acid, which are used 3 times a day - during the first day of the disease, and 2 times a day for the next 6 days). In parallel with Amoxiclav, you need to take the antibiotic Trichopolum (Metronidazole) - 500 mg 3 times a day, for a total of 7 days. In parallel with this, you should use antiseptic rinses with a 0.2-0.25% chlorhexidine solution, as well as a gum gel, for example, Cholisal.
Important: the use of antibiotics and antiseptics for self-medication (without removing deposits and necrotic plaque) will lead to the transition of acute necrotizing gingivitis to a chronic form. As a result, you will get gradual increasing necrosis of the gums, exposure of the roots of the teeth, as well as constant intoxication of the body. Therefore, an urgent visit to the dentist and removal of dental plaque is mandatory! After inflammation subsides, agents are prescribed that accelerate the epithelization of the mucous membrane, for example, Solcoseryl Gel.
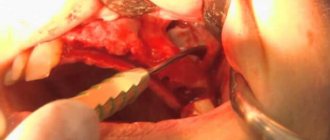
Treatment of hypertrophic gingivitis
The principle and procedure for carrying out treatment procedures is similar to those for catarrhal gingivitis. However, the hypertrophic form sometimes requires surgical intervention.
Gingivectomy is a procedure performed to remove diseased tissue. Its stages can be seen in the figure below. Gingivectomy allows you to get rid of a large amount of excess tissue and prevent the accumulation of plaque, as well as stop the intensification of the inflammatory process.
Stages of gingivectomy
Main causes of gingivitis
Microbial plaque.
In 80–90% of cases, gingivitis is caused by the activity of microorganisms, the nutrient medium for which is dental plaque.
Oral factors:
- uneven functional load on the periodontium - acute and chronic gingivitis can cause malocclusion pathologies, adentia (the absence of several teeth), carious tooth decay, impaired chewing function, and bad habits;
- retention factors - inflammation of the gums is sometimes provoked by poorly polished fillings, poorly installed dentures, caries in the cervical area of the tooth;
- chronic trauma – a factor in the development of acute and chronic gingivitis is often mechanical trauma due to inaccurate brushing of teeth.
Other causes of gingivitis:
- weakened immune system;
- changes in hormonal balance (pregnancy, puberty);
- bad habits;
- general diseases (diabetes mellitus, chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, nervous system, hematopoietic organs).
Up to contents
Treatment of gingivitis at home
Gingivitis is an inflammatory process that can be eliminated without serious medical intervention. At this stage, treatment with folk remedies is effective. But if the disease is left to chance, gingivitis can cause periodontitis, a disease that is much more difficult to cure. Therefore, treatment of gingivitis in children and adults is also reliable prevention.
A decoction of oak bark, medicinal chamomile, sage, as well as commercial anti-inflammatory drugs are used to treat gingivitis at home. They have a soothing, antimicrobial and astringent effect.
Prevention
It is quite possible to protect your gums and teeth from an unpleasant disease if you follow a number of simple rules:
- Visit the dentist 2 times a year. The specialist will identify the disease in the initial stages, which will greatly facilitate treatment. Visits to the doctor will help to diagnose caries in a timely manner and replace low-quality fillings. After all, one of the causes of periodontitis is pathogenic microorganisms and uneven fillings.
- Maintaining oral hygiene at home is another important preventive measure. Brushing your teeth in the morning and evening with a medium-hard brush will help avoid periodontitis. As additional care products, it is necessary to use dental floss, tongue cleaner, and rinses. It is very important to choose the right toothpaste. If you find it difficult to choose, consult your doctor. Perhaps a specialist will recommend a specific paste - with fluoride or medicinal herbs.
- Eating right helps prevent disease by eating solid foods, which put stress on the teeth and gums, strengthening them. The diet should contain vegetables and fruits, dairy products (preferably without sugar), fish and meat.
Prevention does not require special efforts; only a systematic and comprehensive approach is important. And then a reliable barrier will be erected between you and the disease.
Complex dentistry "Sanident", providing services in the urban district of Shchelkovo and Ivanteevka, invites you to undergo digital diagnostics, which will help identify dental pathology at an early stage of development and quickly eliminate it. For treatment, we use modern materials and high-quality painkillers, which allows patients to feel as comfortable as possible during any procedure. Equipping the clinic with the most modern and advanced equipment allows for effective treatment of any dental disease.
We pay special attention to quality and service and strive to ensure that anyone can use our services. Therefore, our prices for dental treatment are affordable, promotions are often held, and discounts apply.
The specialists of the Sanident dental clinic are ready to help right now. Use the consultation registration form on our website.
Simple ways to get rid of a difficult disease: prevention of gingivitis
The best and main method of prevention is compliance with oral hygiene measures.
Personal hygiene
Regular and high-quality teeth brushing (at least twice a day). It is important to know how to choose the right toothbrush; its bristles should not injure the gums, but at the same time remove plaque well. And also use the toothpaste that is suitable for you.
Brushing your tongue is an important part of oral hygiene and should be cleaned as often as your teeth.
It is necessary to use a mouthwash whose antiseptic properties kill most known microorganisms. It is advisable to use it after every meal.
Cleaning the interdental spaces with dental floss at least once a day. It helps remove all food particles that the toothbrush cannot reach, thereby preventing plaque from accumulating in between the teeth.
If you are the owner of dentures, veneers, crowns or implants, then you cannot do without an irrigator. It perfectly cleans the surface of artificial structures, as well as the joints between them and natural teeth.
Visit the dentist every six months
In addition to the consultation appointment, the periodontist will, if necessary, perform professional teeth cleaning. It includes:
- removal of hard dental deposits and soft plaque from tooth surfaces. This cleaning can be carried out using ultrasound or an Air Flow device;
- polishing teeth with a special paste that prevents tartar deposits. In addition to the polishing effect, it has the property of remineralizing tooth enamel, as it contains calcium and fluoride;
- carrying out medical applications on the gums with an antiseptic solution.
Following these really simple methods will help you avoid a whole host of gum and dental problems.
Cure gingivitis is the last opportunity to stop the serious process of inflammation of periodontal tissues - periodontitis, which leads to the loosening of healthy teeth and their loss. In addition, treatment of periodontitis is much more difficult and less effective. Therefore, if you have the slightest problem with your gums, do not forget to see a doctor.
Diet and nutrition
For inflamed gums, it is necessary to include a large amount of fresh fruits and vegetables in your diet:
- Citrus fruits . A higher vitamin C content helps reduce inflammation and bleeding.
- Apples and pears . The presence of pectin and a large number of microelements help accelerate the healing process.
- Blackcurrant, raspberry, blackberry . They contain a large number of minerals and vitamins that increase the body's ability to fight inflammation.
- Cabbage, zucchini, carrots . Contains fiber and vitamins from the antioxidant group. They enhance metabolic processes in the body and accelerate tissue regeneration.
Since a common cause of gum inflammation is a lack of vitamins A, C, E and B in the diet, in some chronic cases taking multivitamin complexes (CENTRUM, VITRUM, THERAVIT, Supradin, Sana-Sol) is indicated.
Remember! Gingivitis is a serious chronic oral disease and can even cause dangerous complications. Therefore, it is impossible to treat this disease without the participation of a dentist. Only an experienced doctor will be able to assess the condition of the gums and recommend optimal treatment methods!