From this article you will learn:
- how to rinse your mouth if your gums are inflamed,
- comparison of the effectiveness of funds,
- The best mouthwash for sore gums.
The article was written by a dentist with more than 19 years of experience.
Mouth rinses for gum inflammation can be divided into – 1) antimicrobial, 2) anti-inflammatory, 3) combined action. Rinse solutions with an antimicrobial effect contain antiseptics or antibiotics, and these components act directly on the cause of gum inflammation - pathogenic bacteria. In dentistry, antiseptics such as chlorhexidine, hexitidine or cetylpyridine are usually used, and among antibiotics, triclosan.
In turn, rinses with anti-inflammatory effects may contain: methyl salicylate, phenyl salicylate, allantoin, bisabolol, thymol and eugenol, as well as medicinal plant extracts. All of them have the property of blocking the so-called “inflammatory mediators,” thereby stopping the inflammatory reaction in the tissues. Some mouth rinses have a combined composition, combining both antiseptics and anti-inflammatory components.
In this article, we will analyze the best mouthwashes –
- chlorhexidine solution,
- LACALUT Active,
- PRESIDENT PROFI Antibacterial “Powerful protection against bacteria”,
- Hexoral (0.1% hexitidine solution),
- miramistin,
- PRESIDENT PROFI Active,
- Periodontocide,
- LISTERINE Expert “Gum protection”,
- Stomatophyte.
Combination of rinses and application gel –
The selection of rinse aid and gel is carried out in such a way that both antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects are equally realized.
Those. if you choose a rinse with antimicrobial components - such as chlorhexidine, hexitidine, cetylpyridine, triclosan, then in parallel you need to use a gum gel containing anti-inflammatory components (this can be choline salicylate, phenyl salicylate, methyl salicylate, etc.). But if you use a rinse primarily with anti-inflammatory components (for example, Parodontocid mouthwash), then you need to choose a gum gel that contains an antiseptic and/or antibiotic. Such gels include Perio-Aid, PRESIDENT Effect gel and others. For more information about anti-inflammatory gels for the treatment of gum inflammation and patterns of their use, read the article:
→ Rating of the best gels for gum inflammation
Mouth rinses may be unsafe -
You may notice that the instructions for rinses with antiseptics and antibiotics (at least from some manufacturers) recommend using them for 3-4 weeks, and in some cases even up to 1-2 months. It is absolutely impossible to follow such recommendations, because... Long-term use of antiseptics radically changes the composition of the oral microflora, and not for the better. Pathogenic microflora tends to get used to antiseptics (as they say, the fittest survive), and therefore, after the end of the use of antiseptics, the rate of destruction of the attachment of teeth to the bone and gums can only increase. Therefore, the course of rinsing with antiseptics should not last more than 10-12 days.
In addition, clinical studies (source) revealed that after just 7 days of rinsing the mouth with chlorhexidine, the ratio of microflora in the oral cavity changed in such a way that strains of pathogenic bacteria that produce large amounts of lactic acid received an advantage. This leads to a shift in the pH of the oral fluid to the acidic side, to a decrease in the buffer capacity of saliva and a decrease in its ability to neutralize lactic acid, which is secreted by cariogenic bacteria. Thus, the risk of developing dental caries increases.
Important for patients with cardiovascular pathology -
Several reputable scientific studies have shown that chlorhexidine interferes with the ability of oral bacteria to convert nitrates (found in foods) into nitrites. This bacterial activity is called “nitrate-reducing” and is one of the mechanisms for maintaining normal blood pressure. Normally, nitrites entering the blood help lower blood pressure and, accordingly, a decrease in their production will lead to an increase in blood pressure.
This is primarily important for patients who already have chronic cardiovascular pathology. This information is confirmed by the clinical study “The increase in plasma nitrite after a dietary nitrate load is markedly attenuated by an antibacterial mouthwash. Nitric Oxide" (2008), authors – Mirco Govoni, Emmelie Å. Jansson, and others. If you wish, you can familiarize yourself with this study using the link above, for example, using a browser translator.
What you don't need to rinse your mouth with -
Many patients who try to be treated at home sometimes treat their gums with hydrogen peroxide.
Of course, hydrogen peroxide is a good antiseptic, and it is excellent in treating many infectious processes (for example, purulent wounds). It can also be used in dentistry, but not for rinsing the mouth, but for rinsing periodontal pockets with a syringe. When hydrogen peroxide comes into contact with any organic matter, it begins to foam, releasing atomic oxygen. When rinsing periodontal pockets, 3% peroxide is drawn into a syringe and the sharp edge of the needle is broken off (so as not to pierce the gum). Then the blunt end of the needle is inserted along the tooth root into the lumen of the periodontal pocket and washed under pressure. As a result, all infection and pus are washed out of the pockets.
But when rinsing the mouth, peroxide will react most quickly only with oral fluid, and other than a full mouth of foam, you will not get any effect. You won’t be able to rinse your pockets with a syringe at home yourself. For this you need a doctor, because... if you suddenly inject peroxide not into the lumen of the periodontal pocket, but directly into the soft tissue of the gums, you will receive a severe chemical burn with subsequent necrosis.
Gargling with infusions of medicinal herbs –
Many patients prepare their own rinse solutions by brewing medicinal herbs such as chamomile or oak bark. Such infusions actually have a good astringent effect, moderate anti-inflammatory, and also a weak antiseptic effect. And this can really help reduce swelling and bleeding of the gums, but such herbal infusions also have one big disadvantage.
The fact is that self-brewed herbal infusions contain a lot of pigments and tannins, which are very quickly deposited on the teeth in the form of pigment plaque. This plaque forms very quickly, and it will serve as a good basis for the already microbial plaque to attach to the surface of the teeth. But it is microbial plaque and tartar that cause gum inflammation. Therefore, if you use solutions with herbs, it is better in the form of ready-made rinses (since manufacturers remove from them all pigments that stick to tooth enamel).
Causes of disease not related to gum disease
Dental disease is not the only factor that causes loose teeth. This process can occur for a number of other reasons:
- As a result of genetic predisposition to the disease.
- Weakening of the immune system.
- Diabetes.
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Psoriasis.
- Trauma to the maxillofacial area.
- Arthritis.
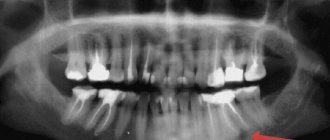
Only a dentist can correctly determine the cause of the disease. If the teeth are loosened as a result of a strong blow, the doctor sends the patient for an x-ray for a more detailed diagnosis, and then decides on subsequent treatment. If the cause is a chronic disease, the doctor will prescribe dental procedures or prescribe the appropriate medication to strengthen the gums.
In what cases are rinses ineffective?
The author of the article has 10 years of experience as a “periodontologist” (documents on advanced training of the state standard in the “Parodontology” program - can be viewed in the editorial section), and we would like you to listen to our experience. The fact is that knowing what to rinse your mouth with when your gums are inflamed is not enough to cure their inflammation (24stoma.ru). Various mouthwashes (even the strongest ones), anti-inflammatory gels are only secondary means.
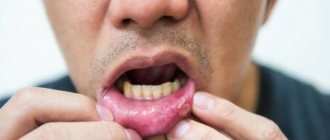
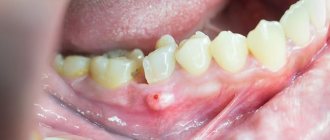
There are 2 main types of gum inflammation – gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis is the initial stage of inflammation, the main symptoms of which are: swelling, redness or bluishness of the gums, pain and bleeding when brushing teeth, bad breath (Fig. 3-4). With periodontitis, these symptoms are accompanied by mobility of teeth, suppuration from periodontal pockets, destruction of bone tissue around the teeth, and in later stages, changes in the position of the teeth (Fig. 5).
Gingivitis and mild periodontitis –
The cause of gum inflammation in both cases is soft microbial plaque, as well as hard supra- and subgingival dental deposits (Fig. 3-5). This is the main cause of inflammation, which is a consequence of insufficient oral hygiene. And the most important part of treatment should not be to reduce symptoms, but to eliminate the real cause of gum inflammation. And for this purpose, dental plaque is removed by a dentist (usually this is done using ultrasound).
Antiseptic rinses act only on the most superficial layer of microbial plaque or tartar. They do not act on the deeper layers, which also consist of pathogenic bacteria, and therefore the use of antiseptics does not lead to complete “disinfection”. Therefore, rinsing with antiseptics and gels for gums (without removing dental plaque) lead only to temporary improvement, and the inflammation in this case will be constant chronic - with periodic exacerbations.
Television advertising very actively promotes all sorts of products for gums, but it does not say that the main treatment is precisely the removal of dental plaque. Remember that a mild form of gingivitis can unnoticeably turn into a severe form of periodontitis if you try to treat the inflammation only with antiseptic rinses and anti-inflammatory gels - without periodic removal of dental plaque by the dentist.
→ How to properly treat gingivitis → Treatment regimens for periodontitis
Toothpastes for gum inflammation -
In complex therapy for the treatment of gum diseases, you can use not only rinses and gel applications, but also special anti-inflammatory toothpastes for gums, which will reduce bleeding and swelling of the gums even faster. Some of these pastes are also suitable for preventing inflammation. We hope that our article on the topic: How to rinse the mouth with gum inflammation was useful to you!
Sources:
1. Dental education of the author of the article, 2. Based on personal experience as a periodontist, 3. PubMed.gov scientific research base, 4. “Optimization of conservative treatment of patients with periodontitis” (Komleva A.S.), 5. Composition of products taken from official websites manufacturers.
Mouthwashes for sensitive teeth –
Mouthwashes to reduce tooth sensitivity may contain 2 types of active ingredients.
Firstly, these are fluorides, which include sodium fluoride, amino fluoride (olaflur) and potassium fluoride. These components work by creating a layer of calcium fluoride on the surface of the enamel, which protects teeth from the influence of chemical, thermal and mechanical irritants. However, the effect of using this group of components develops gradually. The second group of substances includes potassium compounds - such as potassium nitrate and potassium fluoride, which work by reducing the sensitivity of nerve endings in dental tissues. This group of substances acts more quickly, but the effect will disappear immediately after using the product. Therefore, ideally, rinses contain a combination of active substances: both fluorides and potassium compounds.
Rinse aid ELMEX “Sensitive Plus” –
manufacturer – Germany,- active substances are aminofluoride, potassium fluoride, as well as “dimethyl-amino-ethyl methacrylate-polycarbamyl-polyglycol”.
- fluoride content – 250 ppm,
- price for 400 ml – from 260 rubles.
Comments: in our opinion, Elmex Sensitive Plus is one of the best rinses for reducing dental hypersensitivity. It contains amino fluoride, the substance potassium fluoride (which, upon dissociation, decomposes to form active fluoride ions and potassium ions), as well as a special polymer “dimethyl-amino-ethyl methacrylate-polycarbamyl-polyglycol”, which creates a protective biofilm on the surface of the tooth. Ideally, combine this product with Lacalut Extra Sensitive toothpaste.
Rinse aid PRESIDENT “Sensitive Plus” –
manufacturer – Italy,- active ingredients – potassium nitrate, calcium lactate, xylitol, as well as linden and chamomile extracts,
- fluoride content – without fluorine,
- price for 300 ml – from 220 rubles.
Comments: PresiDent Sensitive Plus rinse contains a very high dosage of potassium nitrate, which ensures rapid reduction of hypersensitivity. In addition, the product contains calcium lactate to increase the mineralization of tooth enamel, as well as a high concentration of xylitol (it neutralizes acid in the oral cavity, thereby inhibiting the demineralization of teeth, and ultimately also indirectly helps reduce hypersensitivity.
Important: We would like to point out that mouthwashes to reduce dental hypersensitivity are only a secondary treatment for this problem. They do not allow achieving a greater effect than can be achieved with special toothpastes and concentrated gels used for increased tooth sensitivity. Such rinses are a good option for use in the middle of the working day, and in the morning and evening it is better to use toothpaste for these purposes.