Proper oral care after tooth extraction
To prevent unwanted consequences from occurring, it is important not to do the following:
- touch the wound with your tongue or use other foreign objects for this,
- rinse your mouth generously in the first two days,
- make sudden movements with the facial muscles,
- plunge into hot water or rinse with it,
- Hard to work,
- eat food in the first 3 hours that follow the procedure, it is permissible to drink, but refrain from boiling water.
- You should also abstain from cigarettes at this time,
- alcohol is contraindicated within 24 hours after surgery. If your doctor prescribes the use of antibiotics, you should not drink alcohol until the end of the course of therapy.
What could go wrong
The vast majority of complications are caused by doctor error. The incompetence of an anesthesiologist entails:
- Problems with the respiratory system
. Mucus and blood clots can get into the airways and block them, since during general anesthesia protective reflexes are suppressed. - Problems with the cardiovascular system
. The wrong dosage causes different reactions: a slowdown or acceleration of the heart rate, a drop or increase in blood pressure.
Recovery from anesthesia may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and inappropriate behavior. General anesthesia is a serious shock to the body; it should not be considered harmless.
There are fewer risks with sedation
, but they exist too. These are all the same breathing disorders and hemodynamic processes (problems with blood pressure and heart rate).
A cold compress will prevent swelling
Immediately after the manipulations, it is necessary to apply a cold compress, since after tooth extraction the cheek may swell.
To do this, take some chilled meat products or ice and apply it, after wrapping it in a cloth. Such actions will help to minimize or even eliminate swelling of the soft areas of the face that can form in the event of a serious intervention.
It is recommended to keep the ice for about 5 minutes, apply it 3-4 times, taking a break between applications. It is important to apply cold immediately after surgery, since further this action will not bring the desired effect. Under no circumstances should you use a warm compress or warm the tissue in any other way - thoughtless intervention can cause suppuration.
Why complications arise
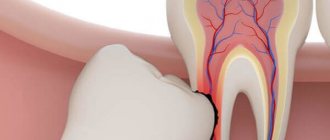
After extraction, a wound is left in the gum and bone in which a blood clot (fibrin) forms. It “seals” the wound, preventing infection, and becomes the basis for the formation of new tissue that fills the space formed after the removal of the 8. After uncomplicated removal, healing lasts about a week. On days 3-4, the blood clot is gradually replaced by granulation tissue, which gradually fills the entire socket. Already after a month, the granulation tissue is completely replaced by connective tissue, and after 3 months - by bone.
Removal of third molars can have negative consequences that appear almost immediately after the intervention. Among the most common complications:
- “dry socket” - when a blood clot does not form or dissolves too quickly;
- paresthesia - damage to the nerve endings around the removed unit;
- alveolitis - inflammation of the socket;
- bleeding;
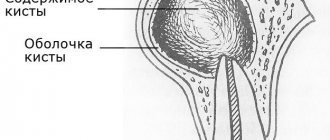
- cyst - fibrous formation at the site of an extracted tooth;
- endogenous periostitis (flux).
In rare cases, stomatitis, osteomyelitis, jaw trauma, and perforation of the bottom of the maxillary sinus are observed. The occurrence of complications is usually associated with ignoring the dentist’s recommendations regarding oral hygiene during the healing period, decreased immunity, and violation of surgical technique.
If your gums bleed after tooth extraction
You can stop bleeding in a number of effective ways. In most cases, this disease affects people with high blood pressure with hypertension or patients who have had a large vessel damaged.
It is worth noting that due to psychological overload and stress during activities, even in people with normal health, blood pressure may rise. The first step is to apply a tightly rolled piece of sterile bandage to the bleeding site, and then measure the patient’s blood pressure. If it is elevated, you need to resort to medications.
With increased blood pressure, the chance of hematoma and blood appearing after tooth extraction increases. This development of events is dangerous due to suppuration, which will then have to be opened, and bleeding can cause dizziness and weakness.
If bleeding appears several hours after removal, you should not wait for the situation to normalize, but seek medical help.
Diabetes mellitus during tooth extraction
If a person has this disease, it is recommended to measure their sugar levels immediately after surgery. Tension leads to the production of adrenaline, which can increase the rate. By measuring sugar, a person will know about his condition and will be able to prevent side effects.
If a gauze pad is placed on the gum
A gauze swab is placed on the hole if it is etching. In other situations, the use of this remedy is undesirable, as it can provoke inflammation. As the tissue is removed, the blood clot that has formed in the socket is also removed.
If the tissue lining is on the wound, it is necessary to carefully remove it after a certain period of time after removing the tooth. A tampon that has absorbed a certain amount of liquid automatically becomes a breeding ground for a wide range of bacteria. You should not keep it in your mouth for a long time to prevent the appearance of inflammatory processes in the hole that remains after tooth extraction.
Antiseptic rinses for suppurations
There is no need to rinse your mouth intensively; instead, use “baths”. In order not to disturb the damaged tissues, take a special anti-inflammatory solution into your mouth, keep it inside, and then spit it out.
What medications are needed?
Antibiotics after tooth extraction are prescribed by the surgeon who performed the extraction. You can replace medications from the list with cheaper analogues, the main thing is that they have a wide range of applications, since there are different microorganisms in the mouth. Amoxiclav is often prescribed because it is effective and has a minimum of contraindications and side effects. The drugs are taken in the course determined by the doctor.
Anesthesia after tooth extraction lasts for several hours, after which pain appears, which can be eliminated with the help of analgesics. Anti-inflammatory drugs, for example Nimesil, and vitamins to strengthen the immune system can also be prescribed.
How to rinse your mouth after tooth extraction:
- chlorhexidine;
- a weak solution of potassium permanganate;
- furatsilin;
- miramistin;
- similar antiseptics.
In addition to pharmaceutical products, rinsing can be done with soda, saline solutions, decoctions of chamomile, sage, oak bark, calendula, and eucalyptus. They not only protect against infection, but also relieve swelling and accelerate tissue healing.
Temperature after tooth extraction is one of the possible symptoms, as tissues are injured and foreign elements penetrate the body. To improve your health, you need to take antipyretics.
Baths should be carried out if:
- an incision was made to expose the gumboil;
- the tooth was removed due to inflammatory processes;
- there are harmful deposits on the teeth and caries;
- removal of the root of a tooth with caries
For procedures with baths, you can use an aqueous solution of chlorhexidine with a concentration of 0.05%. This drug is inexpensive, it can be purchased ready-made, it has excellent antiseptic effects, and tastes bitter. Such procedures must be carried out 3 times a day. The solution must be kept in the mouth for 1 minute.
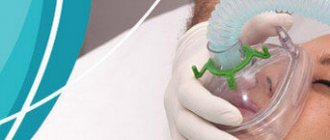
Anesthesia in dentistry: types and principle of action
Anesthesia is a decrease in sensitivity or complete cessation of the perception of pain by disrupting the transmission of sensitive nerve impulses at different levels.
Methods of anesthesia for tooth extraction:
- superficial (other names - terminal, application) - blockade of receptors of nerve endings;
- infiltration - shutdown of receptors and small nerves;
- conduction (regional) - blockade of nerve trunks and plexuses,
- intraligamentary (intraligamentous) - anesthesia of the periodontal cavity and intraosseous space;
- sedation with nitrous oxide - inhalation anesthesia with laughing gas, in small concentrations maintains consciousness, but causes relaxation;
- mask anesthesia - a gaseous anesthetic enters the body through the respiratory tract when the mixture is inhaled;
- Propofol sedation is an intravenous injection of an anesthetic that temporarily turns off consciousness.
Tooth extraction under general anesthesia in Moscow is the most expensive type of anesthesia. The cost depends on the anesthetic and how long it lasts.
Application anesthesia
An anesthetic is applied to the surface of the gum surrounding the tooth. Use sprays and gels containing lidocaine. This technique slightly reduces pain sensitivity. Anesthesia occurs in 3–5 minutes and lasts 10–15 minutes. They are used more often in pediatric dentistry to remove baby teeth and numb the area for needle insertion.
Infiltration anesthesia
This is an injection of an anesthetic into the soft tissue of the gums. Lidocaine and ultracaine are most often used. The most common type of anesthesia for the removal of anterior teeth. Reduces pain sensitivity for an average of an hour. Not an effective method for removing chewing teeth.
Conduction anesthesia
The anesthetic is injected with a syringe into the area of the branches of the trigeminal nerve, which provide sensitivity to the gums and teeth. The drug takes effect a few minutes after the injection, and the numbness persists for another two hours. Used for complex surgical interventions on the gums and molars.
Intraligamentary anesthesia
This is pain relief by injecting an anesthetic between the tooth and gum. With this method of administration, a significantly smaller amount of the drug is consumed, which is especially important for patients with diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Nitrous oxide sedation
The disturbance of consciousness is superficial. Nitrous oxide is administered intranasally (sprayed into the nasal cavity). After stopping the administration, the effect of the drug ends, the condition and reactions stabilize.
The technique allows you to reduce the level of fear and anxiety. More often performed on patients with high anxiety, during traumatic and lengthy dental procedures.
Mask anesthesia
The anesthetic is administered through an inhalation mask. The drug and its dosage are determined individually, taking into account the age and condition of the patient. The dose is adjusted using a special evaporator. Consciousness is restored a few minutes after stopping the supply of the anesthetic drug, the general condition returns to normal within two hours.
Sedation with propofol
Propofol is a short-acting sleeping pill that is administered intravenously. The patient is instantly immersed in a medicated sleep, similar to physiological sleep. The drug is non-toxic, quickly eliminated from the body, and can be used for patients with heart, liver, and kidney diseases. Children are allowed from the age of three.
Such anesthesia is justified for a large volume of treatment, dental phobia, diseases of the central nervous system, which are accompanied by an intellectual disorder.
If your gums hurt after tooth extraction
Tooth extraction leads to damage to soft tissues, which contain a large number of nerves. The doctor performs the procedures under local anesthesia, so the patient feels discomfort only in one thing - the need to spend a certain amount of time with his mouth wide open.
When the analgesic effect ends and the tooth has already been removed, the pain returns. Usually they are of a “aching” nature and do not fundamentally interfere with normal life activities. But in some cases the pain can be intense.
If the tooth extraction was not caused by inflammatory processes, you can avoid the use of painkillers. If pain relief is necessary to avoid severe pain after tooth extraction, it is recommended to take an analgesic until the anesthetic wears off.
Using painkillers after tooth extraction
If you experience intense pain, you can resort to using “Ketans”; The medicine is dispensed by pharmacists in pharmacies only with a prescription - this is due to the presence of side effects. Severe pain can occur during complex and lengthy medical intervention, especially if it was accompanied by drilling of the bone around the tooth, or if the operation was performed poorly, unprofessionally and traumatically.
“Ketorol” (an analogue of “Ketanov”), “Analgin” (will help reduce mild pain syndrome), “Spazmalgon” (in addition to the analgesic effect has an antiseptic effect), “Baralgin” (a drug that contains “Analgin” in its composition).
How is sedation different from anesthesia?
Sedation
– this is depression (suppression) of consciousness to the level of relaxation. At the same time, all protective reflexes are preserved, for example, a blood clot entering the respiratory tract will cause a coughing attack. Sedation reduces the level of reactions, but does not block pain receptors; local anesthesia is used for this.
Anesthesia
causes complete loss of consciousness, so it requires monitoring of all vital functions. General anesthesia turns off pain receptors; no additional pain relief is needed.
The term “sedation” has not taken root in general use, and simple relaxation is often also called anesthesia. It is worth remembering that tooth extraction under general anesthesia is used extremely rarely, mainly in hospitals. This requires a specially equipped operating room, everything necessary for resuscitation, and a qualified anesthesiologist must carry out the procedure.
Therefore, if you are offered to have a tooth removed under anesthesia, clarify what is meant: anesthesia or sedation.
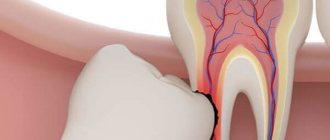
Wisdom tooth removal
Wisdom teeth are the painter or chewing teeth located at the end. When chewing, they do not play a significant role; the structure is no different from ordinary teeth.
There are several generally accepted indications for removal:
- ingrowth of roots into the maxillary sinus,
- partial eruption
- facial neuralgia,
- inclined or lateral position,
- caries damage.
When removing a wisdom tooth, painkillers are used to relieve pain. Consequences after the operation may occur depending on the complexity of the operation, surrounding tissues, location, and access to the tooth.
Negative consequences may occur if the patient does not adhere to the doctor's orders. Baths of soda and herbal decoctions will also help alleviate the condition after removal. It is forbidden to rinse; it is important to preserve the blood clot, which protects the wound from infection.
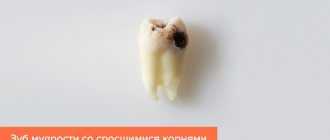
Types of deletion
Wisdom teeth (eights, third molars) are larger than other dental units in the row. They differ not only in size, but also in the complex anatomy of the root system. Eight has from 2 to 6 roots
, which are often closely intertwined with each other. Given the complex arrangement of wisdom teeth, when they are removed, a significant wound is created.
The risk of complications will directly depend on how difficult the figure eight extraction was. With simple extraction, when the tooth is intact, the roots are not intertwined, and there are no other pathologies (pulpitis, periodontitis, etc.), the risk of complications is minimal. In such a situation, the doctor uses forceps or an elevator to remove the tooth from the socket.
If the wisdom tooth is incorrectly positioned (horizontal eruption, severe curvature), intertwined roots, significant destruction of the coronal part, or the presence of inflammation, a more global surgical intervention may be required. An incision in the gum, cutting a tooth into pieces with a drill, removing root fragments through the jaw bone and other manipulations significantly increase the traumatic nature of the procedure. Aching pain, swelling after removal of the figure eight, increased temperature (up to 37.5℃), hematoma on the cheek - this is a normal reaction to the intervention, which lasts no more than 5-7 days.
In what cases is it necessary to remove the nerve of a tooth?
Removing the nerve from a tooth kills it. Almost no nutrients are supplied, causing it to become darker and weaker. During treatment, dentists try to keep the dental nerve alive, but sometimes they have to take forced measures to put the oral cavity in order.
Nerve removal is necessary if:
- Deep caries.
If the disease has destroyed almost the entire tooth, there is nothing to save; the main thing for the doctor is to prevent further destructive process.
- Prosthetics.
To install the prosthesis, an incision must be made in the pulp chamber. This is especially necessary in situations where teeth grow at an inclined angle.
- Incorrect treatment in the past.
This can happen if during treatment the doctor resorted to opening the pulp chamber. In this case, it is necessary to partially remove the nerve.
- Mechanical damage.
Injury can lead to chips in the enamel where the nerve is located. If the front teeth are damaged, the nerve is not completely removed.
Antibiotic therapy after removal of unhealthy teeth
Antibiotics are prescribed by the attending physician - dentist. Drugs are prescribed in case of difficult extraction, to prevent the risk of complications if the tooth was removed due to inflammatory processes.
The drug usually prescribed is Lincomycin 0.25. Take capsules after tooth extraction for 5 days, 2 capsules 3 times. If purulent inflammation is present, the antibiotic is prescribed as intramuscular injections.
Those who suffer from intestinal and stomach disorders can take antibiotics in effervescent forms, for example, Unidox Solutab and Flemoxin Solutab.
Pathology and norm
With any invasive procedure, swelling occurs in the soft tissues. It goes away on its own within a few days. The same can be said about pain. Cheekbones, adjacent teeth, head, and neck may hurt. If after 3 or 4 days the symptoms do not disappear, but increase, then this indicates pathology.
What are the complications after tooth extraction:
- alveolitis, osteomyelitis, most often occurring with dry socket;
- inflammation near the seams;
- damage to the adjacent dental unit;
- perforation of the bottom of the maxillary sinus, if extraction is performed on the upper jaw;
- fracture of the alveolar process, sharp edges of the alveolus that injure soft tissues;
- neuritis of the inferior alveolar nerve;
- postoperative cyst;
- paresthesia, which is characterized by numbness, loss of sensitivity of the cheeks, tongue, jaw and other adjacent areas;
- ondogenic phlegmon, periostitis;
- a hematoma in the neck can occur in people suffering from arterial hypertension (blood leaks out of the vessels into the tissue);
- soft tissue abscesses.
Pus and flux after tooth extraction characterize an acute inflammatory process that requires urgent treatment. Purulent inflammation can occur with insufficient antiseptics during surgery or poor postoperative care, with a dry socket, when food particles get into the hole. A new surgical operation is required to remove necrotic masses.
When to see a doctor:
- on the second and third days the swelling does not subside, but the cheek continues to swell;
- the pain becomes more intense and is difficult to eliminate with medications;
- the high temperature lasts for several days, normally it should decrease within 24 hours;
- no appetite, nausea, weakness;
- when pressing on the gum, pus is released, and its edges turn red;
- when palpating the hole with the tongue, no blood clot is detected.
If inflammatory processes are started, this can lead to the melting of bone tissue, an abscess and the spread of infection.