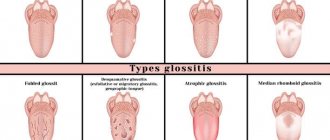
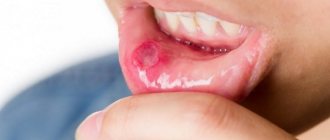
Reasons for the development of stomatitis
The causes of damage to the oral mucosa may be:
- Infection (viruses, bacteria, fungal microflora)
- Allergy
- Weakening of the immune system
- Unbalanced diet
- Some diseases (ENT diseases, diabetes mellitus, anemia, gastrointestinal diseases)
- Microtraumas, burns and other damage to the oral mucosa
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules
- Taking medications
- Hormonal imbalances
- Smoking (“nicotine stomatitis”)
- Genetic predisposition
Allergic stomatitis
They arise as a reaction of the mucous membrane to an allergen. An allergic agent can be toothpastes, mouthwashes, food, medicines, materials for crowns, fillings, etc. Allergies often occur to removable dentures. The mucous membrane is affected precisely at the point of contact with the damaging agent, for example, the hard palate under a removable denture. With allergic stomatitis, the mucous membrane is swollen, red, bubbles appear, which burst with the appearance of painful erosions.
Allergic stomatitis also includes chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis , it begins with swelling and burning, then a painful aphtha appears, and then a healing period begins. This disease is characterized by constant relapses with a certain frequency.
Symptoms of stomatitis
Despite the multiplicity of causes, the symptoms of stomatitis are usually similar:
- Pain and discomfort in the mouth that worsens while eating or talking
- Redness of areas of the mucous membrane, their swelling
- The appearance of painful red ulcers with a whitish center on the mucous membrane
- Increased salivation
- Bad breath
- Bleeding gums
- During the acute phase, there may be an increase in body temperature and enlargement of regional lymph nodes
Viral stomatitis
Herpetic stomatitis
Caused by the herpes virus of the first, less often the second type.
It accounts for 80% of all stomatitis and occurs mainly in children, less often in adults. The prevalence of herpes simplex virus ranges from 65% to 90%8. Infection occurs through airborne droplets and household contact. More common is recurrent herpetic stomatitis, which is manifested by itching, burning, slight soreness in the oral cavity, then vesicles (bubbles) appear, which burst and heal after 7-10 days.
During primary infection, acute herpetic stomatitis occurs; it is characterized by general symptoms such as fever, weakness, aches in the muscles and joints, the degree of these manifestations depends on the severity of the disease. As a rule, the acute form occurs in children.
Varicella zoster virus infection
The mildest form, in which the mucous membrane of the tonsils is affected. The palatine tonsils are not very enlarged, the mucous membrane of the throat is red, there is no plaque or pus.
Stomatitis with measles
Measles is an acute viral, highly contagious disease that is caused by the Polinisa virus and is transmitted by airborne droplets. The disease is extremely contagious. It is characterized by a rise in temperature, symptoms of ARVI, a rash on the face, neck, and then the whole body. In the oral cavity, Filatov-Koplik spots and stomatitis occur, which is characterized by hyperemia, swelling of the mucous membrane and white plaque. Nowadays, thanks to vaccination, this disease practically does not occur.
The importance of nutrition during stomatitis
Proper nutrition for stomatitis not only helps speed up recovery, but can also prevent relapse of the disease.
In addition, if the oral mucosa is damaged, almost any food and drink causes severe pain.
This can cause fear of eating and even refusal to eat, which is completely unacceptable. Therefore, it is necessary to eat with stomatitis according to certain rules.
The duration of such a gentle diet is determined by the doctor based on the form and severity of the disease.
Traumatic stomatitis
Traumatic stomatitis develops as a result of mechanical, thermal or physical trauma. This type of stomatitis occurs:
- superficial (burn of the mucous membrane by hot tea)
- deep (burn with a strong alkali or acid, strong biting of the mucous membrane)
Acute mechanical stomatitis: rare, it can be caused by trauma to the mucous membrane when biting the cheek, tongue, lip while eating, an attack of epilepsy, a blow, trauma during dental treatment and other traumatic factors.
It is manifested by pain, hyperemia, swelling at the site of injury, erosion. With secondary infection, the wound can develop into long-term non-healing ulcers. Most often, traumatic stomatitis is acute, but can also be chronic, for example, constant biting of the cheeks under stress, chronic injury from braces, a sharp tooth edge, or a bad crown. As a result of trauma, painful erosions or ulcers with jagged edges form on the mucous membrane, which can become infected.
The cause of physical injury is most often a thermal burn due to contact with hot liquid, inhalation of steam, or exposure to fire, the latter, as a rule, accompanied by damage to the respiratory tract. The lesion is most often located on the tip of the tongue, lips, and the front of the palate. The mucous membrane becomes swollen, red, painful, and blisters may form, which then burst. With deep damage, the mucous membrane dies, and the damage involves muscles and even bone.
Chemical stomatitis occurs when burned with acid or alkali. In everyday life, this is most often acetic acid; also at a dental appointment, burns can occur with various drugs (phenol, formaldehyde, alcohol, hydrofluoric acid, etc.). The depth of damage depends on the damaging substance and its concentration, and the duration of exposure. First, the mucous membrane becomes bright red and painful, and with severe lesions, foci of necrosis then appear within a few hours.
In case of burns with acids, alkalis, or thermal burns, it is recommended to call an ambulance!
How to eat with stomatitis
The task of nutrition for stomatitis is to provide the body with all the necessary nutrients, as well as to protect the mucous membrane from irritation as much as possible.
Frequent split meals (5-6 times a day) are recommended. Food must be crushed as much as possible, preferably to a puree state. The temperature of the dishes is 35-40 degrees.
After eating, the mouth must be rinsed with an antiseptic solution prescribed by a doctor or simply with boiled water.
For stomatitis, it is important to drink enough liquid at a comfortable temperature (close to body temperature).
Any degree of dehydration of the body should not be allowed, as this makes the mucous membranes even more vulnerable to inflammation.
General diet rules
A special feature of the diet for this oral disease should be food that is as neutral as possible and does not irritate the mucous membranes. It should be well crushed and have an enveloping and slimy consistency.
When organizing meals for a baby with this disease:
- It is necessary to adhere to small, frequent meals. Portions should be small, and the frequency of intake should be five or six times a day. It will be easier for the baby to eat a small portion, and it will be easier for parents to feed him.
- All food should be crushed as much as possible, and the consistency should resemble puree. Meat and fish are used only in the form of minced meat. The temperature of the food should not be higher than forty degrees, neither hot nor cold.
- Before eating, you can treat the child’s oral mucosa with products containing painkillers. You can use: Kamistad, Kalgel, Cholisal. Also, for pain relief before eating, you can give your baby Ibuprofen or Paracetamol. They will numb the mucous membrane in the mouth. You can safely feed your baby.
- After eating, be sure to rinse your mouth with water at room temperature. Then the mucous membrane is treated. For this, any disinfectant solutions are used (Furacillin, Chlorhexidine, Stomatofit, Miramistin). To do this, you can use decoctions of chamomile or sage herbs. This is done in order to disinfect the lesions and prevent the development of a secondary infectious process.
- It is necessary to apply oils to the mucous membrane that have the ability to activate reparation (recovery) processes.
It is impossible to cope with the disease with diet alone; it must be treated.
Menu for stomatitis
Chopped products should be made from meat: meatballs, meatballs, soufflé, pate. It is good to boil the cereals, giving preference to slimy porridges (oatmeal, rice).
It is better to use cottage cheese in the form of casseroles, and make puree from vegetables.
If you have stomatitis, you should not eat sour vegetables and fruits:
- Citrus
- Green apples
- Tomatoes
- Currant
- Sorrel
- Spinach
The menu should contain a minimum of sweets, and chocolate, sweets, and sweet carbonated drinks are completely excluded.
Simple carbohydrates (sugars) are an ideal environment for the development of bacteria in the oral cavity, so their consumption can worsen the condition and significantly interfere with treatment.
You cannot use coffee, alcohol, or add spices to food. Everything sour, spicy, salty, pickled and smoked is excluded from the diet.
All this irritates the mucous membrane and provokes the appearance of new ulcerations.
For the same reason, you should not eat hard, rough foods: stale bread, fresh hard vegetables and fruits, crackers, waffles and more.
List of recommended products and dishes
- Cream soups and broths
- Minced lean meat (chicken, turkey, beef, rabbit)
- Liver (as pate or soufflé)
- Fish, incl. 1-2 times a week fatty varieties
- Milk and fermented milk drinks
- Cottage cheese, soft cheese
- Unrefined vegetable oils (linseed, olive, corn)
- Various cereals in the form of liquid viscous porridges
- Non-acidic stewed or boiled vegetables, purees from them (cabbage, broccoli, pumpkin, potatoes, zucchini, carrots)
- Non-acidic soft fruits and berries (banana, baked apple, watermelon, melon)
- Compotes, fruit drinks, natural juices from non-acidic vegetables and fruits, jelly
Nutrition rules
Many patients complain to doctors that they cannot eat with stomatitis. Such a refusal to eat due to painful sensations is fraught with consequences for the entire body. No matter what type of disease you have, be it viral, bacterial, allergic or aphthous stomatitis, nutrition is key to a speedy recovery. But what can you do to prevent a simple lunch from causing pain? Here are a few simple recommendations that, if followed, will help you eat normally without experiencing discomfort:
- All products must be ground to a puree before use. Grate vegetables and fruits on a fine grater or boil and rub through a strainer;
- it is easier to consume meat, fish and poultry in the form of thermally processed minced meat or soufflé;
- give preference to cream soup or puree soup instead of the usual broth with pieces of meat and vegetables;
- The patient's diet should be rich in vitamins B and C, as they help strengthen the immune system. And vitamins A and E help speed up the healing of cracks, wounds and erosions;
- food should be lukewarm, since both hot and cold food cause additional irritation of the mucous membrane;
- Immediately after a meal, be sure to thoroughly rinse your mouth with clean warm water to remove any remaining food.
Diso Nutrimun for stomatitis
Nutrimun protein mixture for stomatitis will be an excellent additional source of complete, easily digestible protein.
Nutrimun is easily mixed into dishes of any consistency, enriching them with protein of the highest biological value.
With Nutrimun, the body will receive the right amount of protein even in small amounts of food or drinks.
This is especially true for stomatitis, when frequent and split meals are indicated, and appetite is reduced due to pain in the mouth.
What is Nutrimun
SBKS Diso Nutrimun are concentrated milk proteins, easy to digest and complete in amino acid composition.
The mixture has virtually no taste or smell, so your favorite dishes will not change their usual characteristics.
With the addition of Nutrimun, the dish is enriched with healthy, easily digestible protein, necessary for the body to function and successfully fight diseases.
How does he help?
Diso Nutrimun is 5 grams of protein per scoop, it was developed by scientists and recommended by doctors for constant use.
You can add it to any dish: soups, broths, purees, soufflés, porridges, etc. You can stir Nutrimun in drinks: tea, compote, jelly.
Nutrimun is a specialized food product that increases and improves the protein part of the diet.
It contains all the amino acids necessary for the body in the correct ratio to each other for better absorption and greater benefits.
The protein of the Diso Nutrimun mixture is not only complete and balanced in amino acid composition, it is easily broken down in the digestive tract and is easily absorbed by the body.
Sample menu for the day
A sample menu is presented to help you understand what to feed your baby.
| Eating | Dishes |
| Breakfast | 1. Sweet oatmeal with milk and butter.2. Raspberry jelly. |
| Lunch | 1. Curd casserole with jam.2. Rose hip decoction. |
| Dinner | 1. Potato puree soup with meat broth.2. Steamed fish cutlet with zucchini puree.3. Dried fruits compote. |
| Afternoon snack | 1. Pudding with fruit puree |
| Dinner | 2. Chicken soufflé with stewed cabbage.3. A glass of Varentz. |
Food should be varied, dishes should not be repeated for at least seven days. Its task is not only to nourish the child in a gentle manner during the period of exacerbation of stomatitis, it should help strengthen the immune system and the body’s defenses.
Feeding a child with stomatitis
It is more difficult to feed a sick baby than an adult. The discomfort caused by mouth ulcers causes the child to be capricious and refuse to eat. Therefore, it is advisable to discuss with the doctor in advance products that do not cause pain to the little patient. As noted earlier, you need to feed soft food to avoid irritation of the delicate mucous membrane.
What to feed your baby
Nutrition during exacerbation
Only pureed or liquid foods are allowed. Vegetable purees and porridges have a semi-liquid and soft consistency, children like them. If we are talking about an infant, then there is no problem with nutrition at all, the only thing you need to remember is that the baby cannot be weaned from breastfeeding during the treatment period. It is also important that your baby always drinks water after meals (including after breastfeeding). You can give chamomile decoction, which has a disinfecting effect.
It is not yet possible to introduce new dishes for stomatitis, and allergenic foods must be excluded. Give your child white vegetables (for example, zucchini or potatoes) and liquid cereals. Even if we are talking about an older child, he can still be fed with vegetable/fruit baby purees, sold in specialized retail outlets. Ready-made meals will provide complete nutrition, since they contain everything a growing body needs.
- How long does it take for drugs to leave the body?
Baby purees
Nutrition during recovery
Every day you can give fermented milk products and pureed meat dishes if the child is used to them. Also make sure your child rinses his mouth every time he eats. If he cannot yet do this on his own, treat his mouth with your finger wrapped in a clean gauze cloth, after soaking it in an antiseptic/healing preparation. Finally, if the child is older than seven months, use sea buckthorn and rosehip oil for treatment.
Herpetic stomatitis
Important! The baby should eat four times a day; between meals you should not give him anything except herbal infusions and clean water.
Other important aspects of nutrition
In children with stomatitis, gastric juice is less actively produced, which is why dry food should not be given, and the child himself should drink a lot. If he wants to drink his food, don't interfere with him.
In children with stomatitis, the production of gastric juice reflexively decreases
As for the temperature of the food, it should not be too high/low. Otherwise, the foci of inflammation will be even more irritated. Ideally, all food should be at room temperature. You should also adhere to fractional nutrition - that is, feed often, but in small portions. If the baby doesn’t want to eat, there is no need to force him or swear. A few days later, when the foci of the inflammatory process have healed, the child will begin to eat normally again.
Note! If the pain is so severe that the child cannot even drink, let him try to do it through a straw. He can eat liquid soups and broths using the same method.
The child can drink through a straw
After the child eats and rinses his mouth, apply the ointment prescribed by the doctor. If we are talking about herpetic stomatitis, then this is, as a rule, “Acyclovir”, and if we are talking about any other form, then it is pain-relieving anesthetic gels.
"Acyclovir"
Treatment of stomatitis
Treatment of stomatitis depends on the severity and cause of the disease and includes the following measures:
1. For bacterial stomatitis, antibacterial drugs are prescribed. For fungal stomatitis - antifungal drugs, for viral ones - antiviral drugs
Important! Antibiotics, antiviral and antifungal drugs are prescribed only by the attending physician!
2. For high fever and pain, antipyretic and painkillers are prescribed
3. Vitamin therapy. It is especially important to take vitamins A, C, E
4. Immunomodulatory drugs
5. Antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity. Antiseptics are used in the form of solutions, sprays, tablets, ointments
6. Epithelializing agents are used after acute phenomena have subsided
7. Sanitation of the oral cavity, removal of dental plaque
8. A gentle diet
9. Eliminating allergens and taking antihistamines
Important! Stomatitis is treated by a dentist, in some cases together with a therapist, infectious disease specialist, allergist and dermatologist. If you have symptoms, consult a specialist.
Prevention of stomatitis
Consists of the following items:
- strengthening the immune system, giving up bad habits, hardening, playing sports, eating with a sufficient amount of macros and vitamins (especially vitamin C)
- regular visits to the dentist
- adequate brushing of teeth at home, as well as removal of dental plaque in the dentist’s office once every 6 months
- identifying the allergen and avoiding contact with it
- undergoing medical examination for timely detection of diseases
- treatment of systemic diseases
- taking antibiotics only as prescribed by a doctor, together with a course of probiotics, to avoid dysbiosis
- vaccination (against measles, chickenpox)
Tantum® Propolis
It is worth paying attention to Tantum Propolis, since propolis has an immunostimulating effect, promotes healing, and vitamin C, which is part of it, is responsible for regeneration, participating in the synthesis of collagen.
Propolis also has antiviral and antifungal effects. Therefore, vitamin therapy Tantum Propolis is an effective means of preventing stomatitis.12 Find out more
Diagnostic methods
Dentists, pediatricians and pediatric infectious disease specialists treat inflammatory diseases of the mouth in children. During the appointment, the doctor will examine your complaints, review your medical history to identify risk factors, and conduct a physical examination.
As a rule, a general and instrumental examination of the mouth is sufficient to make a preliminary diagnosis, since different forms of stomatitis manifest themselves as peculiar ulcers. Additional research may be required to clarify the nature of the disease.
Answers to popular questions
Which doctor treats stomatitis?
The dentist, if necessary, can refer the patient to other doctors.
Do I need to take antibiotics for stomatitis?
Some forms of stomatitis require the use of antibacterial agents, but in most cases this is not only useless, but even dangerous, since it can lead to dysbacteriosis. Antibiotics should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor in the prescribed dosage.
How long does it take to treat stomatitis?
Depends on the severity and form of the disease. On average 7-10 days.
Is stomatitis contagious?
Not all forms of stomatitis are contagious. Traumatic stomatitis is absolutely not contagious. If stomatitis is caused by viruses, such as herpes or measles, the risk of infection is very high.