Questions and answers on: tooth hurts under a filling
The most common questions patients ask after tooth filling concern pain.
- Question : “A month ago, I had a tooth healed using paste to kill the nerve and installing a temporary filling, but it hurts when pressed. Also, the gums on the cheek side were swollen. After the temporary filling fell out, I did not install a new one. What to do? Is it related to the root or the nerves?” Answer : “Most likely, the periosteum became inflamed because the canals were not treated in time. It was necessary to treat them and put a permanent filling. In your case, the tooth needs to be removed, but if you consult a doctor urgently, there is a small chance of saving it.”
- Question : “Can a tooth hurt after filling? It’s been 2 hours since the filling was placed, but I feel a little pain.” Answer : “Mild pain in a filled tooth is a natural physiological reaction to surgical intervention in the dental cavity. Periodic painful sensations may be felt for 2 months until complete healing. They will pass unless the pain becomes more severe and increasing.”
- Question : “Yesterday we got a filling, but the tooth still hurts. A small rash and itching appeared near him. I can’t stand it any longer, what should I do?” Answer : “You need to see a doctor to replace the filling. You have developed an allergic reaction to it. This is quite a rare occurrence."
- Question : “A week ago I was treated for caries and a filling was placed at the 6th unit below. But the tooth did not stop hurting. It especially bothers me at night; I can’t sleep due to the throbbing pain. Should a tooth hurt after filling?” Answer : “Most likely, the dentist treated you for deep caries due to periodontitis or chronic pulpitis and made a mistake, guided only by a visual examination of the oral cavity. In any case, it was necessary to take an x-ray of the tooth affected by caries. We urgently need to remove the filling and treat the canals.”
- Question : “2 weeks ago a permanent filling was placed without removing the nerve, but it still hurts me to chew. In addition, the tooth reacts to cold and hot food and at times there is aching pain.” Answer : “Such symptoms may indicate the development of chronic pulpitis or the development of an abscess inside the tooth.”
If various pains appear in the tooth after the filling procedure, then the only recommendation is to contact a qualified specialist. After all, the reasons can be completely different.
Toothache after filling
4523 March 25
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Toothache: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
After filling a cavity or canal of a tooth, pressing or bursting pain may occur. Sometimes pain occurs when biting, chewing and tapping a tooth; in some cases, the pain becomes acute with the development of swelling of the gums in the area of the causative tooth.
Types of toothache after filling
Depending on the cause of the appearance, local or diffuse toothache after filling is distinguished. More often it is transient and goes away on its own after a short time (no more than a day).
In some patients, after filling a carious cavity with deep caries or a canal with pulpitis, the intensity of pain gradually increases, it can be paroxysmal in nature, intensify under the influence of cold, and radiate along the branches of the trigeminal nerve. If left untreated, such pain becomes throbbing, the tooth may react to hot food, and swelling and redness of the gums develop. An infiltrate may form on the gum, from which pus or an abscess flows out when opened.
Possible causes of toothache after filling
Impact of irritants on the pulp.
First of all, you need to understand the location, intensity of pain and under what circumstances it occurs. If pain appears immediately after installation of a filling, this may be a consequence of the reaction of the nerves of the tooth and periapical tissues (tissues surrounding the root of the tooth) to mechanical, thermal and chemical influences.
Pain after the cessation of anesthesia indicates restoration of tissue sensitivity. As a rule, discomfort disappears within 24 hours after treatment.
Sometimes strong drugs placed into the tooth cavity lead to overdrying of dentin (the main solid substance of the tooth surrounding the pulp) and even to chemical burns of the pulp. This complication is accompanied by an acute pain reaction to cold and hot foods and sweets.
Incorrect installation of the seal
. If the upper border of the filling protrudes above the chewing surface of the tooth, then all the pressure of the opposite jaw during chewing falls on one tooth. This leads to overload of the ligamentous apparatus of the tooth, injury to the periapical tissues and the occurrence of dull local pain during chewing. To prevent such a complication, the doctor, after installing the filling, conducts a test with carbon paper. The paper is placed on the tooth with a filling and the patient is asked to close the jaws and make lateral and anteroposterior movements. The cusps of the tooth, which are marked with carbon paper, are ground off.
It is a mistake to think that excess filling material will wear off on its own over time.
The process of natural grinding lasts for years, during which time the patient experiences pain when chewing and, ultimately, this leads to traumatic periodontitis (inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tooth). Inflammation of the periapical tissues
and the appearance of pain may be a consequence of pushing the filling material beyond the apex of the root canal. Together with the filling mass, infected tissues from the tooth canal enter the periodontium, which cause periodontitis. In this case, prolonged aching pain occurs, which intensifies when pressing on the diseased tooth. Tapping on a tooth is painful. Nearby lymph nodes (for example, submandibular) may enlarge. There is a risk of accumulation of purulent exudate in the area of the root apex and the formation of an abscess. The gums near the diseased tooth swell and turn red. Sometimes pus breaks through the gum, in these cases the swelling, redness and pain decrease. However, without treatment, this process constantly recurs.
Pain after filling can also occur in cases where one of the canals extending from the pulp chamber remains untraversed.
The number and location of canals in multi-rooted teeth varies from person to person.
If during tooth sanitation one of the canals remains unnoticed, the infection from it penetrates into the periodontium with the development of chronic periodontitis.
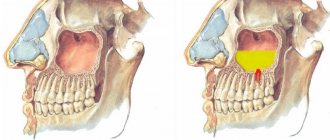
Close location of the carious cavity to the dental pulp
. In some cases, the bottom of the cavity is located too close to the pulp. The thin intermediate layer of dentin is penetrated by short tubes, through which infection from the carious cavity can enter the pulp and cause its inflammation (pulpitis). In these cases, hyperemia of the pulp develops (the initial stage of pulpitis), which, if left untreated, turns into acute pulpitis. There is no pain when tapping on the causative tooth.
A characteristic sign of initial pulpitis is pain that occurs upon contact with irritants (temperature and chemical) and goes away a few minutes after the cessation of their influence.
In other cases, the doctor may not recognize the initial stage of pulpitis when filling a tooth. In this case, sealing the infected pulp leads to acute pulpitis, which is accompanied by sharp, paroxysmal pain, intensifying at night and radiating along the branches of the trigeminal nerve.
Which doctors should I contact for toothache after filling?
If pain occurs immediately after dental treatment, you should contact your dentist. However, in some cases, when there are no signs of malocclusion and periodontitis and pulpitis are not observed on radiographs, the patient may be referred for consultation to an otolaryngologist (if sinusitis is suspected) or (if inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is suspected).
Diagnosis and examination for toothache after filling
The connection between the occurrence of pain and previous dental treatment helps to make a preliminary diagnosis. The presence of an inflammatory process is confirmed by redness and swelling of the gums.
However, accurate diagnosis is only possible after radiography.
In the absence of clear radiological signs of periodontitis, they resort to electroodontodiagnostics (a method for assessing the condition of the pulp, in which its reaction to a weak electric current is checked), it allows one to assess the degree of damage to the pulp.
What to do if you have toothache after filling
Mild, aching pain after tooth treatment may continue for 1-2 days, and this is normal.
However, if the pain does not subside or intensifies, a consultation with a dentist is necessary to diagnose possible complications.
Treatment of toothache after filling
If the pain is caused by malocclusion due to excess filling material, it should be sanded off.
Pain due to the development of pulpitis requires opening the pulp chamber and depulping the tooth. Acute and chronic periodontitis also indicates the need for unfilling of root canals and their mechanical and medicinal treatment. After treating the cavity and canals, the doctor can apply therapeutic and insulating linings, covering the tooth with a temporary filling, then another visit will be required so that the doctor can re-treat the cavity and place a permanent filling.
Sources:
- Clinical recommendations (treatment protocols) for the diagnosis of periapical tissue disease // Moscow State Medical and Dental University named after. A.I. Evdokimov of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. – 2014.
- Therapeutic dentistry: Textbook / ed. Borovsky E.V. – M.: Medical Information Agency. 2004. - 400 p.
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor.
Tooth hurts after nerve removal and filling
Only a dentist after an examination will help you figure out why a tooth hurts after removing a nerve and filling its canals. Treating teeth on your own without a diagnosis is highly discouraged.
In dental practice, the procedure for treating tooth canals by removing a nerve is a rather complex manipulation. Cases of medical error are common. They are fraught with various complications, in which the filled tooth continues to hurt.
The main reason why a “dead tooth” (without a nerve) is bothersome is:
- removal of the filling material beyond the apex of the tooth - this occurs due to incorrect definition
- working tooth length;
- the doctor filled the canal incorrectly;
- a tool broke off in the canal;
- root perforation of the tooth;
- If your tooth aches, you may be allergic to the filling material.
It is worth considering that a tooth under a filling can hurt even without a nerve. After all, during the extraction procedure, only a small part of it is removed from the root canal, which branches off from the main nerve trunk. In addition, when removing and filling canals, dental tissues are damaged. When an anesthetic is applied to a tooth, pain is not felt; it begins to be felt after the anesthesia wears off. Such painful sensations are called post-filling.
After removal of a nerve, neighboring teeth can often be bothered, but it seems as if it is the treated tooth that is hurting. An experienced doctor will examine the dentition to identify and eliminate this problem. However, it is worth sounding the alarm when the nerve has been removed for a long time, and the tooth continues to hurt - this symptom may signal the development of chronic pulpitis or periodontitis.
How long does the nerve removal procedure take?
The duration of the procedure depends on the degree of neglect of the pathology. On average, anesthesia takes about 5–15 minutes, and root canal treatment takes about 30–40 minutes. Sometimes medicine is placed into the cavity and closed with a temporary filling, and at the next visit it is replaced with a permanent one.
This method is rarely used, most often in cases of severe damage to multi-rooted teeth. For single-rooted individuals, one visit to the dental office is usually sufficient.
Important! Independent removal of a temporary filling is strictly prohibited. This leads to infection of the open canal, which is extremely dangerous not only for the oral cavity, but also for the entire body.
Tooth hurts after root canal filling
Dental clinic patients are often concerned about the question of why their tooth hurts after inserting filling material into the tooth canal after removal of the nerve. Since any intervention in the body has its consequences, toothache is an “echo” of the filling procedure.
The most common reasons for a tooth to ache after root canal filling are:
- burns and overdrying of dentin;
- allergic reaction to filling material;
- depressurization of the seal;
- change in bite;
- exposure to polymerization lamps;
- shrinkage of the filling.
After the procedure, the dentist usually advises you on how long the tooth under the filling hurts. However, if you feel increasing pain in a filled tooth for more than 2 weeks, you should urgently consult a doctor. Such pain can occur when an instrument breaks off in the canal, root perforation, or improper treatment of pulpitis.
Standards for quality depulping and guarantees
Effectiveness depends on the physician's adherence to the endodontic treatment protocol. Our Center has developed Unified Quality Standards that all specialists follow.
Endodontic dental treatment in our Center is carried out in the LifeTime Warranty format. We have eliminated the risk of re-infection of the canals at each stage:
- Isolation of the working area with a rubber dam Protects against the entry of saliva with bacteria that provoke inflammation. In our Center it is mandatory and included in the price.
- Measuring the length of the canal using an apex locator is necessary to fill the canal with material along its entire length. Eliminates going beyond the top of the tooth and the possibility of underfilling.
- Abundant antiseptic treatment Continuous treatment with sodium hypochlorite solution ensures sterility of the canal and eliminates the risk of infection.
- High-quality canal filling Dental microscope and 3D filling technologies make it possible to avoid voids in canals with pathogenic microorganisms.
- Mandatory X-ray control during the process. Important for processing and filling canals, taking into account their configuration. The doctor controls the filling of all bends and branches of the canals.
- Hermetic restoration of tooth shape. Guarantee of sterility of sealed canals. The reliable design blocks the access of infection from the oral cavity.
But modern gadgets and technologies are useless if they are in the hands of an inexperienced dentist. Manual skills and the ability to establish contact with the patient are an important condition for successful treatment.
Our Center employs highly qualified general practitioners and endodontists, who are among the TOP 10 general practitioners in Moscow in the categories “Endodontics” and “Dental Restoration.”
Will root canal cleaning save a tooth that is more than 50% destroyed?
Yes, quite, but instead of installing a composite filling, it is recommended to install a microprosthesis or a ceramic crown. The only difference is in the final stage of the operation.
Clinical case: the patient was diagnosed with advanced caries, which developed into pulpitis. The tooth is badly damaged, but the root is intact. The dentist removes necrotic tissue, qualitatively treats the canal passages, cleans them under a microscope, and then places a microprosthesis or a full-fledged crown.
Filling methods
Until recently, the procedure was carried out using pastes, which are inexpensive and do not require complex technologies. Now professional dentists have abandoned them due to insufficient fluidity, which leads to the formation of cavities. Voids lead to depressurization and relapse of inflammation.
At the moment, doctors choose progressive methods:
- Thermophile system. The filling is performed with hot gutta-percha, which hardens as it cools. It is characterized by high plasticity. There is no pain after treatment. The risk of complications is minimal;
- depophoresis. It is used for filling difficult, curved canals, as well as for restoring elements from which it is difficult to remove old fillings and where fragments of ostomy instruments remain in the cavities. Efficiency - no less than 95%;
- E&Q Plus. The latest generation method, which provides various methods of filling the roots of one tooth. The injection gun heats the gutta-percha directly inside the cavity. The doctor can control the temperature of the material using the information display.
Another common method is filling the canals with cold gutta-percha, which is used in several ways:
- lateral condensation;
- softening due to chemical action;
- with one pin. To give the shape, a pin is installed in the canal. Sealing is ensured through the use of paste.
There are other technologies that are selected depending on the location of the channels, the condition of the tissues and the experience of the doctor.
Is it painful to remove a nerve from a tooth?
Modern dentistry has the widest possibilities and powerful universal anesthesia. Thanks to this, removal of the flock nerve is a painless procedure that is carried out during the visit. The only discomfort that the patient may feel concerns the injection into the gum. This can also be easily avoided by applying anesthesia, after which inserting a needle will not cause any discomfort.
Pain may occur in rare cases for one of the following reasons:
- Individual characteristics of the path of nerves, which is why standard techniques provide insufficient pain relief.
- Taking painkillers the day before by the patient, in particular from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), may reduce the effectiveness of anesthesia.
- The patient took alcohol before visiting the doctor.
- The patient belongs to the 2% of all people with immunity to anesthetics.
The solution to the problem in each case is the same - repeated anesthesia.
Description of pulpitis
Those who are not good at dentistry do not even realize that there is a main nerve in the tooth. Its inflammation is called pulpitis. This is a very complex disease, the symptoms of which are almost impossible to miss. At risk are people who have advanced caries with extensive carious cavities. As a rule, the first signs are observed after consuming too hot, cold foods or drinks. The nerve begins to react sharply to aggressive substances, which causes severe pain in the tooth, body temperature often rises and a general loss of strength. If you immediately go to the doctor and begin treating pulpitis, the intensity of the inflammatory process can be quickly reduced. If you try to solve the problem at home for a long time with the help of painkillers and improvised means, you may waste time and the only way will be to completely remove the nerve.
What is a dental nerve?
Simply put, the dental nerve is a neurovascular bundle that is located inside the teeth or in the tissues surrounding the tooth. Simply put, this bundle is also called pulp.
The pulp is needed to ensure the vital functions of the tooth; it helps supply the canine with essential vitamins and minerals. Protects dentin from the penetration of bacteria, prevents the formation of pathogenic flora in the unit.
When the nerve is removed, the tooth becomes essentially “dead.” That is, he does not receive the necessary nutrition. Over time, it will lose its strength, may change color, dentin will become thinner, so these manipulations are done only as a last resort.
What is tooth nerve inflammation?
This pathology is caused by an advanced stage of caries. If a person does not go to the dental clinic in time, then bacteria will gradually destroy dental tissues, eventually reaching the pulp, which leads to pulpitis.
Pulpitis
is an inflammatory process in the tissues of the dental unit.
Treatment of pulpitis always begins with removing the nerve of the tooth and cleaning the canals.
Pain after caries treatment
Immediately after filling a tooth, pain may occur for the following reasons:
- temperature changes (cold food, hot drinks);
- pressure of the filling on the pulp (if the carious cavity was located very close to the nerve).
Increased sensitivity to cold and hot usually goes away after a couple of days. The pain due to the pressure of the filling on the pulp should disappear within a month, as a protective layer of dentin is produced. If the pain lasts longer than 4 weeks, go to the doctor.
If pain did not occur immediately, but several weeks after filling, then the causes are complications, such as:
- the presence of remains of caries-affected tissue under the filling, which provoked the development of pulpitis;
- crooked filling;
- poor oral hygiene, which caused secondary caries.
Note! Go to the doctor if the pain that occurs after filling lasts longer than a month, and also if the symptom does not appear immediately, but after several weeks.