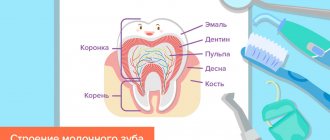
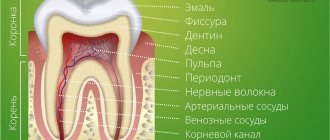
Development of teeth before eruption
The health of your baby’s teeth needs to be taken care of long before they erupt. It is useful for expectant mothers to know that the rudiments of baby teeth are formed already at the 7-8th week of intrauterine development, and permanent ones - at the end of 4 months. Not only the timing of teething, but even the level of mineralization of the enamel of both milk and molars depends on how pregnancy proceeds. Therefore, it is so critical that a woman receives all the vitamins and microelements and is as healthy as possible.
But it’s not just nutrition that’s important. Research results have shown that in the presence of industrial harmful substances in the environment of the expectant mother during pregnancy and numerous stressful situations, the formation of all dental tissues in the child is disrupted and the timing of the appearance of baby teeth is shifted. Among children born to women with high blood pressure, late eruption of primary teeth was observed in 56.7%. In approximately a third of the examined children born to mothers with heart defects, late eruption of primary teeth was detected, as well as deviations in the pairing and sequence of their eruption. The length of pregnancy also plays a role. There is a pronounced dependence of the timing of the eruption of the first teeth on the degree of prematurity: the earlier the baby is born, the later the first teeth erupt [1, 2].
Timing of appearance of temporary teeth
The order in which teeth appear is determined by the importance of each of them in the process of food processing. Therefore, the central and lateral incisors are shown first, then the canines and first molars, and the second molars last. The principle of “pairing” operates in this process. This means that if one central incisor has erupted, a second one will soon appear, and so on. In this case, the teeth of the lower jaw appear first, then the upper ones. The exception is the lateral incisors; they cut faster in the upper jaw. The process of formation of a temporary bite is completed in a period of 2 to 3 years.
Important: the diagram shows average time intervals. But each person is individual, so the schedule may be shifted in one direction or another. It depends on many factors. Parents should not worry if their baby’s teeth begin to appear a little earlier or later than indicated in the diagram. You should contact a specialist if teething has delayed for 2 - 3 months from the maximum period.
Why are baby teeth needed?
Nature has designed the correct order and timing of teething in children. Evolutionarily, this is due to the need to form the bite and jaw bones for chewing and speech. Over the years, the bones grow, and baby teeth, which at the beginning of their appearance were tightly adjacent to each other, diverge by the age of 6-7 years, forming wide interdental spaces that are natural for this period - tremata and diastemas.
There are only 20 teeth in the primary dentition. This is explained by the fact that they must be correctly placed in the small child’s jaw in the first years of the baby’s life, and eliminates the crowding of teeth that provokes dental diseases. The last of the baby teeth are replaced at the age of 10-12 years. However, they are very important for the physiological formation of the jaw bones and the permanent bite.
Proper growth and health of baby teeth helps:
- rebuild the body from lactophoric to mixed type of nutrition;
- reserve space for the normal location of future molars;
- form a mixed bite.
There is a misconception that if baby teeth become infected with caries, they can not be treated, but can be removed immediately. But modern dentists are against such tactics. Early removal is fraught with displacement of adjacent baby teeth and the appearance of problems with an adult bite. Therefore, it is so important to maintain the presence and health of all baby teeth until the permanent teeth erupt on their own [3].
Timing of baby teeth eruption
Teething is a genetically programmed event that occurs at a certain period.
Physiological teething is characterized by three main features: certain timing, pairing and sequence of eruption “Characteristics of exogenous and endogenous factors influencing the eruption of primary teeth in children” Dr. med. Galaktionova M. Yu.
Children's baby teething rates vary depending on their ethnicity. But as research shows, in general, in the world there is a reduction in the time from birth to the moment when the first tooth appears. This is due, according to most researchers, to the global acceleration of human development [1]. How and when baby teeth erupt is one of the indicators of a child’s physical development.
The reasons for violation of the order and timing of teething in children can be:
- heredity;
- climatic conditions;
- nature of feeding;
- some diseases, for example, rickets.
The standards for the eruption of primary teeth according to the American Dental Association are presented in the table.
| Baby teeth | Upper jaw eruption / month. | Lower jaw eruption / month. |
| Central incisor | 8-12 | 6-10 |
| Lateral incisor | 9-13 | 10-16 |
| Fang | 16-22 | 17-23 |
| First molar | 13-19 | 14-18 |
| Second molar | 25-33 | 23-31 |
The indicated periods are average indicators, varying depending on individual and family characteristics [4,5]. But the sequence of appearance of teeth is significant, and it is better to track and record it. From a physiological point of view, the correct order of eruption of baby teeth in children is important for the formation of occlusion .
Typical clinical picture: characteristic symptoms
Classic signs of teething in infants occur approximately 10-14 days before the tip of the upper or lower incisor appears on the gum surface. They are difficult not to notice, as they are of high intensity and affect the general well-being of the child. Parents should be aware of all these signs and symptoms in order to take timely measures and provide the necessary hygienic care and medication if needed.
Increased activity of the salivary glands
This is manifested by hypersalivation - increased salivation. During this period, the child has to be changed every 1.5-2 hours, as his clothes quickly become damp due to constantly flowing drool. Increased attention should be paid to hygiene: a humid environment causes irritation on the skin of the chin and neck and promotes the spread of pathogenic bacteria. A child with excessive drooling should be bathed daily, sometimes even 2 times a day. It is advisable to add a decoction of string or chamomile to the water (you can use regular table salt) - they will relieve inflammation, soothe the skin and eliminate itching.
Note! Secretory activity in some children may also be manifested by watery or mucous discharge from the nose. They should have a transparent color and liquid consistency. There is no need to worry about this phenomenon if the child has no signs of colds or respiratory diseases.
Change in body temperature
The appearance of the first teeth is a difficult process for a child’s body, accompanied by inflammation, to which the immune system reacts with a slight increase in body temperature. Usually this indicator remains within subfebrile values and does not exceed 38°C. If the child feels well, there is no need to lower the temperature. In case of severe discomfort, when the child refuses to eat and is not interested in surrounding objects and people, you can use drugs from the group of antipyretic drugs.
The drugs of choice for children under 1 year of age are those containing paracetamol or ibuprofen. They can be produced in the form of rectal suppositories or syrups for internal use. These include:
- "Ibufen";
- "Panadol";
- "Nurofen";
- "Paracetamol";
- "Ibuprofen."
Important! For children with a tendency to allergic reactions, it is better to use the drug in the form of suppositories (for example, Cefekon), since the oral forms contain aggressive dyes.
External gum changes
The surest way to determine that a child's teeth will begin to grow is to examine his gums. There is a whole range of symptoms that allow you to determine the imminent eruption. These include:
- swelling and swelling of the gums;
- the appearance of a white dense lump on the gum (the upper part of the erupting tooth), when pressed on which the child experiences severe pain;
- hyperemia of the mucous membranes at the site of eruption;
- itching of soft tissues (if a child scratches an inflamed gum, he will close his jaw tightly and make scratching movements);
- bleeding gums.
If the gums begin to bleed, it means that there is very little time left until the first tooth erupts - no more than 3-7 days.
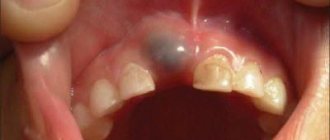
Important ! These symptoms may indicate inflammatory gum disease, such as gingivitis or periodontitis. Despite the fact that they are rarely diagnosed in children in the first year of life, it is necessary to consult a dentist to rule them out. A white lump on the gum may be an abscess or abscess, so it is best to draw conclusions about the causes of the inflammatory process after a medical examination.
Helping your baby with teething
The appearance of baby teeth is not an easy process not only for the children themselves, but also for their parents. The most common symptoms of teething:
- swelling and redness of the gums;
- increased salivation;
- itching and desire to keep hands and toys in the mouth;
- child's capriciousness;
- sleep disturbance;
- refusal to breastfeed, bottle or complementary foods;
- temperature increase;
- bowel disorders;
- runny nose.
The following will help you get through this period as comfortably as possible:
- special teething rings that relieve itching, especially with a cooling effect;
- dental gels with local anesthetic effect;
- antipyretic and painkillers;
light massage with a silicone fingertip, which will bring relief and calm the baby [6]
Pathological signs: when should you see a doctor?
Some symptoms that young mothers consider normal during teething are not directly related to the process and are the penetration of infection into the child’s body. Teething is stressful for the body, and the child’s immunity during this period is greatly weakened, which creates excellent conditions for the growth of pathogenic bacteria and viruses.
Listed below are typical signs that require consultation with a specialist, which cannot be considered as a physiological norm during the appearance of baby teeth in infants.
- Temperature . A slight increase in temperature is considered normal during the eruption of frontal incisors and canines, but it should not rise above the upper limits of subfebrility. If a child has a temperature of 38.1°C or higher, you should consult a doctor - an infection has probably occurred due to reduced immunity.
- Diarrhea. It is normal to loosen stools due to increased activity of the endocrine glands, but stools should not be too frequent, watery, or foul-smelling. There should be no changes in the color of the stool, so consultation with a doctor is necessary if the stool has changed consistency, color or smell.
- Cough . The physiological norm is a slight cough that occurs as a result of saliva flowing down the back wall of the larynx, but a frequent and prolonged cough always indicates a cold infection.
Any changes in the child’s well-being and behavior should be a reason for consultation with a pediatrician or pediatric dentist - only a doctor will be able to assess the baby’s condition and draw a conclusion about his health and the need for any therapy. Read the article for treatment of stomatitis at home.
Caring for baby teeth
As soon as your first tooth comes through, don’t put off going to the dentist. Make a schedule of visits (at least once every 3-4 months). And after the first birthday, it is advisable to also see an orthodontist. If there are no problems, visits to him should be repeated once a year [7,8]
It is important to provide proper care at home.
- An ultra-soft toothbrush with a small head is suitable for baby teeth
- Children's mouth rinses are used from about 4 years of age or from the time the child learns to spit out liquid.
- Parents should supervise the brushing of preschool children's teeth and, if necessary, help and finish cleaning missed areas.
- Adults need to teach their child to rinse their mouth after eating from a very early age.
- Until the child has learned to spit on his own, toothpaste should not contain fluoride.
- A timer in the bathroom or a favorite song helps you keep your teeth brushing to 2 minutes.
- Solid food should be included in the diet daily in sufficient quantities to properly form the bite and stimulate the gums.
These simple recommendations help maintain the health of baby teeth from the very beginning until their natural replacement with permanent ones.
When do teething symptoms appear?
The foundation of baby teeth is laid during pregnancy: doctors recommend that mothers monitor their diet and bad habits, including because all this affects oral health.
During the first six months of life, the child accumulates material for bone tissue growth. When the baby is six months old, you can expect symptoms: at this age, babies begin to erupt their upper (natal) teeth. This happens in most cases, but there are many exceptions. Surely you have heard about children who are born with “hatched” teeth. It also happens that the first incisor appears only at one year of age. Both cases are normal.
In total, 20 milk teeth should appear in the baby’s mouth by the age of three: on each jaw there are 4 incisors (4 central teeth), 2 canines and 4 molars (fourth and fifth teeth).