Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
Before talking about the treatment of pulpitis with unformed roots, you need to understand what unformed roots are.
After the eruption of baby teeth, their roots have an uncovered apex for several years, which is why they are called unformed.
Features of the treatment of pulpitis on teeth with unformed roots
Treatment of pulpitis on such teeth has its own characteristics. Due to the fact that it is impossible to completely treat the entire length of the tooth roots and extract the pulp, traditional devital and vital methods for treating teeth with immature roots are not suitable. Therefore, pediatric dentists use biological treatment methods or the amputation method.
Conservative treatment
It should be noted that biological (conservative) treatment is a rather complex process that has a number of contraindications. The main principle of treatment is maintaining absolute sterility. It is very important to carry out high-quality antiseptic and aseptic processing.
During the biological treatment of pulpitis, the dentist, under anesthesia, removes not only plaque, but also all affected and dead dental tissue, prepares the tooth cavity and applies medicine to the exposed nerve (or to the bottom of the carious cavity). As a rule, this medicinal paste contains calcium hydroxide. After all pain symptoms disappear after a few days, a permanent filling can be installed. The main thing is that as a result of this treatment, the tooth retains its vitality and strength, and the pulp provides nutrients to its tissue.
Amputation method for treating teeth with immature roots
Due to the complexity of biological treatment and the existing contraindications to this method, this method is used infrequently by dentists. And most doctors prefer amputation, during which the doctor removes the infected pulp from the pulp chamber using a vital or non-vital method.
- The devital method using arsenic compounds is not used in every clinic today. Some dental offices use phenol-formalin to necrotize the pulp. To do this, a swab moistened with this solution is applied to the tooth cavity for 4-5 days.
- Most often, pediatric dentists treat pulpitis using the vital method, without the use of arsenic. To do this, doctors use not only local anesthesia, but also various antibacterial drugs, calcium-containing drugs and remineralizing agents. During this method, the pediatric dentist, after taking care of anesthesia, excises the upper part of the pulp and applies a special preparation. Thanks to this method, it is possible to preserve the root pulp, which means that in the future the dental roots will continue their normal formation.
Alternative
Prevention of pulpitis is careful adherence to hygiene rules. Use Asepta toothpastes, which effectively strengthen tooth enamel and prevent the growth of bacteria in the oral cavity.
Principles of treatment of teeth with formed roots
The tactics for treating chronic periodontitis are identical to the approach for treating temporary teeth. If the following conditions are met, it is possible to cope with the disease in one visit:
- there is no gangrenous decay with a putrid odor in the canal;
- there are no granulations grown into the canal;
- there was no exacerbation of such diseases in the anamnesis;
- it is possible to qualitatively process the canal in one visit and dry it;
- the child is somatically healthy and does not take antibiotics, cytostatics, corticosteroids or other immunosuppressive drugs.
In this case, during one visit, the root canal is treated instrumentally and medicinally, obturation is performed with a permanent root filling, and then the crown part is restored. It is much more common to practice treatment in several stages.
On the first visit, the following manipulations are performed:
- necrotomy, formation of a carious cavity;
- opening the canal and removing putride masses from it using a pulp extractor or several - with a very wide canal;
- removal of granulations grown into the canal with injection anesthesia or short-term treatment of granulations with special preparations, for example camphorophenol (very carefully so as not to burn the mucous membrane);
- instrumental treatment of the canal, washing and drying;
- administration of a medication with an antiseptic effect on the turunda or in the form of a paste;
- isolation with an airtight bandage for temporary obturation of the carious cavity.
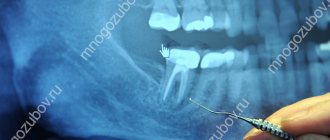
The medicine is left on average for 1-7 days, after which permanent obturation is performed - subject to the conditions of readiness of the root canal. Obturation is carried out with a sealer with gutta-percha, after which X-ray control is necessary, and only then restoration of the crown.
Clinical researches
“Results of clinical use of the Asepta series of products: already at the first control examination (after 1-2 days) of using the Asepta line of products, there is a decrease in complaints of discomfort, but bleeding persists when brushing teeth. On the 7th day, complaints of gum bleeding persisted in 4 patients. Upon examination, a decrease in hyperemia and swelling of the gums was noted, but bleeding persisted upon probing. After the final application of the gel with propolis, normalization of clinical manifestations was revealed, which is manifested by the absence of bleeding during brushing and probing.”
Sources:
- The effectiveness of the use of Asept “adhesive balm” and Asept “gel with propolis” in the treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis and gingivitis in the acute stage (Municipal Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk, Kaminskaya T. M. Head of the therapeutic department Kaminskaya Tatyana Mikhailovna MUZ City Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Aleksandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina) A.I. GRUDYANOV, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department I.Yu. ALEXANDROVSKAYA, Ph.D. V.Yu. KORZUNINA, asp. Department of Periodontology, Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Report on the determination/confirmation of the preventive properties of personal oral hygiene products “ASEPTA PLUS” Remineralization doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
Pulpitis
Treatment of patients with pulpitis
Treatment of children with pulpitis should be carried out taking into account the fact that foci of chronic infection of odontogenic origin can adversely affect the course of general diseases. In this regard, there is a need to reconsider the issue of indications for the sanitation of temporary teeth with chronic forms of pulpitis.
The question of the advisability of treating a child with chronic pulpitis of a primary tooth should be decided after an X-ray examination and comparison of the clinical and radiological manifestations of the disease.
When visiting the dentist, the biggest fear is the drill. Dental interventions are more likely than others to be associated with pain and other unpleasant sensations. Therefore, the problem of premedication is especially relevant in pediatric dental practice. Psychological and pharmacotherapeutic effects on restless children with heightened emotional reactions relieve excessive stress.
For premedication, minor tranquilizers are prescribed - sibazone and mebicar in an age-specific dosage 30-40 minutes before the start of treatment. For young children, it is preferable to use sibazon, and to achieve a stronger tranquilizing effect, a combination of sibazon with mebikar.
For pulp anesthesia, various methods of anesthesia are used: infiltration, conduction, application, intraligamentary, reflex analgesia, electrical anesthesia, as well as anesthesia: mask, intubation, intravenous.
When treated with vital pulp extirpation, intrapulpal anesthesia is sometimes used using a needle-free injector.
Traditional methods of anesthesia - conduction and infiltration - cause a negative reaction in children in the form of fear of the syringe and needle. In this situation, intraligamentary anesthesia is the most appropriate, which has been increasingly used in dental practice in recent years. There are only isolated studies on the use of this method of pain relief in children. In pediatric dental practice, domestic ointments are used for topical anesthesia: 5% pyromecaine and 5% pyromecaine with methyluracil on collagen.
General anesthesia is performed for children who cannot tolerate the anesthetic, with an unbalanced psycho-emotional state, accompanied by fear, fainting, increased gag reflex, as well as children with epilepsy, cerebral palsy, mental retardation, etc. In pediatric dental practice, mask anesthesia with a mixture of fluorothane, nitrous oxide and oxygen is more often used for general anesthesia. By inhibiting salivation, fluorotane has a great narcotic effect (50 times more active than nitrous oxide), ensuring rapid entry into a state of anesthesia and restoration of consciousness. The use of this method provides highly effective anesthesia of the pulp.
Pulp tissue has a significant ability for reparative and plastic processes. The main task in the treatment of children with pulpitis is to eliminate odontogenic infection and, if possible, preserve the viability of the pulp, especially its root part, as well as the prevention of periodontal diseases.
During treatment, it is very important to provide conditions for the completion of the formation of teeth, temporary and permanent, and the physiological resorption of temporary teeth. Conservative and surgical treatment methods are used. Conservative therapy is aimed at preserving the entire pulp. Surgical treatment consists of partial (pulpotomy or amputation) or complete (pulpectomy or extirpation) removal of the entire pulp. The choice of treatment method is determined by the nature of the inflammatory process, the state of the child’s health, the group affiliation of the tooth, the location of the carious cavity, the degree of root formation or its resorption (for temporary teeth).
- Biological method
Preserving the vitality of the pulp of temporary teeth promotes their function until physiological change, prevents the development of complications in the periodontium and jaw bone, and in permanent teeth ensures the complete completion of formation.
Complete preservation of the pulp in children is possible with acute partial pulpitis, including traumatic origin, and chronic fibrous pulpitis. Some authors indicate the possibility of using a biological method for acute general pulpitis that is not accompanied by a reaction of the surrounding soft tissues, but in most cases in children this recommendation is clinically untenable.
The use of a biological method in the sanitation of teeth with pulpitis helps reduce repeated visits from patients by 10 times and saves the dentist’s work.
A contraindication for this method is active resorption of the roots of primary teeth. This method showed the best results in children at the stage of compensation of the carious process. In children with a decompensated form of caries and low levels of nonspecific resistance of the body, conservative treatment of temporary teeth with pulpitis turned out to be ineffective.
Most doctors are supporters of the radical method of treating patients with pulpitis, since in widespread practice the biological method gives a large number of complications. This is due to errors in diagnosis, lack of clinical tests that accurately determine the form of pulpitis and the extent of the inflammatory process. The discrepancy between clinical and pathological diagnoses is 70-90%.
To preserve the vitality of the pulp, it is indirectly coated with the drug, if the pulp is not opened, and directly, during which a medicinal paste is applied to the exposed pulp. Drugs selected for conservative treatment must meet the following requirements: have a pronounced antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effect, stimulate pulp regeneration and not cause irritation, in addition, they must have no allergic component and microbial resistance to them.
Most clinicians both in our country and abroad, when using the biological method, give preference to drugs based on calcium hydroxide. Therapeutic materials containing calcium hydroxide have antimicrobial activity (due to a pronounced alkaline reaction), stimulate the plastic function of the pulp, resulting in the formation of replacement dentin - a “dentin bridge”. The best results are observed in the case of using “Calmecin” in the treatment of temporary molars in children aged 4 to 7 years, when the roots are in a state of physiological rest, and in permanent immature teeth, especially in the treatment of chronic fibrous pulpitis.
In recent years, the number of negative results of treatment with a biological method using drugs based on calcium hydroxide has increased: the possibility of calcification of the coronal and root pulp cannot be excluded; the destruction of all microorganisms in softened dentin is not ensured.
However, at present, preparations based on calcium hydroxide remain popular. In pediatric dentistry, they use Calmecin, Dycal (Germany), Sterimax, Life (USA), etc. Depending on the indications, biological treatment for pulpitis is carried out either in one or two visits.
When treating in two visits, for the first time drugs with antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects are used: antibiotics, glucocorticoids, enzymes. However, neither antibiotics, nor glucocorticoids, nor other antibacterial agents should be left under a permanent filling, so as not to cause inhibition of the dentin-forming function of the pulp and selective suppression of microorganisms.
When treating teeth with immature roots using the biological method, glycosaminoglycan preparations are used - honsurid, luronite. Medicinal pastes containing collagen, bone meal with heparin, and lysozyme with vitamin A are also offered. Zinc-eugenol paste continues to be used, although N.M. Chuprynina believes that this paste rarely gives a positive result.
- Vital amputation method
A viable root pulp serves as a reliable barrier to the penetration of microorganisms into periapical tissues and prevents the development of odontogenic foci of inflammation. Therefore, the vital amputation method is aimed at preserving the vital activity of the root pulp. The apical part of the root pulp, periodontium and growth zone represent a single biological whole. The root pulp is well supplied with blood, the tissue of the growth zone contains a large number of cellular elements with high protective and shape-forming abilities. The root pulp is built like deep-fibrous connective tissue with a small number of cellular elements and is capable of metaplasia and the construction of dentin-, cement- and osteo-like tissue. These features of the root pulp contribute to its resistance, especially in the apical part, to adverse influences.
The indications for using the vital amputation method are the same as the biological method: acute partial and chronic fibrous pulpitis. Incomplete root formation and just begun resorption of the roots of primary teeth serve as direct indications for the use of the vital amputation method. When the crown of a permanent immature tooth is broken with the pulp exposed over a significant extent, vital amputation of the pulp is indicated if no more than 2-3 days have passed since the injury. With significant resorption of the roots of primary teeth, the reactivity of the pulp is reduced, and the method of vital amputation is contraindicated. Opening of the tooth cavity and removal of the coronal pulp is carried out after infiltration or conduction anesthesia. For children with unbalanced psycho-emotional perception, local anesthesia can be combined with psychotherapeutic and medicinal preparation with small tranquilizers in an age-appropriate dosage.
Having opened the tooth cavity, the pulp is removed from the crown and canal mouths and deep amputation is performed to 1/2 or 1/3 of the length of the root, depending on the form of pulpitis, and in case of pulp injury, on the period that has passed since the injury. During pulp removal, it is necessary to avoid the formation of a laceration. To stop bleeding, hemostatic agents are applied to the wound surface for 10-20 minutes. The wound surface of the root pulp is covered with the same medicinal pastes that are used in the conservative method of treating patients with pulpitis. The paste is applied carefully, without pressure. After vital amputation, in teeth with unformed roots, the root continues to grow in length, and a dentinal bridge is formed in the area of the wound surface.
In case of significant infection of the pulp in single-rooted permanent teeth, a method of preserving the apical part of the root pulp and the growth zone is indicated. To do this, the maximum possible removal of the pulp with a boron is carried out under anesthesia, and a mixture of phenol and formaldehyde (in a ratio of 2:1) is applied to the stump for the purpose of mummification and disinfection. Treatment is completed by applying formaldehyde paste to the stump. The paste is prepared extempore: 1 drop of formalin, 1 drop of glycerin, a crystal of thymol and zinc oxide. This creates a layer of mummified pulp, which is separated from the viable apical part and its growth zone. The effectiveness of treatment is monitored after 3-12 months and until the end of root formation. If it is determined that root formation has stopped, treatment is carried out as for chronic periodontitis, i.e. complete removal of the pulp.
- Vital extirpation method
The method can be performed in temporary and permanent teeth with complete root formation, if the root canals are passable. If these conditions are met, the method is applicable for all forms of pulpitis and is carried out in the same way as in adults.
When performing this method, it is necessary to ensure good anesthesia. However, in pediatric dentistry, the vital extirpation method is not widely used, since it is time-consuming and labor-intensive, and children are not always able to withstand long-term multi-stage treatment.
- Devital amputation method
Most often in pediatric dental practice, this method is used for acute general and chronic fibrous pulpitis in temporary molars, as well as in permanent immature molars. Devital amputation is not indicated for chronic gangrenous and aggravated chronic pulpitis. If the tooth cavity is not opened after removing the softened dentin, then it is advisable to open it with a spherical bur No. 1, having previously applied application anesthesia.
Arsenic paste is used as a devitalizing agent, which has a necrotizing effect on the pulp. The use of arsenic paste is due to its ability to quickly diffuse into the tissue. If the arsenic paste remains in the tooth cavity for more than 24-48 hours, arsenic anhydride reaches the periodontium and causes foci of destruction in it.
Necrotization of the pulp with arsenic paste still remains the main method of treating children with pulpitis, since this method makes it possible to spare the child’s psyche as much as possible and to carry out the treatment painlessly on the second visit. In this case, there is no need for local anesthesia, which children are so afraid of. Arsenic paste is used in the same doses as in adults. During the second visit, the coronal pulp is removed, carefully opening the tooth cavity and taking into account the topography of the root canal orifices. A tampon with a resorcinol-formalin mixture (liquid) is left in the tooth cavity, which has the ability to diffuse along the dentinal tubules, and after mummification of the pulp, fill the space between the reduced root pulp and the canal walls. On the third visit, in conditions of a dry mouth, a temporary bandage and tampon are removed, and resorcinol-formalin paste is applied to the bottom of the tooth cavity, which, due to diffusion, completes the mummification of the pulp.
Mummifying substances do not disrupt the process of root formation and resorption of the roots of temporary teeth.
With a low-pain pulp, during the period of active resorption of the roots of temporary teeth, phenol-formalin can be used as a necrotizing agent (the tampon is left for 4-5 days). Since arsenic paste is highly toxic, it is proposed to use pastes containing paraformaldehyde to necrotize the pulp. It causes vasodilation in the pulp, followed by stasis and necrosis, but does not lead to pathological changes in the periodontium, even after prolonged exposure. Treatment is carried out using the amputation method in three visits. Paraformaldehyde paste in a volume equal to the head of a spherical bur No. 3 is applied for 5-6 days. There are ready-made para-formaldehyde pastes: “Sinarsen”, “Fasipulpin”, “Devipulp”, etc.
However, when prepared for future use, they quickly lose their activity. This is due to the fact that paraformaldehyde depolymerizes in air under the influence of water and temperature.
If acute pulpitis in children is accompanied by a pronounced inflammatory reaction of the periodontium and surrounding soft tissues, lymphadenitis, then arsenic paste should not be applied on the first visit. You should carefully open the tooth cavity, create an outflow of exudate and prescribe anti-inflammatory treatment: orally - acetylsalicylic acid (the dose depends on age) after meals; sulfonamide drugs, calcium gluconate, drinking plenty of fluids. The application of arsenic paste is carried out after the inflammatory phenomena have subsided.
- Devital extirpation method
The method is indicated for all types of pulpitis in single-rooted temporary and permanent teeth and permanent formed molars with well-passable canals. The stages of treatment for devital extirpation are the same as for adults.
The method of complete pulp removal is the most reliable in terms of eliminating odontogenic infection and preventing periodontitis, if the pulp is completely removed and the canals are sealed throughout. However, the tops of the roots of temporary teeth are often curved due to the permanent tooth germ located underneath them, and it is not always possible to completely fill them. In this case, resorcinol-formalin paste, which has a mummifying effect, should be used for filling.
For well-passable canals, non-irritating oil-based pastes (eugenol, sea buckthorn oil, etc.) are used for filling.
Errors in treatment and diagnosis are associated with insufficient history taking, incorrect assessment of the signs and extent of pulp inflammation, and underestimation of pain symptoms. They can also arise when there is insufficient justification of the indications and contraindications for the treatment of teeth with biological pulpitis and the method of vital amputation of the coronal pulp, underestimation of the unique course of acute general pulpitis and the reaction of the surrounding soft tissues in young children. A lot of troubles are associated with arsenic paste. If the temporary dressing is not applied tightly, then the arsenic paste that leaks into the surrounding tissue can cause necrosis of the mucous membrane of the gums, cheeks, and tongue. With prolonged contact with tissue, necrosis and sequestration of part of the alveoli are possible. Due to an overdose or prolonged stay of arsenic mouth in a carious cavity, acute arsenic periodontitis develops. In children, the diffusion of arsenic paste into the periodontium occurs faster than in adults, due to the anatomical features of temporary teeth. Acute periodontitis that occurs has a long course and is difficult to treat. For treatment, use the arsenic antidote unithiol, as well as a solution of iodinol and potassium iodide.
A common mistake in treating patients with pulpitis in primary molars is perforation of the bottom of the tooth cavity, when the anatomical features of the structure of hard tissues and pulp of temporary teeth are not taken into account.
In recent years, many criticisms have been leveled at the popular method of treating temporary and permanent immature teeth with pulpitis—devital pulp amputation. Indeed, often due to a diagnostic error in chronic gangrenous pulpitis with significant pulp necrosis, treatment of temporary molars is carried out using the method of devital amputation. Often, the opening of the cavity of a temporary molar is not performed completely, but “somehow.” In order to reduce visits, treatment is carried out not in three, but in two visits. As a result of these medical errors, the necrotic pulp in the root canals does not have time to sufficiently mummify under the influence of impregnation agents, and chronic granulating periodontitis gradually, painlessly develops.
Forecast
Untimely and improper treatment of children with acute and chronic pulpitis can lead to a rapid transition of the odontogenic inflammatory process to the next stage: periodontitis, purulent periostitis, acute osteomyelitis.
Root canal treatment
What is endodontics?
The term "endodontics" comes from two words: "endo" means
“inside”, and “odont” - “tooth”.
Endodontics is
one of the areas
in
therapeutic
dentistry
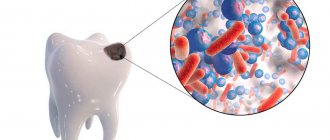
and involves the treatment of complicated caries. During endodontic intervention, depulpation (removal of the nerve from the tooth canal), cleaning and hermetically sealing of the root canal are performed. You have to resort to this treatment:
- when a previously healed carious process gave complications: pulpitis , periodontitis,
granuloma, cyst
. - in case of tooth trauma
- medical errors made during treatment.
Also, an orthopedic dentist can refer a patient to an endodontist. In some cases, before installing a crown or prosthesis, it is advisable to depulp the tooth. This eliminates discomfort after installation of the orthopedic structure. IMPORTANT:
Endodontic treatment is a whole complex
of treatment of the tooth canals
of successive stages of treatment aimed at preserving the tooth.
Stages of prosthetic treatment.
Many people are painfully familiar with the situation when a “dead” tooth suddenly begins to bother you: swelling appears and it hurts to bite. For a person tormented by pain and insomnia, the doctor’s words: “The tooth must be removed! - sound like a sentence, because after the pain goes away, other problems begin - implantation
and prosthetics.
But nowadays it’s not cheap. The main goal of endodontic treatment of tooth canals is
: effective cleaning of the root canal system and microtubules (sterilization), relieving inflammation and preserving the tooth.
STEPS:
- depulpation or unfilling of a previously treated canal
- mechanical expansion (correct formation of the main channel)
- disinfection and medicinal treatment
- canal sterilization
- hermetic obturation (sealing).
IMPORTANT:
Thus, the global goal of endodontic treatment will be achieved - ensuring the integrity of the body by restoring tissue barriers and preserving the tooth.
What do modern endodontists use?
The root of a tooth is a whole system of branched canals that penetrate the entire
tooth root. They connect to the main canal and form a complex network of tubules through which our tooth is supplied with food and innervation. And even the most experienced dentist is physically unable to clean and seal this complex network of canals and tubules. The infection remains in them and waits in the wings. Therefore, the most modern techniques help ensure the absence of complications in the future:
- microscope or binoculars (imaging equipment)
- nickel titanium instruments
- endomotors with built-in apex locator
- ultrasonic treatment
- diode laser
; - various protocols for medicinal treatment of canals.
Important:
Only the latest technologies, the best tools and materials can provide high and stable treatment results. Therefore, modern endodontics deserves special attention.
Why are channels so important? Why is it necessary to treat dental canals?
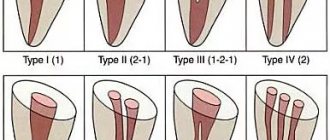
The root of a tooth is a system of branched channels through which useful substances flow and innervation of the tooth is ensured. Damage to the tissues that form these canals and the lack of timely and high-quality treatment will certainly lead to tooth loss. At the same time, the complexity of root canal treatment is evidenced by the fact that the number of roots in a tooth varies, they can have bends and branches.
To carry out endodontic therapy at the highest level, it is necessary to combine high professionalism of specialists, excellent equipment of the dental center, and the use of only high-quality materials.
The Dentist clinic fully complies with all these conditions. IMPORTANT:
To provide high-quality endodontic therapy, it is necessary to have an idea of how many roots the teeth have and what the bends of these roots are.
Materials for canal filling.
The main task that a specialist faces after completing the mechanical and
medicinal treatment of the canal - hermetically seal it. The best result is achieved:
- using the lateral condensation method, which involves the use of gutta-percha pins compacted and fastened together with a cementing substance;
- using the Thermafil system. In this case, gutta-percha heated to 200 degrees under pressure is injected into the canal, which allows you to thoroughly fill all branches and achieve perfect tightness.
- using high-quality antiseptic pastes and cements.
The specialists of the Dentist clinic, striving to perform canal filling with the highest quality possible, use precisely these, the most modern, techniques in their work.
IMPORTANT:
The essence of any canal filling is that the substance introduced after removal of the nerve, mechanical and medicinal treatment of the canal must completely clog the canal to prevent the development of infection in the canal.
Why is mechanical treatment of the canal necessary?
In addition to canal sealing, an equally important part of endodontic treatment is mechanical
canal treatment and sterilization. Experts believe that the persistence of tooth pain after completion of all therapeutic measures, the development of a granuloma or cyst at the apex of the tooth root is due precisely to insufficiently effective actions at this stage. To eliminate the need for tooth extraction due to poor quality treatment, you should entrust the procedure to professionals.
IMPORTANT:
In pursuit of a lower price, during endodontic treatment, patients forget a simple rule: “He who is treated for nothing, is treated for nothing!”
And as a result of this approach, removal followed by implantation
! Although high-quality endodontic treatment would cost much less! But this thought comes to me, it’s too late!
What tools are used?
Treatment of canals is complicated by the fact that narrow convoluted tubules are difficult to treat with medication, and there are difficulties with filling them. Modern clinics, such as Dentist, have the necessary equipment to effectively and efficiently carry out this volume of work. With the use of a multi-functional endodontic handpiece and nickel-titanium instruments, the process has been greatly simplified. Thanks to their sufficient hardness and elasticity, it is possible not only to expand, but also to straighten the tortuous channels. IMPORTANT:
With the advent of the multifunctional endodontic handpiece and
Nickel-titanium instruments, impassable and narrow channels are a thing of the past!
Specialists at the Dentist clinic widely use Japanese endomotors with a built-in apex locator.
With its help, it is possible to achieve unique precision in canal treatment. At the same time, careful execution of all manipulations is guaranteed by triggering the auto-reverse. The presence of a liquid crystal display makes it possible to receive all the necessary information about the channel and fully control the progress of treatment. Endoscopic root canal treatment
is another technology that is used both as a preoperative examination and for active endodontic treatment. With the advent of the endoscope, it is possible to achieve more meaningful monitoring of the working field than with the help of micromirrors and microprobes.
IMPORTANT:
No amount of equipment, even the best, can replace the good hands of a doctor. But such equipment helps the doctor do his job efficiently and with maximum benefit for the patient.
What methods are used?
To carry out endodontic treatment, two methods of instrumentation of canals are used. The Step-back technique is a classic option. It involves expanding the canal, starting from the apex, by using instruments from smaller to larger sizes. Root canal treatment from top to bottom, using the Crown Down technique, is a more progressive and safer technique that provides better access to the apex. In this case, the expansion of the root canal proceeds from the mouth to the apex using instruments from larger to smaller sizes. However, to use this technique you need modern equipment, an endomotor. Using this innovative toolkit, the specialists of the Dentist clinic are ready to carry out the entire course of endodontic treatment at a completely new level, ensure a high-quality result, and completely eliminate the development of complications.
Disinfection and sterilization of the canal.
The most modern methods of disinfection and sterilization of tooth canals are international medicinal protocols for canal treatment, the use of a diode laser and the Depophoresis technique.
Laser exposure
provides a bactericidal, anti-inflammatory, immunostimulating effect.
Conducted Depophoresis
, based on the disinfecting properties of copper-calcium hydroxide in an electric field, promotes the restoration of destroyed bone tissue, protects the tooth root from the action of an infectious pathogen.
Cost of root canal treatment.
In general, such a concept as “impenetrable” root canals is a purely
domestic, which 10-15 years ago was caused by the lack of necessary tools and materials. Unfortunately, endodontics of our time has been divided into two, almost independent layers! It's no secret that the cost of root canal treatment in Moscow
in different clinics varies greatly!
Price for root canal treatment
depends on several factors:
- First of all, is the tooth single-rooted or multi-rooted?
- on the quality of the material
- on the tools and technologies used
- from the qualification of a dentist.
One category of clinics
focuses on the budgetary provision of endodontic services, which includes manual expansion of root canals, their subsequent filling and, as a final step, a targeted radiograph for quality control. The technical capabilities of such dentistry do not allow endodontic treatment of teeth taking into account all the complexities of the internal structure of root canals. Some channels remain unfound or untraversed along their entire length.
Other category of clinics
— modern, knowledge-intensive endodontics! It requires the highest technology and the same qualifications from all personnel. The complexity of this treatment lies in the fact that the internal volume of the tooth can be extremely small; the lumen of the root canals is often so narrow that it is difficult to even detect it. It requires the dentist to have enormous experience and intuition, mastery of a variety of high-tech diagnostic and treatment methods. This is a special high-quality toolkit. But the most important thing is the doctor himself. And the fate of your teeth depends on his ability to apply all the variety of modern treatment methods!
Important:
Endodontists, who have access to the latest technological innovations, spend a lot of time, effort and expensive materials on root canal treatment!
Treatment of root canals near Chistye Prudy metro station.
Treatment of tooth root canals
is a painstaking and delicate work.
Treatment of tooth canals near the metro
Chistye Prudy
is carried out by experienced, competent doctors. Dentist therapists will carry out the entire necessary range of therapeutic and diagnostic measures. The Dentist clinic is equipped with a radiovisiograph and orthopantomograph; in the process of root canal treatment, modern endomotors-apex locators, binoculars and other equipment necessary for thorough diagnosis and treatment are used.
Our advantages:
- We are located in the center of Moscow.
- We attract highly qualified specialists to work.
- We adhere to an honest and transparent pricing policy.
- Positive reviews about our clinic prevail.
- A thorough study of the area of intended intervention will help you build the right treatment plan and avoid complications!
We invite you to undergo endodontic treatment at the Dentist clinic near the Chistye Prudy metro station. Root canal treatment is carried out without pain and stress. Even if you come to the clinic with acute pain, the doctor immediately takes measures to relieve it. We work according to a schedule convenient for patients and accept appointments by appointment.
Treatment of periodontitis in primary teeth
When periodontitis is diagnosed in young children, the dentist makes a decision: to treat or remove the baby tooth.
A diseased tooth becomes a source of infection, which over time penetrates into the deep tissues, affecting the rudiments of the permanent dentition. Severe intoxication worsens the child’s condition. Therefore, removal is recommended.
On the other hand, premature removal leads to negative consequences - delayed growth and development of the jaw, malocclusion and other complications.
Indications for removal of baby teeth
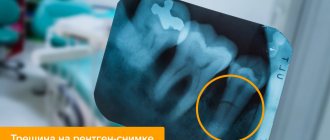
- resorption (resorption) of the root is more than 2/3 of the length - this is determined by an x-ray;
- significant mobility of the baby tooth;
- Less than one year left before teeth change;
- exacerbation of periodontitis after conservative treatment;
- infected tissues provoke sepsis (systemic inflammatory disease);
- reduced immunity, the child’s body is greatly weakened.
Features of treatment of different forms of periodontitis in children
Acute apical periodontitis
It is also called apical because the source of inflammation is located near the apex of the root. The acute form of the disease is accompanied by excruciating constant pain. Possible increase in temperature, symptoms of general intoxication of the body.
We recommend treating the acute form of inflammation as early as possible, before it becomes chronic.
The doctor creates an outflow of infectious fluid through the root canal, prescribes applications of anti-inflammatory ointments, bed rest and plenty of fluids.
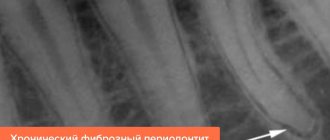
Chronic periodontitis
The chronic form often develops for years without pronounced symptoms. It can be determined by x-ray. For treatment, a swab moistened with a 10% formaldehyde solution is inserted into the dental cavity. For multi-rooted molars, a resorcinol-formalin mixture is used, which penetrates well into all tubules.
Granulomatous periodontitis
With granulomatous periodontitis in children, “bumps” filled with granulations (dead epithelial cells) form in the oral cavity. Treatment includes 3 visits to the doctor. A month after therapy, a control x-ray is prescribed.
Conservative methods
At the slightest opportunity to save the tooth, gentle conservative treatment is used. Endodontic treatment involves repeated root canal treatment.
First visit
- Anesthesia.
- Cleaning out the carious cavity with a drill, removing softened dentin (bone dental tissue).
- Expansion of the root canal mouth using a special hand instrument.
- Removal of the “dead” pulp – the neurovascular bundle inside the cavity.
- Expansion of the canal and its mechanical cleaning.
- Rinsing the cavity with an antiseptic solution - sodium hypochlorite or chlorhexidine bigluconate.
- Opened apical (root) openings for the outflow of exudate.
- Filling the canal with an anti-inflammatory drug: for permanent teeth - a paste based on calcium hydroxide, for temporary teeth - an oil-based paste.
The doctor leaves the tooth in this state for some time - from 2 to 10 days. In the intermediate period, rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions (Chlorhexidine, Miramistin) is prescribed, and less often, taking antibiotics.
Treatment of a tooth with dead pulp
Second visit
- Mechanical cleaning of the canal, removal of medication.
- Washing with an antiseptic.
- Installation of a permanent filling - hermetically closing the cavity with gutta-percha, hydroxyapol or other material.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods are used as an aid in the fight against inflammation. These are inexpensive and painless procedures, children tolerate them well:
- electrophoresis of antiseptics - enhancing the antiseptic effect using pulsed current;
- phonophoresis – introduction of an antiseptic under the influence of ultrasound;
- laser therapy – the laser beam sterilizes the root canals and has a direct bactericidal effect.
Laser therapy
Treatment of pulpitis of a permanent tooth
Child's complaints. Complaints are most often aching in nature, spontaneous or during meals.
Treatment method. It all depends on the state of the tooth roots: formed or unformed. If the roots of a permanent tooth have not yet formed, then a method of partial removal of the nerve is performed. The treatment method is described in detail in the section on the treatment of pulpitis of primary teeth. Hotels in Novosibirsk here, where This method of treatment allows the roots of the tooth to fully form. It is obligatory to have a dental check-up after 3 months, and then 2 times a year, with an X-ray examination.
If the roots of the teeth are formed, treatment is carried out with complete removal of the pulp. Under anesthesia, the pulp is removed, medicinal and mechanical treatment of the tooth canals is carried out, they are filled with sealer (paste) and filler (gutta-percha pins), then a temporary filling is performed. At the next visit, a permanent filling made of light-curing composite material is placed. An obligatory stage of treatment is an x-ray examination, which allows you to assess the condition of the tooth before, during and after treatment.
Recommendations. Visit your dentist every 4-6 months to prevent caries and its complications.