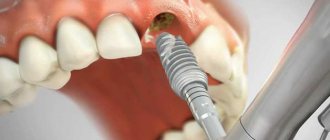
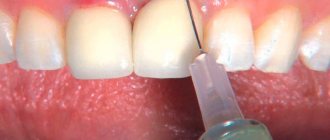
Why is the tooth root exposed?
The reasons for the development of gum recession can be different, and in some cases there is a combination of several factors at the same time.
- aggressive brushing with a toothbrush - there is such a thing as brush gum recession. They occur when there is excessive pressure on the toothbrush when brushing, or when using a brush of unsuitable stiffness (hard). If you have increased tooth sensitivity when brushing, if your toothbrush becomes deformed over time (the villi move in different directions), you should consult a dentist about proper self-hygiene.
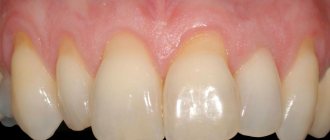
An example of brush gum recession on the upper jaw.
- incorrect position of the tooth in the dentition. Sometimes even a small bite problem can lead to gum pathology. This occurs because the tooth bears excess load when chewing or when teeth are closed, which over time leads to atrophy of the tissues of the supporting apparatus of the tooth, including the gums. In addition, excessive protrusion of the tooth root from the dentition also leads to gum atrophy.
Multiple gum recessions caused by malocclusion.
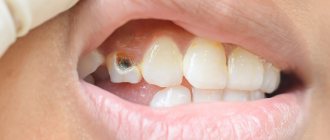
- caries - in cases of gingival caries, gum loss often occurs due to the presence of an infectious focus in the immediate vicinity of the gingival margin.
Gum recession caused by tooth decay in the immediate vicinity of the gum margin.
- Tartar can also cause root exposure.
- anatomical features - for example, a thin biotype of gingival tissue in combination with other factors can lead to recession. Shallow vestibule of the oral cavity (in which the muscles of the lips attach very close to the gingival margin and gradually “pull back” it, exposing the roots of the teeth). In addition, improper attachment of the lip and tongue frenulum can contribute to gum recession.
The frenulum of the lower lip, a thin tissue biotype, caused the exposure of the lower incisor root
- bad or professional habits - for example, chewing a pen/pencil, biting threads (for a seamstress), pinching metal objects with teeth, etc.
- lip or tongue piercing - constantly touching the gums and regularly injuring it, metal jewelry can lead to exposure of the roots of the teeth.
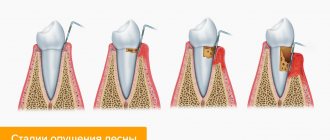
- periodontitis - with inflammatory diseases of the gums, the roots are often exposed due to the resorption of the tissues surrounding the tooth, including gum tissue. Unlike “normal” gum recession, periodontitis is treated differently and the prognosis for such recessions is somewhat worse (as a rule, it is impossible to restore the volume of lost gum by completely covering the exposed root).
How to treat gum recession?
To cover the exposed root, a small operation is performed in the gum area.
There are many methods of gum plastic surgery, but they are fundamentally divided into 2 types:
- gum plastic surgery with local tissues (when the existing gum is “stretched” or moved to the root in a certain way so that the exposed area is closed, and fixed with small sutures, which are removed after healing).
- gum plastic surgery using a “patch” (the patch can be a special collagen-based material or the patient’s own tissue from the hard palate or the area of the far upper tooth - gum transplantation).
The choice of method is at the discretion of the doctor, according to each specific situation.
Gingivotomy: indications
Indications for gingivotomy include:
- inflammatory processes;
- preparation for dental prosthetics;
- deep periodontal pockets;
- gingival fistulas;
- abscesses, relapses of abscesses;
- periodontitis with prolonged discharge of pus;
- generalized periodontal diseases;
- the so-called gummy smile.
During the consultation, the doctor will explain whether intervention is advisable in a particular case or whether conservative treatment is possible.
Is gum grafting painful?
No . Operations to eliminate gum recession are performed under local anesthesia; the surgical intervention is 100% painless. In the postoperative period, especially with gum plastic surgery using local tissues, patients often do not experience pain at all. If pain occurs, it is usually only on the day of surgery, a couple of hours after the intervention, when the effect of the local anesthetic wears off. During this period, the pain is perfectly eliminated with painkillers prescribed by the doctor. During the entire rehabilitation period, on average, 1-2 painkiller tablets are required.
In cases of gum plastic surgery using a “patch,” unpleasant sensations may be added due to the presence of a donor zone, which, according to patients, resembles the feeling “as if you grabbed hot tea,” but this does not always occur. The presence/absence of pain is determined by the area from which the “patch” is taken. If anatomical conditions allow, doctors can remove the graft from the donor area absolutely painlessly.
Gingivoplasty - correction of gum contour
The cost of the procedure is 2000 rubles
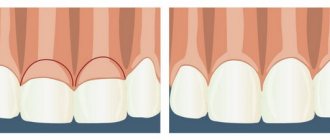
For a beautiful smile, a harmonious relationship between teeth and gums is important. If the front teeth look small and short, and when you smile there is a lot of gum exposed, this is a so-called “gummy” smile. Most of the tooth is under the gum, which is why it looks short.
This problem can be solved quite simply without harm to the teeth and surrounding tissues. A gum correction procedure is carried out, namely the removal of “excess” gum that covers the tooth. This type of gum surgery (or gingivoplasty) can significantly improve the aesthetics of your smile.
Is this intervention painful?
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia and the patient does not feel anything.
Is it possible to predict the outcome of this procedure? What will the gums look like after healing?
Even before treatment begins, the new gum contour is modeled using conventional filling material. It is temporarily applied over the gum, visually lengthening the tooth. And, if the result meets expectations, plastic surgery is performed along the modeled contours. Such modeling allows one to fairly accurately predict the future outcome even before intervention.
Is this procedure harmful to teeth or gums?
During gum surgery, only a small part of it is removed (on average, 0.5-1.5 mm), which can in no way harm either the teeth or gums. The procedure also has no long-term consequences.
Are there any contraindications?
Inflammation of the gums. If there is one, it must first be eliminated.
Why do we use laser to correct gums?
Traditional techniques for excision of excess gum tissue are performed using a surgical scalpel. Laser methods are superior to traditional ones in a number of parameters.
- High precision removal of even minimal amounts of gum tissue with high precision.
- Ability to remove minimal amounts of tissue with high precision.
- Fast recovery after the procedure. The laser beam cauterizes the blood vessels and no stitches are required. The slight swelling disappears within a few days.
- Less traumatic. Much less discomfort for the patient after the procedure.
- Absolute sterility of the procedure.
In what cases is gum correction performed?
- To correct a “gummy smile”
- Uneven, asymmetrical gums. The gum level may be lower on one tooth than on another, giving the appearance that one tooth is longer than the other.
- Preparing the gums before installing veneers, crowns or before teeth whitening procedures to achieve the best aesthetic results.
The procedure is often combined with other dental procedures, such as veneers, dentures, and teeth whitening.
Gum correction + veneers
Gum correction+4 crowns
What to expect after gum correction
There may be some swelling and soreness after the procedure; this is completely normal. This discomfort is minimal. During the first few weeks after the procedure, it is important to continue to practice good oral hygiene, but use caution. The tissue that has been treated may remain sensitive for some time. While recovering from the procedure, you should eat soft foods to avoid worsening your discomfort. Do not use mouthwash with alcohol as it may burn sensitive tissue.
What are the features and complications after gum recession surgery?
With a mild course of the rehabilitation period, patients do not note any peculiarities . But sometimes it is possible:
- the appearance of white plaque on the gums (this is normal, one of the healing options after gum surgery).
- swelling of the soft tissues of the face (from minor swelling to significant) depending on the extent of the surgical intervention (number of teeth involved), the size of the recession, the method of its closure, anatomical features and the patient’s body.
- hematomas on the facial skin (rarely encountered with gum surgery).
- increase in body temperature.
- pain (relieved by painkillers).
Diagnosis of the disease
An effective treatment method for gum recession is selected depending on the causes and forms of the disease. For this purpose, a thorough diagnosis is carried out, which includes:
- Visual and instrumental examination of the oral cavity
- Drawing up a periodontogram - assessing the condition of periodontal tissues, the volume of dental plaque and the depth of periodontal pockets
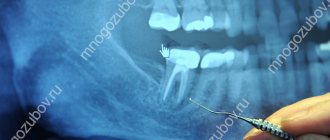
- Computed tomography is the most reliable way to assess the quality of the surrounding bone, the stage of the pathological process, the sunken bone tissue
Computed tomography gives a complete picture of the condition of the bone tissue, on the basis of which the severity of the pathology is determined and the optimal treatment regimen is selected
What are the recommendations and restrictions after gum recession surgery?
- Do not disturb the wound surface (with tongue, food, foreign objects, etc.) this is the main condition for good healing.
- Do not bite (food eaten should be soft or finely chopped).
- Do not brush your teeth in the surgical area with a toothbrush (hygiene in this area should be maintained only as permitted by the attending physician).
- Do not eat or drink hot foods.
- Avoid physical activity.
- Follow the recommendations of your doctor and take prescribed medications.
What happens if gum recession is not treated?
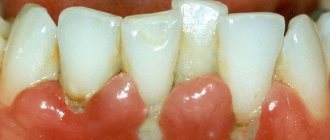
- root caries (the root, unlike the crown of the tooth, is not covered with enamel - a dense “pearl” shell, and therefore is more vulnerable). Normally, the root is covered by the gum and is not exposed to the aggressive environment of the oral cavity (acids, humidity, microorganisms, enzymes). With gum recession, the exposed root is susceptible to destruction.
- abrasion of root tissues (again, due to the lack of enamel, tooth root tissues are not resistant to abrasion).
- increased sensitivity of teeth.
- the transition of a recession to a class that is not subject to complete closure.
- more plaque (the surface of the root is rougher than the surface of the tooth crown, which means that plaque is retained more when the roots are exposed).
Large gum recession, caries of the exposed tooth root, an abundance of soft plaque on the root surface.
Signs of the disease
Gum recession is not an independent disease, but only a manifestation of some other pathology
At the initial stage it is asymptomatic. Usually the problem is detected when the level of mucous membrane has already significantly decreased and tooth roots are exposed. Outwardly it looks like a cosmetic defect in the dentition. In the affected area, the teeth visually appear longer due to a decrease in the height of the gingival margin, and a stepped defect is visible at their base.
Associated symptoms:
- Bleeding gums
- Swelling and redness
- Increased tooth sensitivity
- Painful sensations upon contact with the brush, while eating
- Formation of periodontal pockets
- Tooth mobility