What is a dental formula
A dental formula or diagram is a brief description of the dental structure of the human dentition using numbers and Latin letters.
The letters are abbreviations from the Latin names of teeth accepted in medicine:
- I – these are dentes incisivi or incisors.
- C is for dentes canini or fangs.
- P stands for dentes premolars or premolars.
- M stands for dentes molars or molars.
The alphanumeric dental formula is common in many countries, including America, which is why it is sometimes called American. After the letters in the formula there is always a digital fraction, where the numerator indicates the number of teeth on the upper jaw, and the denominator on the lower jaw.
The dental formula of a healthy adult with a normal bite and 32 teeth looks like this:
This formula indicates that on each human jaw there is:
- 2 pairs of incisors;
- 1 pair of fangs;
- 2 pairs of premolars;
- 3 pairs of molars.
Dental formula in the absence of some teeth
It is not difficult to correctly number dental units with a healthy dentofacial apparatus; it is much more difficult to indicate the location of the teeth if a person does not have any molars, incisors, canines or premolars. In this case, the dentist indicates the number 0 opposite a certain group of teeth, rather than shifting the number series.
If the patient has any anomalies in the development of the dentofacial apparatus, for example, teething in the wrong place (hyperdontia, polydontia), the dentist prescribes an individual formula. In addition to numerical designations, the doctor generates a detailed report on the structure of a person’s dentition.
Reasons for the growth of the second dentition in a child
Double or “shark” teeth in children appear when the baby tooth and the rudiment of the molar are located at different points in the oral cavity. When a new set erupts, the baby tooth remains in place. A tooth grows above a tooth, which not only does not look aesthetically pleasing, but also interferes with the development of the rest of the row.
The most common reason why teeth do not change is improper breathing. A lot depends on how a child breathes. Breathing disorders lead to problems with bite, deterioration of posture and changes in facial shape.
A child’s jaw develops correctly only when he breathes correctly through his nose. The tongue in this position presses on the palate from the inside. A natural semicircular shape of the jaw is formed, in which there is enough space for all the molars. This is why it is so important to teach your child to breathe through his nose to prevent the growth of the second row of teeth.
Description, structure, functions, name and location of human teeth
It is not without reason that human teeth have different shapes, structures and sizes. Each tooth performs certain functions, and its purpose is, one way or another, reflected in the name:
- The incisors are the front teeth that fall into the smile zone. They are quite sharp as their function is to tear or cut food, hence the name. Normally, every person has lateral and central (larger) incisors.
- Canines are cone-shaped teeth that can be used to tear and hold food. They are located immediately behind the incisors.
- Premolars are the small back molars located behind the canine teeth.
- Molars are the back teeth necessary for mechanical processing of food. Wisdom teeth refer specifically to molars.
The listed types of teeth are also found in animals. But in the process of their evolution, some dental units were slightly modified:
- elephants' upper incisors became tusks;
- Poisonous snakes have poison in their fangs.
Many animals have front teeth similar to human ones, but since they are called differently, they cannot always be identified with the usual incisors and canines.
The structure of human teeth
Human teeth consist of a crown and a root part. The first is located above the level of the gum, the second is inside it. The top of the crown is covered with enamel, the strongest tissue in the body. It protects the inner layer of the tooth – dentin – from external influences. Under the dentin there is a hollow chamber with nerves and blood vessels - the pulp.
Despite its strength, enamel is vulnerable to bacteria. If left untreated, caries can affect the dentin and pulp. When the pulp chamber, which contains nerve fibers, is damaged, pulpitis develops, accompanied by acute throbbing pain. If the infection spreads to the root of the tooth, it is highly likely that it will have to be removed.
The basis of the lower part of the tooth is the root canals, which also contain arteries, veins and nerve fibers. Through the apical foramen, all of these structures are connected to the main neurovascular bundle.
The lower part of the tooth is covered with dentin and cement, which is attached to the periodontium using collagen fibers. The roots of teeth are hidden in the alveoli - depressions in the jaw bone.
Do supernumerary teeth need to be removed?
There is no clear answer to the question of what to do with “extra” teeth. Much depends on the shape, position and quantity. The following are subject to mandatory removal:
- baby teeth that interfere with normal growth and formation of permanent teeth;
- strongly dystopic structures - located on the palate or at a large angle to the lateral side of the gums;
- impacted formations that put pressure on the adjacent roots of normal teeth and provoke periodic inflammatory processes of soft tissues.
If the additional tooth does not cause discomfort and does not disrupt the development of the dentition, removal may not be necessary. Moreover, such a superset can play the role of a strategic reserve in case of damage to nearby normal teeth.
How does the removal work?
The removal procedure can be simple or complex. In the first case, the doctor is dealing with a fully erupted tooth, the root of which is not intertwined with the surrounding structures. Simple removal steps:
- The oral cavity is prepared - treated with antiseptics, anesthesia is given.
- Grasp the crown with forceps (in some cases, an additional incision of the mucous tissue is required to facilitate access).
- The elevator destroys the retaining ligaments.
- The root is freed and the tooth is removed.
- Clean the hole from tooth fragments and bones.
- Apply stitches (if necessary) and a healing bandage.
Complex extraction is prescribed in the case of impacted, semi-impacted or dystopic teeth with complex root shapes. The procedure is carried out with a deep incision of soft tissues, in especially severe cases - with opening of the jaw bone to gain access to the roots. The latter option is relevant for deep bone occurrence, position in close proximity to the cranial sinuses and orbits, as well as for irregularly shaped roots and a high risk of damage to complete teeth. A complex removal operation is performed by a dental surgeon.
On what basis are teeth numbered according to different classification systems?
In addition to the Latin names of teeth, digital designations are used in dentistry. The numbering of teeth is based on the order in which they erupt. It starts from the front incisors (from the middle of the jaw) and runs to the left and right of them.
There are several generally accepted systems for numbering human teeth.
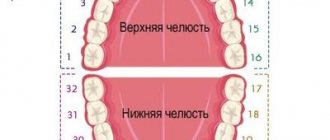
Universal system
Most often, dentists name teeth not by the Latin alphabet, but according to their location in the oral cavity (ordinal number). Moreover, using not Roman, but familiar Arabic numerals.
Names of teeth according to the universal classification system:
- two central incisors are located at number 1 and are called ones;
- the second incisors are numbered 2;
- the fangs are called triplets;
- chewing teeth or premolars are called fours and fives;
- molars are called sixes, sevens and eights.
According to the universal system of classification of dental units, the jaw is divided into 4 segments:
- top left;
- top right;
- bottom right:
- bottom left.
The further name indicates not only the serial number, but also the location of the dental unit in the human oral cavity.
The universal dental numbering system is the most popular and frequently used. It is used by dental therapists and surgeons in various countries.
The picture shows a diagram of the designation of teeth in the oral cavity of an adult according to the universal numbering system:
European system
The European Viola system is one of the newest and most advanced methods for naming human teeth. It is characterized by the division of the jaw into segments (two at the bottom and two at the top). Each segment is numbered (from 1 to 4).
Based on these numbers, each tooth receives a two-digit number. The first digit indicates the segment, and the second is the actual sequence number.
The Viola system is recognized internationally and is therefore popular all over the world. It is used in radiography, making panoramic images and allows dentists from different countries to exchange information about patients, overcoming the language barrier.
Haderup system
To designate dental units according to the Haderup system, Arabic numerals are used and segmentation into the lower and upper jaws is used:
- the “+” sign indicates that it belongs to the upper jaw;
- the “–” sign indicates the lower jaw.
The only disadvantage of such numbering is that it is necessary to additionally indicate whether the dental unit belongs to the left or right side of the jaw.
Zsigmond-Palmer system
The Zsigmond-Palmer system is considered the most imperfect, since it only indicates the numbers of teeth without their location. Standard Arabic numerals are used for numbering.
This tooth numbering system is practically not used in therapeutic and diagnostic procedures. It is used only by orthodontists and maxillofacial surgeons.
Supernumerary teeth: causes of anomaly
The main cause of polyodontia is a violation of the formation or development of tooth germs. Doctors are considering several theories for this phenomenon:
- Heredity – hyperdontia develops as a result of genetic abnormalities that can be transmitted from parents to children. In this case, the pathology should manifest itself in the patient’s closest blood relatives.
- Splitting of the root germ of the tooth in the embryonic period of development. Usually observed after the mother becomes ill during pregnancy. Characteristic of single supernumerary teeth (1–2 pcs.).
- Failure during the embryonic period of tooth formation with the formation of multiple dental buds (up to several hundred). It is observed when the mother lives in unfavorable environmental conditions, during treatment with dangerous drugs, taking drugs, or alcohol abuse.
In more rare cases, polyodontia develops as a result of odontoma, a benign tumor in the area of the jaw arches. The disease is typical for children and young people during the period of active growth of tooth germs. Such a tumor structure may contain several tens or even hundreds of highly deformed dentin-enamel formations.
Provoking factors in the prenatal period:
- malfunction of genes - primarily the Msx1 gene (responsible for the formation of tooth germs);
- viral infections;
- taking teratogenic and potentially dangerous drugs;
- smoking, drug use, alcohol use;
- poor environmental conditions;
- exposure to radiation - not only direct exposure, but also increased general background radiation in the place of residence/work.
Reference! Some scientists consider the presence of supernumerary teeth as an atavism. Thus, it has been scientifically proven that various species of the genus Homo could boast a set of teeth of 36–44 pieces. However, this theory does not explain in any way the appearance of multiple rudiments covering all spaces of the sky (a typical example is an Indian boy who had to remove 230 supernumerary units).
Alternative names for human teeth
In addition to the official names, there are also alternative names for human teeth. They are not written in dental records, but have long been used in informal communication, since these teeth in people are located or grow in certain places or at certain times.
Eye teeth
The upper canines are called eye teeth because of their close location to the branches of the facial nerve. When they become inflamed, the pain radiates to the eye area and upper face. How close the incisive canals and the dental nerve are located to each other is shown in the figure:
Wisdom tooth
The wisdom tooth is the posterior third molar. He was called “wise” because he grows up in adulthood - when a person has already gained wisdom (by about 20 years).
Diagnostics
An erupted supernumerary tooth is detected during examination of the oral cavity; it is often dystopic, that is, abnormally located.
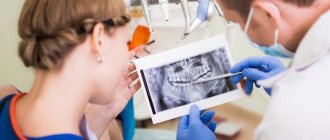
Diagnosis of unerupted (impacted) supernumerary teeth is carried out using x-ray examination. Often, X-ray diagnostics of supernumerary teeth is difficult due to the fact that in the image their contours overlap the contours of the complete teeth. For more accurate diagnosis, 3D computed tomography is used. The results of these studies make it possible to obtain comprehensive information about the relative position of erupted and impacted complete and supernumerary teeth.
Correct names of baby teeth
In Latin, baby teeth in a child are called the same as permanent teeth in an adult. But children do not have all the dental units characteristic of older people. Milk teeth are divided into:
- central incisors;
- lateral incisors;
- fangs;
- first and second molars.
There are different names for teeth, but it is better to focus on Latin terms and serial numbers. In this way, you can identify teeth even without serious knowledge of dentistry.
Symptom relief
Most often, in adults, extra teeth erupt without any symptoms, but for children this can become a problem that needs to be addressed.
Supernumerary teeth erupt with the same symptoms as regular teeth, so the treatment for them is the same.
- To lower the temperature, it is recommended to give your baby Paracetamol or Ibuprofen. If the child is very small, these drugs can be used in the form of suspensions or rectal suppositories. In addition to lowering the temperature, these medications do an excellent job of treating pain and inflammation.
- To relieve gum pain, local anesthetics are used - ointments and gels (for example, Kalgel, Dentinox, Solokoseryl). These remedies cope well with painful sensations and slightly relieve inflammation.
- Adults and children over 2 years of age can be treated with folk remedies: propolis, honey, decoctions of calendula, chamomile and lemon balm. Some decoctions help reduce pain and relieve inflammation. Traditional methods of treatment should be used only after consultation with your doctor.
- If primary supernumerary teeth have partially erupted, stimulation of eruption is prescribed. For this purpose, vibration and electrical stimulation, as well as special massage, are used.