The Greek word "kystis", used to refer to a condition such as a dental cyst, is translated as "blister". This name most accurately reflects the essence of this disease. With it, a cavity is formed at the root of the tooth, which is filled with liquid (bacteria and dead cells), and the comparison with a bubble in this case is most appropriate.
The consequences of untimely treatment of a cyst in the gum of a tooth can be the most unpleasant - including tooth loss. The process may also involve neighboring teeth, which will also require professional dental treatment.
Resection of the root apex (frontal group) - 6,500 rubles.
Resection of the root apex (chewing group) - RUB 9,000.
At CELT you can get advice from a dental specialist.
- The cost of a dental consultation is 1,000
- The cost of an orthodontist consultation is 2,000
Make an appointment
Cyst symptoms
In the initial stages, the cyst is almost invisible. Unlike an abscess, it does not break out, but at the same time continues its development inside, affects healthy tissue of the jaw bone and leads to loosening of the tooth. As the inflammatory process develops, the following symptoms of a cyst in the tooth appear:
- pain in the affected area;
- swelling of the gums;
- increased body temperature;
- swollen and tender lymph nodes;
- flux.
The pathology quickly develops into a chronic stage and is asymptomatic for humans. During an exacerbation, attacks of pain may occur when eating solid foods. Gradually, the tooth enamel becomes gray or yellow, and the tooth shifts. As soon as the immune system fails due to acute respiratory viral infections or exacerbation of chronic diseases, the growth of the cyst accelerates, so the appearance of a fistula, swelling, acute pain, fever and migraine is observed.
Indications
- Bite abnormalities.
- Periodontitis.
- Installation of orthodontic systems.
- Severe deformation of the ligamentous apparatus (tooth loosening).
- Hyperdontia.
Contraindications
- ARVI and weak immunity.
- Chronic and acute forms of diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Nervous and mental disorders.
- Cancerous tumors.
Causes
There are many reasons why this problem occurs, so it is almost impossible to prevent its occurrence. Among the most common reasons for its formation are the following:
- mechanical impact on the lower abdomen (for example, injuries, bruises);
- hormonal deficiency (progesterone deficiency);
- genetic abnormalities of the embryo (developmental defects);
- stress;
- heavy physical activity;
- diseases of the uterus (chronic endometritis, endometriosis, fibroids, uterine malformations (septum, duplication, additional horn, etc.);
- disorders of the blood coagulation system;
- autoimmune aggression (eg, antiphospholipid syndrome);
- sexually transmitted infections, etc.;
- vascular pathology.
Also, noise and vibration (occupational factor) and even the environment can contribute to the formation of a hematoma.
Retrochorial hematoma can be suspected when spotting bloody discharge from the genital tract appears, but it is often an incidental finding during ultrasound, not accompanied by any symptoms. The presence or absence of symptoms is largely due to the location of the hematoma: if it is located high, in the area of the fundus of the uterus, it does not manifest itself in any way, only slight aching pain in the lower abdomen is possible. If the hematoma is located low, at the edge of the ovum, it often empties and “scares” the woman with bloody discharge from the genital tract. Sometimes these discharges can be quite copious, especially if a vessel in the uterine wall is damaged during the formation of a hematoma. And the blood is released liquid and scarlet.
Brown discharge from the genital tract in the presence of a hematoma is considered, as strange as it may sound, a good prognostic sign, since in this way the hematoma empties and disappears. If the discharge from the genital tract is abundant and scarlet, this is already a serious situation - this may indicate an increase in the area of detachment, and, accordingly, an increased risk of threatened miscarriage.
Why does a cyst appear?
The causes of the appearance of a dental cyst, a photo of which can be seen in this article, are injuries due to mechanical stress or infection, which leads to the development of inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tooth. A tooth inside the gum can be injured under a variety of circumstances, for example, when the tooth is hit or when chewing nuts. As for infection, it can get into the root canal if dental treatment is performed incorrectly, in particular, if the dental canal is incompletely filled. A cyst that arose as a result of sinusitis or another infectious disease is relatively rare. In this case, pathogenic microorganisms enter the gums along with the blood flow.
Indications for the use of antibiotics in dentistry
The need for treatment with antibiotics depends on the nature of the infection and the body's ability to withstand the course. The main reasons for prescribing antibiotics include:
- When advanced caries threatens pulpitis, the dentist may prescribe antibiotics to limit the spread of the pathological process. The patient is prescribed antihistamines to complement the effectiveness of antibiotics.
- With the development of an inflammatory process of periodontal tissue (periodontitis), antibiotic therapy allows the destruction of protozoa, gram-negative anaerobes in the oral cavity. Various dosage forms of drugs are used for treatment: gels, ointments, intramuscular and intravenous injections, tablets.
- The proliferation of pathogens, poor immunity, caries and dense plaque can lead to the development of gingivitis. After laboratory detection of the sensitivity of microbes to the antibiotic, a course of treatment is prescribed. Antibiotic drugs are mainly used for catarrhal gingivitis.
- The appearance of purulent accumulations inside the oral mucosa provokes the appearance of a fistula. The process occurs due to the proliferation of anaerobic gram-negative bacteria, streptococci, staphylococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa or Escherichia coli. A doctor-prescribed course of antibiotics, which are also used for dental implantation, will help cope with the infection.
- Inflammation of the connective tissue around the root of the tooth is called periodontitis. The occurrence of the disease is a consequence of dental trauma, a complication of pulpitis, caries, or an error in dental treatment. If the process is not stopped, pus may appear. The effectiveness of antibiotics for periodontal disease is felt after preliminary cleaning of the periodontal tissue.
- The result of inflammation of various origins can be a granuloma - a cavity of granulation tissue filled with fluid. Location: on the gum near the root of the tooth. It is important to start treating granuloma in the early stages. The use of antibiotics facilitates the opening of the granulosa vesicle and suppresses the infection accumulated in it, and serves to prevent infection. Self-medication with antibacterial drugs is unacceptable.
How does the disease develop?
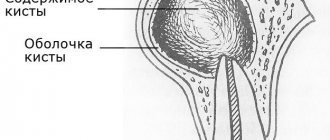
The process begins with periodontitis, when the tissue located between the jaw bone and the tooth root becomes inflamed. As a result, the tissues located around the root begin to grow abnormally. Initially, the size of the neoplasm does not exceed five millimeters (it is called a granuloma). Growing and enlarging, it becomes covered with a membrane and transforms into a cyst.
There are cases when the cyst grows so much that it eats away the bone around the tooth. With the next exacerbation of inflammation, it opens, forming a channel to the outside through the gum mucosa. Such a channel is called a fistula or fistula tract.
It is worth noting once again the insidiousness of this disease, which not only negatively affects the condition of the roots of the teeth, but also affects the general condition of a person. At the initial stage, the pathology develops almost imperceptibly and can only be detected during a visit to the dentist. Pronounced symptoms appear in the later stages of the disease as a result of tumor growth and destruction of bone tissue.
The main danger of a cyst is the fact that, by corroding the bone, it deprives the patient of the opportunity to install an implant in place of a lost tooth without complex manipulations.
Contraindications to treatment with antibacterial drugs
Compositions for suppressing the inflammatory process in gingival and bone tissue during toothache are not suitable for all patients. Restrictions for use are related to age, body reactions, and special conditions. Most antibacterial drugs should not be used by nursing mothers or pregnant women.
Main contraindications for antibiotic therapy:
- allergic reactions;
- liver and kidney failure;
- intolerance to the active substance: you need to choose a substitute with another active ingredient;
- myasthenia gravis;
- damage to the optic nerve;
- severe diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- the patient is taking medications that are incompatible with a certain group of antibiotics;
- tendinitis;
- epilepsy;
- children's age (restrictions are indicated in the instructions for the drug).
A limited range of antibacterial compounds are used in pediatric practice.
It is important to clarify in the instructions the age of the child for safe antibiotic therapy for acute inflammation of tissues in the oral cavity.
In case of purulent inflammation, the development of periostitis and periodontitis, when the gums are swollen, the dentist selects effective antibacterial compounds. Many inexpensive antibiotics work well for dental inflammation and quickly suppress the pathological process. New generation drugs with a minimal list of contraindications and side effects are safer.
Antibiotics for toothache.
Many people consider antibiotics a panacea for all ills and, at the first problem with their teeth, begin to take them intensively. However, such self-medication can cause irreparable harm to other organs and systems of the body, without improving the condition of the teeth. Prescribing antibiotics is the exclusive prerogative of the doctor. In what cases are these medications prescribed?
What complications does a dental cyst lead to?
Untimely treatment or removal will lead to the following complications:
- Periostitis.
- Swelling.
- Abscess.
- Phlegmon.
- Temperature increase.
Usually the cyst does not make itself felt in any way, so complications may appear unexpectedly. To exclude serious consequences, you need to be examined by a dentist at least once every six months. The appearance of a capsule with pus can occur against the background of deep caries or severe inflammation of the gums, so do not delay a visit to a specialist.
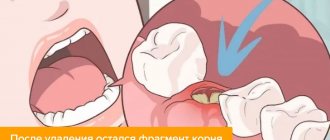
The lack of results with conservative treatment leads to the fact that the cyst has to be removed along with the tooth.
Are antibiotics effective?
Before starting a course of antibiotics, you should determine the cause of your toothache. There are two main factors that provoke it:
- Caries that has developed to pulpitis. When the carious process affects the nerve, the tooth begins to react to various irritants: sour, sweet, cold, hot. Since in this case the pain is provoked by an intradental inflammatory process, antibiotics will be completely useless. For such pain, anti-inflammatory drugs, for example, Ibuprofen, are relevant. In addition to drug treatment, it is also planned to remove the affected tissue and fill the dental canals.
- An infection localized in a “dead” tooth. In such a situation, after removal of the nerve, the tooth does not react to sour, sweet and other irritants, but at the same time it hurts - and more and more every day. It's all about microbes that multiply either in an unfilled canal or in some tiny crack in the root. As a result, a purulent abscess or gumboil develops near the root of the tooth. The latter, by the way, is deadly. If such inflammation of the tooth root occurs, antibiotics are prescribed, but before taking them the patient will have to undergo the procedure of opening the abscess.
Before pinning any hopes on antibiotics, you should understand a few facts about this group of drugs:
- antibiotics help in treating the disease that provokes toothache, and do not relieve the pain itself (there are analgesics for this purpose);
- different antibiotics have different effects on pathogens, so it is almost impossible to successfully select such a medicine on your own;
- the effectiveness of taking antibiotics without concomitant dental treatment tends to zero.
The course of antibiotic treatment should not be interrupted prematurely: incomplete therapy will not lead to the desired result.
Types of dental cyst
The type depends on the place of occurrence. A cyst forms in the maxillary sinus, gum, root or under the crown. To determine the type of capsule with pus, the specialist examines the medical history and assesses the client’s general health. There are 5 types of dental cysts:
- Follicular - formed when the tooth was unable to grow unhindered and most of it remained inside.
- Keratocyst - develops against the background of pathological processes during the growth of the body (the growth of the neoplasm is stimulated by the pharynx-forming tissue).
- Radicular - appears from a granuloma and is a serious complication of deep caries.
- Retention – is formed during the eruption of molars in children.
- Residual – appears due to complications and inflammatory processes after tooth extraction.
What are the contraindications for laser hair removal?
There are temporary factors under which laser hair removal cannot be done. These include:
- Pregnancy and lactation
Women during pregnancy face the physical challenge of removing unwanted hair because they simply cannot reach the right places. Therefore, they begin to think about the optimal method of hair removal and settle on laser hair removal. But this type of hair removal is contraindicated during pregnancy. The fact is that during pregnancy, hormonal levels are unstable, and the skin becomes sensitive. For these reasons, pigmentation may appear, and the process itself will be more painful. In addition, the effect of laser on the fetus has not been studied, and its safety for the embryo cannot be proven experimentally due to ethical considerations. But after giving birth, you can begin to destroy annoying hair, not forgetting about the list of other contraindications.
- Age up to 18 years
Firstly, in children most of the hair is dormant. They contain little dark pigment (melanin) and the laser removal procedure will be practically useless. Around the age of 12-13, active hair growth begins.
Secondly, adolescence is a time of raging hormones and restructuring of the entire body. It’s already difficult for a teenager’s body during this period and it’s better to give time to complete all the processes that have begun.
- Tanned skin
During laser hair removal, you should refrain from visiting the beach or solarium for 2-4 weeks and 2-3 weeks after the procedure. After exposure to the sun, the skin is dehydrated and needs hydration; it becomes dry and irritable, and therefore prone to burns and pigmentation. The laser affects the dark pigment located in the hair follicle. The best result will be when working with dark hair on light skin, and not vice versa. Creams and lotions for artificial tanning are also contraindicated. And after the hair removal procedure, you should not sunbathe, because the skin is susceptible to irritation and needs to be properly cared for. You should use moisturizers and sunscreens on exposed skin.
- Bioepilation
After removing hair with wax or sugar paste (sugaring), 30 days should pass. Because these methods remove roots and the laser hair removal procedure will be ineffective.
- Inflammatory phenomena in the treatment area
After epilation on an inflamed area of skin, the infection present on the surface can spread further. For example, applying a laser to an area of skin with folliculitis, formed due to saprophytic bacteria, can provoke the spread of infection over the entire surface and worsen the situation as a whole. In addition, in the presence of infections in the body, immunity decreases, which affects the timing of tissue healing. Laser hair removal during inflammatory processes can lead to pigmentation of this area. Since a laser beam hitting it can provoke the production of an increased amount of dark pigment (melanin).
- Skin damage
The area where the procedure is planned must be healthy. There should be no peeling, burns, allergic rashes, injuries or microtraumas. Otherwise, hair removal will not be effective and the damage may worsen. The procedure can be done after the skin has been restored.
Cyst on the root of a tooth
This species grows in the alveolar area and can appear in any area of the gum. There are no symptoms except for tingling when eating or touching. Pain appears in later stages of development. A cyst on the root of a tooth is divided into 3 types:
- Peri-root - appears in the upper part of the root.
- Interroot – formed between the roots.
- Radical - appears near the root canal and over time can cause the growth of a malignant tumor of the jaw (if not properly treated).
Prices for treatment and removal of cysts in Moscow
The cost of treatment/removal of a dental cyst will depend on a number of factors:
- Complexities and features of the clinical case;
- The method that will be chosen to treat the dental cyst.
Conservative (medicinal) treatment of a cyst includes a whole set of measures and it can last for more than one month, so the best way to find out its price is to visit the therapists at our Firadent clinic in Moscow. The doctor will conduct a diagnosis, based on which he will draw up a detailed treatment plan for the cyst, indicating the prices for all the manipulations necessary to remove the cyst and high-quality tooth restoration. Attention! Sedation is not included in the price of cyst treatment; this service is paid separately!
Our Firadent clinic also performs surgical removal of cysts:
- The price of cyst removal by cisectomy is 4,500 rubles;
- The cost of removing a cyst by cystotomy is 5,000 rubles.
These are the prices for surgery to remove a cyst, but treatment costs will also include root canal treatment and tooth restoration with a filling or crown. All these procedures have their price. To get a detailed consultation and calculate the full price of treatment/removal of a cyst, call us or write to our chat. You can find out the exact price for cyst treatment at Firadent by making an appointment at our clinic. Choose a convenient time and come to Firadent: for healthy teeth and a beautiful smile. With us, your treatment will take place in a comfortable environment, without pain and stress!
Conservative and surgical treatment of cysts
In the early stages, in the absence of complications, a conservative method is acceptable. The root canal is drilled and cleaned. The capsule with pus is opened and cleaned, and a composition with an antibiotic is poured inside. Next, a bone tissue regeneration paste is applied and a filling is installed. A control check after 6 months demonstrates the absence of a cyst on an x-ray in 80% of cases
Surgical treatment is prescribed if there is no result. With the help of cystectomy, the affected part of the tooth and the capsule with pus are completely removed. Cystectomy is an operation that not all dental surgeons can do. Hemisection is often used, which gives a 100% result and is prescribed for severe root damage. All affected tissue is removed, and the appearance of the tooth is restored with a crown or composite composition.
Complications and prognosis
With timely diagnosis and high-quality treatment, retrochorial hematoma in most cases does not pose a further threat to the course of pregnancy, which ends safely through the natural birth canal, especially if the hematoma occurs in the early stages of pregnancy. But unfortunately, partial chorion detachment can also cause the formation of early placental insufficiency, premature aging of the placenta and fetal malnutrition. The risk increases with bleeding occurring at 7–12 weeks of pregnancy; in this situation, pregnancy may cease to develop in 5–10% of cases. Retroplacental hematoma that occurs in later stages of pregnancy, especially located below the umbilical cord insertion site, is accompanied by the risk of spontaneous miscarriages, premature abruption of a normally located placenta, premature birth, retarded fetal growth and development, and the development of feto-placental insufficiency.
Another important prognostic sign is the size of the hematoma - the prognosis is considered unfavorable if the volume of the hematoma is more than 60 cm³ or if the area of the hematoma is 40% or more of the size of the fetal egg.
Conclusions:
- Retrochorial hematoma may be an asymptomatic, incidental finding on ultrasound.
- Spotting bloody discharge from the genital tract in the presence of a retrochorial hematoma is a favorable symptom of its emptying.
- Even in the absence of bloody discharge from the genital tract, in the presence of a retrochorial hematoma, complete physical rest and adequate complex therapy are necessary (the most effective is in a hospital setting).
- A hematoma that occurs in the early stages of pregnancy, with timely treatment in most cases goes away without consequences.
- The prognosis for the further course of pregnancy after the formation of a retrochorial hematoma depends on the period of pregnancy at which it appeared, its location, and its size.
And most importantly, in the presence of such a complication, do not panic, but strictly follow all the recommendations of the attending physician. Then you will have every chance to safely and happily carry and give birth to a healthy baby on your own!