The appearance of papilloma in the oral cavity can be caused by the following factors:
- infection;
- immune disorders;
- vitamin deficiency;
- wearing plates to correct bites and uncomfortable dentures;
- influence of caustic substances and high temperatures;
- oral injuries;
- genetic predisposition;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- use of other people's hygiene items;
- emotional shock, prolonged state of stress;
- hormonal dysfunctions.
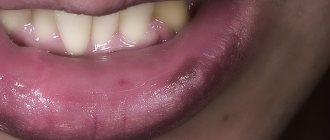
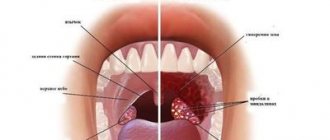
Warts in the mouth can be isolated, however, as a rule, the growths appear in small groups. Most often they are localized on the gums, palate, tongue, inner surface of the cheeks, tonsils and lips.
Papillomas on the oral mucosa can cause significant discomfort to the patient, which motivates him to think about removing the growth. However, inconvenience is not the only reason that determines the need for papilloma surgery. In some cases, the occurrence of warts can affect chewing, eating and may affect diction. New growths in the mouth are characterized by increased pain, which is due to their close location to the nerve endings. In addition, any benign neoplasm can degenerate into malignant. Therefore, if you find warts in the oral cavity, you should consult a specialist.
An important step before removing papilloma will be a preliminary examination of the patient. It includes a consultation with a dermatologist, otolaryngologist, dentist and oncologist (if the growth is suspected of being malignant). The patient may also be shown a cytological and histological examination of tissues, which will determine the nature of the neoplasm. Carrying out a comprehensive diagnosis makes it possible to identify hidden foci, the number, growth and size of papillomas, assess the patient’s health status, and also choose the most appropriate tactics to combat tumors in the mouth. To effectively eliminate papilloma in the oral cavity, complex treatment is carried out, which includes sanitation of the oral cavity, excision of papilloma and drug treatment. According to experts, it is precisely this tactic of combating pathological neoplasms that will reduce the risk of re-formation of warts and prevent the occurrence of adverse side effects.
Sanitation of the oral cavity in the treatment of papillomas
Since pathogenic microorganisms present in the mouth can lead to an exacerbation of HPV, before operating on papilloma, special attention is paid to the sanitation of the oral cavity. This integral stage of wart treatment includes the following activities:
- Treatment of teeth affected by caries;
- Elimination of inflammatory processes;
- Elimination of plaque and tartar;
- Neutralization of pathologies affecting the gums;
- Enhanced oral care (regular brushing of teeth, removing food debris with dental floss, rinsing the mouth with prescribed medications).
How to recognize warts: symptoms and signs
An inexperienced person may confuse warts with other skin growths, for example, moles, calluses, melanomas.
The main differences between warts and moles:
- moles have a dark or black tint, while warts have a light color;
- warts grow tightly together with the skin, moles are separate structures, as if glued to the body;
- moles are soft and smooth to the touch, warts are hard, hard and rough.
It is also easy to distinguish a wart from a callus. When pressing on the growth, painful sensations will occur, and if it peels off, traces of hemorrhages will be visible underneath it. Under the callus is new, tender skin.
You can distinguish a wart from a melanoma by color and shape. This dangerous disease is characterized by heterogeneous red and black shades, proliferation and an uneven contour.
It is not difficult for a dermatologist to make the correct diagnosis using a visual examination. But a good specialist will not be content with just a simple inspection. He will definitely use a special magnifying device - a dermatoscope. If there is a suspicion of a pathogenic process, scraping of the surface layer will be required.
In the case of anogenital warts (located around the anus and on the genitals), consultation with a gynecologist or proctologist is necessary.
Removal of papilloma in the oral cavity
As a rule, removal of warts in the oral cavity is carried out using the radio wave method or using a laser. These two methods are the most effective, safe and painless (in some cases, local painkillers may be used). The essence of laser cauterization of papilloma is the impact of narrowly directed beams of a certain frequency, which leads to destruction and necrosis of pathologically altered tissues. Radio wave removal of warts involves cutting off the papilloma at its base, which allows the removed material to be sent for further histological examination.
The advantages of laser and radio wave treatment of papilloma include:
- Efficiency of the procedure;
- No postoperative scars;
- Minimal damage to surrounding healthy tissue;
- Short rehabilitation period;
- Possibility of removing warts of any size and location;
- No postoperative complications (bacterial contamination, spread of infection, bleeding).
There are also other destructive methods to combat warts in the mouth. These include:
- Cryodestruction (cauterization of papilloma with liquid nitrogen);
- Electrocoagulation (excision of warts with electric current);
- Cauterization of growths with chemicals;
- Surgical excision of papilloma using a scalpel.
However, due to the special sensitivity and increased humidity of the oral mucosa, the listed methods will be less effective and safe.
Contraindications for surgical treatment of warts include the presence of cancer, acute infectious viral pathologies, exacerbation of chronic diseases and diabetes mellitus in the decompensation stage.
The most effective and appropriate method of wart surgery is selected by the doctor after an examination. In this case, the specialist takes into account the age and health status of the patient, the presence of possible contraindications and allergic reactions, as well as the location, size and number of tumors.
Common (simple, vulgar) warts
Common warts are dense, dry growths characterized by an uneven and rough surface to the touch, variable size and rounded shape. They look like a hard, keratinized bubble up to 1 cm in diameter, significantly rising above the surface of the skin.
The surface of common warts is often covered with grooves and projections, which is why the new growth vaguely resembles a cauliflower or raspberry with black dots inside.
This is the most common type of wart, accounting for up to 70% of all such skin neoplasms. Simple warts can appear on the skin at any age, but most often they affect children and young people. This is due to the fact that they have weaker immunity than adults.
Common warts usually appear on the hands (fingers and backs of the hands), knees and elbows, sometimes on the face or feet, and extremely rarely on the mucous membrane of the mouth.
A scattering of small growths may form next to the large “parent” wart. Young neoplasms usually remain flesh-colored; over time, they acquire a dirty gray or grayish-brown tint, less often yellow or pinkish. This is due to their uneven porous surface, which accumulates dirt.
Vulgar warts usually do not cause concern: they do not cause unpleasant symptoms, do not hurt or itch. However, they may cause pain if they are in areas subject to impacts or in contact with clothing. The growths may heal on their own over time, especially if they occur in childhood.
Rehabilitation period after excision of papilloma in the oral cavity
After surgery for papilloma with any of the destructive methods, a recovery period follows, which includes drug treatment and compliance with a number of recommendations of the attending physician (treatment of the oral cavity with medications, proper nutrition, etc.).
As a rule, drug therapy after cauterization of papilloma includes taking antiviral and immunostimulating drugs, as well as vitamins. In the presence of infectious diseases that can provoke an exacerbation of HPV, appropriate medications are prescribed to combat this pathology. Complex treatment will block the virus, speed up the healing of mucous membranes and prevent infection of the postoperative wound.
You can remove papilloma in the oral cavity using one of the destructive methods in our specialized medical center, where experienced and highly qualified specialists work. After the necessary examination, taking into account the patient’s wishes and medical indications, the doctor will select the most appropriate tactics to combat warts. An individual approach to the patient, high professionalism of doctors and the use of advanced equipment will ensure successful and safe treatment of papillomas in the oral cavity.
Attention!
This article is posted for informational purposes only and under no circumstances constitutes scientific material or medical advice and should not serve as a substitute for an in-person consultation with a professional physician.
For diagnostics, diagnosis and treatment, contact qualified doctors! Number of reads: 6376 Date of publication: 08/06/2018
Dermatologists - search service and appointment with dermatologists in Moscow
Are warts always dangerous?
Most warts are completely harmless and can theoretically disappear in a few weeks or at most a month. In this case, patients are more likely to be concerned about a serious cosmetic defect, which causes psychological discomfort and interferes with leading a full lifestyle.
Warts are often painless unless they are on the soles of the feet or another part of the body that is subject to shock or constant contact. But there are cases of itching and discomfort in the affected area.
But as mentioned above, warts are viral in nature, so you cannot expect that the neoplasm will go away on its own or will not bother you for the rest of your life. Any wart should be shown to a dermatologist, and if he deems it necessary, it should be removed using one of the safe methods.
Periungual plantar warts
Periungual warts are small, rough formations with cracks on the surface, located on the hands and feet of a person, namely near the nail plate or deep under it. Externally they resemble cauliflower heads.
They can be flat, pointed or hemispherical. As a rule, periungual warts are gray, but they can also be flesh-colored. They are not too dense, like simple plantar ones, but have a fairly deep root.
This disease mainly affects children and young people. The main factor in contracting the infection is skin microtraumas around the nail. At particular risk are those who bite their nails and pet stray animals, as well as people who carelessly remove cuticles, use undisinfected tools, and work in water without gloves.
This type of neoplasm does not pose a threat to human health; it is mainly only a cosmetic defect. Periungual plantar warts do not cause discomfort or pain when pressed. However, a wart under the nail is not so harmless - over time, the neoplasm provokes depletion of the nail plate and its further destruction.
In addition, various bacteria and viruses enter through cracks on the surface of the growths, which easily form due to frequent hand work, causing re-infection. Also, as warts grow, the cracks can cause pain. The cuticle is often lost and a tendency to become inflamed (paronychia) develops.
Removal of the tumor is necessary to stop the proliferation of growths, which easily spread to healthy fingers. Localization of the wart under the nail plate makes treatment and removal very difficult. When it appears in childhood or adolescence, it can go away on its own.
Mosaic plantar warts
Mosaic warts are a special type of neoplasm. They are plaques, so-called clusters, formed as a result of the fusion of many small plantar warts tightly pressed together. The arrangement of the plaques resembles a mosaic (hence their name).
This formation is usually observed in a small and localized area. It can reach a diameter of about 6-7 cm. In the early stages of development, mosaic warts look like small black punctures. As they develop, they take on the appearance of a white, yellowish or light brown cauliflower, with dark spots in the middle. These spots are formed due to thrombosis of blood vessels.
This type of wart is quite rare. They usually affect the hands or soles of the feet, and are especially common under the toes. Unlike simple plantar warts, mosaic warts cause little or no pain when walking because they are flatter and more superficial.
Mosaic warts are highly contagious. They are difficult to treat due to the multiplicity of foci of viral infection. The success of treatment is facilitated by its timely initiation. As a rule, mosaic growths are prone to recurrence even after surgical removal.
Plantar (spike) warts
Plantar warts are a type of vulgar wart. The manifestation of the disease is most often observed in children and at the age of 20-30 years. Of all skin warts, plantar warts occur in 30%.
Warts on the soles appear as hard, round lumps with papillae in the middle. Inside the wart, characteristic black dots are visible - many small thrombosed capillaries. Along the edges there is a small roll of keratinized skin. The visible part, rising above the surface of the skin by only 1-2 mm, can reach 2 cm in diameter and is only a quarter of the total size of the plantar wart, which mainly forms in the deep layers of the epithelium (skin).
Externally, the spine resembles a callus. A plantar wart can be differentiated (distinguished) from a callus by the visible interruption of the skin pattern in accordance with the wart.
This type of neoplasm usually affects the feet (sole, sides and toes), and less commonly the palms. They appear on the skin as small whitish, pinpoint skin lesions, sometimes itchy. Over time, their surface becomes rougher and changes color - from yellow to dark brown.
Plantar warts themselves do not pose a threat to health, but when walking they cause a person significant discomfort, cause pain, which often intensifies, and can even bleed. This is due to the location of the tumor and the specifics of its growth. Since the spine grows inward, the weight of the body when walking compresses the pain receptors.
The incubation period of the disease ranges from several days to several years. The infection enters the body and goes into waiting mode for a favorable environment to activate. Plantar warts regress without treatment in 50% of cases. But this process lasts from 8 months to one and a half years.
Without treatment, plantar warts will enlarge and multiply, even to the point of producing large clusters of tumors. This can even lead to temporary loss of a person's ability to work due to unbearable pain that prevents walking.
Based on the characteristics of the lesion and its location, plantar warts are divided into 3 types:
- simple;
- periungual;
- mosaic.