53560
Crooked, unhealthy teeth can ruin the appearance of an otherwise attractive person. Oral health is important not only for our attractiveness, because the main function of teeth is to grind food. The condition of the stomach and intestines depends on this, which directly affects health and life expectancy .
How to determine?
A distinctive characteristic is the tight contact of the upper and lower jaws when closing . The upper teeth are superimposed on a third of the lower crowns, leaving no distance between the upper and lower molars.
photo: this is what a correct bite looks like
The shape of the dentition and their relative sizes are also important. The top row has a semi-oval shape, the bottom row has a parabolic shape. The lower incisors are in contact with the palatal cusps of the upper ones. During chewing, the molars constantly touch without losing contact.
Correct bite forms a harmonious face , the lower and upper jaws are symmetrical, the vertical axis of symmetry of the face coincides with the junction line between the incisors.
Signs of a correct bite are also:
- no speech defects;
- comfortable biting and chewing of food;
- absence of uncomfortable sensations and clicking in the mandibular joint.
If you notice that plaque appears only on individual teeth, this means that they are not involved in the process of grinding food . In this case, it is worth visiting a dentist: this is a sign of a defectively formed dentition.
Our teeth are like stones
Tooth enamel is the outer protective shell of the tooth, which is 97% composed of hydroxyapatite crystals (Fig. 4) - Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 - and foundation proteins: amelogenins and emellines, on which during the development of enamel (amelogenesis ) and hydroxyapatite crystals are strung [2], [3], [6], [7].
Figure 4. This is what the “closest relative” of our enamel looks like - hydroxyapatite. It’s good for him, because he doesn’t know anything about caries!
"Wikipedia"
Hydroxyapatite, although the hardest part of man, is still very sensitive to acids. Acids “stuck” in dental plaque, especially in the area of fissures (Fig. 5) - folds of enamel - begin to destroy the mineral, leading to demineralization of dental tissue, in other words, to softening. The mineral decomposes, forming calcium salts with other acids [3].
Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 + acid → 10Ca2++ 6HPO42– + 2H2O
Notably, hydroxyapatite can remain dissolved for up to two hours after ingestion. In addition to carbohydrates, the main role here is played by fruit acids. That is why after eating fruit you feel a feeling of cleanliness of the enamel. Over time, saliva neutralizes the effects of acids due to its buffering properties [2]. The more often high-carbohydrate foods are consumed, the more constant the acidification process in the oral cavity becomes. Thus, tooth decay does not depend on the amount of sugar you take, but on the frequency of its consumption: do not eat a bag of sweets during the day, but eat a large dessert once a day.
Figure 5. Enamel folds - fissures - are the favorite place for the “seeds” of caries. It is here that demineralization processes occur especially actively.
drawing by Anastasia Prokhorova
What types are there?
There are temporary and permanent bites. The bite in children before the eruption of permanent teeth is called temporary. 6-9 years – time of replacement bite. During this period, the child has simultaneous presence of permanent teeth and milk teeth.
Peculiarities of eruption influence the formation of the maxillofacial system. Any removal of replacement teeth earlier than a year before natural loss causes the risk of various deformities:
- asymmetrical dentition;
- midline shift;
- blocking chewing movements of the jaw.
A permanent bite is formed when a teenager reaches 15 years of age, when the formation of roots in relation to the position of the teeth ends. Their number during this period is 28 (32 - if the third molars have erupted).
Permanent dentition can be physiological or abnormal.
Physiological
photo: this is what a correct bite looks like from the side
Physiological ones include types of occlusions that provide:
- the most efficient and comfortable chewing of food;
- correct speech formation;
- aesthetic appearance of the maxillofacial area.
There are several varieties:
- Orthognathic. This is the standard bite that provides maximum functionality of the jaws. Premolars and molars intersect with antagonists of the opposite row. The upper incisors and canines overlap the lower ones due to a slight outward slope.
- Straight. It differs from orthognathic in the type of closure of the incisors. The edges of the upper ones do not overlap the lower ones, but touch end to end. The molars have good tight contact. A big disadvantage is the rapid wear of the upper and lower incisors due to contact of the cutting edges.
- Progenic . The lower jaw is pushed forward. The dental arches close tightly, the chewing function of the jaw is preserved.
- Biprognathic. The incisors and canines have a greater angle of inclination forward than with orthognathic. The contact of the anterior teeth is good. The incisors meet at the edges.
- Opisthognathic . The upper and lower incisors are inclined towards the oral cavity. The molars and premolars are tightly closed.
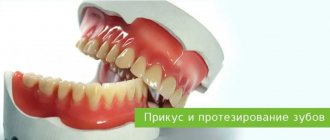
Abnormal
photo: malocclusion
Malocclusion is characterized by a complete or partial absence of tooth contact in occlusion. Such a bite distorts the face, disrupts the chewing process and can affect the formation of speech defects.
There are several types of abnormal bite:
- Deep. Its peculiarity is that the upper incisors overlap the antagonists by more than a third. The wear of the cutting edge is increased, causing the masticatory muscles to experience hypertonicity. This type of bite is also determined by constant sensations of tension in the temporomandibular joint and headaches.
- Open. A rather complex defect that entails disruption of several body systems at once. With the open type, some teeth do not have contact with the antagonists. There are lateral and frontal types.
Symptoms indicating the presence of an open bite are elongation of the mandibular part of the face, constant tension of the facial muscles, speech disturbances, difficulty swallowing, discomfort when chewing.This type may have a rachitic and traumatic origin. The rachitic variety is difficult to correct and usually requires surgical intervention. The traumatic variety is formed in childhood as a result of bad habits or trauma; at a young age it is quite easy to correct.
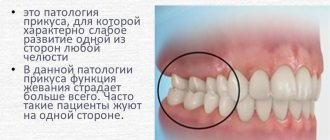
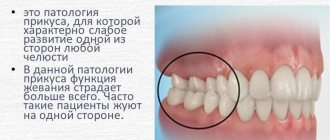
- Cross. The displacement of the lower jaw to one side forms a noticeable asymmetry of the face, the dentitions close like scissors crosswise.
A person with such a defect has difficulty chewing food and chews only on one side. Poorly chopped food provokes stomach diseases, discomfort in the jaw joint during eating, and the development of periodontal diseases. - Distal. The defect is formed as a result of good development of the upper jaw and at the same time underdevelopment of the lower jaw.
With this anomaly, the upper incisors stick out forward, leaving a large gap between the upper and lower incisors. In the formation of such an anomaly, heredity, poor posture, and removal of baby teeth (more than a year before the appearance of permanent teeth) become decisive. - Mesial . Characterized by a protracted lower jaw. With such a defect, the chin protrudes strongly and the facial profile is curved. The lower teeth are located in front of the upper teeth during occlusion.
Classification, purpose of teeth and structure of their root system
All teeth differ in appearance and purpose. Depending on the location and functional load, the following are distinguished:
- Incisors are the front teeth. There are 8 of them in total, 4 on each jaw. With their help, biting and cutting of solid food is realized.
- Fangs. The origin of the term “fangs” is associated with their resemblance to the teeth of predatory animals. The number of fangs is 4 pieces, 2 on each jaw.
- Premolars. There are 8 premolars in the mouth of an adult, the first four are located on the upper jaw, the second on the lower jaw. They perform a chewing function.
- Molars. The total number is 8 pieces, they are responsible for chewing food.
Photo: differences in the structure of teeth of different types
The photo shows the molars of the upper teeth
The picture shows lower molars
Shapes of crowns and roots of incisors
The incisors are distinguished by the presence of a flat, chisel-shaped crown with pointed cutting edges. The two central incisors of the upper jaw reach the largest sizes.
The lateral incisors of the lower jaw are larger than those located above. All teeth of this species are united by the presence of one root, flat, cone-shaped.
Shapes of canine crowns and roots
The canines have the longest roots among all human teeth. Their task is to cut food into small components.
On the side of the tongue there is a groove dividing the crown of the tooth into 2 unequal parts. The shape of the crown is cone-shaped. And its edge represents a single, clearly defined tubercle.
Shapes of crowns and roots of premolars
Premolars perform a chewing function. The first upper molar has a prismatic shape, and on the cheek side it is rounded. The cutting surface is represented by voluminous rollers, between which there are wide natural recesses. The root is forked and flattened.
The main feature of the second premolar is the root system. It is distinguished by its cone-shaped shape and the presence of slight compression on the front side of the root.
The first premolar of the mandible has a rounded shape and two cusps as a cutting base. The single root is flattened.
The second lower premolar is larger than the first and upper ones. Its contact surface is represented by two large bumps separated by natural grooves in the shape of a horseshoe.
Shapes of crowns and roots of molars
The upper first molar is the largest tooth. It has a rectangular crown. The root system consists of three parts - one root in the center, the rest on the sides.
The second molars of both jaws are characterized by a square shape and more modest dimensions. The mandibular first molar has two roots and five cusps on the crown.
Many people have missing third molars or wisdom teeth. They look the same as second molars. The main difference is their root system - it is curved, with a large number of roots (up to five pieces). The final formation of the roots of the eighth tooth occurs at the age of 24 years.
Causes of anomalies
Let's look at the main reasons why defects occur:
- Genetic factor. Mesial and distal occlusion are most often inherited.
For parents, knowing about the high risk of such a defect occurring in their child, it is easier to control treatment in childhood, during the formation of the maxillofacial system. - Developmental anomalies in the prenatal period. Various pregnancy pathologies can often affect the formation of the fetal dental system.
- Birth injury. Mesial occlusion is caused by displacement or dislocation of the baby's lower jaw during difficult childbirth.
- “Wrong” habits in childhood. These include constant pacifier or finger sucking, improper nipple latching, and improper sucking during bottle feeding. If the hole in the nipple is too large, the child’s lower jaw practically does not work when sucking and remains undeveloped.
- Frequent sinusitis and rhinitis, due to which the child constantly breathes through his mouth. With such breathing, the development of facial bones is disrupted.
- Violation of tooth change. Early removal of baby teeth often causes abnormal maxillofacial development.
- Incorrect prosthetics, lack of prosthetics.
- Hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles due to stress provokes abrasion of the incisors and displacement of the jaws.
- Various injuries of the maxillofacial area.
Stains on an adult's teeth
Chalky stains on the teeth of an adult can signal dental caries. Tooth decay destroys teeth if they are not carefully cared for. Then dietary fiber remains in the interdental spaces, which is a breeding ground for pathogenic microbes. They begin to secrete organic acids, which contribute to the leaching of calcium from the teeth.
How to form?
photo: diagram of the correct bite in a person
What do orthodontists advise to form the correct position of teeth:
- Breastfeeding is very important for a child; it lays the foundation for the correct development of the jaws.
If you had to feed your child with formula, it is best to purchase a pacifier that does not spoil the bite. The sucking hole should be made narrow so that the baby has to suck with effort. The lower jaw in infants is underdeveloped and muscle exercises (forceful sucking) are important for its proper functioning in the future. - Formation of correct chewing habits. You should not accustom your baby to a pacifier. From the moment of teething, the baby should be offered complementary foods for the habit of proper chewing.
- Parents should pay attention to how their child breathes. Physiological breathing through the nose. Breathing through the mouth is a sign of ENT diseases. They must be treated: in addition to general damage to health, this is a dangerous factor in the formation of a defective bite.
- From the moment of complete eruption of baby teeth, regular examinations by an orthodontist (every six months). When abnormalities are diagnosed at an early age, they are much easier to treat.
A perfect smile with veneers and lumineers
Restoration of the smile area using veneers and lumineers is suitable if you have absolutely healthy, but not very beautiful teeth. Indications for the use of veneers are:
- Chips, microcracks in teeth;
- Darkening of the enamel that cannot be eliminated by bleaching;
- Noticeable stains on the surface of the teeth;
- High-quality fillings, but darkened over time;
- Large interdental spaces;
- Slight crowding of teeth;
- Deviation of the position of the teeth from the axis;
Microprostheses are fixed on the outer surface of the teeth to change the visual perception of the dentition and create a beautiful smile. The color of the veneer is chosen so that it matches your own teeth. In this case, the presence of veneers is invisible. People around you simply notice your beautiful smile. They are not suitable for restoring severely damaged teeth. In such cases, it is better to choose ceramic crowns rather than veneers.
Installation of veneers and lumineers requires grinding of teeth. Since without it, the lining will protrude above the teeth due to its own thickness. Your teeth won't look beautiful and your smile won't look perfect. The amount of grinding depends on the individual characteristics of the patient and his teeth. In some cases, it is indeed possible to completely do without turning, but the doctor will be able to tell how microprosthetics will work in your case only after an examination.
Dental restoration with lumineers and veneers takes time, since microprostheses are made individually. The entire process of creating a Hollywood smile takes place in several stages:
- Preliminary inspection. The task of this stage is to identify indications and contraindications for the installation of veneers;
- Sanitation of the oral cavity. Plaque and stone are removed from the surface of the teeth;
- Grinding of teeth for veneers. This step is not always required;
- Preparation of casts. After the teeth are completely prepared for restoration, the doctor takes impressions to make veneers;
- Manufacturing. Veneers are made in a dental laboratory using CAD/CAM technology. Lumineers must be ordered from the manufacturer;
- Installation. Once the veneers are ready, they are fixed to the teeth with dental adhesive.
You can see the result of dental restoration and decide whether it is necessary even at the preparation stage. To do this, the doctor will make a 3D computer model of your new beautiful smile.
Types of correct bite
The above describes the orthognathic bite, which is the reference. It occurs in only 5% of people. But there are other types of teeth closure in which violations are not detected. What does each one look like? Experts identify the following bites:
- Biprognathic. Both jaws are slightly pushed forward, and the teeth are slightly directed towards the lips.
- Opisthognathic. The opposite of the previous type. The teeth are directed inward. Opisthognathic occlusion is rare. Its features are noticeable when viewed in profile.
- Progenic. The lower jaw protrudes slightly, but this feature is not pathological. The functioning of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) and the functionality of the teeth are not impaired.
- Straight. The upper row of teeth is parallel to the lower one. The incisors touch their cutting edges. This feature is not a deviation, but it threatens rapid wear of the teeth due to increased load.
Sometimes, if you have one of these malocclusions, minor adjustments may be needed. But the treatment in this case will be easy.
The main methods of treating missing lower teeth
In the case where a tooth is completely missing (even the root is missing), restoration of the lower jaw teeth is carried out using one of the methods below:
- Installation of a fixed bridge prosthesis. The method is used when one or more teeth are destroyed or lost; the remaining healthy teeth serve as supports for the bridge structure. Fixed dentures cannot redistribute the chewing load on the jaw; therefore, when chewing, the load is not distributed evenly, but only on the supporting teeth to which the denture is attached. The fixation of fixed dentures is permanent, and it is impossible to remove such dentures yourself without the help of a dentist. The advantages of the method are aesthetic characteristics, restoration of chewing function, fast treatment time and relative low cost compared to dental implantation. Disadvantages - the need to depulp possibly healthy teeth, uneven distribution of the load, ongoing atrophy of the bone tissue of the alveolar crest in places where teeth are missing.
- Use of removable dentures. Most often they are used for long-term defects in the dentition (the absence of 3 or more teeth in a row). However, sometimes they are used in the absence of only 1-2 teeth (butterfly dentures) - if the patient does not want to undergo implantation or grind adjacent teeth for crowns. It is recommended to remove removable dentures once a day for hygienic procedures. Such dentures are less comfortable than fixed ones, because... occupy a significantly larger volume. Due to anatomical features, removable dentures for the lower teeth are smaller in size than the upper ones. Advantages: low cost, minimally invasive treatment, acceptable aesthetics. Disadvantages - does not restore chewing function, does not prevent bone tissue atrophy, the need for daily removal and periodic relining.
- Dental implantation. Implants are installed both when one or several teeth are lost in a row. Their purpose is to replace the biological root of a tooth; in prosthetics, implants are used as supports for artificial crowns: metal-ceramic or ceramic with a zirconium dioxide frame. Three main stages of implantation: installation of the implant into the bone tissue, formation of aesthetic gums, fixation of abutments on the implants and installation of crowns on the abutments. Implants can also be used in cases of complete absence of teeth in the lower jaw. The main advantage of implantation is the almost complete restoration of chewing function, and, as a result, the cessation of bone atrophy; such prosthetics also provide excellent aesthetics.
If the root of the tooth is not removed and there is a possibility of preserving it for use under a fixed prosthesis, the stump of the tooth is first restored, onto which a crown - metal-ceramic or completely ceramic - is fixed.
How to find out what kind of bite you have
Patients are often interested in how to determine whether their bite is correct. Usually the presence of abnormalities can be identified by facial features. It is also worth taking into account the criteria for correct bite described above. Go to the mirror, open your mouth and clench your teeth. In some cases, violations are immediately visible. Just because your smile looks aesthetically pleasing does not guarantee that everything is fine.
Even if you know what a correct bite should look like, it is impossible to make a correct diagnosis on your own. Only a specialist can do this. In addition to a visual examination and medical history, the doctor diagnoses the problem based on the results of a CT scan (computed tomography). Such an examination allows you to comprehensively assess the condition of the oral cavity. Disturbances in the placement of teeth are also identified by an impression made from an alginate mass. The orthodontist also needs photographs of the person’s face taken from several angles. Using them, you can evaluate the occlusal relationships of the dentition.