Proper brushing of teeth and gums
Plaque on teeth is a common cause of many oral diseases, so it is important to remove it regularly. Buy a soft toothbrush and brush your teeth with it twice a day. Gently massage your gums, this will help strengthen them. Be extremely careful and learn to brush your teeth properly. Remember to clean your tongue using the special back of your toothbrush. Use toothpastes labeled “for bleeding gums.” They usually contain aluminum lactate, baking soda, herbal extracts and other substances that help fight the problem. Don't forget about the power of dental floss: it can be used to remove plaque from hard-to-reach interdental spaces.
How to treat bleeding gums?
If your gums bleed frequently, you should consult a dentist. Treatment of this pathology consists of several stages.
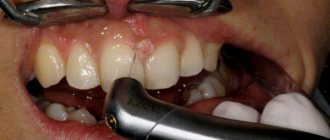
First, professional oral hygiene is performed. It is in dental plaque that ideal conditions are formed for the proliferation of harmful bacteria, which threaten not only the condition of the gums, but also the condition of the teeth. Plaque formation under the gums is especially dangerous. To get rid of it, dentists prescribe sandblasting or ultrasonic cleaning procedures.
After this, the doctor checks the condition of the fillings and dentures. If there are poorly treated teeth or crowns, pathogenic bacteria can develop there. To stop the inflammation, they may have to be replaced.
Your doctor will give you recommendations on how to properly brush your teeth. In some cases, a specialist may recommend special oral care products. The doctor will help you choose a brush and toothpaste that is suitable for a particular patient. If you brush your teeth incorrectly, inflammation can become chronic.
If necessary, the doctor may prescribe certain medications:
- antiseptic solutions for rinsing the mouth;
- special gels or ointments that eliminate inflammation or have an antiseptic effect;
- antibiotics and drugs that relieve inflammation.
In difficult cases, the doctor may suggest surgical treatment.
Rinse
By rinsing, we remove food debris, pathogenic bacteria, and treat gums locally. You can rinse your mouth with a solution of soda, decoctions and diluted herbal tinctures (chamomile, St. John's wort, nettle, sage, oak bark) or special dental rinses. Read the instructions for use carefully! In folk medicine, hydrogen peroxide, carrot juice, and sauerkraut are used (it must be chewed periodically). Please note that rinsing for many diseases is only an additional, concomitant method of treatment.
What to prepare for rinsing gums at home?
Chamomile
A powerful natural antiseptic used to eliminate inflammation. Among herbs for rinsing gums, chamomile occupies a leading place.
How to use:
Pour 1 tablespoon into a glass of boiling water, let it brew for 40 minutes and rinse 3 times a day after meals.
Oak bark
Oak bark is an indispensable rinse for gums. Has an astringent and hemostatic effect.
How to use:
Pour 3 tablespoons of bark into a glass of boiling water, keep in a water bath for half an hour, strain, bring the volume to 200 milliliters with boiled water and rinse 5 times a day after meals.
Sage
Rinsing with sage has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect.
How to use:
Pour 200 milliliters of boiling water over 1 tablespoon of leaves, leave for 40 minutes, rinse 3 times a day after meals.
Baking soda
A baking soda rinse for gums reduces pain and promotes healing.
How to use:
1 teaspoon per glass of boiled water. If your gums are inflamed, rinsing with soda should be done after eating, after brushing your teeth. Use immediately, do not store!
Salt
Rinsing gums with salt has a disinfecting effect.
How to use:
1 teaspoon of salt per 1 glass of boiled water. To enhance the medicinal effect, it is best to rinse with salt and soda at the same time!
5% iodine solution
Has an antimicrobial effect.
How to use:
To rinse your gums with iodine, one drop per glass of boiled water is enough. It is better if it is lightly salted, for example, sea salt.
Propolis
The waste product of bees relieves pain well and heals wounds.
How to use:
Propolis for rinsing gums is used in the form of an alcohol tincture: 30 drops per 1 glass of boiled water, rinse 3 times a day after meals.
If you don’t have time to brew herbs, you can just as easily use pharmaceutical alcohol tinctures made from them to rinse your gums.
Medicines
Among the medications that are traditionally used for bleeding gums, we can name Cholisal, Metrogyl Denta, Kamistad, Asepta. All these gels have both an analgesic, antiseptic and wound-healing effect. If a child has problems with gums, then such gels will be the best first aid medicine.
Among the herbal remedies, we found the liquid rinse preparation Stomatofit. It is made on the basis of extracts of medicinal herbs that heal gums. It has no side effects, but is not recommended for people allergic to chamomile and arnica.
Why else can your gums bleed?
Bleeding is not always associated with gum inflammation. The cause may be a disruption in the functioning of the body, various diseases and dental interventions.
Here are a number of other reasons that can cause bleeding gums:
- vitamin C deficiency;
- hemophilia is a bleeding disorder, a hereditary disease;
- blood cancer;
- blood thinning medications;
- gum injury during tooth extraction or implant installation;
- alcoholism;
- smoking;
- hormonal imbalance (pregnancy, puberty).
To prevent bleeding gums, you should eat a balanced diet, maintain oral hygiene and regularly visit the dentist.
Dental care
Try to take care of your dental health regularly. Be sure to remove plaque, as it is an excellent breeding ground for bacteria. Plaque and tartar can also be removed in the dentist’s office using professional teeth cleaning and the AirFlow method. This significantly improves the health of the oral cavity, restores the natural balance of bacteria, cleans hard-to-reach places, and restores the natural whiteness of teeth. Moreover, such care is absolutely painless for the patient! It is recommended to have professional teeth cleaning once a year.
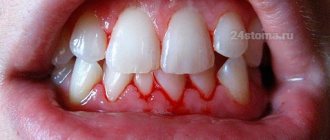
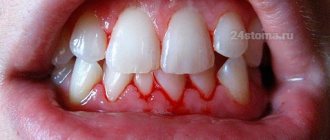
Why do my gums bleed?
Often the gums begin to bleed due to diseases of the oral cavity:
- Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gum tissue, due to which they cease to perform their protective functions. Due to tartar and plaque, bacteria begin to multiply, which become the cause of the inflammatory process.
- Periodontitis is inflammation of the internal periodontal tissues. If the disease is not treated, the inflammation will become chronic and can cause tooth loss.
- The third cause of bleeding gums is periodontal disease. Because of it, the structure of tissues and blood flow change, and teeth can become mobile. Bacteria first infect the oral cavity and then end up in the gum pockets. After this, the gums swell and begin to bleed, especially when brushing your teeth.
- Bleeding can be caused by the formation of tartar in the gum area. It occurs due to improper oral care. Dentists advise cleaning off plaque at least once a day.
- Bleeding from the gums can begin during pregnancy, as a woman's hormonal levels in the body change.
- Another reason is a too hard toothbrush. To avoid damaging delicate tissues, preference should be given to soft or medium-hard bristles.
- Sometimes gums swell and bleed due to a lack of certain vitamins or minerals in the body.
- Bleeding gums can cause a worsening throat condition.
Treatment
Modern dentistry will offer many effective techniques; after determining the diagnosis, an individual program is selected. The treatment will be comprehensive, all measures are aimed at eliminating the cause that led to complications.
Much depends on the diagnosis, but most often the following is recommended:
- taking medications for inflammation;
- high-quality removal of tartar and plaque;
- taking immunomodulators and vitamin compounds;
- a course of using dental ointments and gels;
- electrophoresis, gum massage, balneotherapy, etc.
Even with mild bleeding, it is worth visiting a doctor, since it is much cheaper to prevent the problem and avoid significant harm to the teeth and gums.
How dangerous is bleeding?
If the symptoms occur regularly, they are dangerous because the tissues around the teeth are gradually destroyed and the epithelium becomes less elastic. So the teeth cannot stay in place, the molars and incisors begin to shift and move, interfering with chewing and harming the entire digestive system. If treatment is absent or ineffective, the tooth that is too loose must be removed. It is worth promptly removing plaque from your teeth at the dentist, removing tartar, and also making an appointment with the dentist in case of bleeding or other problems in the oral cavity.
Treatment of bleeding gums
To effectively get rid of this uncomfortable symptom, it is important to eliminate secondary trauma to the damaged areas of the gums. To do this, select special teeth cleaning products: a soft or ultra-soft toothbrush, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory toothpaste that eliminates bleeding, and a mouth rinse. In the diet, it is temporarily necessary to avoid dry and solid foods: chips, apples, crackers, etc. The doctor prescribes general drug therapy aimed at strengthening capillaries and eliminating inflammation, as well as local therapeutic procedures: dental gels, applications, rinses.
General information about the structure of the oral cavity
The oral cavity is a real laboratory, simultaneously carrying out taste analysis of food, the breakdown of carbohydrates, immunological protection, chewing, participation in breathing and pronunciation of words. Therefore, for normal functioning, all its soft components must be enriched with oxygen and nutrients. This requires proper blood supply. When the gums become inflamed and bleeding, it is disrupted. This is fraught not only with discomfort at the moment, but also with delayed serious problems.
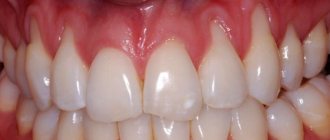
Typically, bleeding comes from the depths of the gingival sulcus - the physiological area between the tooth and the soft tissue. The appearance of blood during mechanical action is a sign of inflammation. It may indicate the beginning of destruction of the tissues surrounding the tooth.
Protecting and taking preventive care of your gums is no less important than regular dental care. People rarely go to the dentist if they notice bleeding gums when brushing their teeth. Experts recommend reporting all such cases not related to mechanical trauma in order to find out the causes of bleeding gums and prescribe timely treatment [1.2].
Minerals and beneficial elements necessary for healthy gums and teeth
In addition to vitamins, certain minerals are essential for healthy teeth and gums.
Thus, calcium and phosphorus are necessary for the formation of bone tissue and tooth enamel. And vitamin D can help absorb these elements, which promotes their penetration into dental dentin and accumulation.
Experts from the World Health Organization note that a modern adult does not receive 500 mg of calcium every day. But replenishing its reserves is not at all difficult: to do this, it is enough to eat nuts, dairy products, leafy salads, legumes and cabbage. Or you can take adult dental vitamins that contain calcium.
A mineral such as fluorine plays an equally important role. It is he who protects teeth from caries and destruction. Sufficient amounts of fluoride are found in meat, any seafood, oatmeal and buckwheat, apples and tea.
Zinc
Many people do not sufficiently understand the benefits of this microelement, but due to its deficiency, the integrity of hard tissues can be impaired. To replenish zinc in the body, you need to consume cocoa, pine nuts, pumpkin seeds, peanuts and sesame seeds as often as possible.
The development of anemia is caused by a lack of a microelement such as iron. In this case, a person may experience light colored gums, and teeth begin to crumble. Iron can be “found” in foods such as red meat, liver, buckwheat, dried fruits and legumes.
Medicines
The choice of medications is determined based on the type and stage of the disease. Miramistin, chlorhexidine, furatsilin can be used for rinsing the mouth. In the presence of inflammation, you can use ointments that have anti-inflammatory and disinfectant effects. Infections are treated with the following:
- antibiotics;
- antiseptic drugs;
- antifungal agents;
- immunostimulants;
- vitamins.
Home treatments can be used as aids. Good results are shown by rinsing with herbal infusions of calendula, chamomile, and yarrow. To eliminate pain and strengthen soft tissues, use propolis tincture or a solution of soda and sea salt.
How to treat increased bleeding
12.01.2022
More than 60% of women and more than 35% of men answer affirmatively to the question about the tendency to bruises, small bruises on the skin, and frequent bleeding. This is called hemorrhagic syndrome.
A hematologist deals with such problems. The doctor determines treatment tactics depending on the type of hemorrhagic syndrome, each of which has its own symptoms.
- Hematoma⠀
It is characterized by painful extensive hemorrhages in the subcutaneous tissue, muscles, and joints. In this case, compression of nearby organs, nerves, and blood vessels often occurs.
- Petechial-spotted (bruised)
It manifests itself as hemorrhage into the skin and mucous membranes. Characteristic is the “blooming” of elements from crimson-red-violet to greenish and then yellowish. Most often they are located on the abdomen, legs, face, and mucous membranes.
- Vasculitic purpuric
This type is characterized by pinpoint rashes of bright red color. They can merge and do not disappear when pressed. And when a secondary bacterial infection occurs, ulcers and necrosis may appear. Such rashes are located symmetrically, most often on the legs, feet, lower back and abdomen.
- Angiomatous
Small, bright red elements protruding above the surface of the skin and mucous membranes, like “spider veins”, turning pale when pressed. Localized on the skin of the face, torso, fingertips, lips, nose, mucous membranes.
- Mixed
Most often, petechial and hematoma types appear simultaneously. As a rule, this occurs against the background of hemostasis disorders in diseases such as disseminated intravascular coagulation, sepsis, or an overdose of anticoagulants or thrombolytics.
- Senile purpura
This is a typical problem among older people, occurring on average in 80%, more often after 60 years of age. It does not pose a threat to health, but is manifested by visible aesthetic defects and causes discomfort in patients. The disease is characterized by small dark purple “bruises” that are usually located on the arms and appear for no apparent reason. Such changes are associated with increased fragility of blood vessels and other age-related changes in skin structure.
Diagnostics
The examination of patients with hemorrhagic syndrome takes place in several stages.
1. History taking
- Localization of hemorrhagic syndrome - bleeding from small/deep wounds, nasal, uterine, gastrointestinal bleeding, hemarthrosis, intramuscular hematomas
- Duration of bleeding
- Provoking factors
- Collecting a family history to identify the hereditary nature of the disease
- Presence of concomitant severe somatic and systemic diseases
- Taking medications
2. Examination of the patient
- Thorough visual examination of the skin, mucous membranes and joints
- general examination of organs and systems
3. Instrumental diagnostic methods
- Search for sources of bleeding using ultrasound and endoscopic methods, CT, MRI, angiography, etc.
4. Laboratory studies of the hemostatic system
- Complete blood count with platelet count according to Fonio
- Screening tests to assess hemostasis (APTT, PT, fibrinogen concentration)
- Determination of the concentration of individual coagulation factors (VIII, IX, von Willebrand factor; D-dimers and other indicators in this particular clinical situation).
After examination and assessment of the clinical picture, the doctor prescribes treatment.
Return to articles
Signs of bleeding gums
The symptom of bleeding is a pathological condition that indicates damage to the epithelial cover as a result of injury or inflammation, and is one of the signs of a wound (gaping, pain, bleeding)
“Therapeutic Dentistry,” ed. G. M. Barera.
There are simple markers that help detect the problem of bleeding gums:
- a metallic taste in the mouth, usually worse after brushing teeth or eating;
- pink toothpaste foam when spitting;
- burning sensation in the gum area when drinking sour, salty drinks or food;
- traces of blood on solid food when biting into it [1,2].
The degree of damage to soft tissues due to bleeding can only be detected by a doctor with special vertical and horizontal probing
Prevent bleeding
To minimize the risk of bleeding, you should use a brush recommended by your dentist (hard ones can cause injury) and brush your teeth regularly.
You can use specialized rinses if they contain ingredients that strengthen the gums and relieve inflammation. You also need to eat well, have your teeth treated in a timely manner, have your teeth cleaned and have professional oral hygiene. It is not recommended to whiten your teeth at home without first visiting your dentist and getting his approval. You can consult about bleeding gums at the Genesis39 clinic, where experienced specialists can always provide decent assistance and solve the problem. ←Return to list of articles
Folk remedies: herbal treatment
If a patient's gums are bleeding, folk remedies can improve his condition, reduce bleeding and pain. Herbs for bleeding gums help reduce the source of inflammation, cure itching, burning, swelling, and cleanse the surface of the mucous membrane from bacterial plaque.
Homeopathy should not replace full-fledged anti-inflammatory therapy; it only complements the treatment regimen prescribed by the doctor.
You can prepare solutions and infusions yourself or use ready-made pharmaceutical preparations.
Oak bark
It has an astringent effect, strengthens the gums, and is used in the form of a decoction for rinsing. Brew a tablespoon of raw materials in a glass of boiling water. Rinse your mouth regularly for two weeks.
Chamomile
It is famous for its healing, anti-inflammatory, soothing effects, suitable for external and internal use. Pour boiling water over two tablespoons of flowers and leave for 20 minutes.
Sage
A unique folk antiseptic and analgesic, suitable for rinsing, applications, and baths. Steam 2 tablespoons of the herb in 200 ml of water, use daily, after each meal, until complete recovery.
Nettle
An excellent hemostatic agent. Infuse 2 teaspoons in 200 ml of boiling water, strain, cool. Rinse your mouth until a stable therapeutic effect appears.
water pepper
Increases the density of vessel walls, stops bleeding, increases blood clotting, and relieves inflammation. Used as an extract and infusion for rinsing.