NBR is one of the methods of bone augmentation before implantation. Surgery is used to guarantee the primary stability of the implant and eliminate the risk of rejection of the titanium root and the development of tissue inflammation. The lack of bone is filled with a bone substitute, which is secured with a membrane. They use their own or synthetic materials. The method is safe: surgery is performed under local anesthesia, small tissue incisions are made, bone material is grafted, and the process of graft engraftment is monitored.
What is Guided Bone Regeneration
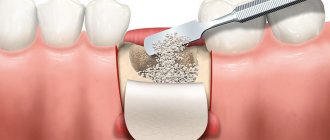
Guided bone regeneration is an operation to compensate for the lack of bone tissue with a substitute, which is secured with a barrier membrane. After the procedure, a framework is formed around the transplant (it is formed by vessels and osteocyte cells that produce new tissue). Natural bone is gradually replacing artificial material.
Extensions using the NDT method are carried out according to classical parameters:
- thickness of the vestibular bone wall (at the cheek) - up to 2-2.5 mm;
- bone thickness between the implant and the root of the adjacent unit - up to 2.5-3 mm;
- The thickness of the bone wall between two titanium roots is up to 3 mm.
Expert opinion
Emir Romanovich Omerelli
Maxillofacial surgeon, implantologist
Experience: more than 13 years
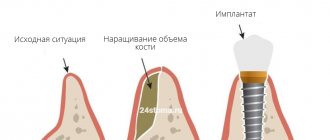
If, based on the results of the examination, the doctor diagnoses a lack of bone tissue, it is necessary to increase its volume before implantation. Placing implants in low or narrow bone carries serious risks. The bone may fracture or the implant itself may fall out after a short period of use. To prevent this from happening, before classical implantation of the upper teeth, it is necessary to carry out a sinus lift, and for the lower teeth, extension through osteoplasty. The only exception is the basal protocol, according to which implants can be installed without bone grafting and without risks.
If the bone tissue is not wide enough, that is, it is very thin, the operation can be performed by splitting the alveolar ridge: first the gums are exfoliated, then the bone is cut along the length and artificial or natural bone material is placed inside.
Also, the problem of narrow bone tissue is solved by transplanting a bone block borrowed from another bone of the patient himself. To do this, a piece of bone is placed under the gum, fixed with special screws, sprinkled with bone chips around it, covered with a barrier membrane and gum - the mucous membrane is sutured. This option is more preferable, since in most cases the own bone survives.
Bone tissue augmentation surgery, depending on the indications, can be performed simultaneously with the installation of classical implants without their subsequent loading. That is, the artificial roots are fixed in the bone, but are covered by the gum - the dentures will be fixed in 3-4 months. In order for classical implants to take root in the bone, it is necessary to ensure their rest and relieve any pressure.
Complications after bone tissue regeneration
The operation of bone tissue augmentation is considered one of the safest in dentistry, complex, but if carried out correctly, without any unpleasant consequences. In the first days after the operation, it becomes clear whether the block will take root or the operation will have to be performed again. Among the unpleasant sensations are slight tissue swelling and pain in the area where the bone block was taken and the site where it was transplanted. But after 2-4 days, all unpleasant sensations go away on their own.
After bone augmentation
After the bone regeneration procedure, the patient must take precautions: be sure to take medications prescribed by the doctor to quickly restore the body, and do not ignore painkillers. You should refrain from eating food for 2-3 hours after surgery; afterwards it should be warm, but not too cold or hot. It is recommended to chew foods on the side opposite the surgical procedure. In addition, it is necessary to give up physical activity for a while and provide the body with rest for a couple of days after the operation. Do not forget to visit your doctor for a preventive examination and monitor the results of treatment.
Other jobs
Indications
The operation allows you to increase the “necessary” volume for high-quality classical implantation, helps restore the functions of the jaw, and returns the gums to an attractive appearance.
The bone is built up “with reserve”, since after the operation the surface layers will be supplied with a small amount of oxygen due to their lower blood circulation. Therefore, the volume of inevitable tissue resorption is calculated.
In addition to implantation, indications for NRC are:
- rapid restoration of physiological parameters after tooth extraction;
- congenital or acquired defects of the bone around the teeth;
- prevention of tooth displacement, loosening, and loss due to periodontal tissue diseases.
Why does atrophy occur?
Causes of jaw bone deficiency
The effectiveness of a labor-intensive procedure aimed at maximizing the improvement of the jaw depends on the volume of bone tissue, which tends to deteriorate during a person’s life for the following reasons:
- inflammatory processes in a decaying tooth;
- injuries of the maxillofacial apparatus;
- destruction of bone tissue due to surgical removal of a tooth, that is, most dentists perform this operation with the capture of the alveolar process or part of it;
- resorption of bone tissue due to sharply reduced pressure on it due to the absence of a tooth;
- congenital deficiency, which is manifested by malocclusion, speech defects, as well as aesthetic nuances.
Bone deficiency can be noted both in height and in width of the anatomical part bearing the dentition. Almost all types of reduced volume of the bones of the lower or upper jaw can be restored using modern methods. Of course, there are some disadvantages of bone grafting , but, in this case, the end justifies the means.
What bone materials are used
Osteoplasty involves the use of bone replacement materials. Previously, transplants were used that were not widely used due to frequent rejection of foreign material:
- Allografts
are donated bone from other people. The material was obtained from corpses, processed, sterilized, and stored in bone tissue banks. - Xenografts
are animal bones (cattle, pigs). The material was freed from proteins by heating (to eliminate the possibility of an allergic reaction after transplantation).
We do not use outdated techniques. Nowadays, many synthetic components have been developed that promote the growth of our own bone, which we use to build bone tissue.
Synthetic materials have a high degree of affinity and compatibility with natural bone and are its analogues. These are granular formulations based on:
- calcium phosphates;
- chondroitin sulfate;
- bioglass.
The effectiveness and safety of artificial materials has been confirmed by numerous studies. They are easy to use, take root well, promote the regeneration of your own bone, and are hypoallergenic.
With osteoplasty, a combination of an artificial substitute and a person’s own bone in the form of chips (autograft) is possible. The technique helps preserve the volume of built-up bone tissue and speed up the rate of recovery. The same method helps if you have to grow a large amount of tissue.
If there is a slight shortage, you can only get by with synthetic materials.
Preparations for bone tissue regeneration in dentistry
As a result of long research and testing at various medical universities and leading surgical centers, drugs for bone regeneration were developed. The most common ones in Moscow dental clinics are Swiss ones - Bio-Oss and Bio-Gide, from Geistlich Pharma AG. They are based on animal material, namely the mineral component of bones and collagen. Strict control at all stages of obtaining the drug, as well as a high degree of sterilization, make it possible to obtain a truly high-quality product. Compliance with all standards of the United States of America and Europe ensured widespread distribution and great demand for this material. Bone tissue regeneration - Bio-Oss and Bio-Gide preparations are far from the only area of application. In addition, the drug is widely used in periodontics, maxillofacial surgery, and implantology.
Types of membranes
The membrane technique used by the surgeon is needed to isolate the space from fibrous tissue - creating conditions for normal tissue regeneration. There are several requirements for membranes:
- biological compatibility;
- strength;
- prevention of migration of epithelial cells;
- corresponding resorption period.
In practice, two types of membranes are used:
- Resorbable.
They dissolve on their own 6-24 weeks after extension. Membranes are used for small defects (when you need to build up no more than 2 mm) - they do not hold their shape as well as the next type. - Non-resorbable.
They do not dissolve - they are eliminated several months after surgery.
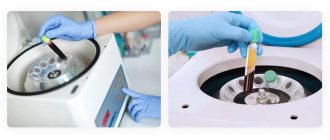
To quickly fuse the artificial material with the jaw bone tissue, in some cases membranes from the patient’s blood plasma are used.
Resorbable membranes
Products in this category are used to isolate the area of surgical intervention, forming a barrier at the site of tissue dissection. The protocol is lengthy and involves a significant amount of work, but provides high levels of bone structure density. As a rule, it is recommended in preparation for operations to replace elements of the maxillary row.
Vertical operation requires the presence of holes up to three millimeters wide, however, in this case, the formation of a full-fledged structure is complicated by the presence of areas of other tissues. One of the advantages of resorbable type membranes, reflected in their name, is self-resorption after achieving the set goal, eliminating the need for a repeat operation. The elements have a limited range of action, restoring surfaces with a volume of no more than two millimeters, which reduces the possibilities for installing implants and requires high precision when planning and executing the installation.
Non-resorbable plates
Membrane inserts belonging to the non-resorbable category are considered the optimal tool for targeted regeneration. The advantage of membranes is the ability to form bone that meets the specified parameters and characteristics. Products are divided based on the presence of a titanium frame, thanks to which a clear boundary is created that prevents violation of the configuration. Non-resorbable plates are used to restore large areas of bone tissue, both in the horizontal and vertical planes.
Fixation technique
The protocol for installing a non-resorbable membrane involves performing the following sequential manipulations:
- Incision of mucous tissue and detachment of the flap part;
- Decortication of the surface of the bed for installation of a membrane with osteomaterial;
- Fastening the product using a screw connection;
- Sewing the surface tissue using thin threads;
- Antiseptic treatment of the intervention site.
The use of non-resorbable membranes allows you to achieve the desired result in the field of restoration of bone tissue of the jaw. Even with large lesions, large damaged areas can be restored using a titanium frame. The completed cycle of directed regeneration allows us to proceed to implantation of dental dental structures into the strengthened bone.
NDT stages
The operation is performed under anesthesia. The surgeon acts according to the classical algorithm:
- He cuts the gum along the hole of the lost tooth, makes several cuts on the side - peels off the gum flap.
- Fixes the implant into the exposed bone (if the operation is organized simultaneously with implantation).
- Replaces the missing volume with a graft, covers it with a membrane with a protrusion of 2-3 mm beyond the bone material. If it does not exclude the fact that the membrane is being pressed into the defect, a titanium mesh is placed on top.
- Secures the membrane (with sutures or screws).
- Brings the edges of the wound together and applies stitches.
The operation lasts 1-1.5 hours.
Can it be done simultaneously with implantation?
Two operations are combined into one if the following conditions are met:
- the shape of the defect allows you to correctly install the artificial root in any of the planes;
- when installed, the implant is located within the bone contour (does not go beyond the tangent drawn to the bone line);
- eliminate a horizontal (not vertical) defect.
The implanted implant can become a barrier to the growth of blood vessels and inhibit the formation of new bone. If the implant protrudes beyond the contour of the bone tissue, the risk of developing fibrous tissue with inclusions of the implanted material cannot be ruled out.