Implantation today is one of the most popular procedures in dentistry. However, it is not available to everyone. In order for the implant to reliably take root, strengthen and withstand daily loads in the future, it needs a solid base, the role of which is played by its own bone tissue.
Sometimes, for various reasons, there is not enough natural bone tissue for implantation. In this case, osteoplasty helps to cope with the problem.
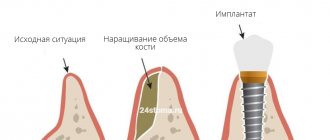
Bone augmentation in dentistry is a surgical procedure in which the missing volume of bone tissue is restored to the patient to install one or more artificial tooth roots.
Indications and contraindications for bone augmentation
The main indication for osteoplasty is the lack of native bone tissue for implantation.
Bone augmentation in dentistry
Bone augmentation is also prescribed in the following cases:
- various types of jaw injuries;
- elimination of complications after tooth extraction, especially if the patient does not take proper care of the oral cavity;
- large areas of damage or atrophy of the alveolar ridge that have arisen against the background of infectious diseases or injuries.
Like any surgical intervention, osteoplasty has a number of contraindications:
- oncological diseases;
- diseases of the immune system;
- some diseases of the circulatory system (for example, bleeding disorders);
- allergy to anesthetics;
- epilepsy or other mental disorders;
- sinusitis or tonsillitis - surgery in this case is postponed until the patient has fully recovered.
Sinus lift for recovery
The sinus lift procedure is designed to increase bone tissue by elevating the maxillary sinuses. It is used provided that the patient has no pathologies or allergic reactions.
If the patient has a history of chronic runny nose, sinusitis, or multiple septations, the operation will not be performed.
The procedure allows you to increase the missing volume of bone tissue, but there remains a risk of developing a chronic runny nose or inflammatory process in the future.
Types of bone tissue augmentation
Before deciding how osteoplasty will be performed, it is necessary to undergo a thorough examination.
The choice of method is influenced by several parameters: the height and width of the patient’s bone, its structure, as well as the location of large blood vessels and the mandibular nerve.
Autogenous transplantation
Autogenous transplantation is one of the most effective methods, since the donor material is the patient’s own bone tissue. The material is taken from the area of the chin or wisdom tooth and used to restore the atrophied part.
The operation is carried out in two stages, since additional surgical intervention is required to extract the donor material. This increases injury and the recovery process (up to one month), but the risk of rejection of structures in this method is minimal.
Xenogeneic and allogeneic transplantation
When using this method, additional surgical intervention is not required. The donor material is bone tissue from other patients or animal bones (mainly cows).
Before transplantation, such materials are carefully sterilized and processed to improve compatibility. During the procedure, only one incision is made, due to which the healing process is significantly reduced.
Alloplastic transplantation
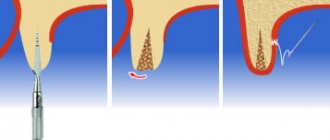
This method is also called guided tissue regeneration (GBT). This technique uses two components to build bone: bone material and a barrier membrane made of an ultra-thin elastic film.
The membrane isolates the mucous membrane and prevents it from penetrating into cavities formed due to bone tissue atrophy. The membrane also protects against the effects of bacteria and other adverse factors.
The recovery process during alloplastic transplantation proceeds quickly; membranes made from modern materials dissolve over time or become a framework on which new bone tissue is formed. Since alloplasty does not seriously injure the jaw, it has recently been used much more often.
A significant disadvantage of this method is long-term rehabilitation. It often takes 4 to 6 months for the new bone to form and for the graft to heal.
Sinus lift
Sinus lifting
In modern dentistry, the most popular technique for building bone tissue is sinus lifting. This operation is performed in the lateral parts of the upper jaw, by raising the bottom of the maxillary sinus and increasing the alveolar ridge.
Sinus lifting comes in open and closed types.
The open technique is used in cases where it is necessary to build up a large volume of bone tissue, which entails serious surgical intervention. The healing process is very long and the installation of the implant is delayed for several months.
A closed sinus lift is used when the patient's bone tissue reaches a height of at least 7-8 millimeters. This procedure is not as traumatic as an open sinus lift. The implant is installed immediately after the bone has been grown in the upper jaw.
The advantages of these bone augmentation methods:
- the use of ultra-thin blades and drills makes this method less traumatic;
- relative speed of the operation - depending on the qualifications and experience of the doctor, the duration of the procedure ranges from 30 minutes, if there are no complications, to an hour, if there are complications;
- reliability of the result - in most cases, any sinus lift method gives a high percentage of a favorable prognosis.
One of the most advanced methods of bone augmentation in the upper jaw at the moment is the balloon sinus lift.
This technique allows you to simultaneously create a base and install an implant even on the thinnest bone. All manipulations are performed through a small hole for installing an artificial root. Through this hole, a special balloon is inserted into the maxillary sinus, which is filled with liquid and, increasing in volume, carefully separates the soft tissue from the bone. Then bone material is placed into the resulting cavity and an implant is installed.
Non-carious lesion of tooth tissue
One of the reasons for the appearance of bone tissue atrophy is damage for various reasons. This disease takes second place in visits to the dentist after caries. It can affect one tooth or several and manifest with various symptoms.
Non-carious lesions of tooth tissue can be congenital or acquired. One of the phenomena of damage may be erosion. The enamel is damaged, which leads to darkening, increased sensitivity and aesthetic problems. The disease can last a long time and lead to tooth loss. Sometimes the cause of the development of pathology is a diet with a high content of acids and salts. Marinades and orange juice provoke the development of the disease. At the initial stage, the disease is not diagnosed, because the loss of enamel shine is not very noticeable. But over time, the patient begins to complain of pain. Prevention of erosion is an important component to prevent the development of damage to dental hard tissues and atrophy.
Another common cause of dental damage is increased tooth sensitivity. Under the influence of temperature, severe pain occurs, which quickly subsides. The disease can bother one tooth or affect several. If left untreated, there is a risk of surgery or removal. To replenish missing minerals in tooth tissues, vitamin and mineral complexes are taken.
Possible complications after bone grafting
Even the use of modern technologies does not provide an absolute guarantee against the possible negative consequences of bone grafting.
After the procedure, some patients may experience the following problems:
- The appearance of edema within several days is a natural protective reaction of the body to surgical intervention.
- Bleeding is normal immediately after surgery. If it does not stop within several days, the cause may be loose sutures or medical error. In this case, it is definitely recommended to consult a doctor.
- The appearance of pain in the cervical spine is the result of prolonged anesthesia. It is enough to stretch your neck and avoid heavy physical exertion.
- A feeling of numbness in the jaw area is normal in the first 2-3 days. If numbness persists for a longer period, nerve damage may have occurred. You should definitely consult a doctor.
If the discomfort does not go away for a long time (more than 72 hours), this may indicate the first sign of rejection, it is recommended to immediately go to the hospital, preferably to the doctor who performed the operation.
Protecting the jaw from atrophy
Atrophy of the dental bone tissue is treated surgically, but this can be avoided if the destruction of hard tissue is prevented.
To do this, it is necessary to restore lost teeth in a timely manner and prevent the loss of existing ones. Implants are much better than other methods, because they have a root and create a load on hard tissues. Removable dentures do not provide full load on the lower jaw, and over time, atrophy of the hard tissues of the teeth will occur. Treatment is similar for significant loss of jaw bone. If hard tissues subside gradually, then correction of the prostheses will be required without treating atrophy.
When treating atrophy, the choice of treatment method depends on the wishes of the patient. What does he want to achieve? Complete restoration of bone tissue and its function or create external beauty?
To prevent atrophy and other oral diseases, you should visit the dentist twice a year.
First letter "d"
Second letter "e"
Third letter "n"
The last letter of the letter is "n"
Answer to the question “Bone tissue of the tooth”, 6 letters: dentin
Alternative crossword questions for the word dentin
Type of bone tissue
Bone tissue of teeth
Main tooth mass
Hard tissue that makes up the bulk of the tooth
Definition of the word dentin in dictionaries
Explanatory dictionary of the Russian language. D.N. Ushakov
The meaning of the word in the dictionary Explanatory Dictionary of the Russian Language. D.N. Ushakov (de), dentin, pl. no, m. (from Lat. dentes - teeth) (med.). Bone substance of the tooth.
Great Soviet Encyclopedia
The meaning of the word in the Great Soviet Encyclopedia dictionary (from Latin dens, genitive dentis ≈ tooth), a type of bone tissue that makes up the main mass of the tooth and is also found in placoid scales. Unlike other types of bone, the ground substance of D. does not contain cavities with cells, but is penetrated by tubules, ...
New explanatory dictionary of the Russian language, T. F. Efremova.
The meaning of the word in the dictionary New explanatory dictionary of the Russian language, T. F. Efremova. m. Hard tissue that makes up the bulk of the tooth of vertebrates and humans.
Wikipedia
The meaning of the word in the Wikipedia dictionary Dentin (dentinum, LNH; - tooth) is the hard tissue of the tooth, constituting its main part. The coronal part is covered with enamel, the root part of the dentin is covered with cement. Consists of 72% inorganic substances and 28% organic substances. Consists mainly of hydroxyapatite...
Explanatory dictionary of the Russian language. S.I.Ozhegov, N.Yu.Shvedova.
The meaning of the word in the dictionary Explanatory Dictionary of the Russian Language. S.I.Ozhegov, N.Yu.Shvedova. [de], -a, m. (special). Bone tissue of the tooth.
Encyclopedic Dictionary, 1998
The meaning of the word in the dictionary Encyclopedic Dictionary, 1998 DENTIN (from Latin dens, genitive dentis - tooth) a type of bone tissue that makes up the main mass of teeth; In the crown area, dentin is covered with enamel, in the root area - with cement. Also found in the scales of cartilaginous fish.
Rehabilitation after osteoplasty
After the bone restoration operation has been performed, the patient begins a rehabilitation period, which can last from 2 to 6 months depending on the chosen method of osteoplasty, as well as on the individual characteristics of the body.
During this period, it is important to strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations:
- Chew food on the non-surgical side. If both sides were operated on, then chew alternately.
- After eating, be sure to rinse your mouth with an antiseptic. Minimum 4-5 days.
- For a week, adhere to a gentle diet - exclude the consumption of any thermal and food irritants (salty, sour, spicy and hot foods).
- Refrain from smoking and drinking alcohol - this can provoke bone rejection.
- In the first week, avoid air travel so as not to provoke surges in blood pressure, as the stitches may come apart.
- Eliminate the possibility of heavy physical activity, avoid visiting saunas and baths.