The appearance of ulcers in the mouth and inflammation of the mucous membrane are signs of stomatitis. The disease is inflammatory in nature. It occurs as a result of an immune response to external stimuli, often pathogenic microorganisms. It is important to carry out adequate treatment in a timely manner, identify and eliminate the causes. If the disease is not treated, it can become chronic and negatively affect the health of teeth and respiratory organs. A common complication after stomatitis is the addition of a secondary infection.
Reasons for development
Stomatitis often occurs in people with reduced immunity and impaired microflora. If these 2 conditions are observed simultaneously, then even opportunistic microorganisms can cause severe inflammatory processes. Many other factors also influence the development of the disease.
Inflammation of the oral mucosa can occur in the following cases:
- mechanical, chemical, thermal injuries - hot burn, injury from solid food, cheek bite, etc. leads to tissue damage, penetration and spread of infection;
- poor nutrition, lack of vitamins, especially C, group B, minerals - zinc, iron and others;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules, eating unwashed fresh berries, vegetables, fruits, dirty hands while eating;
- treatment with medications that reduce salivation, antibiotics that destroy beneficial microflora, and a number of other medications;
- Frequent brushing of teeth with a paste containing sodium lauryl sulfate leads to a decrease in saliva secretion and dry mucous membranes, which become more susceptible to aggressive substances;
- poor-quality prosthetics and dental treatment due to which the gums are constantly injured;
- smoking, drinking alcohol;
- dehydration with prolonged diarrhea, vomiting.
Stomatitis often occurs during pregnancy due to hormonal imbalance. At risk are patients with diseases of the heart, blood vessels, gastrointestinal tract, pathologies of the immune and endocrine systems, and those with helminthic infestation. In diabetes mellitus, the aphthous form is diagnosed. People who use hormone inhalers to relieve asthma attacks suffer from candidiasis.
To answer the question whether stomatitis is contagious or not, differential diagnosis is necessary. Bacteria, viruses, and Candida fungi can be transmitted from person to person. The most contagious is the viral form of the pathology. However, with good immunity, the infection will not necessarily develop. It is also important how stomatitis is transmitted. If this is direct contact, for example a kiss, then the risk of getting sick is higher.
Aphthous stomatitis in children: treatment
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis in children is no different from treatment of this disease in adults.
Since in most cases it is not possible to establish the exact cause of stomatitis, treatment will be multifocal, that is, several drugs will be used simultaneously.
The choice of treatment regimen will depend on the following factors:
- severity of symptoms;
- how often do symptoms of the disease appear;
- Are there factors predisposing to the development of the disease?
At the initial stage, treatment is always aimed at reducing the patient’s pain, at further stages - at healing the ulcers as quickly as possible and preventing their occurrence in the future.
All patients are divided into three groups:
- stomatitis occurs no more than a couple of times a year, the pain is low. As a rule, in this case, the provoking factors may be incorrectly installed fillings or the use of products with sodium lauryl sulfate. The child is advised to avoid solid and spicy foods, minimize the consumption of sour juices and chocolate. Treatment of such patients involves the use of antiseptic rinses and gels that reduce pain.
- chronic aphthous stomatitis, which occurs on a monthly basis and forces a person to change habits (for example, brushing teeth less often due to pain). Provoking factors are identified in order to eliminate them. The physician advises the patient to understand the signs of an imminent outbreak so that topical treatments can be used before ulcers occur.
- ulcers appear constantly (the previous ones do not have time to heal before the next ones appear) and are extremely painful. Local therapy in this case is practically useless - only systemic therapy helps.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms depend on the type of pathology, but there are common clinical manifestations. As a rule, the disease does not begin acutely. The mucous membranes become red, swelling, pain, and a burning sensation appear in the affected area. You can see what stomatitis looks like in the photo.
If it is a bacterial infection, then after a day an ulcer appears at the site of infection with a red halo radiating from the center. The ulcer is covered with a white coating. During this period, salivation increases and an unpleasant odor appears. Pain bothers the patient not only when eating, but also at rest.
Pimples and ulcers appear anywhere in the oral cavity; in severe cases, stomatitis develops in the throat. Stomatitis on the tongue is especially painful, since there are many nerve endings there. Some types are characterized by bleeding gums.
With further development of the pathology, the temperature may rise, the lymph nodes may enlarge, and symptoms of intoxication may appear - weakness, nausea, lack of appetite.
Forms of the disease
Candidal stomatitis is a fairly common disease that manifests itself in various forms. The symptoms can determine how much it is progressing. Treatment depends on the severity of the disease.
In the earliest stages, a mild form of the disease appears. It is characterized by the formation of single small white spots on the tongue or cheeks.
In the next middle stage, ulcers may form, and white spots themselves cover most of the tongue and mouth.
And at the most severe stages, plaque cannot be removed - it completely covers the entire oral cavity and forms a white film. Also, candidal stomatitis is classified separately depending on the location:
- Candidal stomatitis of the corners of the mouth. Very small cracks appear at the corners of the mouth, which cause pain. This is especially evident when opening the mouth.
- Yeast glossitis usually occurs on the surface of the tongue. It is characterized by a white coating and even swelling of the tongue.
- Thrush - the so-called yeast stomatitis - is a disease in which plaque forms on the cheeks and gums. The mucous membrane itself becomes reddened.
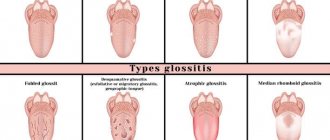
Types of stomatitis
The disease has a broad classification, which includes the nature of the course, the cause of its occurrence, and the features of the clinical picture.
Pathology can be acute or chronic. If the symptoms are pronounced, there is swelling, redness, pain, ulcers, bleeding - this is acute stomatitis. How long this phase lasts depends on the form of the disease. Usually the duration of the acute period does not exceed two weeks.
If the disease is not treated, remission occurs or the inflammatory process becomes chronic. In the chronic form, the symptoms are mild, and the disease can be detected only during periods of exacerbation.
Drug-induced stomatitis
With increased sensitivity and intolerance to drug components, characteristic symptoms of the disease appear: blisters, erosions, swelling, redness of the pharynx, tongue, palate, burning, dense white coating. The list of medications that cause inflammation of the mucous membranes often includes antibiotics, iodine, barbiturates, novocaine, and sulfonamides.
Traumatic stomatitis
Inflammatory processes develop against the background of tissue injury from objects, chemicals, hot food, etc. Stomatitis on the gums usually occurs due to injury from the uneven edge of a tooth or prosthesis. Bacteria penetrate the wound and it becomes inflamed. Symptoms of catarrhal form are characteristic.
Bacterial stomatitis
Occurs when mucous membranes are damaged by staphylococci and streptococci. It is characterized by the appearance of pustules, which, when opened, transform into erosive foci.
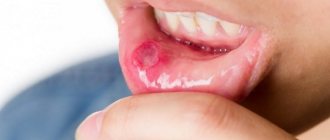
Aphthous stomatitis
It may manifest itself acutely or have mild symptoms. Small spots up to 5 mm of round shape appear - aphthae with clearly defined boundaries, covered with a grayish coating. The spots can be single or multiple. In acute cases, body temperature rises and lymph nodes enlarge. Risk factors include diabetes mellitus, reduced immunity, autoimmune pathologies, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, especially the large intestine. In the chronic form, it manifests itself asymptomatically; sluggish symptoms are observed during exacerbation.
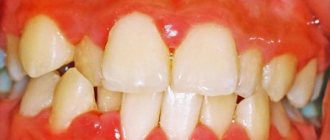
Catarrhal stomatitis
Diagnosed more often than other forms. It is characterized by mild symptoms: redness, swelling, bleeding gums. Occurs due to poor oral hygiene, decreased immunity, and injuries. It can be a complication of other diseases - influenza, pathologies of the digestive system, blood diseases, vitamin deficiency, endocrine disorders.
Radiation stomatitis
It is the first symptom of radiation sickness. It is characterized by severe dry mouth, pinpoint hemorrhages on the mucous membranes and under the tissues, expansion of periodontal pockets, swelling of the tongue, gums, and palate. Advanced stomatitis of this form is manifested by necrotic foci, strong bad breath, dirty saliva with bloody streaks. Even after treatment, relapses may occur. Scars remain in place of the injured tissue.
Ulcerative stomatitis
It is the next stage after the catarrhal type. Symptoms intensify, ulcers appear, thick plaque, severe pain. Lymph nodes enlarge, and the concentration of leukocytes in the blood increases. At risk are patients with gastrointestinal diseases.
Candidal stomatitis
Fungal infections almost always have a long course. With thrush, a white dense coating appears on the cheeks, tongue, and lips, accompanied by hyperemia and cyanosis of the mucous membranes. In the fugonous form, severe swelling, erosion, and foamy plaque are observed. There is also angular stomatitis, in which fungi affect the corners of the lips (jams). Stomatitis on the lip can be fungal or viral.
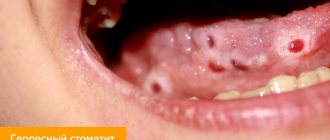
Herpetic stomatitis
Develops due to the activity of the herpes virus. Blistering rashes with clear liquid can be seen in the mouth and lips. After the bubbles burst, erosions appear in their place.
Why treatment is necessary
If a person ignores the presence of stomatitis for a long time, the disease develops into a form that is difficult to treat, for example, gangrenous or ulcerative. Then not only soft tissues, but also jaw bones are included in the destructive process, and this is very dangerous.
Also, if you refuse treatment, complications such as:
- severe bleeding gums;
- formation of scars on the mucous membranes;
- destruction of periodontal joints;
- addition of secondary infections.
Canker sores should not be underestimated. They pose a threat to the entire body. In rare cases, they lead to disruption of the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory organs.
How to treat the disease
Therapy involves the use of local and sometimes systemic drugs. The treatment regimen for the disease depends on what type of stomatitis is diagnosed. For this reason, you should not self-medicate, as it may turn out to be useless and the pathology will continue to develop into dangerous conditions.
The exception is mild catarrhal inflammation associated with poor hygiene. It is enough to exclude the cause and rinse your mouth with antiseptics for several days.
Treatment at home for other types should be discussed with your doctor. The use of folk remedies is not contraindicated, but they can only be used as a supplement to the main therapy. Only a dentist can evaluate the appropriateness and harmlessness of a particular prescription.
Effective drugs for adults
To relieve inflammatory processes, combat pathogenic microflora, and relieve pain, rinses, gels, sprays, lozenges, and ointments are prescribed. For severe pain, pain medications can be taken orally. Since treatment must be carried out regularly, it is important to choose a medicine for stomatitis that will be convenient to carry in your purse and use at work.
Popular medicines:
- Chlorophyllipt, Inhalipt, which have an antiseptic effect. Available in the form of sprays. Apply up to 5 times a day for one week. Sprays are convenient to use if there is stomatitis in the palate or throat.
- Solcoseryl accelerates tissue regeneration, restores mucous membranes, and protects against the development of ulcers. The gel is applied several times a day. The course is from 7 to 14 days.
- Cholisal has a detrimental effect on bacteria, relieves inflammation, and improves tissue healing. The gel is used three times a day for at least a week. An analogue of the drug is Kamistad. Excellent help with aphthous, bacterial form of the disease.
- Viferon, Acyclovir are prescribed to patients with a viral infection. Ointment for stomatitis in the mouth is applied to areas of inflammation several times a day. The course of therapy is up to 2 weeks.
- Lidocaine Asept, Lidochlor are used for any form of pathology, since the main purpose is to relieve acute pain. Available in spray form. Can be used up to four times a day, no more than 1 week.
- Lugol kills bacteria, treats ulcers, and relieves inflammatory processes. The oral cavity is treated with a spray 2 - 3 times a day.
- Miconazole and Nystatin are prescribed for fungal infections. In severe cases of the disease, the ointment is used in combination with systemic medications. Apply to affected areas 2 to 4 times a day.
Any medication for stomatitis must be prescribed by a doctor. The symptoms of the varieties of the disease are similar and it is impossible to independently understand the cause of the inflammatory reactions.
What can you rinse your mouth with?
To treat pathology, you can use pharmaceutical drugs aimed at destroying bacteria, reducing inflammation and healing tissue.
Medicinal solutions that can be bought at the pharmacy:
- Aqualor with sea salt;
- Stomatofit, Dr. Theiss Sage based on sage;
- Romazulan with chamomile extract;
- Chlorhexidine (pre-diluted with water).
Decoctions and infusions for rinsing are easy to prepare at home from chamomile, calendula, aloe juice, sea buckthorn, linden flowers and other medicinal plants. A solution of salt and soda helps a lot.
How to get rid of stomatitis?
Stomatitis is perhaps the most common and unpleasant disease of the oral cavity. When an infection enters the body, ulcers form in the mouth. They cause discomfort and can subsequently lead to serious complications. How to treat stomatitis ?
Treatment of any infectious diseases first of all involves going to the doctor. Antibacterial therapy should be carried out under medical supervision. Bacterial disease most often goes away in 1-2 weeks. If the stage is not advanced, it can be treated independently. How to treat stomatitis at home :
- Rinse your mouth with soda solution. Add 1 spoon of soda to a glass of warm water. You can also use boric acid (1 teaspoon per 150 ml of water) or hydrogen peroxide (1 teaspoon per half a glass of water).
- Chamomile decoction. Heals wounds quickly.
- Sea buckthorn oil has an antibacterial effect. You can use antiseptics: chlorhexidine or miramistin.
- Anesthetic dental gels will help relieve severe pain. They should contain lidocaine.
Soda solution can also be used to treat stomatitis in infants .
Wipe the mouth and tongue with moistened gauze. If signs of stomatitis (bacterial) do not disappear, you should consult a doctor.
In case of aphthous form of the disease, you should urgently go to the clinic. How to determine:
- multiple large and deep ulcers;
- grayish coating in the center;
- red rim around the wound.
This type of stomatitis should not be treated at home. It is forbidden to cauterize ulcers with alcohol, iodine, or brilliant green. An advanced disease can lead to suppuration and tissue death.
How to get rid of stomatitis in children?
Basic methods of local therapy:
- Treating the oral cavity with baking soda. For preparation you will need 1 tablespoon per glass of boiled water. Apply 3-6 times a day.
- Rinse with Blue solution. Or 2% boric acid.
- Use of antifungal agents. This includes medicated creams and ointments. For example, Clotrimazole, Pimafucin, Nystatin, Candide.
Symptoms of stomatitis in children and treatment can be determined by a doctor. Treatment is carried out in accordance with the doctor's prescriptions. If the dosage is not followed correctly or the course is interrupted, side effects may occur.
You should not self-medicate, as this can harm the baby.
Only a pediatric dentist will prescribe the correct therapy. He can also advise treating stomatitis in children at home .
Types of stomatitis
Depending on the depth of tissue damage and the cause of inflammation, experts distinguish the following types of stomatitis:
- catarrhal;
- aphthous;
- candida;
- ulcerative;
- herpetic;
- traumatic;
- allergic.
The catarrhal form of stomatitis is the mildest and rarely causes complications. But treatment is still required, mainly local. The most severe course is ulcerative necrotizing stomatitis, which often causes bacterial complications.
The candida type occurs more often in young children.
Each type of disease has its own characteristics, causes of development and symptoms. It is difficult to determine the shape yourself.
Sometimes even specialists do not have enough clinical picture to make an accurate diagnosis. Additional laboratory tests are often required to determine why stomatitis occurs in the mouth and whether it is associated with other diseases.
Prevention
In the oral cavity of any person there is a conditionally pathogenic microflora, which can be activated when immunity decreases. For this reason, it is important to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat well, and treat illnesses.
Hygiene rules must be observed. Do not eat dirty vegetables, wash your hands before eating, and replace your toothbrushes regularly.
For persons predisposed to the disease, any trauma to the oral mucosa should be excluded. Do not eat scalding, hard foods or spicy seasonings. If a wound appears, you should immediately treat it with an antiseptic.
It is imperative to carry out timely treatment of dental and ENT diseases. Chronic diseases and advanced caries are sources of infection.
Forms of aphthous stomatitis in adults
There are two forms of the disease:
- chronic;
- spicy.
In acute aphthous stomatitis, round whitish ulcers appear. The mucous membrane swells and turns red.
This form of the disease has the following symptoms:
- pain when eating;
- body temperature rises;
- weakness and a feeling of fatigue occurs, regardless of the work performed;
- lymph nodes become inflamed.
The stage lasts a maximum of ten days, provided that the treatment prescribed by the doctor is followed. The ulcers heal completely without leaving any marks behind. If no action is taken, the disease can progress to a chronic stage, which is much more difficult to get rid of.
Chronic stomatitis is associated with an immune system that is unable to overcome the acute stage. In most cases, a decrease in the protective properties of the immune system is caused by some disease (for example, inflammation of the nasopharynx, gastrointestinal diseases, etc.). Treatment takes longer because after the ulcers disappear, they appear again after some time.
Symptoms
The development of the disease occurs in several stages.
At the initial stage, the symptoms are very similar to the manifestations of acute respiratory infections: there is an increase in body temperature to 40 degrees, enlarged lymph nodes, the person experiences general malaise, weakness and loss of appetite. Already at this stage, the patient begins to experience unpleasant painful sensations in the mouth, which intensify while eating or talking. When examining the oral cavity, you may notice redness.
The appearance of ulcers (ulcers) with clearly defined boundaries, up to 5 mm in size, marks the beginning of the second stage of the disease. Aphthae can form on the tongue (on its lateral surfaces), on the inner surface of the lips and cheeks. The ulcer is bright red in color, covered with a fibrous coating, and severe pain occurs when touched. As a rule, the inflammatory process at this stage is accompanied by enlargement of the lymph nodes, and it becomes problematic for the patient to eat solid food. Within two weeks, the mucous membrane is restored to its previous state.
However, a chronic form of the disease, characterized by swelling of the mucous membrane, acquiring a pale tint, cannot be excluded. On average, the chronic stage lasts 2 weeks: if treatment is not resorted to, the ulcers can begin to increase in size and bleed, causing a lot of inconvenience.
Aphthous stomatitis: drugs
The main task of the doctor is to achieve the disappearance of the disease or its remission. In this matter, competent selection of medications and an integrated approach to treatment are important.
Local treatment consists of using healing and antiseptic drugs and rinsing.
Modern medicine offers a wide range of drugs that help fight stomatitis: the choice is so wide that it can be difficult for a person far from medicine to make a choice.
The following drugs have proven themselves to be the best:
- Miramistin - it is used to treat the oral cavity;
- Diphenhydramine is a cheap remedy that helps with allergic reactions;
- Cholisal is an effective drug at the initial stage of the disease, helping to stop its further development;
- Stomatofit-A – helps fight canker sores;
- Hexoral is a remedy that is effective in secondary manifestations of the disease.