Head on one side
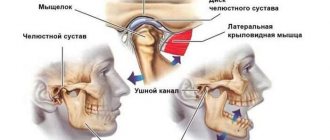
Discomfort in the jaw is most often associated with problems in the temporomandibular joint, formed by the head of the lower jaw and the tubercle of the temporal bone, which, together with the articular disc, are enclosed in the articular capsule.
The movements in this joint are very complex: they are carried out not only by the masticatory muscle, but also by six other adjacent muscles. The movements of the lower jaw help us not only when eating, but also during conversation, laughter, and coughing. Related article Most patients with jaw dislocation are women
It is not surprising that the temporomandibular joint, according to medical observations, serves as the center of balance for the entire human body. With a symmetrical position of the lower jaw, the head muscles do not experience tension, and displacement of the lower jaw in any direction leads to an imbalance of the head. Problems in this area affect the muscles of the head, neck, temporomandibular joints, and cranial nerves and cause chronic pain on one side or, less commonly, on both sides of the face and head. Usually this condition has a very depressing effect on the patient; he completely “loses himself” and is unable to think about anything other than eliminating the pain.
Pain may appear in the morning, during the day or in the evening, this depends on the different types of joint damage and is important for the doctor to make a diagnosis.
Mouth shut. What to do if you have problems with your jaw joints
Read more
How does the disease manifest itself?
Painful sensations in the jaw area are usually associated with dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint. It, like all other joints, has a capsule where quite complex muscle movements occur. And this is not surprising, because with its help many life processes occur, such as biting, chewing, yawning, communicating, coughing, laughing, etc.
According to many scientists, this joint is also responsible for balance in the body. So, if the jaw is in the correct position, then the remaining muscles of the face and head, in general, are not subject to heavy loads and do not experience discomfort. When the joint is shifted to one side, the center of gravity of the head changes, as a result of which not only the head, but also the neck begins to suffer. In addition, the cranial nerves may be pinched, causing the person to experience constant spasms.
Unpleasant sensations, such as cramping and pain in the jaw, can be present both day and night. Moreover, at night the pain can become even stronger. Much here depends on the psychological state of a person. Any stressful situation or lack of sleep can cause increased pain.
To the dentist!
The cause of discomfort may also be due to incorrect position of the teeth. In this case, you will need the help of a maxillofacial dentist who will supply temporary or permanent splints and dentures that correct the incorrect position of the jaw.
Article on the topic
A tooth for a tooth: what happens if the jaws don’t close?
A rehabilitation doctor can help if the pain is caused by increased tone or tension of the masticatory muscles, limited mobility of the lower jaw, incoordination of contractions of the masticatory muscles, excessive mobility of the head of the lower jaw (sometimes this causes “clicking” in the temporomandibular joint).
Pain and clicking disappear after normalization of the function of the masticatory muscles and joint, except in cases where arthrosis deformans and inflammation in the joint are diagnosed. Then treatment should begin with following the recommendations of a rheumatologist and orthopedist.
Pain due to injury
Everyone knows that surgical interventions in the jaw area, various injuries and damage to the face and neck do not pass without leaving a trace. A severe blow to the face can result in a jaw fracture. In addition, the jaw joint may be damaged, causing the jaws to be in an incorrect position and lose mobility, and an attempt to close them will be accompanied by acute pain in the joint area. If pain is associated with injury, swelling often appears at the site of injury.
Attention - facial expressions!
After complex treatment, patients are recommended to use medicated mouth guards at night. They are made individually by the orthodontist. The pads reduce pain in the joint, an unpleasant feeling of heaviness, fatigue in the masticatory muscles, neck muscles, and normalize mouth opening.
In order to prevent this very annoying nuisance from happening again, you need to avoid active conversations while eating, an excited manner of speaking when a person does not notice what is happening with his facial expressions, as well as hypothermia, which can provoke inflammation in the joint, which makes him more prone to to incorrect movements, more vulnerable.
Why does jaw pain occur?
Read more
Bruxism
A disease such as bruxism is manifested by strong clenching of the jaws during sleep and grinding of teeth. As a result of the disease, teeth become less stable and begin to loosen. Plus, the crowns wear out. Often this pathology leads to disruption of the functioning of the maxillotemporal joint.
Bruxism is characterized by spasmodic pain that appears after waking up. The pain can radiate not only to the jaw, but also spread throughout the head. People with this disease often complain that their teeth and jaw are cramping, which indicates overstrain of the joint.
Many “owners” of bruxism may not even know about the existence of the disease until someone tells them that they grind their teeth a lot in their sleep, or until they visit a dentist who sees that there is a problem.
Causes of trismus
The causes of trismus are diseases that affect the TMNS:
- inflammatory processes in the oral cavity of an infectious nature;
- mechanical damage;
- incorrectly performed anesthesia of the teeth of the lower jaw;
- arthrosis of the temporal and mandibular joint - a disorder in the movement of the jaw caused by injuries, inflammation, and improper metabolism;
- diseases of the ENT organs: throat, nose and ears;
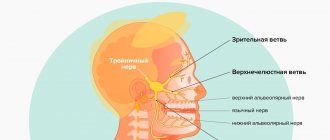
- trigeminal neuralgia in the form of an attack of short-term, sharp, intense pain;
- abscesses and other purulent diseases of the oral cavity;
Also, spasm of the masticatory muscles can occur against the background of neurological diseases, such as pseudobulbar palsy, epilepsy, inflammation of the spinal cord or brain, cerebrospinal meningitis, rabies, muscle cramps, tetanus, as a result of the presence of malignant and benign tumors, exhaustion of the body and deficiency of important microelements.
Symptoms of neuralgia of the submandibular and sublingual nodes
The first manifestations of the disease will be paroxysmal pain (paroxysms) on the side of the inflamed ganglia. The duration of a painful attack varies from several minutes to an hour. The pain syndrome is characterized by intensity and pulsation in the area of localization of the affected ganglia. A distinctive feature of most vegetative ganglionitis of the face and head is a tendency to expand pain. The stronger and more advanced the inflammatory process, the more extensive areas are affected by pain during paroxysm.
Attacks begin from the inflamed node in the area of the root of the tongue and tonsils, then the pain spreads and occupies increasingly larger areas - over the entire half of the head, neck, collarbone, shoulder and arm. The occurrence of pain can be triggered by tension in the facial muscles and thermal effects, that is, during a conversation or eating hot, spicy food.
Neuralgia of the submandibular and sublingual nodes is divided into two stages:
- The initial ganglioneuralgic phase of neuralgia of the sublingual and submandibular ganglia: characterized by the paroxysmal pain described above, may be accompanied by swelling, increased sensitivity of the tongue and mucous membranes of the oral cavity. The pain may migrate to various areas of the head and upper torso.
- The ganglioneuritic phase of ganglion neuralgia is already a transition to a chronic form. At this stage of the development of the disease, dull pain in the affected side is constantly present, disturbances in salivation, trophic ulcers appear, possible decrease in sensitivity and signs of autonomic neurological Bernard-Horner syndrome.
In some cases, during a severe painful attack, patients experience such manifestations of the disease as chills, increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, gastrointestinal spasms, nausea, vomiting, feelings of anxiety and fear. The chronic form of the disease is the most dangerous, fraught with peripheral circulatory disorders, spasms and autonomic changes in nerve endings in the submandibular and sublingual area, as well as in nearby areas.
Treatment
If the jaw is cramped on one side and at the same time there is elevated temperature and swelling, the first thing to do is contact a surgeon. It is possible that this condition arose as a result of purulent inflammation in this place. Similar symptoms may indicate the development of a paratonsillar abscess associated with tonsillitis.
When the lower part of the face is brought together on one side with irradiation into the orbit, inflammation of the facial artery can be suspected. In this case, you should visit a surgeon.
Severe and boring pain radiating to the jaw may indicate inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, and here you cannot do without a visit to a neurologist.
If the jaw is cramped due to improper placement of the dentition, you will need the help of a dentist who will install splints and dentures to avoid problems in the future.
Constant pain in the jaw may indicate the appearance of a tumor in the facial area. As the disease progresses, the pain will become more severe and aching. Therefore, if jaw contraction and pain persist for a long time and the pain is pulsating in nature, you should urgently consult a doctor in order to begin treatment on time and stop the growth of the tumor.
Jaw spasms when yawning
No less common are complaints that the jaw tightens when yawning. Their frequency is due to the fact that people yawn frequently, and during this process the tone of the jaw muscles is lost for a certain time. If there was residual tension before yawning, then at the end of the process the muscles become hypertonic, the jaw joint undergoes increased stress, as a result of which the jaw cramps.
If consolidation occurs with every small yawn, especially when the process is accompanied by pain and slight swelling, you should go to a neurologist, traumatologist or dentist. There is a possibility that in this way an old injury makes itself felt or an orthodontic defect develops in the oral cavity. Also, a tumor in this area can interfere with a full yawn.
One way or another, if there is discomfort when yawning, it is recommended to apply a cooling compress. On this day, you should consume ground food so as not to strain the jaw muscles when chewing and give the joint a chance to rest.
Why does my jaw cramp?
Women may experience single or multiple symptoms of jaw spasms during pregnancy; they can be short-term or long-lasting. They occur in the following cases:
- when yawning;
- if you suffer from bruxism (grinding your teeth in your sleep);
- for nervous tension;
- for osteochondrosis and other lesions of the cervical spine;
- with muscle strain;
- for some dental problems.
The reasons for the appearance of unpleasant sensations on the right or left side of the jaw in a child or an adult may be associated with injury. What causes jaw cramps and how to cope with this condition – a specialist will tell you.
Lower jaw only
If you have cramping in your lower jaw, this may indicate damage to the trigeminal nerve, which is responsible for innervation of the face. Therefore, such pains radiate to the teeth and one half of the face; they differ in average duration from 10 to 20 minutes.