| Congenital pit under the lip | |
| Speciality | Maxillofacial Surgery |
| Normal start | At birth |
| Care | Fistulectomy |
| Forecast | Great |
Congenital lip pit
or
labial sinus
is a congenital disorder characterized by the presence of indentations and possibly associated fistulas in the lips. They are often hereditary and can occur alone or in combination with cleft lip and palate, called van der Woude syndrome. [1]
Types of acquired red moles on the body
- Simple (capillary). Proliferation of newly formed capillaries, small venous and arterial vessels. Looks like a red spot.
- Cavernous. A spongy cavity with blood - a red or bluish nodule. Often forms under the skin.
- Branched (racellose). A plexus of tortuous dilated capillary trunks. They pulsate, noise and trembling are detected. It is rare and occurs on the extremities or face. If injured, life-threatening bleeding may occur.
How to identify hemangioma? Press on top of it and it should fade or disappear.
What to do if a hemangioma hurts
Typically, the formation of such a formation does not cause physical discomfort. It appears when its surface begins to ooze. This phenomenon poses a threat to human life: any ulcer on the mucous membrane or skin is an open gate for infection. It can cause blood poisoning and death. Therefore, if any pain occurs, you should immediately consult a dermatologist.
- Some aspects of the diagnosis of renal cell and transitional cell carcinoma of the kidney
A hemangioma growing on the lower lip may be accompanied by swelling. It causes nagging pain. Discomfort also occurs when the formation grows deep and begins to compress the nerve endings. It intensifies during physical activity, under the influence of high and low temperatures, often becomes unbearable and forces a person to take drastic measures.
Are red moles dangerous?
In themselves, these formations are harmless and are not precancers.
If you have a lot of red moles on your body, the cause may be a serious liver or pancreas disease. Pay attention to this - this is a reason for examination.
Problems may arise in case of traumatization of hemangiomas. Even fairly small formations threaten heavy bleeding, which is not easy to stop.
Clinical case
Patient L, 26 years old, presented with a traumatized mass in the axillary region. According to her, she tore off a convex hemnagioma with the edge of a rigid corset of a wedding dress almost a few minutes before the start of the wedding ceremony. The hemangioma bled very heavily and a large blood stain appeared on her white dress. She had to wear the witness's jacket over her wedding dress. It was in such a strange outfit that the wedding took place.
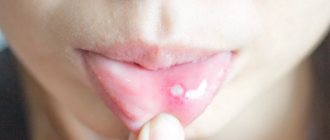
Why can a lump appear on the lip?
Lumps on the lips indicate pathological conditions in the body. They appear in diseases and injuries of various origins.
If a lump appears on your lip, the reason may be as follows:
- injury to the lip and oral cavity;
- dental infections;
- viral diseases of various body systems;
- bacterial and fungal inflammatory diseases;
- tumor and cystic neoplasms.
These causes can be divided into pathological, caused by diseases, and normal, caused by other factors.
An example of the appearance of a labial growth in the photo.
Possible diseases
If a seal appears on the lip, it may be caused by the following diseases:
| Disease | Symptoms |
| Respiratory tract infections | With viral and bacterial diseases of the respiratory tract, small red and flesh-colored balls may appear on the outer surface of the mouth. They appear due to decreased immunity, and after recovery they disappear on their own. |
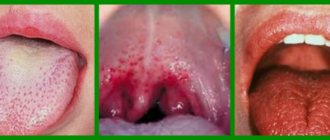
| Stomatitis | Stomatitis is an inflammatory disease of the mucous membranes of the mouth, most often found in children. Depending on the cause of the inflammation, the bump on the inside of the lip may be clear, red, white, blue or dark brown. |
| Candidiasis | With candidiasis, small white bumps form in the oral cavity, painless on palpation. They can be localized on the inside of the lips, gums or tongue. |
| Herpes | When infected with the herpes virus, a round, painful lump forms on the inside of a person’s lips, which is a blister with clear liquid inside. The inflamed area is itchy and may become covered with a purulent crust. |
| Human papillomavirus | A warty, white or flesh-colored growth occurs when infected with HPV. In the early stages of the disease, the tubercle appears in a single copy, after which their number increases, and the edges of the growths merge with each other. |
| Syphilis | A person infected with syphilis develops a chancre near the lip: a small hard ball resembling a subcutaneous pimple. Chancre signals the onset of the disease and disappears when syphilis enters stage 2. |
| Leukoplakia | With leukoplakia, keratinization and thickening of the epithelium on the oral mucosa occurs. Small white growths form inside the lip, on the tongue and gums. If left untreated, they develop into cancer. |
| Lip cancer | When a malignant tumor occurs, a large red or black lump appears on the oral mucosa. It can be localized on the lip, gums or throat. The lump hurts when touched and may bleed. |
Other factors
Other factors that can cause a lump on the lip include:
- Lip injuries
. A retention blood cyst occurs in wounds: when biting, after a cut or after a blow, when wounded by dental instruments during examination and treatment by a doctor. - Burn when eating hot food
. Hot food or drinks cause thermal damage to the lip tissue. Like mechanical injuries, it causes lumps to appear. - Insect bites
. Blisters caused by an insect bite in the mouth area can take a hard form and turn into a lump. - Malocclusion.
The abnormal position of the teeth causes permanent injury to the lips on the inside, leading to the formation of a pineal growth. - Orthodontic problems
. Incorrect installation of braces or dentures, as well as the retention period of orthodontic treatment, can cause mechanical injury to the lip. - Chemical burn.
When taking certain medications and consuming alkali, a burn may occur in the mouth, leading to the appearance of a lump. - Allergic reactions.
Upon contact with an allergen, the patient may experience small white growths in the oral cavity, including on the lips. - Punctures, wearing piercings.
Trauma and constant friction against the lip tissue causes cystic neoplasms with blood located next to the irritant. - Bad habits.
Smoking and drinking alcohol can cause chronic burns. Like a simple thermal burn, it provokes the appearance of neoplasms.
In case of bite pathologies, incorrect installation of braces and dentures, you should consult a specialist: a dentist or orthodontist.
The remaining reasons listed in the list do not require medical intervention.
Diagnostic procedures
When the first signs of lip cancer are detected, the patient should contact an oncologist. The doctor will examine the affected area and palpate the lips, gums, cheeks, and regional lymph nodes. The condition of the outer covers of the red border of the lips will allow the oncologist to make a preliminary diagnosis. If signs of a malignant process are detected in the neoplasm, the patient receives a referral for an ultrasound examination of the lips, radiography of the lower jaw, and panoramic tomography. The oncologist will collect biomaterials (smear-imprint) from the tumor for laboratory tests. Histological analysis is performed after a biopsy of the primary cancer site.
If the patient has symptoms of lymphatic metastasis, the doctor takes a biopsy sample from the lymph nodes. The search for hematogenous metastases is performed using chest x-ray or ultrasound.
Causes
There are a number of factors that increase the likelihood of developing this disease:
- Mechanical – constant injury from the edges of teeth or poor-quality dentures.
- Temperature - addiction to too hot drinks and food, smoking.
- Chemical - smoking, contact with certain carcinogens, chewing certain mixtures.
- Meteorological - the influence of wind, frost, humidity, excessive ultraviolet radiation.
In addition, some viruses can be provoking factors, in particular the herpes . Among these factors are also called malocclusions.
A malignant tumor of the lip always develops as a consequence of the transformation of other pathologies. Precancerous conditions are:
- limited precancerous hyperkeratosis ;
- warty precancer;
- cheilitis Manganotti.
In addition, the following diseases can develop into a malignant tumor:
- keratoacanthoma;
- leukoplakia;
- chronic cheilitis ;
- post-radiation stomatitis ;
- ulcerative and hyperkeratotic forms of lichen planus ;
- papilloma.
According to observations, this disease often develops in rural residents of the southern regions. The risk of its development is increased by poor oral hygiene, deficiency of vitamins A, E, C and beta-carotene, and gastrointestinal diseases.