We are used to the fact that we need to go to the dentist if we have problems with our teeth or gums. What to do if you have inflammation of the tongue or glossitis? Dentists identify more than 10 types and subtypes of infection. The infection can be caused by both fungus and bacteria. Viral infection is less common. Inflammation can be caused by a lack of certain vitamins and minerals, or hormonal changes. There are many reasons for the disease, so it is important to identify what exactly caused the inflammatory process.
Causes of glossitis
- improper oral hygiene;
- bacterial infection;
- fungal infection;
- heavy metal poisoning;
- bad habits (smoking, alcoholism);
- congenital pathologies of the tongue (folded tongue);
- allergic reaction;
- tongue injury (often caused by malocclusion);
- oral infections;
- lack of iron in the body;
- burn of the mucous membrane (hot food or drinks);
- infectious diseases (AIDS, tuberculosis, scarlet fever, measles).
Biting your tongue - everyone knows this
Biting the tongue, cheek or lip is accompanied by painful sensations, as damage to the mucous membrane occurs.
Obviously, the initial goal after a bite is to reduce pain. So, what should you do if you bite your tongue, what and how to relieve pain and inflammation?
The main rule is to remain calm. Calm down and try to come to terms with the pain, because tantrums and tears will not help heal the damage.
And then you should do the following:
- Be sure to stop bleeding , if any. An elementary solution would be to repeatedly rinse with cold water: it will help narrow the blood vessels and reduce bleeding activity. A worthy alternative would be a piece of ice.
- Cotton swabs soaked in 2% Lidocaine help in the fight against painful sensations . Another variation to reduce pain is eye drops with an anesthetic - Tetracaine, Alcaine.
- It is important to disinfect the entire oral cavity : brush your teeth thoroughly and rinse your mouth.
- Maintain regular rinsing : it is advisable to wash away the remains of eaten food after each meal.
- Use antiseptics such as Antiangin, Trachisan, Furacilin in the form that is optimal for you: spray, lozenge or solution.
- Avoid eating rough, cold or hot foods . During the restoration of the oral mucosa, it is advisable to create a daily menu of liquid soft foods at medium temperature: purees, soups.
- Avoid cold foods - ice cream, frozen juice and other foods with temperatures below zero - they slow down the healing process.
- Take a course of vitamins to help restore damaged areas. The optimal solution would be to include vitamin C and group B in the diet.
Do not forget to adhere to sanitary and hygienic measures: do not reach into the oral cavity with dirty hands, do not put pressure on the resulting injury.
Never pour iodine or brilliant green or peroxide into a wound: give preference to treating the environment around the injury. Antibiotics can only be used as prescribed by a doctor.
In practice, there are cases of tongue biting. In such a situation, it is important to remain cool, act quickly and in an organized manner: place the “particle” in a bag filled with ice and go to the hospital. To relieve painful sensations, it is permissible to ingest cold food: suck ice cream, frozen juice, ice, drink water.
The most common types of glossitis
The most common occurrences in dental practice are:
- acute catarrhal glossitis;
- tongue abscess;
- desquamative glossitis.
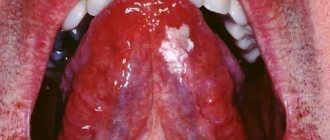
Acute catarrhal glossitis is the most common type of inflammation. Inflammation can be caused by microbes or mechanical damage to the tongue. The predominant symptoms are pain, redness and swelling.
A tongue abscess is the appearance of an abscess in the tongue. The abscess can be superficial, under the mucous membrane, or maybe in the thickness of the tongue. Abscesses in the thickness of the tongue, in addition to pain in the tongue, can cause a disturbance in the general condition. A person develops a fever, a headache, and weakness. Most often occurs due to injury to the tongue.
Desquamative glossitis, also known as “geographic tongue,” most often appears in children. It appears in the form of various spots on the tongue, which look like a white coating, alternating with areas of pink mucous membrane. There are no changes other than appearance. Scientists have identified a clear reason for it. The main factors are believed to be bacteria, allergic reactions and hormonal imbalances.
Diagnostic signs
If vital processes are balanced, the body functions without failures, the human tongue has a healthy appearance. This is manifested in its smooth, velvety surface, uniform pink color and transparent coating of saliva. There should be no discomfort, burning, tingling or lack of sensitivity in any areas.
Photo: tongue of a healthy person
In the human body, pathologies are determined by the following characteristics:
- Color and its uniformity on the surface of the tongue.
- Smell, color and consistency of plaque.
- Relief.
- The shape of the organ and the lines in the middle.
- Movements.
- Sensation of taste.
Diagnosis of health using the tongue should be carried out as follows: stick it out as much as possible, look in the mirror and analyze all the indicated characteristics. The sensations of taste and touch, as well as the accumulation of plaque, should be monitored throughout the day. All features that were identified should be compared with text descriptions.
If the patient tells the doctor about changes in health status and language diagnostic results, he is prescribed an examination to clarify the diagnosis.
Correspondence of tongue zones to internal organs
Ancient Chinese doctors determined that each section of this muscular organ is associated with a specific element. Modern medicine has established how the areas of the human tongue are associated with diseases of the internal organs. The correspondence is shown in the table:
| Zone | Element | Organs |
| Tip of the tongue | Fire | Small intestine, heart muscle |
| Transverse stripe between tip and central area | Metal | Colon, immunity, respiratory system |
| Middle | Earth | Stomach, spleen, pancreas |
| Sides | Tree | Gallbladder, liver |
| Rear end | Water | Organs in the lower abdomen, reproductive and urinary systems |
| Fold dividing the tongue into left and right parts | — | Spine |
For a more informative diagnosis, it is necessary to take into account both the general condition of the tongue and the condition of its individual sections. It is important to understand that the doctor draws conclusions not only from indirect external changes, but also from the results of laboratory and instrumental studies, and when making a diagnosis, one should rely more on conclusions confirmed by analyzes.
Diagnosis by color: what does the color of the tongue mean?
The color of this organ partly depends on the shade of its own tissues, and partly on the plaque accumulated on it. By studying the color of the tongue, you can determine what this sign indicates and go to a therapist to check your assumptions. Below is a comparison of the color of tongue coating and diseases that may be associated with it:
- A coated yellowish tongue is a symptom of improper functioning of the liver, gastrointestinal tract and a sign of people who smoke.
- Bright red plaque indicates the presence of hematological and cardiovascular pathologies.
- A reddish coating is a sign of inflammation of infectious or non-infectious origin.
- A dark red coating is a manifestation of intoxication.
- A red tip of the tongue is a symptom of pelvic organ diseases.
- Burgundy plaque – the presence of acute infections.
- Crimson – a manifestation of a severe infection with severe fever.
- A blue or purple tongue is a symptom of lung or heart disease.
- Blue plaque is a sign of kidney disease.
- Gray – the presence of chronic gastrointestinal diseases.
- Black plaque is a sign of infection with a chromogenic fungus or a state of acidosis.
- Pallor is a symptom of fungal infection, acute respiratory viral infection, anemia, tissue dehydration, and exhaustion of the body.
- A pale underside of a person’s tongue is a sign of liver disease and the associated gallbladder.
- A dirty gray coating is a consequence of the vital activity of parasites.
Presence of stains
In some diseases, the color of the tongue is uneven; distinct or unclear spots and stripes may be observed:
- The presence of red and white spots indicates the presence of scarlet fever.
- White spots on the edges or over the entire surface indicate the development of thrush.
Thrush on the tongueWhite scaly spots on the tongue indicate the presence of lichen planus.
- White spots on the lower part of the tongue are observed with vascular diseases of the brain or with oxygen starvation.
- The presence of one round white spot indicates a shift in the acid-base balance of gastric juice.
- A red spot on the tip of the tongue or along the edges is an injury caused by rough food or biting with teeth.
- Red dots on the top indicate mononucleosis or problems with hematopoiesis.
- Reddened areas with horny scales are a likely sign of a tumor.
- A red spot surrounded by yellowish blisters is a symptom of erythema.
- Reddened areas on a dry tongue are a sign of brain disease.
- Red blisters around the edges are a symptom of herpes.
- Yellow spots are a sign of inflammatory processes, diseases of the hematopoietic organs, oncology, necrosis, and a consequence of smoking.
- Purple areas indicate blood stagnation.
- Brown spots are a sign of a circulatory system disease or bleeding in the mouth.
- Blue spots are a sign of hemangioma, intoxication or blood diseases.
- Blackening of individual areas is a sign of chemical burns, a consequence of smoking, long-term use of antibiotics, stomatitis or gastrointestinal disorders.
Diagnostics by form
The definition of a human disease by language is also based on an analysis of its outline and shape of the midline:
| Tongue shape | Definition of disease by language |
| Thin | Metabolic failures |
| Thick | Dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract and liver |
| Long | Heart problems |
| Convex | Pulmonary pathologies |
| Hydropic | Disturbed digestive processes |
| Midline curvature | Spine pathologies |
| One side of the tongue is adjacent to the cheek | Pathologies of cerebral circulation, strokes |
| The tongue has changed shape and relief | Hypo- or vitamin deficiency |
It is difficult for a person without medical education to determine from photographs or descriptions which organ shape is normal for him. Thus, a thick tongue can be mistaken for swelling. Therefore, you should not draw conclusions about your health status and treatment on your own ; it is better to consult a doctor and tell him about your assumptions.
Nature of the relief
Normal taste buds form a smooth, velvety surface. By the relief of the tongue you can determine the disease in an adult or child, how to do this:
Photo: symptom of “varnished tongue”Excessive roughness indicates dehydration, problems with the salivary glands, overdose of antibiotics, atropine drugs or fat-soluble vitamins.
- Increased roughness on a person’s dry tongue, sometimes with tooth marks, can indicate a gastrointestinal disease, such as appendicitis, intestinal infections, and ulcerative pathologies. If cracks and uneven edges are added to the dryness, this is a possible sign of diabetes.
"Cardinal's language"The “varnished tongue” symptom, in which the surface becomes excessively smooth due to atrophy of the taste buds, is observed with colitis, stomach cancer or problems with the absorption of vitamin B
- Diagnosis by the color of the tongue and its relief is clear in case of pellagra - hypovitaminosis of nicotinic acid and vitamin B. The tongue looks ribbed due to cracks and is covered with a brown coating that is difficult to remove. The scarlet "cardinal tongue" shown in the image to the right then forms. At a later stage, a “varnished tongue” appears.
Photo: “geographical language”Alternating normal and inflamed papillae form a “geographic tongue” - a peculiar pattern with grooves that is more common in children with allergies or mental disorders. The projection of spots onto internal organs will help diagnose which organ suffers from food allergies, vitamin deficiency, and atopic dermatitis.
Movement and sensitivity
Normally, a person moves his tongue without difficulty, without trembling or muscle pain . If there are diseases of the nervous system and neurasthenic syndromes, characteristic trembling appears, and with strokes, patients find it difficult to chew and talk. With hemorrhages in the brain, both the sensitivity of taste buds and the sense of touch on surfaces are partially or completely absent.
The causes of trembling can be not only neurological, but also endocrine. The progression of brain diseases in later stages leads to a decrease in muscle size.
If uncharacteristic sensations or burning occur, you should contact a neurologist. If only the surface of the organ hurts, it is covered with plaque, turns pale, you need to show it to the dentist, this may be a sign of inflammation of the mucous membrane - stomatitis.
The function of taste buds is also used in diagnosing diseases by the tongue; it can change with burns, smoking or hormonal imbalances and is often accompanied by the accumulation of plaque.
In pregnant women, a change in taste preferences and aversion to normal food may appear in the first trimester or persist for the entire 9 months. For some women, this feature is the first sign of successful conception.
Symptoms of glossitis
- increased salivation;
- swelling and redness;
- pain and burning when eating;
- plaque on the tongue in the form of spots;
- bad breath;
- papillomas or warts on the tongue;
- speech disorder;
- foreign body sensation.
Prevention of glossitis - high-quality oral hygiene and no bad habits. It is important to undergo timely preventive examinations and also eat well. All these factors actively contribute to the development of the disease and bring a number of problems.
History of the name of the disease
If the smallest filiform papillae on the tongue gradually atrophy and smooth out, due to which the surface of the muscular organ becomes as if polished, then glossitis can be suspected from this symptom. In general, the pathology is an inflammatory disease of the tongue. However, depending on the reasons for its appearance and the main symptoms, glossitis varies. For example, desquamative, rhomboid, folded. You will find what its most common varieties look like in the feature article on the website.
With non-infectious Gunther-Miller glossitis, the tongue becomes smooth
If the tongue becomes smooth, then, as a rule, we are talking about non-infectious glossitis Gunter-Miller or Gunter-Möller (in some descriptions of the scientific literature1). The pathology received its name in honor of the British physician William Hunter (in outdated pronunciation - Gunther) and the German surgeon Julius Otto Ludwig Möller, who were the first to describe the characteristic symptoms of the disease in their works. The first mentions of the syndrome are found in the literature of the distant 1851 and 1909.
In various sources you can find the following names and definitions of Gunter-Miller syndrome: Gunter's, Hunter's, hot, atrophic glossitis, crimson, smooth, polished or glossy tongue.
Treatment of glossitis
A specialist must make an accurate diagnosis and identify the cause of the disease. If you suspect that you have glossitis , and all symptoms indicate this, contact your dental clinic. This is the only way to create the right treatment plan and provide timely assistance. Quite often in such cases, doctors prescribe antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and rinsing the mouth with special antiseptic solutions. In advanced stages, glossitis is treated surgically. Deep abscesses must be opened in the maxillofacial department. Under no circumstances should you take medications without a doctor’s recommendation.
You can cure glossitis, caries or any other diseases of the oral cavity right in your sleep. Family Dentistry Center "Medexpert" provides dental treatment under medicinal sedation. Thanks to this approach, the patient falls into a healthy sleep, ceases to feel pain and discomfort, while the vital functions of the body remain unchanged. Sedation is widely used in pediatric dentistry and even helps fight dental phobia. Dental treatment can be comfortable and painless - tested for yourself.
Treatment of the disease: what doctors usually prescribe
For Gunther-Miller glossitis, doctors prescribe complex treatment.
If Gunter's glossitis is not treated, in advanced cases this can lead to the disappearance of the papillae on the tongue and a reduction in the muscle organ itself, speech impairment, problems with breathing and adequate food intake. All this will significantly worsen the quality of life. In addition, advanced disease is fraught with phlegmon of the tongue and purulent melting of tissue, which does not exclude sepsis and even death.
Drugs that help eliminate symptoms of pathology
Local antiseptics “Furacilin”, “Chlorhexidine”, “Miramistin”, and chamomile decoction help to reduce swelling of the tongue and signs of inflammation, remove ulcers and prevent the appearance of new ones. To eliminate pain, it is usually recommended to use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, for example, Nurofen.
"Chlorophyllipt" can also be used for rinsing
In order for wounds on the tongue to heal faster and delicate tissues to regenerate successfully, doctors prescribe retinol solution, vinylin, Solcoseryl, and rosehip oil to patients for local treatment of the affected areas.
During illness, you must follow a special diet. You should avoid spicy, hot and smoked foods. There is no need to season food with spices. It is better to give preference to boiled and stewed dishes with a soft or liquid consistency. Doctors also advise drinking more fluid in the form of plain water, herbal teas, berry infusions and fermented milk drinks.
Medicines to replenish vitamin deficiencies
Here we are not talking about classic vitamin and mineral complexes, which are presented in a wide range in pharmacies and are available to any person. If you suspect you have anemia or pellagra and simply buy such a drug, you will do little to improve the situation.
What is usually prescribed? For anemia, as a rule, injections with vitamin B12. Each age has its own dosage. They must be placed within 4 weeks, after which maintenance therapy is recommended every 6 months and follow-up for 2 years. Doctors note that some patients develop iron deficiency anemia during treatment with vitamin B12, which is subsequently eliminated with iron supplements2.
For anemia, vitamin B12 injections are prescribed
Sprue may require taking tetracycline drugs, as well as injections of vitamin B12 and folic acid. For pellagra, niacin or nicotinamide is prescribed in combination with B vitamins (thiamine, riboflavin) and vitamin C.
During treatment, as well as after it, the patient is not recommended to take actions that lead to increased consumption of B vitamins: physical and emotional overload, smoking, drinking alcohol.
Drug therapy
In order for a smooth tongue to regain its healthy appearance, doctors may prescribe, in addition to the measures listed above, the use of antibiotics, antidepressants, immunostimulants, sedatives and hormonal drugs. The liver of medications and further actions will be determined by what causes the pathology.
Notice
: Undefined variable: post_id in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content/themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
45 Notice
: Undefined variable: full in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content /themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
46
Rate this article:
( 3 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
language
- Lyulakina E.G., Chizhov Yu.V. Oral diseases in elderly and senile people // Clinical gerontology, – 2011.
- Rumyantsev A.G., Maschan A.A. Federal and clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of anemia caused by B12 deficiency, 2014.
Expert “Smooth Gunter's tongue can be a symptom of deficiency conditions that often occur against the background of bacterial and fungal lesions of the oral cavity, helminthiasis, unbalanced nutrition, HIV and syphilis, gastritis, cirrhosis of the liver, cardiovascular pathologies, systemic and genetic abnormalities (for example, syndrome Down, Sjögren's syndrome), blood diseases." Dentist-therapist Elena Vladimirovna Orlova
Consulting specialist
Varlamova Tatyana Vitalievna
Specialization: Dentist-therapist Experience: 6 years
The best way out is to avoid injury
Statistics show that most tongue injuries are mechanical in nature, which, in turn, is evidence of negligence. To avoid damage to the oral cavity, follow these simple rules:
- do not get lost in thoughts while eating;
- When eating, do not be distracted;
- do not talk with your mouth full of food;
- Chew your food thoroughly and slowly.
Often the cause of wounds is a malocclusion or unsuitable dentures. An improperly growing or filed tooth also poses a risk to the integrity of the oral cavity.
Be extremely careful and remember that it is better to prevent a traumatic situation from occurring than to suffer trying to cope with its consequences. If you observe suspicious symptoms, be sure to seek help from a dentist or ENT doctor.
Malocclusion
Incorrect bite formation leads to permanent injury to the mucous membranes of the mouth and tongue. As a result, the muscle organ swells and increases in size. Due to constant biting, teeth marks are left on the sides of the tongue.
The disease can be cured only after correcting the malocclusion. To do this, the doctor selects a design to straighten the dentition. For minor violations, patients are prescribed to wear orthodontic plates, trainers, and silicone trays. In case of more serious pathology, the defect is corrected using braces. The course of treatment can take from 3 months to 2 years.
Nervous system diseases
With disorders of the nervous system, unpleasant painful sensations occur, tingling in the tongue, a disturbing feeling of dry mucous membranes, hyperesthesia, burning, disturbances of taste, diction, swelling and the appearance of bacterial plaque. This disease is called stomalgia, most often it affects women during menopause or after suffering shocks. Symptoms of the disease decrease with eating, especially when eating spicy foods. Unpleasant sensations are localized on the tip and sides of the swollen tongue, its edges are wavy, and dents from the teeth are visible.
The main causes of pathology are recently experienced tragic events in life: the death of relatives, cancer of loved ones, personal problems. Patients are easily excitable, constantly look at their tongue in the mirror, and are pathologically afraid of developing cancer.
Treatment of stomalgia is carried out comprehensively. It includes medication, psychotherapy, physiotherapy, acupuncture, and oral sanitation.
Uneven, wavy edges of the tongue may indicate the development of a serious illness. Therefore, if such a symptom appears, you should consult a dentist and therapist. Timely treatment will help avoid the development of severe complications.
Traditional medicine at the service of the people
Here is a selection of recipes for solutions, the use of which will help disinfect, heal wounds and reduce pain:
- A decoction of bedstraw helps to cope with tongue pain . Brew 1 tablespoon of dried herb with boiling water, leave for half an hour, strain the resulting mixture. The decoction is suitable for both rinsing and internal use.
- Sage tincture is an assistant in the fight against pain during the treatment of oral injuries. By brewing 2 tablespoons of the substance with half a liter of boiling water and letting the infusion “rest” for 30 minutes, you will get an excellent antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory medicinal drug. Rinse frequency: 5-11 times a day.
- Pour 1 tablespoon of chamomile 250 ml of boiling water and let it brew. Use the strained solution after meals and before bed to heal wounds and relieve inflammation.
- St. John's wort tincture is a panacea for pain caused by a tongue injury. Use 40% alcohol and dried herb in a ratio of 5 to 1, respectively. Add 30-40 drops to 250 ml of water and rinse your mouth.
- Finding potatoes in a cellar or drawer is not difficult, but peeling them is a matter of two minutes. Feel free to use sliced raw vegetables to relieve pain from burns.