Oral anatomy
The oral cavity is the beginning of the digestive apparatus. The oral cavity is divided into two sections by the alveolar processes of the jaws and teeth: the vestibule of the mouth and the oral cavity itself.
The vestibule of the mouth is the space located between the lips and cheeks on the outside and the teeth and gums on the inside. The vestibule of the mouth opens outward through the oral opening. The transverse oral fissure is limited by the lips, which are muscle folds, the outer surface of which is covered with skin, and the inner surface is lined with mucous membrane.
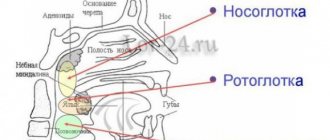
The oral cavity is located on the inner side of the alveolar processes, limited above by the hard palate and the anterior portion of the soft palate; the bottom is formed by the diaphragm of the mouth and is occupied by the tongue.
The oral cavity is lined by the oral mucosa, covered with stratified squamous non-keratinizing epithelium. It contains a large number of glands. The area of the mucous membrane attached around the neck of the teeth on the periosteum of the alveolar processes of the jaws is called the gum. The oral cavity communicates with the pharynx through the isthmus of the pharynx.
The cheeks are covered on the outside with skin, and on the inside with the oral mucosa, which contains the ducts of the buccal glands and is formed by the buccal muscle. Subcutaneous tissue is especially developed in the central part of the cheek. Between the masseter and buccal muscles is the fatty body of the cheek.
The upper wall of the mouth (palate) is divided into two parts. The hard palate is located in the anterior part of the oral cavity, formed by the palatine processes of the maxillary bones and the horizontal plates of the palatine bones. The palatine bones are covered with a mucous membrane, along the midline of which there is a suture of the palate, and on the sides there are several transverse palatine folds.
The hard palate passes into the soft palate, formed mainly by muscles and aponeurosis of tendon bundles. In the posterior part of the soft palate there is a small conical protrusion, called the uvula, which is part of the so-called velum palatine. Along the edges, the soft palate passes into the anterior palatoglossal arch and the posterior palatopharyngeal arch. Between the arches on each side, in the recesses lie the palatine tonsils. The lower palate and arches are formed mainly by muscles that help swallowing.
The muscle that lifts the velum palatine of the soft palate and narrows the pharyngeal opening of the auditory tube begins on the lower surface of the petrous part of the temporal bone and attaches to the middle section of the aponeurosis of the palate, intertwining with bundles of the muscle of the same name on the other side.
The palatoglossus muscle narrows the pharynx, bringing the anterior arches closer to the root of the tongue. Its beginning is located on the lateral edge of the tongue root, and its attachment point is on the aponeurosis of the soft palate.
The triangle of the velopharyngeal muscle brings the velopharyngeal arches closer together, pulling the lower part of the pharynx and larynx upward. The muscle begins on the back wall of the lower part of the pharynx and attaches to the aponeurosis of the soft palate.
The tongue is a mobile muscular organ located in the oral cavity and facilitates the processes of chewing food, swallowing, sucking and speech production. The tongue is divided into the body of the tongue, the apex of the tongue, the root of the tongue and the dorsum of the tongue.
From above, from the sides and partially from below, the tongue is covered with a mucous membrane, which fuses with its muscle fibers, contains glands, lymphoid formations and nerve endings - receptors. On the back and body of the tongue, the mucous membrane is rough due to the large number of papillae of the tongue, which are divided into four groups:
- Filiform papillae are located throughout the body of the tongue and represent a conical body with racemose appendages at the apexes.
- Fungiform papillae are located on the back of the tongue closer to its edges and have the shape of pineal growths.
- Leaf-shaped papillae are concentrated in the lateral sections of the tongue and represent 5-8 folds separated by grooves. They are unequal in size and are most pronounced in the posterior parts of the tongue.
- Cylindrical papillae, surrounded by a ridge of mucous membrane, the largest, but weakly protruding above the surface, are located on the border between the root and body of the tongue.
The muscles of the tongue are represented by skeletal muscles and the actual muscles of the tongue. Skeletal muscles connect the root of the tongue to the bones of the skull. The actual muscles of the tongue have points of origin and attachment points in the thickness of the tongue, located in three mutually perpendicular directions: the lower longitudinal muscle shortens the tongue; the superior longitudinal muscle flexes the tongue, shortening it, and raises the tip of the tongue; the vertical muscle of the tongue makes it flat; The transverse muscle of the tongue reduces its diameter and makes it transversely convex upward.
When the mouth is closed, the tongue with its upper surface comes into contact with the palate. The mucous membrane, passing to the lower surface of the tip of the tongue, forms the so-called frenulum along the midline. On either side of it, at the bottom of the mouth, on the sublingual fold, the ducts of the submandibular gland and sublingual gland open, which secrete saliva and are therefore called salivary glands.
The submandibular gland is an alveolar-tubular protein-mucosal gland located in the lower part of the neck in the submandibular fossa, below the mylohyoid muscle.
The sublingual gland is an alveolar-tubular protein-mucosal gland located under the mucous membrane of the mouth on the mylohyoid muscle under the tongue.
The excretory duct of the third, the parotid salivary gland, opens in the vestibule of the mouth on the mucous membrane of the cheek, at the level of the upper second molar.
Teeth, depending on their structure and functions, are divided into large molars, small molars, canines and incisors. All of them are strengthened in the sockets of the alveolar processes of the lower and upper jaws.
Each tooth consists of a part that protrudes above the gum - the crown of the tooth, a part covered by the gum - the neck of the tooth and an internal part - the root of the tooth. Moreover, some teeth have two or more roots.
The bulk of the tooth is dentin, which is covered with enamel in the crown area, and with cement in the neck and root area.
The root of the tooth is surrounded by a root membrane - the periodontium, which, with the help of tooth ligaments, attaches it to the dental alveolus. Inside the crown of the tooth there is a tooth cavity, which continues into a narrow canal of the tooth root. Vessels and nerves pass through a small hole in the apex of the tooth root into the tooth cavity containing the pulp, or pulp.
According to data from dental reference books
A full range of dental services in Istra for adults and children: from consultation to complex operations within one clinic “Doctor Nebolit”
Consultation and appointments daily from 9:00 to 19:00
- +7 (49831) 4-42-12
- Contacts
How to strengthen oral immunity?
As already mentioned, the most vulnerable protective barrier of the human body is the local immunity of the mouth
, which performs a number of important functions: prevents the penetration and weakens the activity of pathogenic microorganisms, forms an immune response and immune memory to already known bacteria and viruses. It is very important to maintain the structural integrity of this barrier, otherwise the oral immunity will not cope with its protective function.
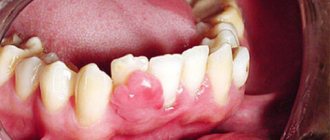
Local immunity of the oral cavity weakens for a number of reasons. One of the main ones is various diseases of the teeth and gums. That is why it is very important to pay special attention to the health of the oral cavity and carry out timely treatment of any dental diseases, such as stomatitis, gingivitis, caries, periodontal disease, periodontitis, etc.
How to increase local immunity
oral cavity:
- If any diseases of the teeth and gums are detected, consult a doctor promptly and undergo the necessary treatment.
- For effective cleaning of tooth enamel, where pathogenic microorganisms regularly accumulate, professional hygienic cleaning or ultrasonic teeth cleaning is recommended.
- Observe all preventive measures and hygienic oral care.
- Have regular preventative dental checkups.
Oral Care Tips
We have collected the top 5 tips from dentists that must be followed to keep your teeth beautiful and healthy.
- Don't go to bed with unclean teeth. Otherwise, the microbes will secrete lactic acid, which causes caries.
- Learn proper teeth brushing techniques. For example, clean them with smooth circular movements without strong pressure, hold the brush at an angle of 45 degrees, treat not only the outer, but also the inner and chewing surfaces of the teeth.
- Clean your tongue at the end of each brushing of your teeth, as plaque, consisting of dead mucous cells, food particles and microorganisms, is regularly deposited on it.
- Eat more fruits and vegetables. Plant foods contain dietary fiber that helps remove plaque from your teeth and tongue. In addition, fruits are excellent sources of vitamins to maintain oral health.
- Limit your consumption of starchy and sweet foods. The fast carbohydrates they contain stimulate the growth of cariogenic bacteria.
Possible complications of dysbiosis
It is important for each patient to closely monitor the state of the oral microflora. Lack of treatment for dysbiosis can lead to such unpleasant diseases as:
- pathological halitosis – bad breath caused by an imbalance of the oral microflora;
- caries – destruction of hard tooth tissues;
- pulpitis - inflammation of the pulp - the internal tissues of the tooth;
- periodontitis – inflammation of the tooth root membrane and adjacent tissues;
- gingivitis – inflammation of the oral mucosa;
- stomatitis – damage to the oral mucosa;
- periodontitis is a deep lesion of the periodontal tissue.
In addition, the close relationship between the state of the oral microflora and the state of the cardiovascular system has been scientifically proven. In 2008, it was proven in the USA that periodontal disease, as a source of chronic inflammation, is an independent risk factor for coronary heart disease (CHD).
So, now you know the role of normal oral microflora in the human body. Treat yourself carefully, and your healthy body will delight you every day.
We need hygiene, hygiene is important to us
Let's now talk about how a patient can take care of himself and his teeth at home
How to carry out proper dental hygiene at home.
Let's start with the fact that no one has canceled mechanical teeth cleaning with a toothbrush. The toothbrush must be selected according to the condition of the oral cavity, based on the current conditions in the oral cavity. After all, it happens that a patient is prescribed, due to a number of factors, a soft brush, a medium-hard brush, or a hard one. It's not just how it's done.
In a good way, the selection of household hygiene products in the dental line should be done by a hygienist, at a minimum. But here, it turns out, everyone prescribes their own brush and toothpaste and uses whatever they want.
So, the personal hygiene item that Vasily should have is a toothbrush - this is the first
. And, by the way, the toothbrush also needs its own hygiene. But few people remember this.
Selection of oral hygiene products in the form of toothpastes and powders
now more than diverse. But it is impossible to recommend anything effective for patients; this is a known fact. Moreover, in the household line of toothpastes, their composition is approximately the same, and the use of medicinal toothpastes as a means of treatment is best discussed with the dentist at a clinic appointment.
Second
— Vasily’s mandatory use of floss. Floss is a dental floss that can be used to clean areas where brushing is not possible. Also, be sure to use floss after meals - this is very good.
How to improve gum microcirculation
In addition to threads, there are devices such as irrigators.
There are a large variety of them, ranging from portable ones to stationary irrigators that need to be installed at home.
This is a separate topic, and I think it’s a very good tool in a comprehensive approach to hygiene.
The irrigator helps clean out food debris (and not only food debris), helps clean the oral cavity and also massages the gums. Under the influence of an irritating massage, when streams of water hit the gums, the bed of blood vessels expands. Due to this, blood flow to this particular place increases, that is, through this massage we improve trophism - that is, nutrition, blood circulation. The greater the blood circulation, the more nutrients and microelements there are in the tooth tissue, because they are also nourished.
As a matter of fact, if you take Vasily through all the above mentioned on oral hygiene as a whole, then it will be simply great to be healthy. Your teeth will be perfect!
But remember that professional teeth cleaning has never been canceled.