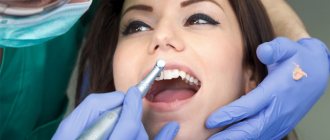
A salivary gland ranula (sublingual ranula) is an oral cyst located at the exit site of the salivary gland ducts, although it can occur anywhere in the sublingual region. According to the classification, it belongs to retention cysts; its formation is caused by blockage of the sublingual or submental salivary gland. There is no consensus on the nature of this pathology; many doctors associate the appearance of ranulas with the influence of some pathogenic factor on the gland ducts: mechanical damage or inflammation with subsequent blockage.
Causes
The mucous membrane of the mouth is a fairly resistant surface to various influences. But when it is injured, or an imbalance occurs in the body due to diseases, an inflammatory process can occur, which leads to the formation of a bubble under the tongue. Other problems can also be the main causes of pathology.
Injury
Mechanical disruption of the salivary duct of the gland leads to the thickening of the connective tissue and this causes the appearance of a ball under the tongue. A toothbrush with rough bristles, fish bones, a chipped tooth, a toothpick, breaking the cover, activates inflammation.
Antihygiene
In this case, a blister under the tongue appears due to failure to observe basic oral hygiene. This could be someone else's toothbrush, spoons, forks, or rare care.
Syphilis
This disease tends to negatively affect the condition of the mucous membranes, causing tumors.
Complications after illness
The bubble occurs after suffering from mumps, sore throat, or influenza. The salivary gland swells, and against the background of this, stagnation of secretion occurs.
Infection
Microtraumas that occur on the mucous membrane can be infected with bacteria and microbes, fungus, which leads to the formation of an inflamed blister.
Oncology
The disease provokes the formation of a tumor that puts pressure on the area under the tongue. In the early stages, the disease goes unnoticed, but over time, saliva production decreases and a transparent cyst appears, which eventually grows to 3 centimeters.
Food and medicine
A blood ball under the tongue appears for the following reasons:
- Injury that occurs from biting the mucous membrane while eating.
- Chemical burn.
- Hot food or drink.
- Medicines.
- Spicy and salty foods.
- Blocking the duct with a stone.
Ranula
A ball under the tongue can cause ranula. It appears against the background of an inflammatory process in the sublingual area or when the normal functioning of the salivary gland is disrupted. Initially, the disease manifests itself as a bluish discoloration in the oral cavity. After which a bubble appears, which after some time bursts and is observed again in the same place.
On this topic
Find out what to do if a pimple on your tongue hurts
- Olga Alexandrovna Novikova
- August 30, 2022
Experts still cannot establish the causes of this disease. Some believe that the pathology arose against the background of an inflammatory process, while others suggest that these are epithelial inclusions of germinal origin. That is, the tumor is a cystic epithelial neoplasm.
The pathology develops against the background of blockage of the salivary gland duct and does not allow saliva to be released into the oral area. This leads to the fact that it accumulates in the gland, which increases to 5 cm in diameter. After which the formation is ruptured on its own or opened by a surgeon using a scalpel.
The ranula looks like a bubble with a clear liquid, which does not cause pain, but brings discomfort to the patient in the oral mucosa.
Aphthous stomatitis
Aphthous stomatitis is also one of the causes of a bubble under the tongue. This is an inflammatory process that occurs in the area of the oral mucosa, which is manifested by the appearance of aphthae. Aphthous stomatitis is a common disease and can be treated by a dentist. The main factors in the occurrence of pathology are:
- disruptions in the functioning of the immune system;
- viruses;
- hormonal fluctuations;
- heredity;
- allergic reactions;
- diseases of the digestive tract;
- diseases of the gums and teeth;
- injuries;
- lack of nutrition;
- hypovitaminosis;
- stress, depression, nervous tension;
- accompanying illnesses;
- violation of personal hygiene rules.
Aphthous stomatitis is very common in young children, especially during teething. At this point, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Malignant sublingual tumor
Rapid and uncontrolled cell division in the sublingual area are the main signs of a cancerous tumor. In this case, the lump can reach enormous sizes and proceed in three directions:
- infiltrative - with expansion of the tumor inside the tissues under the tongue;
- papillary - along the surface of the oral mucosa;
- ulcerative - with the formation of a crate-shaped ulcerative defect on the surface of the cone.
At the initial stage of the appearance of a lump under the tongue, the tumor may not have any pronounced symptoms. The person continues to live in his usual way. However, as the size of the tumor increases and cancerous changes in the tissues intensify, the lump causes more and more discomfort to the patient.
Gradually, the tumor covers more and more areas of tissue under the tongue, spreading in thickness and depth. Then it spreads beyond one area and metastasizes - cancer cells move to the nearest lymph nodes and neighboring organs.
The treatment strategy for a malignant tumor under the tongue consists of surgical excision of the primary focus - the lump, followed by radiation and chemotherapy.
The prognosis is favorable only at the initial stage of a malignant tumor - if it is small in size, there are no metastases, and timely and comprehensive treatment is performed. Otherwise, due to late treatment, poor-quality treatment, or the patient’s failure to comply with the doctor’s recommendations, the lump comes out from under the tongue and occupies the entire oral cavity. A person dies from cancer intoxication.
Symptoms
Symptoms of the pathology depend on the reason for which it arose.
With injuries in the tongue area, blisters may appear not only under the tongue, but also on the side. It is mainly pink in color or engorged with blood, which is visible to the naked eye.
If any blood manifestations are absent, then this indicates the superficial nature of the pathology; most often, such a bubble goes away on its own and does not cause noticeable harm to health. When a blood clot appears, the hematoma is very deep and can become a breeding ground for pathogenic bacteria, most often this leads to an inflammatory process.
On this topic
How to quickly get rid of a pimple on the gum
- Maria Konstantinovna Tevs
- July 29, 2022
A small bubble that has popped up may be the cause of vitamin deficiency. In this case, the patient feels almost no discomfort. Such manifestations disappear within a few days. To prevent the bubble from appearing again, you need to reconsider your diet and enrich your diet with vegetables, fruits, meat and dairy products. It is also recommended to undergo a course of treatment with vitamins.
Diagnostics
If a bubble appears in the sublingual area, you should definitely consult a doctor, as this may signal disturbances in the functioning of the body and dangerous diseases. The specialist is obliged to carry out diagnostic measures that will help find the causes of the pathology:
- Study of all symptoms and complaints.
- Determining the presence of chronic diseases and injuries in the oral cavity.
- External examination of the tongue.
- Laboratory tests of blood and saliva.
- Puncture of the contents of the bladder under the tongue.
- Examination by a dentist.
The specialist analyzes the results and prescribes the correct treatment, in some cases surgery.
Other signs
The most common reasons for the appearance of a lump on the surface of the tongue are the above diseases: hematoma, stomatitis and ranula, but in addition to these diseases there are a number of others.
Below we list the main reasons:
- Lipoma. A rounded flat shape appears on the tongue. Often located slightly further than the middle of the tongue. Quite a rare disease. At the beginning there are no painful effects, but over time the lump can grow several times larger and discomfort in the oral cavity will be felt. You won't be able to remove a lipoma on your own. This will require the help of a specialist.
- Papilloma. A lump that appears on absolutely any part of the tongue and has a grayish light gray tint. This disease is transmitted through sexual intercourse, excessive consumption of alcohol, tobacco products, and also due to stress.
- True pemphigus. Not uncommon in infants. The main symptom of this serious disease is many small blisters on the surface of the mucous membrane of the tongue. This disease can be transmitted from mother to child, as well as due to disorders of the autoimmune system.
Drug treatment
Therapy for a bubble under the tongue is prescribed depending on the causes of its occurrence:
- For aphthous stomatitis, a number of antiseptic drugs are used; physiotherapy and mouth rinsing using decoctions of medicinal herbs such as calendula and chamomile are also recommended. The affected area is periodically treated with sea buckthorn oil.
- In case of infectious diseases, the cause of the disease is initially eliminated: herpes - Acyclovir; candidiasis - antifungal medications Clotrimazole, Fluconazole, Flucostat; glossitis - anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics; syphilis - antibacterial therapy: Tetracycline, Macrolide, Penicillin.
- In case of vitamin deficiency , the diet changes and a number of vitamin complexes are prescribed.
- For endocrine diseases and disorders, hormones are prescribed, after special tests have been carried out.
- Neoplasms and cysts are removed surgically. After removing the blisters, a course of treatment with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory medications is carried out.
The following medications are also used:
- Lorgexidine is an antimicrobial agent used to irrigate the oral cavity.
- Miramistin has an antiseptic effect.
- Stomatophyte is an anti-inflammatory agent.
- Proposol relieves pain.
- Cholisal-gel – reduces pain, fights inflammation.
- Metrogyl denta is an antimicrobial and antiseptic agent.
- Actovegin-gel – accelerates the healing process.
Frog bladder - ranula under the tongue: what is it and how to treat it?
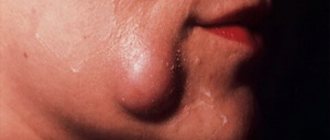
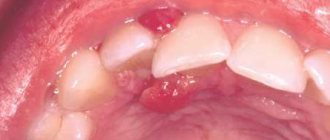
Ranula (lat. ranula; from rana - frog) under the tongue, sublingual retention cyst - a tumor-like formation of the anterior floor of the mouth.
The name has been preserved since ancient times due to its similarity in appearance to the pharyngeal bladder of a frog.
A salivary gland ranula (sublingual ranula) is a cyst in the oral cavity, located at the exit of the salivary gland ducts, although it can occur in any part of the sublingual region.
According to the classification, it belongs to retention cysts; its formation is caused by blockage of the sublingual or submental salivary gland.
There is no consensus on the nature of this pathology; many doctors associate the appearance of ranulas with the influence of some pathogenic factor on the gland ducts: mechanical damage or inflammation with subsequent blockage. When it reaches a large size, it interferes with eating (especially in children).
HOW TO SCAN (PROTOCOLS)
Parotid gland
The parotid gland can be easily examined with the patient's head turned to the side and in a hyperextension position. A summary of the scanning procedure is provided in Box 3.
| Box 3 Parotid gland scanning procedure
|
First, the gland is scanned in cross section, starting from the angle of the jaw to a point slightly above the tragus. Then the longitudinal projection is scanned. The ultrasound probe must be adequately applied to the surface of the skin, using a sufficient amount of gel, especially in the area of the angle of the jaw.
Submandibular gland
If the patient's head is moderately extended, the submandibular gland can be examined ultrasonographically without any problems. First of all, along the midline of the neck, the ultrasound sensor moves in the transverse direction from the hyoid bone to the horizontal branch of the mandible. Sometimes both submandibular glands may be visible at the same time. Then, by moving the transducer sideways, parallel to the horizontal ramus of the mandible, a clear image of the corresponding submandibular gland can be obtained. Here it is necessary to ensure good contact of the gel with the sensor on the skin.
Sublingual gland
The sublingual gland examination does not have significant differences in procedure compared to the submandibular gland examination. The transducer is placed on the skin in a transverse plane in the midline just below the mandible, allowing visualization of both sublingual glands. It is important to note that all averaged structures must be within 0.2 mm of each other, and any outliers are carefully assessed and discarded and, if necessary, reanalyzed.
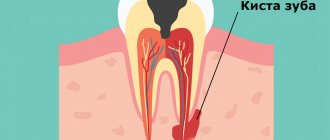
Causes of ranula formation
Among all diseases of the oral cavity, a cyst under the tongue is considered one of the most problematic and common, as it progresses quite quickly and causes severe discomfort. It is not advisable to ignore this problem, because the larger the cyst, the higher the risk of its spontaneous rupture with subsequent relapse of the disease.
The mechanism by which ranula occurs is that a blockage of the salivary gland duct (usually Bartholin's or Wharton's duct) prevents the resulting saliva from entering the oral cavity. It begins to accumulate in the gland, which gradually increases in size, at times reaching five centimeters in diameter.
Summary
Ultrasonography has established itself as the primary imaging technique in the diagnosis of salivary gland diseases. Sonographic examination is usually sufficient to diagnose sialolithiasis. If chronic sialoadenitis or sialoadenosis is suspected, and sonographic data are insufficient, standard sialography may be required in some cases. A histological examination is necessary as soon as the diagnosis of a neoplasm is established. If the tumor's enlargement and connection with surrounding tissues cannot be determined sonographically, subsequent computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging should be performed. To conduct research, we recommend using a device from GE Voluson E8 .
Classification
Based on their location, ranulas are divided into superficial and diving.
- Superficial ranulae form directly on the oral mucosa, forming characteristic bulges (bubbles) under the tongue.
- Diving ranulas are called that way because they are located a little deeper, hiding behind the mylohyoid muscle. This type of ranula cannot be detected by visual examination of the oral cavity; patients with this pathology experience a swelling or lump under the chin, which is sometimes confused with an enlarged lymph node.
Ranulas are also divided according to their structure: true (retention) cyst, false (post-traumatic) and mucocele.
- A true, or retention cyst, occurs due to a violation of the outflow of secretions and various pathologies of the glands.
- False (post-traumatic) most often forms after soft tissue injury.
- A mucocele is a cavity-like cyst-like formation containing mucus.
Few people think about the fact that the salivary glands are extremely susceptible to various inflammatory and other pathologies.
Salivary gland cyst - a detailed analysis of the disease. You can read about the reasons for the formation of stones in the salivary glands here.
Do you know what sialolithiasis is? If interested, read the information at the link.
Conditionally benign tumors
The formation of a growth under the tongue from tissues other than mucous can also be called a lump. Dentists distinguish the following types of conditionally benign tumors.
Lipoma - formed from adipose tissue cells located under the tongue. Education is benign. The cone has a dense capsule, inside of which there is soft tissue separated by bridges.
Papilloma is formed from epithelial cells. Visually it resembles an oval or round bump of a pale pink hue. Sometimes not one, but several similar formations form under the tongue. If injured, it can transform into a cancerous tumor.
Hemangioma - grows from blood vessels under the tongue. The lump appears to be a cavernous type of formation - convex in shape and size. However, it does not rise above the surrounding tissues under the tongue.
Lyphangioma is the formation of a warty structure with vesicles. Often inflamed when injured by pieces of food.
The fight against benign formations consists of their timely identification and surgical excision. The optimal methods of surgical intervention are determined by the doctor after analyzing all the information obtained on the basis of diagnostic procedures.
Treatment of ranula with folk remedies
The traditional treatment method is surgical removal of the ranula.
A dentist or maxillofacial surgeon, using a scalpel under local anesthesia, first drains the ranula (releases fluid) and then removes it from the bed.
This is necessary to prevent recurrence of the cyst.
Sutures are placed on the edges of the wound, which dissolve after a few days. The whole procedure takes a little more than half an hour. The question of whether the ranula needs to be removed is decided individually together with the attending physician.
Ranula can only be eliminated surgically. It is preferable to remove the cyst after making an incision in the oral mucosa. In cases where it is impossible to completely remove the cyst, only its anterior wall is excised, the cyst cavity is lubricated with tincture of iodine and tamponed for 5-7 days.
The timing of the operation depends on the size of the cyst. If there is difficulty swallowing or breathing, surgical intervention is carried out immediately upon diagnosis, including in infants. In the postoperative period, oral toilet is prescribed.
Like any cyst, a ranula can be removed surgically.
But this is not always necessary. To get started, you can try a few folk remedies.
Mix two tablespoons of eucalyptus essential oil and 200 ml of boiled water. Rinse your mouth with the resulting solution 3-4 times a day.
Also, eryngium herb is often used to rinse the mouth. Pour 200 ml of boiling water over a tablespoon of the mixture and leave for about 2 hours. Afterwards, the broth needs to be cooled and strained.
Baking soda solution
Mix ½ teaspoon of soda and 200 ml of warm boiled water, add the same amount of iodized salt. You can also use a weak solution of potassium permanganate or furatsilin for rinsing.
Healing decoction of pine needles
Boil a liter of water, add 5 tablespoons of young pine needles to it and boil for about 30 minutes. Then cool, strain and take orally 2 times a day.
The main feature of salivary gland cysts is that they can be asymptomatic for a very long time. Parotid salivary gland cyst - the clinical picture of the pathology is described in the article.
The anatomy of the salivary gland is described in detail in this material.
Oak bark decoction
Pour 300 g of dried oak bark with a glass of boiling water.
Leave in a water bath for half an hour, strain the resulting broth and bring with boiled water to a volume of 300 ml.
Rinse your mouth 3-4 times a day, store the broth for no more than two days.
Lemon juice rinse
Squeeze the juice from three lemons and leave in the refrigerator for 48 hours. Grind the remaining zest with 33 cloves of garlic. Pour the resulting mixture with two liters of boiled water and place in a warm place for a day. Then strain and add lemon juice. Rinse your mouth five or more times a day.
Rehabilitation, prevention and prognosis
In the postoperative period, special attention is paid to oral hygiene. Teeth brushing is done with the utmost care. Do not damage the mucous membrane with a toothbrush. At first, you should follow a diet: sour, spicy, carbonated foods are prohibited.
Excessively cold and hot foods should be avoided.
During rehabilitation, alcohol and nicotine are prohibited.
For pain and swelling after opening the ranula, Ibuprofen or Ketanov is prescribed.
Adequate dental care will help prevent recurrence.
If the problem lies in an incorrectly selected denture or chipped teeth, then dental care cannot be avoided.
During the healing stage and in order to prevent cyst formation, rinse your mouth with a soda solution. For a glass of warm boiled water, take 1/2 spoon of soda and the same amount of iodized salt. It is useful to rinse with decoctions of herbs such as chamomile, sage, immortelle, and calendula.