Calcium gluconate: what is it and what is it for?
This drug is a dietary supplement that compensates for the lack of calcium in the body. This macronutrient performs a number of important functions:
- promotes the transmission of nerve impulses;
- ensures normal muscle function, and, in particular, the heart muscle;
- part of bones and teeth;
- participates in the process of blood clotting.
Calcium deficiency in the body can lead to a condition such as tetany.
In addition, due to the effect of calcium, such as reducing the permeability of the vascular wall, this drug has an anti-inflammatory and antiallergic effect.
Features of toothpastes with calcium
The basis of bones and hard tooth tissues consists of calcium. He is responsible for their strength. During nutrition, an acidic environment is created in the oral cavity, which destroys calcium compounds. If the substance does not enter the body in the required quantity, over time, foci of demineralization appear, tooth enamel becomes thin and sensitive, and as a result, caries appears. Without proper care, hard tissues become fragile. Under mechanical loads, pieces may break off from them.
To avoid negative manifestations, use specialized personal hygiene products. They replenish the mineral composition of the enamel, eliminate hypersensitivity and protect the surface from caries. When used in a timely manner, drugs not only have a preventive effect, but also treat diseases in the initial stages.
Toothpaste with calcium helps restore and reduce enamel sensitivity.
Who is calcium paste recommended for?
Calcium-based medicinal paste is indicated for use if a person has:
- poor enamel resistance to acids;
- manifestations of dental demineralization;
- increased sensitivity of teeth;
- minor manifestations of caries;
- fragility of teeth, tendency to chip;
- plaque.
How to choose the right pasta for an adult
When choosing, it is important that the paste contains calcium compounds that can be easily absorbed. Substances such as gluconate, carbonate or calcium fluoride are not well tolerated by our body, and therefore it is better to avoid products that contain these substances. In a good product, this mineral is usually present in the form of the following chemical compounds:
- glycerophosphate;
- pantothenate;
- synthetic hydroxyapatite;
- citrate;
- lactate
It is very important to monitor the composition of such medicinal products. It is undesirable to use a product whose components are both calcium and fluoride. Individually, these substances are extremely beneficial for teeth and the body as a whole, but when they are combined, an insoluble salt is formed. When brushing with such a paste, active particles of neither element will enter the teeth, that is, no therapeutic effect will follow from such a procedure.
You should also pay attention to the presence of auxiliary components. A good paste should contain xylitol or similar enzyme substances. You should not purchase a teeth cleaning product if its components include parabens, sodium lauryl sulfate, or aluminum oxide. These substances are harmful and can provoke metabolic disorders in the body.
Recommendations for use
In order for the teeth cleaning product to bring as much benefit as possible, you need to adhere to a number of rules:
- You should first clean the spaces between your teeth using dental floss.
- You should brush your mouth for at least 3 minutes.
- If possible, immediately after brushing, rinse your mouth with a mouthwash containing sodium fluoride or aminofluoride. The rinse aid will help ensure that the calcium that gets into the enamel is securely attached to it.
When is the drug prescribed?
Experts recommend using this drug for:
- osteoporosis;
- rickets and osteomalacia - conditions in which vitamin D metabolism is impaired;
- increased levels of phosphates in the blood in patients with renal failure;
- presence of high calcium needs: during pregnancy and lactation;
- poor diet;
- bone fractures;
- postmenopausal calcium deficiency;
- chronic diarrhea.
In addition, the drug as a component of complex therapy is used in dermatovenerology for the treatment of itchy dermatoses, urticaria, and angioedema. It is also used for the treatment of bleeding of various etiologies and nutritional dystrophy.
Preparations for remineralization of teeth
The classic dental gel, which is used in remotherapy, contains two basic components - xylitol and calcium glycerophosphate. The first inhibits pathogenic bacteria that stimulate the development of caries. The second forms an invisible film on the surface of the elements, which prevents the leaching of calcium.
The world leader among remineralization preparations is R.O.K.S. gel. Medical Minerals without fluoride. The drug is used in two ways: the composition is applied to the teeth using a toothbrush (applicator) or the gel is placed in mouth guards, which are worn on the teeth for up to half an hour.
Other products for strengthening enamel include products Blend-a-med, Fluocal, Fluodent, Global White (for sensitive teeth).
What does a calcium gluconate injection do?
Calcium gluconate injections are best known as an adjuvant treatment for allergic diseases. However, they are also used to treat pathology of the parathyroid gland, in which there is an increased excretion of calcium from the body.
In addition, injections are also prescribed for conditions such as:
- eclampsia;
- nephritis;
- hyperkalemia;
- liver intoxication.
Injections of calcium gluconate help reduce the intensity of itching in atopic dermatitis, psoriasis and eczematous rashes.
Assessing the effectiveness of remineralization –
The effectiveness of the remineralization course is easy to assess if your teeth have caries in the white spot stage. But it is very important to distinguish white spots during initial caries from white spots of non-carious origin, which can occur with enamel hypoplasia or fluorosis. To check this, you need to apply a dye (1-2% solution of methylene blue), which is sold at any pharmacy, to the surface of the stains. If the white spots are areas of demineralization, they will temporarily turn blue. With hypoplasia and fluorosis, staining of the spots does not occur, because The enamel in these diseases is very dense and is not able to absorb dye.
Therefore, the disappearance of white spots is an excellent indicator of the effectiveness of remineralization. However, it is not always possible to achieve this, and in some cases we can only count on reducing the size of spots and reducing their visibility, which also allows us to talk about the positive effect of the remineralization course. Minimal effectiveness will also be indicated by the fact that there will simply be a stabilization of the number and size of white spots (this is not a very good result, but still a result). If the patient does not have white spots, a criterion for the effectiveness of remineralization can be a decrease in the frequency of caries development (relative to previous periods).
Expected effectiveness of white spot remineralization:
The effectiveness of caries therapy in the spot stage depends on two criteria: 1) the clinical size of the white spot, 2) the level of its permeability to the dye. In turn, the level of permeability for the dye clearly correlates with the degree of destruction of the hydroxyapatite crystal lattice, i.e. the higher the destruction, the higher the permeability for the dye.
If the size of the spots is up to 3.0-5.0 mm2 inclusive, and the spots demonstrate a low degree of permeability to the dye (up to 3 points inclusive on a 10-point printed scale of blue color) - we can most likely hope for their complete disappearance after a course of remineralizing therapy + normalization of hygiene. By the way, according to some authors, small spots in 50% of cases can disappear without a trace – just after normalization of oral hygiene (in this case, only the remineralizing potential of saliva will be involved).
But the situation is completely different if the white spots show a high degree of permeability to the dye, and also if the white spots have dimensions greater than 5.0 to 30.0 mm2. In these cases, you can only count on a reduction in the size of the spots (foci of demineralization), as well as a decrease in their visibility - this is due to a decrease in the brightness of the spot and restoration of the shine of the enamel. But if left untreated, white spots are highly likely to simply turn into carious defects over time.
To determine the permeability of white spots for dye, the Okushko V.R. test is used. (synonyms: enamel resistance test or TER test). Sensitivity to the dye is determined by a 1% solution of methylene blue. The interpretation of the results is carried out based on the intensity of coloring of the white spots, for which a 10-point blue scale is used. Coloring of only 1-3 points indicates a high probability of disappearance of white spots after a course of remineralization. A color score of 6 or more indicates that you should only count on reducing the size and improving the appearance of the spots.
Using the drug for allergies
If allergic reactions occur, calcium gluconate is a safe and effective remedy, the use of which practically cannot lead to an overdose. When the drug enters the body, the permeability of the vascular wall decreases and the allergen practically does not penetrate into the bloodstream. Thus, the development of an allergic reaction is inhibited. Calcium gluconate can be taken for preventive purposes.
The duration of the course depends on the characteristics of the disease. Calcium gluconate is prescribed by specialists together with antihistamines.
Dental remotherapy: what is included in the procedure
The main share of the cost of therapy falls on the production of individual mouth guards, which are filled with a therapeutic composition. The child will have to use such products at home - wear them for 20-30 minutes a day. The gel will penetrate the dental tissue and strengthen it. Course duration is 2-4 weeks.
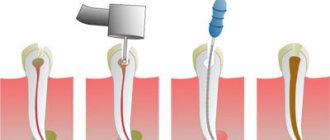
An alternative option is to remineralize tooth enamel in the dentist’s office. In this case, the procedure includes:
- mechanical cleaning of the tooth surface using a special paste;
- treating the elements with a 0.5-1% solution of hydrogen peroxide, drying the enamel;
- applying tampons soaked in a 10% calcium gluconate solution to the enamel layer (they are changed at intervals of 5 minutes);
- carrying out an application with a 2-4% sodium fluoride solution (duration – up to 5 minutes).
The course consists of 15-20 applications, which are repeated every day or every other day. Upon completion of the last procedure, the doctor coats the dried enamel with fluoride-containing varnish. The last option of remotherapy is suitable for older children.
How to give calcium gluconate to children
The drug can be given to children from the first year of life if indicated. At the age of up to 12 months, the optimal daily dose is 3 tablets. Children 1-4 years old are recommended to take 6 tablets per day. Children under 9 years of age can take from 6 to 12 tablets per day, depending on the doctor’s recommendations. Adolescents under 14 years of age can take 12-18 tablets per day.
The daily dose of the drug is divided into 2-4 doses.
Calcium gluconate in the form of a solution is used to treat children of any age as an emergency treatment for severe allergic reactions and the development of bleeding.
Does calcium help maintain teeth in old age?
Yes, in old age, taking calcium supplements helps preserve your teeth. A study was conducted that confirmed this fact. So, two groups of people after 65 years of age took three years in a row: the first took calcium supplements and vitamin D, the second took a placebo (“dummies”). After this, the subjects were observed for another two years. It turned out that in the first group people lost teeth less often than in the second. But this is not due to the fact that calcium makes teeth stronger. Here, the main role was played by strengthening the jaws, and consequently, better fixation of the tooth in the jaw.
For whom the drug is contraindicated
The drug is not used in patients with:
- intolerance to any of the components;
- increased calcium levels in the blood;
- tendency to form blood clots;
- sarcoidosis;
- severe atherosclerosis;
- urolithiasis with the formation of calcium stones.
Calcium gluconate is also not prescribed to patients taking cardiac glycosides.
Dental care after remotherapy
After therapy, the doctors of our dental clinic advise parents to continue the natural remineralization of enamel at home, namely:
- give the child vitamins, calcium-containing products to strengthen the enamel layer, vitamin D, fish oil;
- regularly brush your child’s teeth using special children’s toothpastes;
- rinse the baby’s mouth with pharmaceutical compounds;
- enrich the child’s diet with dairy products, meat, fish;
- limit intake of sweets and sour foods.
Overdose symptoms
With prolonged use of the drug, accumulation of calcium salts in the body is possible. In case of overdose, the following manifestations are observed:
- dyspeptic disorders: constipation, nausea and vomiting;
- increased fatigue and irritability;
- abdominal pain;
- constant thirst;
- muscle weakness and decreased blood pressure.
If these symptoms appear, you must stop taking the drug. Particularly severe cases may require intravenous calcitonin.
What symptoms indicate the need for remineralization?
An early manifestation of demineralization is a focal lesion of the enamel layer, which is most often diagnosed in children under 11 years of age. Light spots appear on the surface of children's teeth (or at their junctions). The formations may be barely noticeable and cover the entire element. Among the secondary signs of weakening enamel:
- decreased dental shine;
- dullness of elements;
- porosity, surface roughness of elements;
- darkening of white spots - color change to brown.
The demineralization process cannot be stopped without taking proper measures. When primary signs of destruction of the surface layer appear, the child should be shown to the dentist.