Every person experiences a sore throat sooner or later. But this seemingly harmless symptom can cause serious problems.
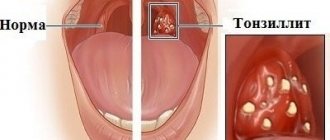
Acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis) is an infectious disease that causes inflammation of the tonsils. Statistics show that about 15% of children suffer from an acute form of the disease. In the adult population, this figure is lower - 5-10%. But almost every person in large cities suffers from chronic tonsillitis. Why? Let's find out!
The acute form of tonsillitis, which goes away with an increase in body temperature and severe pain in the throat, is more familiar to us as a sore throat. In the chronic form, the patient may not even realize that he has this disease for a long time. A person may feel that periodic sore throats and frequent colds are simply the result of a weakened immune system. Such a careless attitude towards one’s health can cause serious complications and pathologies. To avoid them, it is necessary to diagnose the problem in time: know the first signs, symptoms and treatment.
Make an appointment right now!
Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
Why are tonsils needed?
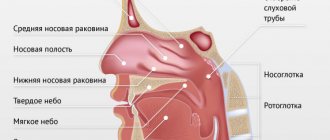
The tonsils are an integral part of our immune system. And their main purpose is to protect the body from the penetration of pathogenic bacteria and viruses. In total, a person has six of them: palatine and tubal (paired), pharyngeal and lingual. By their names you can roughly understand in which part of the pharynx they are located. Their general arrangement resembles a ring. This ring acts as a kind of barrier for bacteria. When we talk about inflammation of the tonsils, we mean only the palatine tonsils (aka tonsils). Let's look at them in more detail.
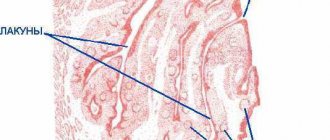
If you open your mouth wide, then in the mirror you can easily see two formations that look like almonds - tonsils, these are tonsils. Each tonsil consists of small openings (lacunae) and winding canals (crypts).
Bacteria that enter the air, in contact with the tonsils, are rebuffed and are immediately disposed of, without having time to cause an outbreak of a particular disease. Normally, a healthy person does not even suspect that real fighting is taking place inside him. Now you understand the importance of the mission of the palatine tonsils. Therefore, a good otolaryngologist will never rush to recommend their removal. Although to hear from a doctor, speaking about tonsils: “They need to be removed!” - a common phenomenon in our time. Unfortunately, today not all clinics can offer high-quality treatment for tonsillitis, and sometimes the turnaround rate is off the charts. That is why it is sometimes easier for a doctor to brush it off and refer the patient for surgery.
Causes of tonsillitis
Depending on the nature of the course, tonsillitis can be:
- acute (also called sore throat),
- chronic1,2,3.
The cause of acute inflammation of the tonsils is infection1. It can be viral, bacterial or mixed1,2.
The viral nature of sore throat predominates in adults and children over 15 years of age1,2. It usually develops with ARVI, which is caused by rhinoviruses, adenoviruses, and parainfluenza viruses1. In this case, tonsillitis is accompanied by rhinitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis and other respiratory tract diseases1.
In children 5-15 years old, bacterial tonsillitis is more common, and in first place (up to 30% of cases) among them is the most dangerous type of sore throat, caused by beta-hemolytic streptococcus of group A1. In adults, this type of tonsillitis is much less common1, and among the bacteria that cause the disease, streptococci of other groups, corynebacteria, Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria, and staphylococci predominate1.
The cause of chronic tonsillitis is also an infection, but, unlike acute processes, it is caused by less aggressive pathogens2. In this case, there may be no acute inflammation of the tonsils; the process is initially chronic in nature and is hidden behind frequent acute respiratory viral infections and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity and pharynx (non-anginal form of chronic tonsillitis)2.
Chronic inflammation leads to the death of functional, that is, lymphoid, tissue of the tonsils and its replacement with connective tissue1. The tonsils gradually lose their protective functions, often become easy prey for microbes and viruses, become inflamed and turn into a breeding ground for infection1 and an irritant for the immune system. As a result of chronic tonsillitis, immune disorders often occur, leading to the development of infectious-allergic and autoimmune diseases1,2.
Up to contents
Types of tonsillitis.
The disease occurs in two forms - acute and chronic. Acute tonsillitis is an illness of an infectious nature and manifests itself in acute inflammation of the tonsil. The cause of exacerbation is staphylococci and streptococci. Acute sore throat in children and adults is also divided into catarrhal, follicular, lacunar, ulcerative-membranous and necrotic.
Chronic tonsillitis is a long-term, persistent inflammatory process in the tonsils. It manifests itself as a consequence of past inflammation, acute respiratory viral infections, dental diseases, and reduced immunity. Chronic exacerbation of the disease in adults and children occurs in three forms: compensated, subcompensated and decompensated. In the compensated form, the disease “dormants”; exacerbation of tonsillitis symptoms occurs infrequently. In the case of a subcompensated form of the disease, exacerbations occur frequently, the disease is severe, and complications are common. The decompensated form is characterized by a long, sluggish course.
Classification of forms of tonsillitis (tonsillitis)
- I catarrhal form (the inflammatory process is manifested by redness and swelling of the tonsils).
- II follicular form (yellowish purulent dots appear on the surface of the tonsils - festering follicles).
- III lacunar form (liquid pus or purulent-caseous plugs form in the lacunae).
- IV fibrinous form (characterized by the formation of a single continuous plaque of a whitish-yellow color, which can extend beyond the tonsils, often occurs in people with reduced immune system function).
- AIDS, blood diseases, hunger, old age.
- V herpetic form (most often caused by adenoviruses, herpes simplex viruses, characterized by vesicular rashes on the back of the pharynx or soft palate, predisposed to ulceration).
- VI phlegmonous form (intratonsillar abscess) is a complication of acute tonsillitis (lacunary, catarrhal, follicular) or chronic tonsillitis, which is an acute purulent inflammation of the peritonsillar tissue.
- VII ulcerative-necrotic form (gangrenous form) - characterized by the formation of yellow-white blisters (ulcers) on the tonsils, in some cases the spots spread to the entire oral cavity and throat.
- VIII mixed forms (a variant of the disease in which colonization of lymphoid tissue occurs by several pathogens at once, as a result of the addition of a secondary infection or with a severe decrease in immunity).
Symptoms of tonsillitis.
A symptom that combines both types is pain in the throat. The pain can be both severe and tolerable. The patient experiences severe discomfort while eating and swallowing.
Sore throat is much more severe than a chronic disease and is accompanied by the following symptoms:
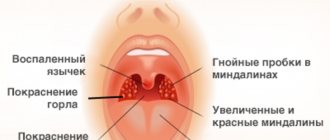
- increased body temperature (up to 40°C);
- very severe sore throat;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- accumulations of pus on the tonsils (plaque, pustules);
- enlarged tonsils;
- headache;
- weakness.
The symptoms and treatment of chronic tonsillitis are somewhat different from the manifestations of tonsillitis. With a chronic disease, the temperature remains at 37°C. A sore throat, cough, and bad breath are added. There is a white coating on the tonsils. The symptoms are less pronounced, since the course of the disease itself is characterized by remissions and exacerbations. A patient suffering from a chronic form of the disease loses his ability to work, gets tired quickly, and loses his appetite. Often a person suffers from insomnia.
Possible complications.
Both forms of the disease: chronic and acute, can cause serious complications. One of the most severe consequences of the disease is rheumatism. Practice shows that half of the patients suffering from rheumatism had to be treated for chronic tonsillitis or treated for acute conditions a month earlier. The disease itself begins with unbearable joint pain and increased body temperature.
There are frequent cases of heart disease caused by tonsillitis. Patients experience shortness of breath, interruptions in the functioning of the heart muscle, and tachycardia. Myocarditis may develop.
If inflammation spreads to tissues nearby the tonsil, paratonsillitis appears. The patient suffers from a sore throat and fever. If the infection from the tonsils spreads to the lymph nodes, lymphadenitis appears.
Untreated tonsillitis also leads to kidney disease.
Features of the acute stage of the disease
Acute tonsillitis or tonsillitis is a rapidly developing and short-lived infectious inflammation of the tonsils, followed by complete regression of symptoms and a return of the lymphoid tissue of the pharynx to its original state. Often the inflammatory process involves the adjacent palatine arches and the mucous membrane of the pharynx, which is called tonsillopharyngitis.
Characteristic manifestations of angina include:
- Rapid onset of the disease, development of the main symptoms within a few hours.
- A sore throat. It intensifies with swallowing, and its localization depends on the side of the lesion.
- Redness, swelling, enlargement of the tonsils and palatine arches. With the catarrhal form of the disease there are no other changes. With follicular angina, whitish-yellow lesions appear on the surface, as if translucent from the inside, and the lacunar form is characterized by the appearance of plaques and purulent films.
- Increased body temperature, signs of general intoxication.
- Enlargement and tenderness of the submandibular and upper cervical lymph nodes.
If the disease is treated incorrectly, the tonsils may remain enlarged and inflamed even after the patient’s well-being returns to normal. In their crypts, purulent plugs remain, and the protective function is disrupted. The tonsils themselves become a focus of infection, which can periodically activate and spread.
Pregnancy and chronic tonsillitis.
The health of the expectant mother and baby requires close attention. Complications caused by the disease can lead to dangerous consequences, including miscarriage or provoke premature birth. Self-medication in this case is dangerous: it is necessary to undergo treatment with an ENT specialist in the clinic. The doctor will prescribe washing the tonsils, treating them with ultrasound and gargling with antiseptics that are safe for the expectant mother. Physiotherapy is contraindicated for pregnant women.
If you are just planning a pregnancy, it is worth carrying out planned therapy for prevention in order to reduce the negative impact of pathogens on the tonsils. At the planning stage of pregnancy, it is recommended that both parents undergo an examination to reduce the risk of this disease in the child.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
Acute tonsillitis. Treatment.
Self-medication for this disease is unacceptable! To choose an effective method of treatment during exacerbation, it is necessary to treat tonsillitis in children and adults under the supervision of an ENT doctor. It should be remembered that the acute form of the disease is extremely contagious. When the first signs of the disease appear, a number of measures must be taken to promote a speedy recovery of the patient:
- the sick person must be isolated by placing in another room. He must have his own towel, linen and dishes, since the disease is very contagious;
- during the treatment period the patient is prescribed strict bed rest;
- take care of the patient’s nutrition: food should not be solid, so as not to cause unnecessary concern to the sore throat;
- do not forget about drinking plenty of fluids;
- a course of antibacterial therapy is prescribed (Amoxiclav, Azithromycin, etc.). It is necessary to completely drink the entire course of antibiotics, even if the patient feels a noticeable improvement;
- For local treatment, drugs with an antibacterial effect are used;
- when treating a throat with tonsillitis, the drugs “Tantum-verde”, “Inhalipt”,
- rinsing with antiseptics (“Chlorgequidine”, “Furacilin”);
- lubricating the tonsils with Lugol's solution;
- to relieve swelling of the tonsils, you need to take allergy medications;
- If your body temperature is above 38°C, take antipyretics based on ibuprofen or paracetamol.
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis.
When treating this disease, the rule applies: exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis should be treated in combination with the treatment of concomitant diseases of the nose and nasopharynx. Inflammation of the glands can be treated, but, for example, mucus constantly flowing down the wall of the pharynx due to constant inflammation of the inferior turbinates will provoke new inflammation.
Tonsillitis treatment clinics offer two treatment options: conservative and surgical. For compensated and subcompensated forms, conservative therapy is prescribed. In the decompensated form, when all conservative methods of therapy have been tried and they have not brought results, they resort to removing the tonsils. But by losing them, a person loses his natural protective barrier, so the surgical method should be considered as a last resort.
Drug therapy for the chronic form of the disease includes:
- treatment with antibiotics prescribed by an otolaryngologist;
- use of antiseptics (“Miramistin”, “Octenisept”);
- antihistamines to relieve swelling of the tonsils;
- immunomodulators to stimulate weakened immunity (for example, Imudon);
- homeopathic remedies (“Tonsilgon”, “Tonsillotren”)
- herbal decoctions: chamomile, sage, string;
- if necessary, prescribe painkillers;
- adherence to a diet (no solid food, very cold or hot, alcohol, coffee and carbonated drinks are excluded).
Why is chronic tonsillitis dangerous?
Chronic tonsillitis is dangerous due to its complications associated with the spread of infection throughout the body. We often see that after treating tonsillitis, our patients are no longer bothered by all sorts of chronic diseases and allergies. The most severe complications of tonsillitis are rheumatism and severe kidney damage - glomerulonephritis. Toxins produced by some microbes tend to damage ligamentous and cartilage tissues, cause inflammation, as well as pain in joints and muscles.
How chronic tonsillitis affects the heart. Heart valve prolapses and heart rhythm disturbances are common findings when examining the heart in patients suffering from chronic tonsillitis. The fact is that the protein of beta-hemolytic streptococcus group A, which often parasitizes the tonsils, is similar to the protein of the connective tissue of the human heart and joints. Therefore, response aggression of the immune system is possible not only against streptococcus, but against one’s own heart and joints.
Chronic tonsillitis and allergies. Sometimes one course of treatment for tonsillitis is enough for allergic rashes, itching and even attacks of bronchial asthma to “magically” go away. The fact is that the long-term presence of an infectious focus in the tonsils not only reduces immunity, but also distorts its reactivity, causing allergic changes.
Washing the tonsils.
The procedure for washing the tonsils has a great positive effect, as a result of which pus is released from the lacunae and the medicine is administered. There are several ways to carry out the procedure.
The oldest, so to speak, ancient method is sanitation with a syringe. It is used quite rarely due to its low efficiency and traumatic nature, compared to the advent of more modern methods. The syringe is used when the patient has a strong gag reflex or very loose tonsils.
In other cases, a more effective method is used - vacuum rinsing with a special attachment of the Tonzillor apparatus.
But it is not without its drawbacks:
- the container into which the purulent contents of the tonsils are “pumped out” is opaque, and the doctor cannot see whether the rinsing is complete;
- The design feature of the nozzle is such that when the pressure necessary for complete rinsing is reached, the nozzle can injure the tonsils.
Our clinic for the treatment of tonsillitis offers its patients an alternative painless option for washing the tonsils using the improved “Tonsillor” nozzle - this is the “know-how” of our clinic. There are no analogues of our nozzle in other medical institutions in Moscow. It eliminates the disadvantages of a conventional nozzle: the rinsing container, which is suctioned to the tonsil, has transparent walls, and the otorhinolaryngologist can see what “comes out” of the tonsils. This eliminates unnecessary manipulations. The nozzle itself is non-traumatic and can be used even by children of school age.
Complex therapy of chronic tonsillitis at the ENT Clinic of Doctor Zaitsev.
The method of complex treatment of the disease did not appear immediately. Our specialists have tried various methods of treating tonsillitis in practice. As a result of many years of experience in the study and treatment of chronic tonsillitis, this technique has taken root and is the most effective. It includes several stages.
The first stage is anesthesia of the tonsils. The tonsil is lubricated with lidocaine. The second stage is vacuum washing of the tonsils from caseous masses. The third stage is medicinal treatment of the tonsils using ultrasound. The fourth stage is irrigation of the tonsils with an antiseptic.
Stage five - lubricating the surface of the tonsils with Lugol's antiseptic solution. The sixth stage is physical therapy using a laser - this procedure relieves swelling and inflammation of the tonsils. The next stage is a vibroacoustic effect on the tonsils, due to which the blood flow rushes directly to the tonsils, and pathogenic substances are removed with it. The final stage of complex treatment is a session of ultraviolet irradiation, which heals the tonsils and fights pathogens.
The entire session takes about twenty minutes. To achieve a positive result, the patient usually needs five complex procedures.
Why treat chronic tonsillitis?
Chronically inflamed tonsils become a constant source of infection. With a decrease in immunity, it can spread to other tonsils and peripharyngeal tissue, invade the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses, and descend into the underlying parts of the respiratory tract.
But the inflammatory reaction of the tonsils is not the main problem of chronic tonsillitis. Constant irritation of the immune forces not only weakens the protective response, but also creates the preconditions for the occurrence of abnormal reactions. Antibodies appear in the body, which are initially produced against β-hemolytic streptococcus, but show aggression towards connective tissue.
This secondary pathology is called rheumatism or Sokolsky-Buyo disease. It is a systemic acquired disease with an autoimmune mechanism, with the favorite targets for antibodies being heart valves and the synovium of small joints.
The key focus of streptococcal infection and the site of primary formation of rheumatic autoantibodies is the inflamed tonsils. Therefore, competent treatment of chronic tonsillitis is an effective prevention of rheumatism and its complications.
Treatment of tonsillitis in Moscow
Chronic tonsillitis in Moscow, in fact, like the acute form of the disease, should be treated only by an otolaryngologist. The main thing is to choose the right medical institution where you will receive qualified assistance. Treating tonsillitis at the Doctor Zaitsev clinic means entrusting your health to professionals. Modern equipment and patented treatment methods allow us to provide the most effective care to patients. Our prices remain one of the best in Moscow, since our price list remained at the 2013 level. You can sign up for the clinic by calling the reception desk daily from 9 a.m. to 9 p.m. or through the online registration form on the website. Come, we will be glad to help you!