Chronic tonsillitis is a chronic inflammation of the tonsils.
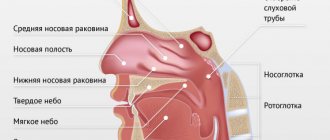
The palatine tonsils (popularly called tonsils) are an important part of the human immune system.
Bacteria, viruses, and microscopic fungi enter us with food and air. They settle on the mucous membranes, where they are picked up by a constant current of mucus, and this “river” flows in the direction of the oropharynx, just where the tonsils are located behind the palatine arches.
The palatine tonsils are like a sponge. They are dotted with gaps. When we swallow a bolus of food soaked in infected mucus, this mucus enters the lacunae of the tonsils. There, foreign microorganisms are attacked by the guard cells of the primary immune response: neutrophils and macrophages. The latter not only kill the infection, but also “cut” it into small molecular fragments, on which young cells of the secondary immune response—lymphocytes—are then “trained.” Prepared and trained lymphocytes emerge from the tonsils and “spread” throughout the mucous membranes of the pharynx and nose, forming a fairly reliable secondary specific defense.
Types of chronic tonsillitis
Depending on how the disease progresses, chronic tonsillitis can be:
- compensated;
- decompensated;
- protracted;
- recurrent;
- toxic-allergic.
Compensated tonsillitis occurs secretly: the tonsils do not bother with discomfort and inflammation, the patient does not experience an increase in temperature, but upon external examination redness is visible, the tonsils are usually enlarged.
With chronic tonsillitis, discomfort in the throat appears from time to time - soreness, slight pain. Exacerbations of the disease - tonsillitis - worry the patient with a recurrent form of tonsillitis.
Toxic-allergic chronic tonsillitis is divided into two forms:
- the first form is characterized by the addition of complications such as joint pain, fever, pain in the heart without deterioration of the electrocardiogram, and increased fatigue to the main symptoms;
- the second form turns the palatine tonsils into a persistent source of infection, which spreads throughout the body and complicates the functioning of the heart, kidneys, joints, and liver. The patient feels tired, performance decreases, heart rhythm is disturbed, joints become inflamed, and genitourinary diseases worsen.
Depending on the location of the inflammatory process, chronic tonsillitis can be:
- lacunar, in which inflammation affects the lacunae - the depressions in the tonsils;
- lacunar-parenchymal, when inflammation occurs in the lacunae and lymphoid tissue of the tonsils;
- phlegmonous, when the inflammatory process is accompanied by purulent melting of tissues;
- hypertrophic, accompanied by increased proliferation of tissue of the tonsils and surrounding surfaces of the nasopharynx.
Risk factors
The risk of developing chronic tonsillitis of the throat increases if the patient has a hereditary predisposition to the disease. About 3% of all recorded cases are transmission of the inflammatory process from parents to children. Also, the protracted course of infectious diseases is caused by formations in the nasal cavity, polyps and sinusitis. The source of infection can be a carious tooth, gum disease, or periodontitis. Additionally, the body is weakened by poor nutrition, bad habits, constant stressful situations, and prolonged use of potent drugs.
Causes of chronic tonsillitis
Chronic tonsillitis in most cases develops after the patient has suffered an acute form of the disease - acute tonsillitis or tonsillitis. An untreated sore throat may reappear or worsen due to plugs in the lacunae and crypts of the tonsils, which are clogged with caseous-necrotic masses - purulent discharge, waste products of bacteria and viruses.
The main causative agents of the disease are most often:
- viruses - adenoviruses, common herpes, Epstein-Barr virus;
- bacteria - pneumococci, streptococci, staphylococci, moraxella, chlamydia;
- fungi.
In addition, the following factors can affect the appearance of chronic tonsillitis:
- non-compliance with safety regulations in production: a large amount of dust, the presence of smoke, gas contamination, suspensions of harmful substances in the inhaled air;
- chronic diseases of the oral cavity, ears, nasopharynx: chronic otitis, sinusitis, caries, pulpitis, periodontitis and periodontal disease, in which purulent discharge reaches the tonsils and provokes the development of the inflammatory process;
- decreased immune function of the palatine tonsils: the protective substances secreted by the lymphoid tissue can no longer cope with a large number of bacteria and viruses, which, in turn, accumulate and multiply;
- abuse of household chemicals;
- eating food containing low amounts of vitamins and minerals, irregular meals, poor quality food;
- heredity factor: one of the parents suffered or is suffering from chronic inflammation of the tonsils;
- bad habits - drinking alcohol and smoking, which, in addition to having a negative effect on the immune system, complicate the course of the disease;
- frequent stressful situations, prolonged stay in a state of strong emotional stress;
- lack of a normal work and rest schedule: lack of sleep, overwork.
Conservative methods of treatment. Are they effective?
Treatment of acute tonsillitis in children of different ages and adults is traditionally carried out conservatively. But such therapy has a number of disadvantages:
- Antiseptic local remedies for sore throat act superficially and do not last long, and are quickly washed off with saliva. Therefore, when using them, it is impossible to achieve complete cleansing of the tonsil crypts and cope with deep-seated foci of inflammation.
- Local treatment of acute tonsillitis in children is often associated with certain difficulties. Parents are faced with the insufficient effectiveness of rinses and the child’s negative attitude towards the use of sprays and inhalations.
- The use of antibiotics is associated with inhibition of the native microflora of the oral cavity, intestines, and genitals. The resulting dysbiosis (dysbiosis) negatively affects well-being and digestion, and disrupts the functioning of the immune system. Therefore, many parents prefer to treat their child’s disease without using antibiotics, increasing the risk of complications.
- Antimicrobial agents should be selected taking into account the sensitivity of the microflora isolated from the tonsils, and the bacteriological analysis necessary for this takes several days and is not always available.
- Patients often complete treatment immediately after the sore throat disappears, without following the recommended duration of antibiotic therapy. This is fraught with the preservation of a dormant infectious focus, creating conditions for relapse of the disease and the development of microflora resistance.
- In most cases, it is not possible to limit yourself to using only one drug, and complex therapy requires time and adherence to a specific treatment regimen.
To fully cure acute tonsillitis means not only to relieve the patient of intoxication and sore throat. A competent doctor tries to achieve complete sanitation (cleansing) of the tonsils and elimination of the inflammatory reaction, but conservative therapy cannot always provide an adequate solution to this problem.
Symptoms of chronic tonsillitis
It is extremely difficult to determine on your own whether a person has chronic tonsillitis: this should be done by an experienced otolaryngologist. However, you need to know the main symptoms and signs of the disease, and if they appear, you should immediately consult a doctor:
- headache;
- unpleasant sensation of foreign bodies in the throat: crumbs with sharp edges, small fragments of food (caused by the accumulation of putrefactive deposits and plugs of mucus, waste products of bacteria and viruses in the gaps and scripts);
- persistent skin rash that does not go away for a long time, provided that the patient has not had any rashes before;
- increased body temperature;
- pain in the lumbar region: chronic inflammation of the tonsils often causes complications in the functioning of the kidneys;
- pain in the heart area, unstable heart rhythm;
- pain in muscles and joints: chronic tonsillitis often leads to rheumatic joint damage;
- fatigue, decreased performance, bad mood;
- enlarged lymph nodes behind the ears and on the neck;
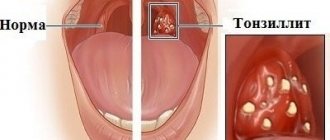
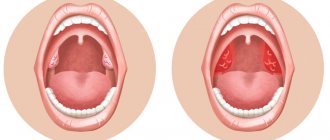
- enlargement of the palatine tonsils;
- the appearance of scars, adhesions, films on the tonsils;
- plugs in lacunae - formations of yellow, light brown, brown shades of solid or mushy consistency.
Most additional signs of chronic tonsillitis appear when other organs and vital systems malfunction: the heart, kidneys, blood vessels, joints and immune system.
For example, beta-hemolytic streptococci of group A, which is similar in protein structure to the connective tissue of the heart, can parasitize inflamed tonsils. With tonsillitis, the immune system may mistakenly attack the tissues of the heart, trying to suppress microorganisms that cause inflammation of the tonsils, as a result of which unpleasant sensations appear in the heart area, the general condition worsens, and there is a danger of serious heart diseases - myocarditis and bacterial endocarditis.
To treat or not to treat?
This question is often asked by patients suffering from periodic exacerbations of this disease. Many are sure that it is pointless to treat it, since the symptoms will return again. Yes, the treatment of chronic inflammation is a long, complex process that requires a lot of patience from the patient and high qualifications and experience of the otolaryngologist. The bacteria that cause the disease adapt very quickly to antibiotics. Therefore, it is extremely important and necessary to cure the disease in its acute form, all its manifestations. Others do not consider this disease dangerous in principle: unpleasant, yes, but not dangerous. Both approaches are completely wrong!
You cannot treat the disease carelessly, much less let its development take its course. If the disease is not cured, the bacteria can spread to other organs, causing serious complications: for example, joint diseases, myocarditis, glomerulonephritis.
Pregnant women are at particular risk: if a woman is planning a child, it is simply necessary to treat tonsillitis. After all, the disease can provoke miscarriage or premature birth. In addition, the disease greatly complicates the course of pregnancy and affects the fetus.
Diagnosis of chronic tonsillitis
Only an otolaryngologist can correctly determine the presence, form and type of chronic tonsillitis, so a timely visit to the clinic is the key to a quick diagnosis and treatment.
The most accurate signs of a chronic disease are obtained by studying the medical history and conducting an external examination of the tonsils: the greatest likelihood of tonsillitis will be indicated by frequent sore throats, as well as purulent deposits and plugs in the lacunae and crypts.
In addition to studying the anamnesis and examination, laboratory blood tests and bacterial cultures from the throat are used for flora and sensitivity to antibiotics.
How to treat acute tonsillitis
A sore throat in a preschool child becomes a reason to consult a doctor, but an adult patient is often prone to self-medication. This approach predisposes to the transformation of acute tonsillitis into a chronic and complicated form.
35ef9ecf3f83207e5d6dabda7b.jpg" />
This infectious disease in an adult should also be treated under the supervision of a competent specialist. This will not only allow you to quickly cope with uncomfortable symptoms, but will also prevent the unfavorable course of the disease.
Treatment of acute tonsillitis is usually complex and may include:
- The use of topical (local, local) agents with analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial effects. These can be lozenges, lozenges, sprays, pharmaceutical and homemade rinsing solutions. Treatment of acute tonsillitis at home in most cases is limited to the haphazard use of these remedies.
- Systemic antibacterial therapy, drugs are prescribed in the form of tablets, suspensions for ingestion or solutions for injections. Antibiotics are often required even in the case of sore throat due to ARVI, to suppress the activating opportunistic bacterial flora.
- Physiotherapy.
- Inhalations.
- Immunomodulatory therapy.
- Symptomatic drugs (for example, antipyretics, painkillers). They do not affect the course of the disease and do not change the prognosis, but they improve the patient’s well-being.
- Modern minimally invasive techniques (intratonsillar laser destruction).
Treatment of acute tonsillitis in adults and children in most cases is carried out conservatively. But the addition of purulent complications, the spread of the process to the peripharyngeal tissue may require surgical intervention (operation).
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis
Conservative and surgical methods are used to treat chronic tonsillitis. An otolaryngologist prescribes surgery only as a last resort: the palatine tonsils play an important role in the human immune system, protecting the nasopharynx from the penetration of pathogens. Removal of the tonsils can only be carried out if, due to a pathological change in the tissue, they can no longer perform their protective function. When deciding on surgical removal of the tonsils, you need to remember once again that this is the most important part of the body’s overall immune system, responsible for protecting the organs of the nasopharynx.
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis is carried out on an outpatient basis in a medical facility by an otolaryngologist. The treatment process can be divided into several stages, each of which performs its own function.
Stage one: rinsing the tonsils
At this stage, the patient’s tonsils are washed, freeing the lacunae and crypts from caseous-necrotic masses and plugs. In the absence of modern equipment, such work is usually performed with a conventional syringe: a disinfectant solution is drawn into it and a piston is used to squeeze it onto the surface of the tonsils and into the lacunae. The disadvantages of this method are that the pressure of the solution jet is too weak, which does not allow deep rinsing and cleansing of the crypts, as well as the possible occurrence of a gag reflex caused by touching the tonsils with the syringe.
In most cases, modern equipment is used - the ultrasonic vacuum device "Tonsillor", used by modern clinics and ENT centers. The rinsing attachment allows you to thoroughly rinse your tonsils without touching them, without causing gag reflexes. The advantage of using the attachment is that the doctor can observe and control the process of washing out pathological contents from the tonsils.
Stage two: antiseptic treatment
After cleansing the tonsils, an antiseptic is applied to them using ultrasound: ultrasonic waves convert the antiseptic solution into steam, which is applied under pressure to the surface of the tonsils.
To consolidate the antibacterial effect, the tonsils are treated with Lugol's solution: it contains iodine and potassium iodide, which have powerful antibacterial properties.
Stage three: physical therapy
One of the effective, painless and side-effect-free methods of physiotherapy is laser therapy. Its positive properties:
- anesthesia;
- activation of metabolic processes;
- improvement of metabolism in the affected organ;
- regeneration of affected tissues;
- increasing immunity;
- significant improvement in the properties and functions of blood and blood vessels.
Ultraviolet radiation is used to neutralize harmful microorganisms in the oral cavity.
The number of procedures for washing, treatment with antiseptics and physiotherapy is prescribed by the doctor on an individual basis. On average, in order to completely cleanse the tonsils and restore their ability to cleanse themselves, rinsing must be repeated at least 10-15 times. In order to completely eliminate the need for surgical intervention, courses of conservative treatment are repeated several times a year.
In extreme cases, when the lymphoid tissue of the tonsils is replaced by connective tissue as a result of the disease and the tonsils cease to protect the body from microorganisms, being a constant source of pathogens, tonsillectomy is prescribed. Tonsillectomy is a surgical operation to remove the tonsils. It is performed in a hospital setting under local or general anesthesia.
How to quickly cure a disease at home, is it possible to get rid of a sore throat forever?
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis with traditional medicine should be carried out taking into account a number of important principles:
- Constant medical supervision. Any, even the most harmless, means must be agreed upon with a doctor so that he can confirm their effectiveness. This is important because the causes of the disease can be different, as well as the manifestations, which affects the selection of remedies.
- It is not worth treating the acute form of the disease with folk remedies, so as not to cause complications. But chronic tonsillitis suggests the possibility of treatment with “grandmother’s” recipes.
- It is recommended to combine treatment with folk remedies with the use of medications prescribed by a doctor. They will help enhance the effect of medications and speed up recovery. But first you should ask your doctor about the compatibility of certain drugs with medicinal herbs and other components that make up folk remedies.
- Follow all directions given in the recipe. Do not change the volumes of components and doses.
- The treatment should be absolutely safe and harmless, so before you start, try the product: apply it to an area of the mucous membrane (for example, on the inside of the cheek) and evaluate the reaction. If nothing happens within 2-3 hours, then start using it.
- Remember that some medicinal plants may have contraindications and side effects.
To prepare products, use high-quality raw materials. Products must be fresh, and it is recommended to purchase medicinal herbs at a pharmacy.
Gargling with folk remedies
For tonsillitis, one of the effective home remedies is gargling. Here are the best recipes for rinsing solutions:
- The best recipes for treating arthritis with folk remedies at home
- Garlic rinses. Crush two large cloves of garlic, pour in 1 glass of boiled warm milk, strain and gargle while warm.
- Vinegar solutions. Dilute 1 teaspoon of apple cider vinegar in 1 glass of warm boiled water.
- Celandine rinses. 1 tbsp. Pour a spoonful of celandine herb into 1 cup of boiling water, hold for 5-10 minutes in a steam bath, strain after half an hour. Rinse with a very warm, closer to hot, solution.
- Dilute alcoholic tinctures of herbs or ready-made herbal concentrates (rotocan, elekasol) with warm boiled water and rinse, alternating them.
- Rinse collection No. 1. Take 2 tbsp. spoons of marshmallow root and sweet clover herb, 1 tbsp. spoon of anise seeds, burdock roots, calendula, chamomile and linden flowers, St. John's wort herbs, wild mallow, thyme and add 250 ml of water. Leave for 25 minutes, then strain and gargle.
- Rinse collection No. 2. Take 1 tbsp. spoon chamomile herb, calendula flowers, eucalyptus leaves, pour 400 ml of water, boil for 2 minutes, strain after 30 minutes. Start gargling at a decoction temperature of 26 °C and, gradually reducing the temperature of the solution by 1 °C, bring it after 10 days to 16 °C. Find out about gargling with soda and salt for a sore throat here.
Medicinal teas, decoctions, tinctures
Collections for the treatment of chronic tonsillitis include plants that have anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and enhances the body's immune responses. The following plant substances can provide this effect:
- Alkaloids;
- Essential oils;
- Phytoncides, tannins (tannins);
- Resins;
- Vitamins.
Traditional medicine recommends using proven herbs for tonsillitis, compiled by experienced herbalists who are well aware of all the intricacies of plant interactions. We offer several effective preparations and recipes for the treatment of chronic tonsillitis.
Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory herbal tea
Compound:
- St. John's wort;
- Calamus root;
- Calendula;
- Coltsfoot;
- Peony root;
- Wormwood grass;
- Chamomile;
- Black currant leaves;
- Dill herb;
- Thyme herb;
- Sage herb;
- Eucalyptus leaves.
Take all components in equal quantities. Pour one teaspoon of the mixture into 200 ml of water at a temperature of 18-25˚C, leave for 4 hours. After this, strain. Take the medicine 100 ml 2 times a day. Also gargle with this mixture.
Immunostimulating and antibacterial collection
Compound:
- Volodushka herb (20 g);
- Horsetail (10 g);
- St. John's wort (15 g);
- Ephedra herb (5 g);
- Wild rosemary herb (15 g);
- Chopped rose hips (25 g);
- Licorice root (5 g);
- Rhizome with Leuzea roots (15 g);
- Calamus rhizome (25 g);
- Rhizome with roots of peony evasive (20 g);
- Elecampane root (10 g).
When preparing the collection, use a pharmacy scale.
1 tbsp. Add 200 ml of water to a spoonful of the mixture, boil for 10 minutes over low heat and leave for 1 hour. Strain the infusion and take 50 ml 6 times a day, adding honey to taste.
Anti-inflammatory and antiseptic collection
Compound:
- Calendula flowers (15 g);
- Chamomile flowers (10 g);
- Licorice root (10 g);
- Ledum herb (10 g);
- Linden blossom (10 g);
- Elecampane root (10 g);
- Sage herb (15 g);
- Eucalyptus leaves (20 g).
Method of preparation: 1 tbsp. Add 200 ml of water to a spoonful of the mixture, boil for 5 minutes, then leave for 6 hours. Use the infusion for rinsing, as well as for oral administration, 1 tbsp. spoon 3 times a day.
- Benefits for joints and contraindications for using chestnut vodka tincture recipes
Propolis at a 10% concentration in butter is very effective for tonsillitis: use 10–15 g of propolis oil 2–3 times a day 1–1.5 hours before meals for 10–14 days.
Another recipe using propolis: Take 20 g of crushed propolis per 100 ml of 70% alcohol and leave for 3 days at room temperature. You can take 20 drops orally, diluted in warm water or milk 30 minutes before meals or 1.5–2 hours after meals. Use this remedy 2-3 times a day.
For chronic tonsillitis, it is useful to drink hot tea with honey and lemon, and blackcurrant juice. In general, drink plenty of warm drinks: green tea or herbal tea (with or without honey).
Herbs for tea:
- Mint (any);
- Pharmaceutical camomile;
- Rhodiola rosea (golden root);
- Raspberry branches, leaves and berries;
- Currant leaves and fruits;
- Blackberry branches and berries;
- Clover flowers;
- Elecampane;
- Althaea officinalis;
- Rose hip.
An excellent remedy for chronic tonsillitis is licorice root. In the spring, take it with ginger root (preferably raw), in the fall - with tricolor violet. Crush licorice, brew in boiling water, add ginger, cook for 2 minutes and take hot at night. You can learn about the benefits of raspberry jam by following the link.
Home inhalations
Inhalations are very helpful in treating respiratory diseases. In case of tonsillitis, they can also be used. Let's look at a few recipes:
- Add eucalyptus alcohol tincture to hot water (1 tablespoon per 1 liter of water). Breathe the steam for at least 10-15 minutes.
- Use an alcoholic infusion of St. John's wort flowers for inhalation according to the same recipe. This tincture can be prepared for future use: 100 ml of alcohol per 20 g of flowers. You need to insist for 2 weeks.
- Pour boiling water over dry crushed sage (1 cup per 1 tablespoon of herb), let it brew for 15-20 minutes. Add to hot water for inhalation (1 glass of product per 1 liter), breathe for 10-15 minutes.
- Inhalations with alcoholic tinctures of aloe and chamomile infusion are also effective.
Lubricating the throat
You can lubricate your throat with honey and aloe. Take adult aloe leaves, squeeze the juice out of them and mix 1 part aloe juice with 3 parts honey. Lubricate your tonsils with this mixture on an empty stomach in the morning and do not consume anything from food or drink for 2 hours. Carry out this course for at least 2 weeks.
Mix garlic juice with the same amount of water. Lubricate your tonsils with the resulting mixture several times throughout the day. This procedure is carried out once every 2 days.
Pour crushed St. John's wort (0.5 cup) into 250 ml of flaxseed, almond or olive oil, leave this mixture for 21 days, then strain and squeeze. Lubricate your tonsils with the product three times a day for 10 days in a row. Keep refrigerated.
- How to treat arthrosis of the shoulder joint at home with folk remedies
Symptoms and treatment of tracheitis in adults
Treatment of adenoiditis in children - features of the disease and why surgical intervention in this case brings only benefits is described here.
Consequences of a deviated nasal septum //drlor.online/zabolevaniya/nosa/iskrivlenie-nosovoj-peregorodki/diagnostika-i-metody-lecheniya.html
Compresses
For tonsillitis, wet compresses are used. They must be applied in a certain sequence:
- Cleanse your skin.
- Dry the patient with a warm, damp towel.
- Apply the active substance: to do this, take a large piece of clean gauze, roll it several times to form a thick layer, soak it in the medicine, and apply it to the throat. The area of application must necessarily include the tonsils, but not the thyroid gland.
- Cover the top with compress paper and then with a thick layer of cotton wool.
- Secure the entire structure with a bandage, scarf or handkerchief folded several times.
- Leave this bandage on for the required time (you can do it all night), it will warm your sore throat and make breathing easier.
- During the day it is better to update it every 2-3 hours.
Treatment with compresses can be carried out only after consultation with the attending physician, since in case of purulent forms of sore throat, the use of warm compresses is prohibited. In this case, they will contribute to the growth of the number of bacteria and their spread throughout the body.
We offer several of the most effective ways to prepare compresses:
- Alcohol dressing. Soak gauze in vodka and apply it to the throat, then covering it with special paper or a plastic bag, insulating it with cotton wool and wrapping it with a bandage. The alcohol must be diluted in a 1:1 ratio. For children over 3 years old, alcohol compresses (only as prescribed by a doctor) are made based on a 1:3 ratio.
- Compress of cabbage leaves and honey. Before putting cabbage leaves to your throat, lightly beat them with a kitchen hammer or cut them with a knife so that they release juice. Spread a small amount of honey on top of the leaves and cover with another chopped cabbage leaf. This bandage, which has both a warming and absorbable effect, can be left on all night.
- Cottage cheese compress. Apply 200 g of cottage cheese at room temperature to the sore throat and secure with a bandage. Leave it overnight: cottage cheese has excellent stretching properties.
- Potato compress. Boil 3-4 potatoes in their jackets, add 1 tbsp. spoon of vegetable oil, crush. Spread the resulting puree onto gauze, add a few drops of iodine on top, apply to your throat and secure. Make a compress quickly, as the iodine evaporates instantly.
- Compresses with essential oils. You can use tea tree, lavender, eucalyptus, rosemary, sage, and chamomile oils. Dilute 5 drops of oil in 200 ml of water, soak gauze in it, squeeze well and apply according to the standard algorithm. Change every 1-1.5 hours.
Such dressings can be applied to children only if there is no allergy.
Prevention of chronic tonsillitis
Preventive measures to avoid relapse of the inflammatory process in the area of the tonsils include several comprehensive measures:
- proper nutrition: do not eat food that irritates the mucous membranes of the tonsils - citrus fruits, hot, spicy, fried, smoked foods, strong alcoholic drinks;
- strengthening general immunity: hardening, walking in the fresh air, taking vitamin and mineral complexes;
- rest and work regime: you need to get enough sleep, take time for proper rest, avoid working for long hours without breaks.