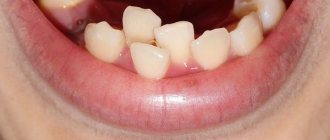
What to do if your child has a pink tooth
The tooth consists of both hard and soft tissues. Inside it is soft pulp and nerves. The pulp is made up of a semi-solid material called dentin. Dentin helps form the bulk of the structure and protect the sensory nerves and blood vessels inside. Enamel is a thin coating over dentin that adds another layer of protection. Enamel helps protect dentin and pulp from bacteria. Caries that gets into the enamel and dentin and reaches the pulp can lead to its death. When decay reaches the pulp, it creates a pathway for bacteria to infect the tissue. A healthy pulp will respond to infection the same way as any other part of the body: with inflammation.
Another thing that can cause redness is injury. If you are struck in the jaw by a fall or while playing sports, it can damage blood vessels. The tooth needs blood, so when there is no more blood, it dies. This usually happens slowly over time and does not cause as much pain as when decay reaches the pulp.
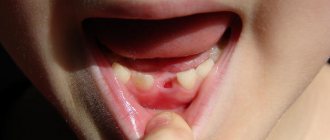
During eruption, root resorption occurs. The root is absorbed and begins to dissolve. Once the root is completely resorbed, the baby tooth will fall out - so there will be no visible root. If resorption continues, a pink tint may appear. It may take about 2-3 weeks for the color to change. If the tooth turns red, this is the result of thinning or translucency of the enamel. This looks strange, but is not a cause for alarm. Parents can always consult a dentist if the child is bothered by pain or the shade becomes more intense.
The damage is usually irreversible, but sometimes it can be repaired, especially if it is caused by tooth decay. The dentist will make a diagnosis and recommend treatment.
How to identify milk caries?
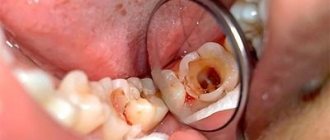
It is quite simple to identify caries in young and older children. White or brown spots appear on the teeth, a painful reaction to hot and cold is observed, and the child may develop bad breath. When these first symptoms of caries appear, it is already worth sounding the alarm, since the carious process is developing very rapidly. It is characterized by almost instantaneous damage to several teeth, and if measures are not taken, the entire dentition may be affected. Of course, it is often difficult for a child to articulate that his baby tooth hurts. He may refuse to eat or chew on only one side. This should also alert parents and encourage them to take their child to pediatric dentistry.
How to treat a pink tooth in a child
A pink tooth in a child should not cause panic. It is important to know that this is usually not a serious situation. The problem often occurs in young children and, as a rule, it is harmless - there is no harmful effect on the health of the jaw. A red tooth in a child is a sign of resorption.
If the pink discoloration is persistent, it may indicate a more serious problem and parents should consult a dentist.
The doctor can:
- put a seal;
- remove dentin;
- apply intracanal bleaching.
Treatment depends on various factors and the exact cause of the change in shade.
Treatment of stained teeth at the Family Dentist clinic
We have experienced doctors who have been treating caries and non-carious lesions for 15–20 years, and accurately identify the spotted form of hypoplasia. White spots on teeth are similar to early caries and fluorosis. We identify the disease by its shape, color intensity, localization of lesions, smoothness or roughness of the enamel layer. We dry the teeth, examine them under fluorescent lighting, and stain them with methylene solution.
Our pediatric dentists provide attention and care, treat restless and capricious little patients with patience, and make diagnosis and treatment comfortable. Children leave in a good mood and are not afraid to come again.
Dental hypoplasia is irreversible; treatment consists of strengthening the enamel layer and restoring chips, cracks, and color. We select treatment tactics depending on the severity of the disorders and take into account the condition of hard tissues.
We perform remineralizing therapy to strengthen the enamel and prevent caries at the site of the spots. We apply applications or mouth guards with preparations containing phosphorus and calcium. To increase the effectiveness of remineralization, after completing the course we fluoride the teeth to prevent calcium leaching. For hygiene, we recommend prophylactic pastes with fluorides, phosphates, hydroxyapatite crystals, and calcium. In Minsk there are good pastes: Apadent Kids, Children's Pearls, Lacalut Kids, Biorepair Kids.
We excise areas with erosion and install a filling if we are treating brown spots on children’s teeth. Our clinic uses reliable filling materials with fluoride, which are indistinguishable in shine and color from natural enamel. Filling prevents the appearance of cracks, the penetration of microbes, and gives the smile an aesthetic appearance.
We use whitening in older children with slight clouding of the enamel. Whitening methods are effective for isolated chalky stains.
If you notice white or brown spots on your child's teeth, make an appointment with our family dentistry. We will strengthen the enamel, restore damaged areas, and eliminate cosmetic defects.
What to do if an adult’s tooth turns red
As resorption occurs, the pink or red color becomes more noticeable and the structure changes. If you catch the early stage of dying, there is a chance to preserve the external structure. The internal, damaged pulp can be cleaned out and replaced with a hard filling material that will help protect the structural integrity. Preserving as much of the original structure as possible is important for oral health. Gaps in your smile can lead to poor jawbone health, uneven bites, bacterial growth, and cosmetic problems.
If severe damage is observed, removal will likely be the best option. It is recommended to get an implant to maintain the health of your jaw and mouth.
Prevention of caries in children
Prevention of childhood caries includes several areas, which boil down to proper nutrition, as well as home and professional hygiene.
- Individual oral hygiene. Home hygiene means that as soon as the first tooth hatches, a brush for the baby should appear in a glass next to the parents’ brushes. The same applies to toothpaste. At first, the paste can be applied to gauze or a fingertip to clean your teeth so as not to injure your delicate gums. You need to clean your teeth from all surfaces vertically, then wipe them with a brush soaked in water. Thus, firstly, plaque will be removed, and, secondly, parents will teach the baby to take care of the oral cavity.
- Prevention of caries with the help of a well-chosen diet. As for nutrition, parental duty is to breastfeed the baby from the very beginning. There is no need to talk about the beneficial properties of breast milk, and the sucking process greatly affects the developing jaw system. Then the baby should be accustomed to fermented milk products. By six months, the child should be fed kefir, and later - cottage cheese and cheese. Parents should remember that the main formation and formation of permanent teeth occurs up to 3 years. This means that calcium must always be present in the daily diet.
- Professional oral hygiene. This type of prevention involves periodic visits to the dentist and hygienist. The first visit should occur on your first birthday. The specialist will not only give recommendations for care, but also create a diet regimen and examine the mouth. When the first teeth emerge, you and your child will be shown how to brush their teeth properly at an appointment with a hygienist. If there is a problem such as tartar in children, you cannot do without professional hygienic cleaning. It is important for parents to make it a rule to visit the doctor twice a year. And if there are problems with teeth, then more often - once every three months. This is largely due to the fact that various pathologies develop too quickly in childhood. Meanwhile, early diagnosis will lead to quick, painless and relatively inexpensive treatment of caries.
As you can see, in most cases, when caries can attack children's teeth, parents are able to rebuff it decisively. Of course, there is no escape from genetic predisposition. But it’s not without reason that dental experts say that sweets are the main cause of the development of the disease! So isn’t it better to eliminate the constant source of bacteria and, instead of harmful carbohydrates, offer the child fruits, which are much healthier, after the main meal? Ultimately, your child will thank you in the future for being vigilant and maintaining healthy teeth!
Make an appointment
right now!
Dzedzits Olga Alekseevna
Surgeon, Therapist, Pediatric dentist, Hygienist
Why does a filled tooth suddenly turn pink?
If dental treatment was successful, but the healed tooth hurts, this does not indicate any problems, but gives reason to consult a dentist. If the filled tooth turns pink, this may be the result of the fact that the paste contained resorcinol and formaldehyde. But most often the change signals pulpitis, periodontitis, traumatic injury or rupture of a vessel in the pulp.
If a tooth turns red, you should immediately contact your dentist to get a diagnosis. A potential infection should not be left unattended; it is important to ask what treatment options are available and make an informed decision.
Reasons for the development of pathology
There are two reasons for the development of granulomas on the root of a tooth.
1. Untreated pulpitis. The development of caries leads to the appearance of a deep cavity in the tooth. Pathogenic microorganisms enter the pulp, it becomes inflamed, and severe pain appears. Lack of medical care leads to the gradual death of the pulp. Bacteria penetrate beyond the tooth through root canals. A focus of inflammation appears at the apex of the root. We are talking about periodontitis.
A deep carious cavity in this case is not always observed. Inflammation can develop internally when secondary caries appears under the filling.
2. Poor quality endodontic treatment. Granuloma can develop at the root of a tooth in which root canal filling was previously performed. Usually there is underfilling: the doctor has not completely filled the canals with material. In the remaining voids, pathogenic bacteria develop, and the tissues surrounding the root react with inflammation.
These causes cause most cases of granuloma formation. But there are others, less common:
- poor quality orthodontic treatment;
- previous dental trauma;
- other inflammatory diseases - tonsillitis, abscess, etc.
In the latter case, the infection enters the tissues through the blood or lymph flow.
Ask a Question
Experts' opinion
The effectiveness of the ASEPTA series products has been proven by multiple clinical trials conducted in the country's leading research institutes.
For example, a study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents from the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases, conducted by A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Alexandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina in the Department of Periodontology of the Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery of Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow, made it possible to identify the fairly high effectiveness of the Asepta gum balm and the Asepta mouth rinse for moderate periodontitis. The use of Asepta mouth rinse for inflammation also turned out to be quite effective. In addition, no phenomena of mucosal irritation or brown staining of fillings were recorded. This indicates that the use of this rinse for a two-week period provides an obvious clinical effect in the absence of negative side effects.
Diagnosis of granuloma on the tooth root
At the early stage of development of the disease, it will not be possible to notice any visual changes. The first signs of pathology become noticeable as the size of the infected area and the amount of pus increase.
To treat the disease with therapeutic methods, it is necessary to examine the affected area in detail: a complete picture of the granuloma must be obtained, which will allow one to detect key signs of the disease that differ from other diseases.
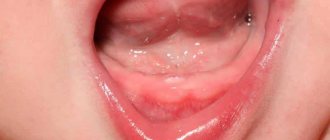
When suppuration occurs, the gums become very red and swollen, and pain appears, which can radiate to the head area in general and the ear in particular. This is the first symptom that should make you wary.
The following methods can be used to make an accurate diagnosis:
- use of classical x-rays;
- the use of radiovisiography or, in simpler terms, computer x-ray.
In the picture, the affected area looks like a dark spot with a clear border in the upper part of the tooth. The size of the spot indicates the following:
- 5-8 mm – the probability of having a dental granuloma is high;
- more than 8 mm – formation in the form of a cyst.
In rare cases, a large granuloma, up to 1.2 cm in size, may occur. Therefore, X-rays may not be enough for diagnosis: it is recommended to perform a biopsy of tissue cells from the area affected by the disease.
In most cases, granuloma is discovered during treatment of other dental diseases: the doctor may pay attention to increased swelling and swelling of the gums. In addition, the bone tissue near the top of the tooth may also bulge.
An increased risk of developing granuloma is observed in patients with crowns and pulpless teeth. Such people are advised to undergo regular examinations in order to promptly identify any changes affecting the gums and teeth.
Surgery
Surgical treatment of dental granuloma may be required only in a few cases:
- obstruction of the root canals - complex, tortuous structure, too thin, narrow canals;
- impossibility of unsealing channels;
- the presence of a pin in the root canal - attempts to remove it may cause injury;
- patient's reluctance to remove the crown.
Many patients prefer granuloma removal because they do not want to resort to long-term treatment and remove a good crown. In this case, an apical resection operation is performed - part of the root is removed along with the granuloma through a small incision in the gums. Less commonly used is hemisection - removal of one root of a multi-rooted tooth along with part of the crown. In this case, further restoration of the crown of the tooth with a prosthesis will be required.
In rare cases, it is not advisable to preserve a tooth with granuloma. For example, if the crown is severely damaged and cannot be restored. In this case, when removing a tooth, the doctor must remove the granuloma from the socket in order to prevent the development of inflammation.
If purulent complications develop against the background of a granuloma, it is important to get help from a doctor immediately. The specialist will provide first aid: relieve acute pain by opening the tooth. Previously sealed canals are opened, and purulent contents are subsequently removed through them. In this case, relief comes instantly.
If severe swelling of the gums or cheeks appears, this may be due to the release of inflammatory contents under the periosteum or oral mucosa. In this case, a small incision is made to drain the pus. Further treatment is possible only after relief of acute symptoms. Drug therapy will also be required - the doctor will prescribe a course of antibiotics. You should not take them on your own. Moreover, it makes no sense to be treated only with antibiotics in the hope that the inflammation will go away - they are not able to eliminate the source of the disease or even reduce it, it is important to take local measures to eliminate the inflammatory process.
Irreversible change in enamel color
It also happens that after erupting a tooth immediately stands out in an unusual color - from purple or green to different shades of brown. Parents cannot even imagine why their child’s tooth has darkened. The main reasons for this condition may be the following:
- Taking tetracycline drugs by the mother during pregnancy or treating the baby with tetracycline without the knowledge of the doctor.
- Hemolytic disease of newborns without adequate correction.
- Fluorosis. In this case, the teeth become mottled with dark spots on the glossy white enamel. The disease develops when drinking water with a high concentration of fluoride is consumed during the formation of dental tissues. It's not dangerous, but not aesthetically pleasing.
Teeth with such types of pathology remain multi-colored until the bite changes.
My gums hurt after filling a tooth, what should I do?
If, after installing a filling, your gums are very sore and even your cheek is swollen, you cannot do without the help of a dentist. Moreover, it is necessary to contact as soon as possible so that there are no even more unpleasant consequences.
A few tips to relieve pain:
- applying an ice compress to the cheek at the sore spot for several minutes or a compress with ice cubes;
- alternate application of compresses with warm rinses from decoctions of medicinal herbs or infusions;
- painkillers;
- balms to strengthen teeth and gums.
Attention! Under no circumstances should you apply hot or warm compresses - they actively provoke inflammation and pain!
Taking antibiotics without a doctor's prescription is also extremely contraindicated, because this can lead to a decrease in immunity and complicate further treatment.
Preventive measures
After filling a tooth, during the first week, you must strictly follow the main rules so that pain does not occur, or it disappears as soon as possible:
- do not drink or eat too cold or too hot, as temperature changes provoke pain;
- every time after eating, brush your teeth and rinse your mouth with special anesthetic rinses (the ASEPTA series includes rinses with an analgesic and disinfecting effect);
- try to eat softer foods so as not to damage the periodontal tissues, and it is preferable to chew only on the healthy side;
- do not smoke, as the tooth disturbed by treatment is very sensitive in the first days.
Features of prevention
The main condition for the prevention of dental granulomas is timely assistance from a dentist when caries occurs. You should not allow severe tooth decay or the development of pulpitis. The peri-root tissues are healthy until the pulp becomes inflamed. Therefore, if symptoms of caries or pulpitis appear, it is important to immediately consult a doctor.
Endodontic treatment also increases the likelihood of developing periodontitis. Therefore, it is better to eliminate caries in the early stages and avoid the need for root canal filling. If this is unavoidable, it is important to carefully choose a dental clinic - the professionalism of a specialist will help eliminate possible mistakes and prevent complications.
Complications after granuloma at the site of an extracted tooth
Lack of timely treatment and hope that the disease will go away on its own is fraught with serious consequences. Among the most common complications it is worth highlighting:
- development of periodontitis and further formation of a fistula;
- the occurrence of alveolitis is a consequence of the presence of an inflammatory process;
- formation of purulent flux;
- suppuration of the perimaxillary tissue;
- entry of pathogenic bacteria into the lymph nodes, from where they penetrate the cardiac system and internal organs (kidneys, liver and brain);
- development of facial asymmetry;
- the emergence of new foci of infection;
- infection of the body due to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the blood vessels.
Timely removal of granuloma is a guarantee to avoid unpleasant health consequences.
Tooth granuloma: symptoms of the disease
Only a doctor can make a diagnosis based on an x-ray, where a darkening will be visible in the root area. Any darkening in the image is a sign of the presence of a cavity, but if a granuloma occurs, it means that periodontitis, which is chronic in nature, begins to develop.
For a long time, the tooth may not bother a person at all. Sometimes pain may occur when biting or when eating hot food: these are the first signs of the development of chronic periodontitis. An exacerbation of the disease is observed during periods of weakening of the body's immunity: then the pain intensifies significantly, which is especially noticeable when biting. During such periods, as a rule, the gums become swollen, and in the area of inflammation it becomes painful to touch.