Purulent sputum
Purulent sputum is a mucopurulent substance consisting of white blood cells, dead tissue, cellular debris, serous fluid and liquid mucus.
The color intensity of the purulent secretion can vary from milky with yellow to green, and manifests itself in pneumonia, bronchiectasis, abscess pneumonia, prolonged bronchitis or acute infectious lesions of the respiratory system.
A cough with purulent sputum is a good reason to consult a doctor, because if pus is coughed up, its shade will allow you to determine the pathology and choose the appropriate therapy.
- Yellowish-purulent and yellowish-greenish (mucopurulent) abnormal secretions indicate that antibiotic therapy will help reduce symptoms.
- A green or greenish tint indicates a long-standing respiratory infection, pneumonia, ruptured lung abscess, chronic infectious bronchitis, infected bronchiectasis, or cystic fibrosis.
- Bright yellow and orange mucus is produced by pneumonia (caused by pneumococcal bacteria), pulmonary embolism, bronchioloalveolar cancer, or tuberculosis.
- Discharge of a pale, milky, yellowish or yellowish-gray hue (clearly visible on a white background) indicates the ineffectiveness of antibiotic treatment, since the symptoms of the disease are associated either with a viral infection or with allergies (even asthma), and not with microbiotics that are sensitive to antibiotics .
- A foamy pink color is characteristic of severe pulmonary edema.
- Foamy white indicates pulmonary obstruction or edema.
- Light yellow sputum with blood indicates a possible inflammation of the throat or bronchi, or the presence of bleeding erosions, ulcers or tumors of the lower airways. The abundant presence of blood clots in bronchial secretions indicates tuberculosis, bipolar disorder, pulmonary embolism, and abscess pneumonia.
How to correct a deformed nasal septum?
In cases where a deviated nasal septum requires surgical intervention, endoscopic septoplasty is performed. This operation is performed according to indications and is not aesthetic. But often rhinoplasty is performed together with septoplasty, since a deviated nasal septum can have pronounced signs, as a result of which the shape of the nose also changes.
The indications for endoscopic septoplasty are as follows.
- Impaired nasal breathing. This is the main symptom requiring septoplasty.
- Constant swelling of the mucous tissues in the nasopharynx.
- Frequent sinusitis.
- Snoring, wheezing breathing.
- A constant sensation of a lump of mucus in the nasopharynx due to improper outflow.
With a chronic inflammatory process, benign neoplasms – polyps – can form. That is why it is recommended not to delay treatment, and if you have problems with nasal breathing, frequent colds, or you constantly feel a lump of mucus in your throat, then you should contact specialists who can diagnose the degree of curvature of the nasal septum and perform surgical intervention if necessary.
What is sputum? Which one is normal? Why is it needed?
The sputum takes on a yellow or yellowish-green tint if it contains impurities of pus, which indicates the development of inflammation, which is caused by a bacterial infection. The bright yellow (canary) color of phlegm is due to an increased content of eosinophils and is observed with eosinophilic infiltrative processes in the lungs or bronchial asthma.
The discharge of yellow mucus may also be due to subjective reasons. Tobacco and nicotine tars give the mucous exudate a yellow-rusty hue. Eating large amounts of carrots or citrus fruits can also cause the formation of large amounts of yellow exudate.
It is a thick, viscous, jelly-like substance that is released when you cough up. Secreted in the mucous epithelium of the lower airways by submucosal and unicellular glands.
Its composition includes high molecular weight glycoproteins, immunoglobulins, lipids and other substances. Simply put, phlegm contains:
- Impurities of saliva;
- Slime;
- Red blood cells;
- Fibrin;
- Epithelial cells;
- Bacteria;
- Foreign inclusions (dust particles, food residues, etc.).
The norm of phlegm released per day from the tracheobronchial tree is 10-100 ml. This is the amount of substance that a person ingests during the day without noticing.
Diagnosis of sputum by consistency and smell
In order to evaluate this criterion, it is necessary to expectorate sputum into a transparent glass container, evaluate it immediately, and then remove it, cover it with a lid, and let it sit (in some cases, the sputum may separate, which will help in diagnosis).
- Mucous sputum: it is released mainly during ARVI;
- Liquid colorless is characteristic of chronic processes developing in the trachea and pharynx;
- Foamy white or pinkish sputum is released during pulmonary edema, which can accompany both heart disease and inhalation gas poisoning, pneumonia, and inflammation of the pancreas;
- Sputum of a mucopurulent nature can be released with tracheitis, sore throat, bacterial bronchitis, complicated cystic fibrosis and bronchiectasis;
- Vitreous: characteristic of bronchial asthma and COPD.
An unpleasant odor is characteristic of complicated bronchiectasis or lung abscess. A fetid, putrid odor is characteristic of lung gangrene.
If the sputum separates into two layers when standing, it is probably a lung abscess. If there are three layers (the top one is foamy, then liquid, then flaky), this may be gangrene of the lung.
Folk remedies for coughs
When talking about how to treat a cough, we should not forget about traditional medicine. Some of the most accessible and effective recipes include:
- Infusion of coltsfoot. Preparation boils down to pouring 1 tablespoon of herb into 1 tbsp. boiling water, infuse for 10-15 minutes, strain. Take 1 tsp of this infusion orally. up to 4 times a day.
- An infusion of a mixture of plantain, thyme, elecampane root and wild rosemary herbs. 2 tbsp. dry mixture of herbs is poured with 1 liter of boiling water, infused for 2 hours, filtered. A solution of 1 tbsp is taken. orally up to 4 times a day.
- White cabbage juice. Freshly squeezed juice is mixed with honey in a 2:1 ratio. The finished mixture is taken orally, 1 tsp. 6 times a day.
- Lemon juice. Mix 2 tsp. product in a cup of warm water, add honey to this mixture, and take 3-4 times a day.
In addition, treatment for cough with yellow sputum involves frequent gargling with saline solution.
You need to dissolve 1⁄2 tsp. salt in a glass of warm water and gargle with the resulting solution as often as possible. This process clears trapped mucus.
Traditional treatment:
Diagnostics
If the patient suffers from phlegm in the throat without coughing, the reasons are determined by the doctor. Based on the results of the examination, a diagnosis is made, which is corrected with the help of certain medications, traditional methods and lifestyle changes.
Diagnostic measures include:
- examination (larynx, tonsils, oral cavity, nose);
- listening to breathing with a fanendoscope (determining wheezing or determining its absence);
- bacteriological culture of sputum;
- studying anamnesis, determining chronic diseases;
- blood test and instrumental studies (if necessary).
Causes caused by pathological processes
Green sputum without cough is always the cause of an infectious disease. It can form or accumulate in the throat with the following pathologies:
- pharyngitis (inflammation of the larynx);
- rhinitis (inflammation of the nasal mucosa);
- nasopharyngitis (inflammation of the nasopharynx);
- bronchial or pulmonary diseases (usually chronic);
- tonsillitis (inflammation of the tonsils);
- allergy.
Most often, the feeling of phlegm in the throat occurs in people who suffer from laryngopharyngeal reflux or esophagitis.
Mucus drains from the nose down the back of the throat. Or it is thrown from the lower respiratory tract, esophagus. Irritation that occurs inside the pharynx increases the formation of sputum.
Viral and bacterial diseases that cause excess mucus in the throat are often accompanied by elevated body temperature. When fluid comes back from the esophagus, there is an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
What diseases does it occur with?
Yellow thick sputum when coughing is observed with:
- Bronchitis - a certain color of discharge is characteristic of different types of disease. Yellow sputum during bronchitis is observed in acute or chronic form. The patient first develops a dry, then a wet cough. At the same time, sore throat, fever, and chills are observed.
- Cellulitis, abscesses, pleurisy - due to purulent processes, the discharge becomes yellow in color.
Any disease requires strict medical control.
Bronchial asthma
Signs characteristic of bronchial asthma.
- high-pitched wheezing when exhaling;
- difficulty breathing, chest tightness, cough that worsens at night;
- seasonal deterioration of the respiratory system;
- development of eczema or allergies;
- systematic colds that “descend” into the lower respiratory tract;
- the appearance or exacerbation of symptoms during physical activity, emotional overload, inhalation of polluted air, contact with allergens;
- stabilization of the condition after taking antihistamines and anti-asthmatic drugs.
Discharges in this disease differ in:
Sputum must be taken for analysis. Based on the results of the study, the nature of the disease is determined and a treatment method is selected.
A bright yellow or greenish color indicates the death of eosinophils, a type of white blood cell. When a vessel in the lung tissue ruptures, blood appears. With malignant tumors, a rotten smell is noted.
Pneumonia
Yellow sputum when coughing is characteristic of an acute form of pneumonia. It requires immediate medical intervention.
- elevated temperature;
- fever and chills;
- chest pain;
- sleep disturbance;
- persistent cough;
- feeling of lack of oxygen;
- sweating;
- weakness and loss of strength.
To diagnose the disease, an X-ray of the lungs is performed. To identify the pathogen, sputum culture, blood and urine tests are prescribed. Based on the results of the study, broad-spectrum antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and expectorant medications are prescribed.
Parasitic lesions of the lungs
- dirty hands and household items;
- unwashed food.
Larvae hatch in the gastrointestinal tract. They penetrate the veins and travel through the blood vessels to the capillary system of the lungs. The further path lies through the alveoli into the lumen of the bronchi, trachea and pharynx. A person swallows them along with secretions of the bronchial glands and saliva. The larvae return to the digestive system.
A cough that produces mucus may be caused by:
- concentration of parasites in the lungs;
- entry of larvae into the tissues of blood vessels of the respiratory organs;
- the presence of helminths that impede the access of oxygen in the bronchi;
- movement of larvae through the respiratory system.
Parasitic infection of the lungs provokes the development of diseases:
- pneumonia;
- exudative pleurisy;
- eosinophilic pneumonia.
The presence of heartworms is difficult to diagnose because symptoms often do not appear for several years. Some of the signs are characteristic of colds:
- temperature increase;
- paroxysmal cough in the morning;
- sputum discharge;
- loss of appetite;
- muscle pain;
- nausea.
To diagnose helminthic infestation at an early stage, a general blood test is performed. For bronchopulmonary syndrome, radiography is prescribed. The photographs show where the larvae penetrate into the tissue.
In the chronic stage, feces are examined for the presence of helminth eggs. This method is relevant no earlier than 3 months after infection. If only males, immature females or old individuals entered the body, then traces of their presence will not be found.Cough is a symptom that is familiar to everyone
It accompanies both the common cold and serious diseases, including diseases of the lungs, heart and even stomach.
Most people prefer to treat their cough on their own. But not everyone knows that it is not the cough itself that needs to be treated, but the disease that led to its occurrence. A little anatomy A person takes about 20,000 breaths a day. At the same time, approximately 8000 liters of air enter the respiratory tract. The respiratory tract is divided into upper and lower: upper respiratory tract
- this is the nasal cavity
- pharynx (nasal, oral and laryngeal parts)
- larynx
lower respiratory tract
- these are the trachea and bronchi
Normally, about 2 liters of mucus are formed in the respiratory tract per day, which contributes to the natural cleansing of the respiratory tract. The mucous membrane of the bronchi is designed in such a way that the mucus, with the help of special cilia, rises up into the pharynx and is then swallowed. And from the upper respiratory tract (nose and nasopharynx), mucus freely flows down and is also swallowed.
If there is a violation of the mucous membrane (for example, smokers have no cilia in the bronchial mucosa) or any factors cause thickening of the mucus, then it cannot be excreted freely and stagnates. All this leads to irritation of the so-called. cough receptors (special cells that are involved in the cough reflex). It turns out that cough receptors are present not only in the respiratory tract, but even in the heart and stomach. Those. diseases not only of the respiratory tract will be accompanied by a cough.
Thus, a cough that occurs as a result of severe arrhythmia helps the patient not to lose consciousness and even helps restore the normal rhythm of heart contractions. What is a cough like? The cough can be constant and short, barking and silent... Coughs are also divided into wet (doctors call it “productive”) and dry (“unproductive”).
A wet cough produces sputum. It can be liquid or thick, mucous (transparent) or purulent (yellow, green). If the sputum is red or brown, contains streaks or blood clots, then this symptom is called hemoptysis. The amount and nature of sputum gives the doctor information about the cause of the cough. For example, thick green sputum indicates severe inflammation that should be treated with antibiotics.
And depending on whether sputum comes out at all, it will depend on what medications need to be prescribed. For example, if you have hemoptysis, you should not take expectorants, because they may increase the amount of blood in the sputum. And with a dry cough, the use of expectorants can intensify the cough, even to the point of suffocation. A cough that takes up to 3 weeks to cure is an “acute” cough; it most often accompanies ARVI. If the cough persists for more than 3 weeks, it is called “chronic.” Chronic cough is a sign of a serious illness.
Different diseases - different coughs.
Diseases of the upper respiratory tract The most common cause of cough is the familiar acute respiratory disease (ARI). The cough is usually dry, accompanied by pain and sore throat. A runny nose during acute respiratory infections can also cause coughing due to mucus draining down the back wall of the throat.
Bronchial asthma In approximately 10% of cases, the only manifestation of bronchial asthma is a cough.
With an exacerbation of bronchial asthma, a narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi occurs, which complicates the passage of air mainly during exhalation and leads to coughing, wheezing or attacks of suffocation. A typical cough is that it occurs at night and in the early morning hours.
Inflammatory diseases of the bronchi and lungs: bronchitis and pneumonia Inflammation and the presence of mucus in the respiratory tract leads to irritation of cough receptors during bronchitis and pneumonia. With these diseases, the cough is very rarely dry and is always accompanied by an increase in body temperature.
Smoker's cough Smokers are characterized by a cough in the morning with the discharge of thick sputum and frequent coughing throughout the day. If smoking has not led to the development of a chronic disease, then it is enough to give up the bad habit for the cough to disappear on its own.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease This disease causes the valve that separates the esophagus from the stomach to relax. Reflux is the reflux of food from the stomach back into the esophagus. Heavy eating, bending the body, and even singing can provoke the contents of the stomach to enter the esophagus. The acid contained in the gastric juice irritates the esophagus and can lead not only to heartburn, but also to cough. Sometimes a cough is the only sign that something is wrong with your stomach.
Cardiac cough Most heart diseases result in the heart not being able to pump the required amount of blood. Blood “stagnates” in organs, incl. and in the lungs. This leads to irritation of the cough receptors. A dry cough occurs, worsening in a horizontal position. The cough may be accompanied by palpitations, a feeling of shortness of breath, and shortness of breath. There is no treatment for such a cough; it will disappear on its own if the signs of heart failure are eliminated.
Cough due to medications Taking a number of medications can lead to side effects such as coughing. The reasons for this effect of drugs have not yet been sufficiently studied. It helps to recognize that medication has led to the development of a cough if there was no cough before the medication was prescribed. The cough bothers you mainly in the daytime, it is dry, and more often it is a small but debilitating cough. 3-7 days after discontinuation of the drug, the cough disappears. Cough with tumors Some lung tumors for a long time can manifest themselves only as a cough: dry or with the release of a small amount of light sputum. No changes are detected on radiographs of the lungs. Only visiting a doctor and carrying out special research methods helps make a diagnosis at an early stage.
Cough with whooping cough Whooping cough is an infectious disease that occurs with a prolonged paroxysmal spasmodic cough. In the first 2 weeks, the cough is similar to the cough of a common cold and may be accompanied by a runny nose and a slight increase in body temperature. Starting from the third week, a period of debilitating cough begins. The cough comes in attacks that are repeated from 2 to 15 times in a row. Such a cough must be treated, because... it leads to serious complications. Complications that a cough can lead to. Frequent persistent cough, especially in the form of prolonged attacks, leads to an increase in intrathoracic pressure and can contribute to the development of: - pulmonary emphysema - cardiac complications (arrhythmias, increased ischemia, development of cor pulmonale) - hemorrhage in the sclera of the eyes - dizziness - fainting - deterioration of cerebral blood circulation (especially if there have been previous strokes) - lung rupture
In addition, cough can lead to headache, vomiting, sleep disturbances, and urinary and fecal incontinence in an elderly, debilitated patient. Chronic cough can lead to the formation or enlargement of existing hernias (diaphragmatic, inguinal, scrotal, etc.). Chronic cough can cause depression, which complicates the patient's relationships with others, which ultimately significantly worsens the quality of life. What research needs to be done.
In order to avoid serious complications and make a timely diagnosis, you must consult a doctor.
Depending on the characteristics of the cough, its duration, and based on the results of the examination, the doctor will prescribe an examination. As a rule, this is a clinical blood test, fluorography and a study of external respiratory function. If the results of these studies do not help determine the diagnosis or even during the examination one can suspect that they will not be enough, the doctor prescribes more complex studies (for example, bronchoscopy, computed tomography, lung scintigraphy) and consultations with specialists. You can hardly find a person who has never coughed. And, of course, there is no need to consult a doctor every time at the first sign of a slight sore throat or slight cough. These disorders are transient. However, it should be remembered that only a doctor can reliably recognize the cause of cough and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Symptoms that should alert you and prompt immediate medical attention: - hemoptysis (sputum is uniformly red or with red/brown streaks) - increased body temperature for more than 3 days - choking or shortness of breath - cough for more than 3 weeks - chest pain - nausea and vomit"
Analysis of yellow sputum: diagnosis. How is it researched?
Samples of secretions taken from the throat for analysis make it possible to determine the cause of changes in the shade and consistency of tracheobronchial secretions.
The material is collected in a sterile glass container in the morning on an empty stomach, after thoroughly treating the mouth and throat with saline solution. If it is not possible to collect pathological clots during coughing, bronchoscopy is prescribed to obtain the necessary material.
Sample examination is carried out using several methods:
Microscopic analysis makes it possible to determine the content of leukocytes, erythrocytes, alveolar macrophages, epithelial cells in phlegm, detect Kurshman spirals, drusen of actinomycetes, fungi, Charcot-Leyden crystals, eosinophils, neutrophils. Macroscopic analysis determines the daily volume of secreted exudate, its smell, density and color
Special attention is paid to the delamination of the material when left in glass containers for a long time. Bacteriological analysis (Bakposev) allows you to determine the types of bacteria present and their sensitivity to drugs
Causes of mucus discharge when coughing
Blood in sputum almost always becomes a sign of dangerous diseases of the respiratory system. An exception can be considered a rupture of a small bronchial vessel, which occurs during severe physical overload or a sharp, hysterical, barking cough. Usually the sputum in this condition is brown. Treatment is simple - anticoagulants are used.
Relatively safe sources of a frightening symptom include complications after improperly performed medical procedures. Blood in a cough can be a consequence of bronchoscopy, arterial catheterization, or pulmonary puncture. Such hemoptysis begins unexpectedly, usually the next morning after diagnostic or surgical operations. The pathological symptom goes away without drug treatment.
Lung diseases that cause blood in the sputum when coughing
Almost always, the doctor begins the diagnosis with a test for tuberculosis. In addition to blood in the cough, this disease is accompanied by increased sweating, increased body temperature, and sudden weight loss.
If such a disease is not confirmed, the doctor will prescribe additional tests to rule out:
- traumatic injury to the lung (a dangerous condition accompanied by a decrease in blood pressure, pain, and breathing problems);
- infectious, parasitic, fungal infection (in addition to blood clots in the sputum, the patient complains of general weakness, bronchial obstruction, allergic manifestations);
- adenomas in the bronchi (hemoptysis is accompanied by discharge of pus in the mucus when coughing, hiccups, and a constant feeling of fatigue);
- heart attack, lung abscess (streaks of blood in the sputum have an unpleasant odor, tachycardia, cyanosis, severe shortness of breath, fever occur);
- pneumonia (blood in the mucus appears when infected with staphylococcus, legionella, pseudomonas);
- cancer (prolonged cough with blood discharge may indicate lung cancer).
Blood in the sputum after bronchitis often occurs after improper treatment of the disease. A symptom is considered the body’s first “bell” about the transition of the disease to the chronic stage or an exacerbation of the acute form.
Rare respiratory diseases
After collecting anamnesis, the doctor recommends undergoing a comprehensive examination for unpopular lung diseases. Blood in sputum may be a sign of bullous emphysema, silicosis, foreign body aspiration, or aploidosis. Such diseases are usually accompanied by additional symptoms. During the medical history, the doctor asks questions about shortness of breath, heaviness in the chest, dizziness, loss of coordination, and tinnitus. A visual examination is carried out to determine widened intercostal spaces and changes in the shape of the chest.
Cough with blood in diseases of the heart and blood vessels
The cause of the appearance of uncharacteristic secretions in the mucus may be a change in the condition of the heart and blood vessels
It is important to promptly identify and begin treatment of pathologies such as mitral stenosis, aortic rupture, cardiac outflow of the lung, and blockage of arteries during a heart attack. In addition to the appearance of blood in the sputum, the described diseases are characterized by significant shortness of breath, pain
Most often, the cough worsens after physical activity.
Possible causes of sputum without cough and additional symptoms
Sputum is mucus that is secreted by glandular cells of the trachea, nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses and bronchi. Normally, no more than 100 ml of mucus accumulates in the tracheobronchial tree per day. It has bactericidal properties and is involved in the removal from the respiratory tract:
- dust;
- allergens;
- pathogenic agents.
When the mucous membrane is irritated, the activity of glandular cells increases 10 times or more.
Therefore, in case of illness, up to 4 liters of pathological sputum are produced per day. Expectoration of mucus without coughing is a nonspecific symptom that accompanies pathologies of various systems:
- respiratory;
- digestive;
- endocrine;
- nervous.
To find out the cause of the condition, you need to determine:
- the nature of sputum - elasticity, transparency, color, smell;
- associated symptoms – chest pain, sore throat, burning sensation in the nose;
- factors that provoke exacerbation are strong odors, physical activity, drinking hot drinks, etc.
Expectoration of mucus without coughing in half of the cases indicates damage to the nasopharynx or bronchopulmonary system.
Sinusitis and rhinitis
Thick mucus is released without coughing in case of inflammation of the nasopharynx and paranasal sinuses. Copious sputum is expectorated in the following diseases:
- The best cough syrup for children from all types
- Rhinitis (runny nose). Inflammation of the nasal mucosa is accompanied by the secretion of viscous mucus. Its transparency and elasticity depend on the form of the disease. An infectious runny nose produces yellow or green mucus. In people with insufficient tone of blood vessels, vasomotor rhinitis occurs, in which a transparent secretion is formed. With atrophic rhinitis, foul-smelling green sputum occurs.
- Sinusitis. When the maxillary sinuses become inflamed, sinusitis occurs, the ethmoid sinuses - ethmoiditis, the sphenoid sinuses - sphenoiditis, and the frontal sinuses - frontal sinusitis. If you cough up white, thick mucus without coughing, the cause of the illness is a viral infection or allergy. With bacterial and fungal inflammation, it acquires a yellow or green tint and an unpleasant odor.
Expectoration of mucus without coughing occurs mainly in the morning, as during the night it flows down the back wall of the throat into the hypopharynx.
Pharyngitis, laryngitis, tonsillitis
Phlegm in the throat without cough in children and adults occurs due to inflammation:
- palatine tonsils – tonsillitis;
- pharynx – pharyngitis;
- larynx - laryngitis.
If the secretion is transparent, this indicates the onset of the disease or the attenuation of inflammation. In the absence of complications, the cough does not bother you, and small amounts of sputum are expectorated. If it becomes thick and green, purulent inflammation is possible.
The release of viscous mucus without coughing after laryngitis is a sign that the inflammation has become chronic.
Reflux esophagitis
If there is no cough, but there is sputum in an adult, the cause may be the reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus - gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Gastric juice contains hydrochloric acid, which irritates the mucous membrane and provokes the production of mucus.
GERD manifests itself:
- heartburn;
- sour taste in the mouth;
- swallowing disorder;
- hoarseness of voice;
- heaviness in the stomach after eating.
GERD is characterized by insufficiency of the esophageal sphincter.
The contents of the stomach enter the esophagus when the body is tilted or in a supine position. Therefore, clear mucus is coughed up after waking up. If you accidentally inhale gastric juice, a spasmodic cough occurs, accompanied by a burning sensation in the laryngopharynx.
Tuberculosis and other lung infections
Viscous mucus accumulates in the respiratory tract during infectious inflammation of the bronchi and lungs. Green sputum occurs when the ENT organs are damaged:
- Koch's bacillus;
- adenovirus;
- Staphylococcus aureus;
- pneumococcus;
- coronavirus;
- measles virus;
- peptostreptococcus;
- pyogenic streptococcus;
- corynebacterium.
Pathogenic microorganisms produce toxins, so signs of intoxication (poisoning) come to the fore:
- weakness;
- lack of appetite;
- headache;
- drowsiness;
- sweating
With viral inflammation, the sputum is clear, with bacterial inflammation it is yellow, and with purulent inflammation it is green.
If there is no cough and mucus accumulates in the bronchi, breathing becomes harsh. When listening with a stethoscope, moist rales are heard in the lungs.
Allergy
Sputum production without coughing is one of the signs of a respiratory allergy. Irritants (allergens) are:
- medicines;
- plant pollen;
- Food;
- fumes from household chemicals;
- dust mites.
Manifestations of respiratory allergies:
- Night cough in children and adults - causes of dry and wet cough, diagnosis and treatment methods
- labored breathing;
- redness of the throat mucosa;
- nasal congestion;
- lacrimation (with hay fever);
- pain when swallowing;
- hoarseness of voice.
Depending on the location of the inflammation, the allergy occurs with or without a cough.
Patients complain of expectoration of clear, viscous sputum, which sometimes becomes glassy. In the absence of treatment, the clinical picture is supplemented by new symptoms - spasmodic cough, shortness of breath, swelling of the mucous membranes.
Bronchitis
With inflammation of the bronchi, the production of bronchial secretions increases 5-7 times. At the initial stage, the cough appears and then disappears. When accumulated mucus irritates the receptors, coughing attacks occur. Without taking mucolytics, she does not expectorate, so wheezing appears in the lungs.
Symptoms of bronchitis:
- malaise;
- hard breathing;
- chest discomfort;
- nasal congestion;
- moderate increase in temperature.
After 2-3 days, the mucus begins to come out abundantly, so a productive cough occurs. It intensifies at night or in the morning, with a sharp change in temperature.
Sjögren's syndrome
Sputum without fever and cough is one of the signs of Sjögren's disease. It is characterized by damage to connective tissue and exocrine glands. Accompanied by sinusitis and tracheobronchitis, separation of rusty sputum.
Symptoms of Sjögren's disease:
- muscle and joint pain;
- dry eyes;
- seizures in the corners of the mouth;
- violation of the act of swallowing;
- prostration;
- dry tongue;
- formation of crusts in the nose;
- enlargement of the parotid glands.
The mucous membrane of the throat dries out and acquires a bright red tint.
If the glands are insufficient, the saliva becomes viscous. Due to dysphagia (impaired swallowing), the patient cannot swallow it. Therefore, there is a feeling of mucus accumulation in the throat.
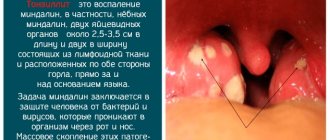
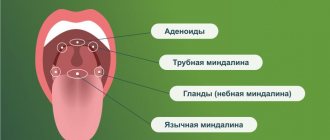
Inflammation of the adenoids
Sputum without cough in a child appears against the background of adenoiditis. This is the name for inflammation of an enlarged nasopharyngeal tonsil. The adenoids block the nasal passages, so viscous secretions accumulate in the nasal cavity. During sleep, it flows into the throat through the back wall of the pharynx.
Manifestations of adenoiditis:
- night snoring;
- violation of nasal breathing;
- coughing up yellow mucus;
- restless sleep;
- headache;
- elevated temperature.
There is no cough while awake. It occurs in the morning or immediately after waking up due to irritation of the throat by nasal secretions. If left untreated, the Eustachian tube becomes inflamed (eustachitis), so the child complains of decreased hearing acuity and ear pain.
Esophageal diverticulum
An esophageal diverticulum is a saccular bulge in the wall of the esophagus. It manifests itself as dysphagia, bad breath, and a feeling of a lump in the throat. Many people experience hypersalivation - excessive production of saliva, so they complain of copious sputum discharge without coughing attacks.
Associated symptoms depend on the location of the diverticulum. The most striking clinical picture when a protrusion forms in the clavicle area:
- change in voice timbre;
- nausea;
- scratching in the throat;
- expectoration of thin sputum;
- regurgitation of food;
- backflow of mucus from the esophagus into the throat.
Large diverticula put pressure on the respiratory system, causing coughing. It is combined with chest pain and dizziness.
Consequences of smoking
Non-infectious bronchitis is a problem faced by smokers with more than 7 years of experience. Systematic damage to the bronchi by tobacco smoke leads to irritation and inflammation of the mucous membrane, which increases the activity of glandular cells.
Symptoms of smoker's bronchitis:
- rawness in the throat;
- occasional cough;
- mucus department;
- dyspnea;
- hard breathing;
- tachycardia (against the background of coughing attacks).
During the day, sputum passes without coughing. But during sleep, it accumulates in the throat, so in the morning coughing attacks occur, during which clots of transparent mucus are released.
Worm infestation
If a child or adult does not cough up clear or white sputum, the cause may be helminthiasis. In the acute phase, parasite larvae circulate in the blood and enter the bronchi. They irritate the mucous membrane, causing a productive cough. A person complains about:
- chest pain;
- swelling of the mucous membranes;
- shortness of breath;
- nausea.
When the mucus is swallowed, the worms enter the intestines, where they develop into adults. In the later stages, helminthiasis manifests itself:
- abdominal pain;
- unstable stool;
- weakness;
- sleep disturbance;
- elevated temperature;
- convulsions.
With a chronic disease, immunity decreases, so rhinitis, tracheitis, and influenza often recur.
Other reasons
Foul-smelling mucus without coughing is a dangerous symptom that occurs against the background of purulent inflammation of the ENT organs. Without treatment, complications are possible - abscess and gangrene of the lung, sepsis (blood poisoning).
Possible causes of expectoration:
- lungs' cancer;
- pulmonary syphilis, disintegration of syphilitic gum;
- bronchopulmonary carcinoma;
- cystic fibrosis;
- pulmonary mycosis;
- actinomycosis;
- bullous disease;
- pleural empyema;
- COPD
Yellow sputum without cough is a sign of bacterial diseases of the nasopharynx. If clots of dried blood are found in it, this indicates mucopurulent inflammation. Brown sputum in the morning without cough occurs with bronchiectasis and cardiac pathologies.
If you cough up green sputum: treatment
How to treat a disease depends on the causes of its occurrence.
At the same time, patients are often recommended not only classical drug therapy, but also a number of special procedures that can be easily performed at home.
For bacterial infections, antibiotics are prescribed (Augmentin, Flemoxin, Lincomycin, Unidox, Sumamed, Azithromycin, Cefix, Cefuroxime, Hemomycin, Ampiox, Doxycycline, Clarithromycin, etc.), which will help get rid of pathogenic microflora, as well as:
- mucolytics: ACC, Fluimucil, Mucaltin, Carbocysteine, Fluditec, Pectolvan, Prospan, Acetin, licorice root syrup, Libexin Muco;
- expectorants: Ambroxol, Lazolvan, Ambrohexal, Ambrobene, Gedelix, Bromhexine, Flavamed, Doctor Mom, dry medicine, Pertussin, Herbion primrose syrup;
- antihistamines: Zodak, Erius, L-cet, Suprastin, Edem, Loratadine, Claritin, Tavegil, Aleron, Alergodil, Fenistil, Cetirizine;
- immuno-strengthening: Umkalor, Aflubin, Isoprinosin, Lavomax, Oscilococcinum, Amiksin, Anaferon, Immunal, Proteflazid, Immunorix, Derinat, tinctures of echinacea, ginseng, lemongrass, etc.
It would not be superfluous to carry out inhalations using a nebulizer or improvised means, for example, a pan of boiled potatoes.
What medications should be used for inhalation therapy in a nebulizer are prescribed to the patient by the doctor; as part of self-medication, only saline solution is allowed.
If there is no fever, it is useful for patients to walk in the fresh air. Required:
- ventilate the room;
- drink plenty of warm drinks;
- use household humidifiers.
More serious pathologies, such as tuberculosis, are treated in hospitals according to specially developed schemes.
Cough with green sputum in adults
Treatment of colds in adults requires bed rest, as otherwise undesirable consequences may develop.
This will allow you to cure the disease in the shortest possible time with minimal risk to the body.
It is much more difficult to carry out therapy for expectant mothers. Nevertheless, it is they who need it in the first place, since frequent coughing attacks can increase the tone of the uterus and in certain women provoke the threat of miscarriage.
Therefore, during pregnancy, self-medicating and not paying attention to the problem is strictly prohibited.
In such cases, you should definitely contact a therapist, who will select medications that are acceptable for this period.
Child coughs up green mucus
As a rule, pediatricians recommend supplementing drug treatment for a child with a special massage:
The baby is placed on his stomach on the adult's lap, while he must rest his hands on the floor and raise his legs as high as possible. An adult initially rubs the baby's back with light movements until a feeling of warmth and barely noticeable redness appears. Using light tapping movements with the fingers of a relaxed hand, the adult begins to actively hit the child’s back for several minutes.
It is very important to control the force of the impact: they should be noticeable, but not painful.
The effectiveness of this massage has long been proven. Most children begin to cough more easily within a few minutes of completing the procedure. Here's a video:
https://youtube.com/watch?v=7RFEP4cbKLc
You should not force feed your child if he refuses to eat. During illness, the body spends all its energy fighting microbes, and eating food leads to a redistribution of energy costs and a decrease in the quality of the fight against infection.
Smokers
Mostly brown sputum appears in a smoker in the morning. When a person sleeps, mucus accumulates, and when he wakes up, phlegm begins to leave the bronchi naturally. A person who smokes for a long time eventually develops so-called smoker's bronchitis. Moreover, the cough becomes his constant companion. Naturally, smokers do not monitor their health, so they do not pay due attention to the color of the discharge. They are accustomed to a morning cough and do not consider this a cause for concern. However, brown sputum is considered an ideal breeding ground for bacteria.
Thus, by introducing harmful smoke into the body, smokers slowly poison it with heavy elements. Therefore, it is better to give up such a bad habit in order to exclude more serious diseases and complications in the future. People who have continuously consumed harmful cigarette smoke for several years in a row need to cleanse their lungs. To do this, you can use breathing exercises, which are popular today, with which you can improve the health of the entire body. The doctor may also prescribe you expectorant medications or a more gentle healing option using inhalations. Visit the clinic and the doctor will tell you which method is best for you. The doctor will monitor your health throughout the course of therapy, so no complications will arise.
Symptoms during the formation of mycetoma
In the early stages, a patient with mycetoma feels absolutely nothing, because there are no symptoms of the disease yet.
And as the fungal growth increases in size, it will become more difficult for the patient to breathe due to nasal congestion on one side, while the nose will be clean, without discharge. But sometimes the discharge can be in the form of crumbly masses of a gray-dirty color. In addition to the symptoms listed earlier, the patient may experience dizziness, headaches, when the mycetoma grows strongly, it occupies the entire volume of the maxillary sinus, creating excess pressure, including in the orbital area. And, of course, with a large growth of mycetoma of the maxillary sinus, sinusitis is possible. The patient may have pain in the upper teeth in the lateral part from the side of the mycetoma. And, as I said earlier - difficulty breathing, the patient switches to mouth breathing as a result of acquired chronic sinusitis.
How extensive can a mycetoma be?
Molds can grow until the maxillary sinus is completely filled. And when the mold ball occupies the entire maxillary sinus (it usually takes 5-7 years to grow), the diameter of the ball reaches an average of 3-5 centimeters.
For example, here is a photo of a mycetoma of the maxillary sinus, when the growth of fungi has almost completely “captured” it. The cause of the formation of mycetoma in this case was a part of the root filling of the tooth that was removed into the maxillary sinus:
We describe in detail how the root filling got into the maxillary sinus in this clinical case.
Causes of phlegm in the throat
The most common cause of constant mucus is acute infectious diseases, colds. During the first days, sputum is produced abundantly from the nose, and later from the bronchi and trachea. Such discharge is temporary and stops after recovery. If there is no acute disease, but mucus is formed steadily, we can talk about pathology, an unhealthy lifestyle, or the development of some complex disease.
Lump in throat when swallowing
Patients complain that mucus constantly accumulates in the throat, something foreign is stuck. For this reason, they cannot swallow completely and experience great discomfort from this. The main reasons causing this symptomatology:
- Disorders of the thyroid gland caused by iodine deficiency (diffuse goiter, autoimmune thyroiditis).
- Gastrointestinal pathologies (ulcers, reflux disease, gastritis).
- Neurological reasons. A feeling of “choking the throat” can occur, for example, with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
- Chronic tonsillitis, sinusitis, purulent plugs.
- Depression, stress and other psychological problems. Women often feel a lump in their throat during pregnancy.
- Oncological diseases.
Snot in throat
This unpleasant symptom greatly complicates life: it interferes with eating and provokes coughing. When mucus flows down the back of the throat and accumulates in the nasopharynx, we can assume the presence of:
- bronchopulmonary diseases;
- inflammatory processes of the sinuses (pharyngitis, sinusitis);
- diseases of the esophagus (chronic esophagitis);
- allergic reactions;
- various types of irritations (if a person smokes a lot, eats spicy dishes, the body turns on a “defensive reaction” - mucus begins to actively cover all organs).
No cough
If sputum appears, but there is no cough, none of the above causes can be excluded. The disease is provoked by diseases of the respiratory system, gastrointestinal tract, inflammation of the tonsils, colds, lifestyle, and stress. If the mucus in the throat does not clear up, the reason for this may be low air humidity, foreign objects in the nasal cavity, and various muscle diseases.
With an unpleasant odor
According to research, excess mucus and sticky saliva feed the bacteria in the throat, which is the source of the unpleasant odor. Among the main reasons:
- colds, chronic runny nose, sore throat;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- bad teeth;
- chronic tonsillitis and other diseases of the nasopharynx;
- pathologies of the nasopharynx, sphenoiditis.
If your throat hurts
The cause of phlegm can be bacterial throat infections and inflammatory processes (tonsillitis, pharyngitis). If a person has a sore throat, a cough, laryngitis is possible. There are other reasons that cause pain and accumulation of mucus - for example, glossopharyngeal neuralgia, tumor processes, thyroid diseases. With these diseases, no increase in temperature is observed.
With blood
Inflammatory diseases of the upper respiratory tract, accompanied by damage to small vessels
To determine the exact cause, you need to pay attention to the color of the sputum. For example, if it is yellow or green mixed with blood, it means that a person has chronic inflammatory diseases
White mucus with blood may be a sign of bleeding in the esophagus or lungs. Viral diseases of the respiratory tract. Severe cough and other reasons leading to rupture of small vessels. Thrombosis, mitral pulmonary artery defects. Lung diseases (bronchitis, tuberculosis).
Symptoms of mucus in the throat
Typical symptoms of mucus in the throat include:
- Feeling of burning and rawness in the throat;
- Sore throat;
- Unpleasant sensations when swallowing;
- Constant desire to cough;
- Lump in throat.
Common symptoms include headaches and enlarged cervical lymph nodes. When a person begins to experience a sore throat or a pleasant sensation while swallowing, these symptoms may indicate mucus in the throat. In other words, a lump in the throat is felt due to a constant desire to cough.
The method of treating mucus in the throat is determined only by an ENT doctor after a comprehensive examination.
Treatment of yellow sputum when coughing
In the absence of elevated body temperature, outpatient treatment following the doctor’s instructions is sufficient. If the temperature rises above 38 degrees, bed rest or hospitalization is recommended, depending on the diagnosis. Complex therapy includes dietary nutrition with the exception of fried, salty, smoked foods, excessive consumption of sweets - junk food provokes the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria.
Preference is given to boiled and steamed foods; it is advisable to consume large amounts of fiber in the form of fruits and vegetables, and dairy products. Maintaining cleanliness in the living space, regularly ventilating the room, and quitting smoking during illness contributes to a speedy recovery.
Based on the individual characteristics of the patient and the complexity of the inflammatory process, it is recommended to take the following medications:
Expectorants - remove phlegm from the upper respiratory tract - Trypsin, Thermopsis, Sodium Benzoate; Bronchodilator medications - promote the release of sputum from the bronchi - Stoptussin, Erespal, Bromhexine, Gedelix; Broad-spectrum antibiotics - for the treatment of yellow sputum, it is important to choose the right antibacterial drugs in addition to symptomatic treatment; Inhalations - have an anti-inflammatory, antiseptic, expectorant effect - Berodual, saline solution; Antihistamines - if the cough is of allergic origin, antiallergic therapy is prescribed
4.Treatment
Depending on the diagnostic results obtained, etiotropic therapy is prescribed, i.e. measures are taken to eliminate the root cause of retronasal drip. In some cases, the primary goal is desensitization and relief of allergic inflammation (solved with medication and by minimizing contact with allergens), in others it is impossible to do without surgical restoration of normal anatomy, patency, ventilation and drainage of the nasal passages, in others, one or another strategy for the treatment of sinusitis is used , gastroenterological treatment, a course of physiotherapy, etc. are prescribed.
It is important to understand that constant and abundant flow of mucus down the back wall of the throat is not normal; this condition requires specialist consultation, examination and treatment. Effective assistance is provided in all cases.